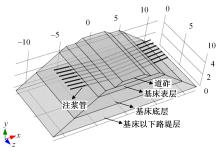
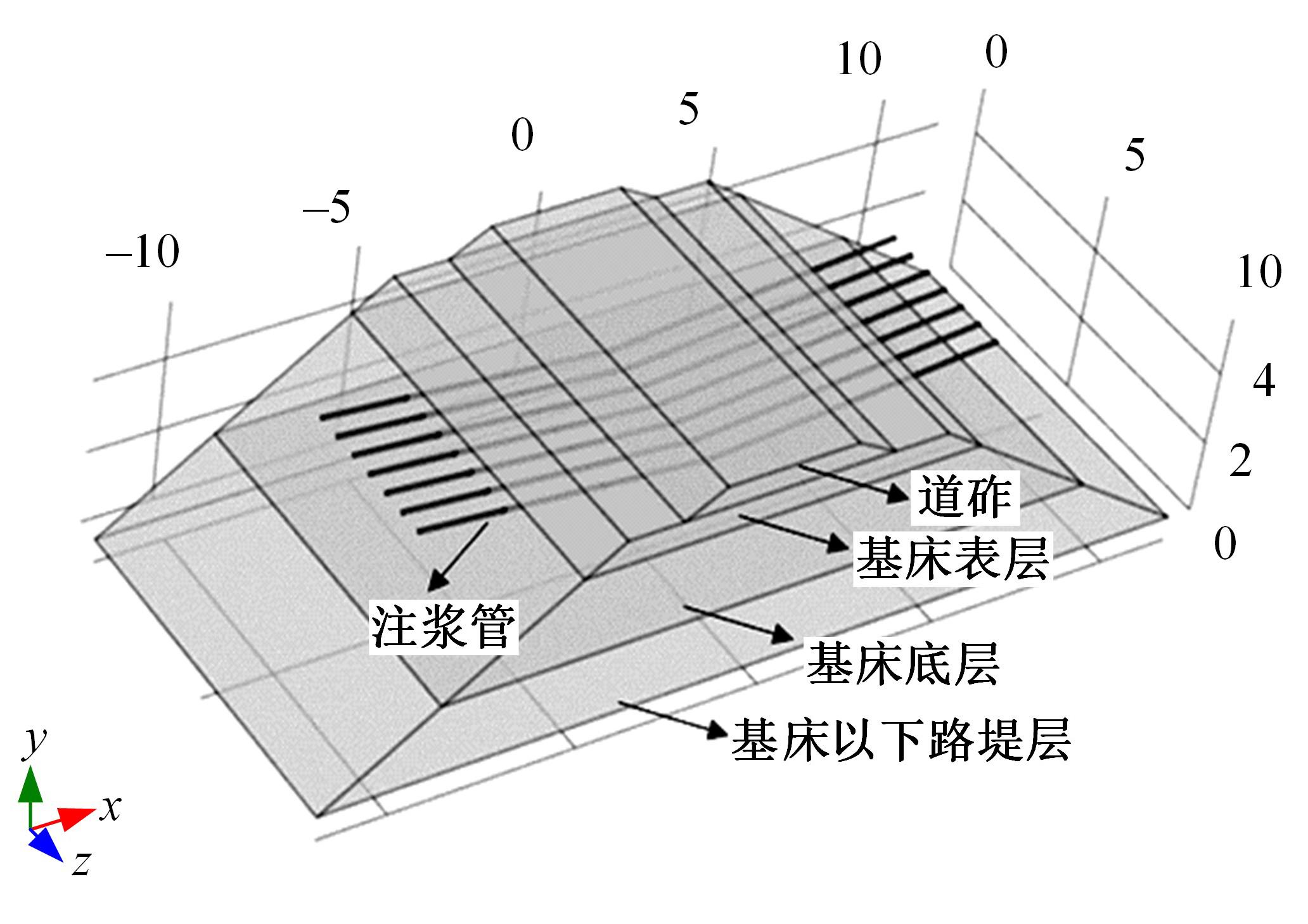
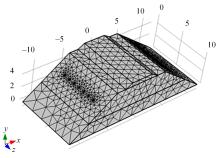
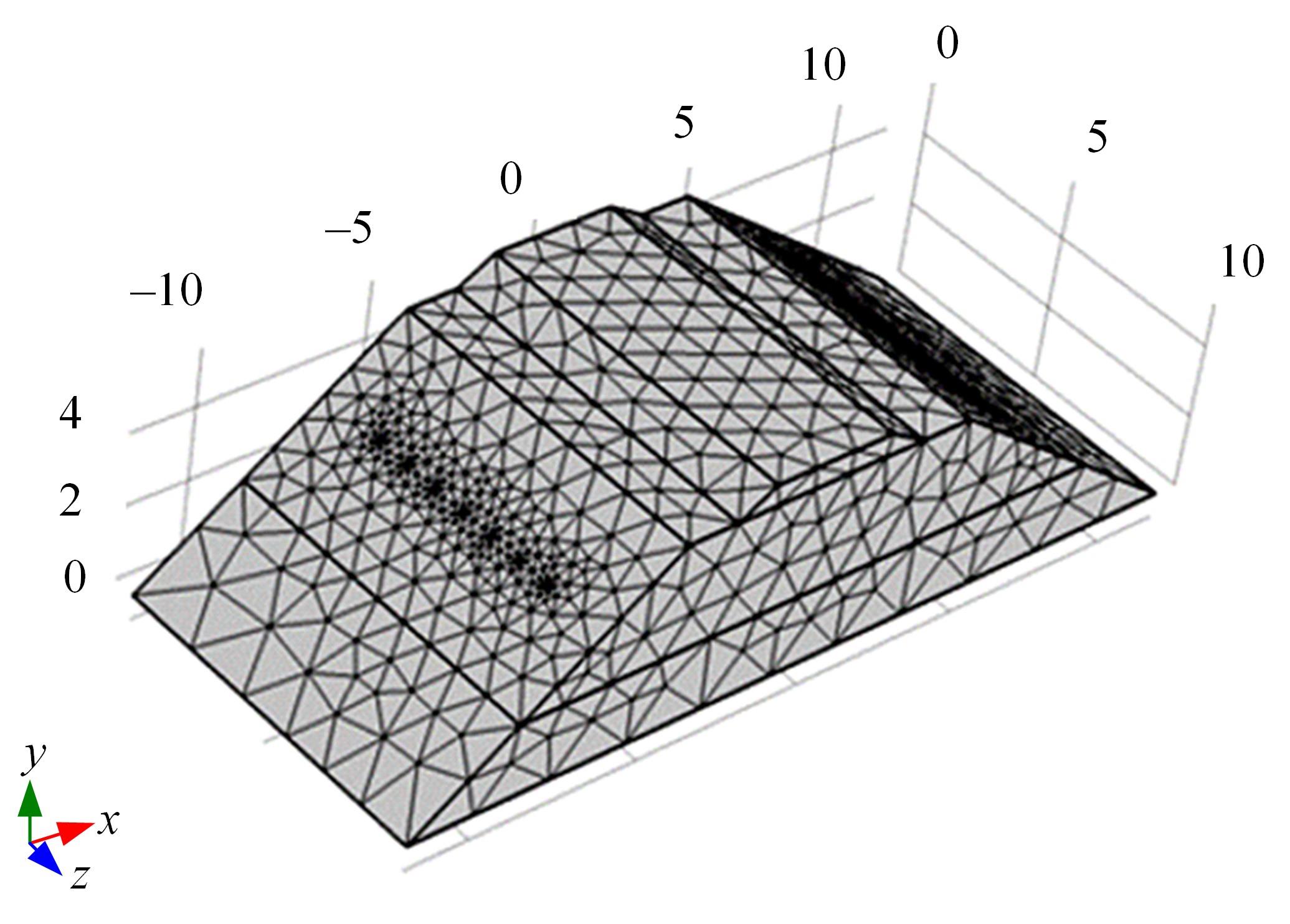
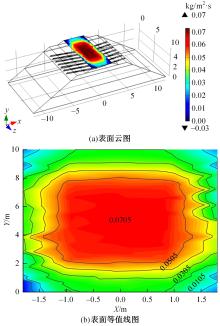
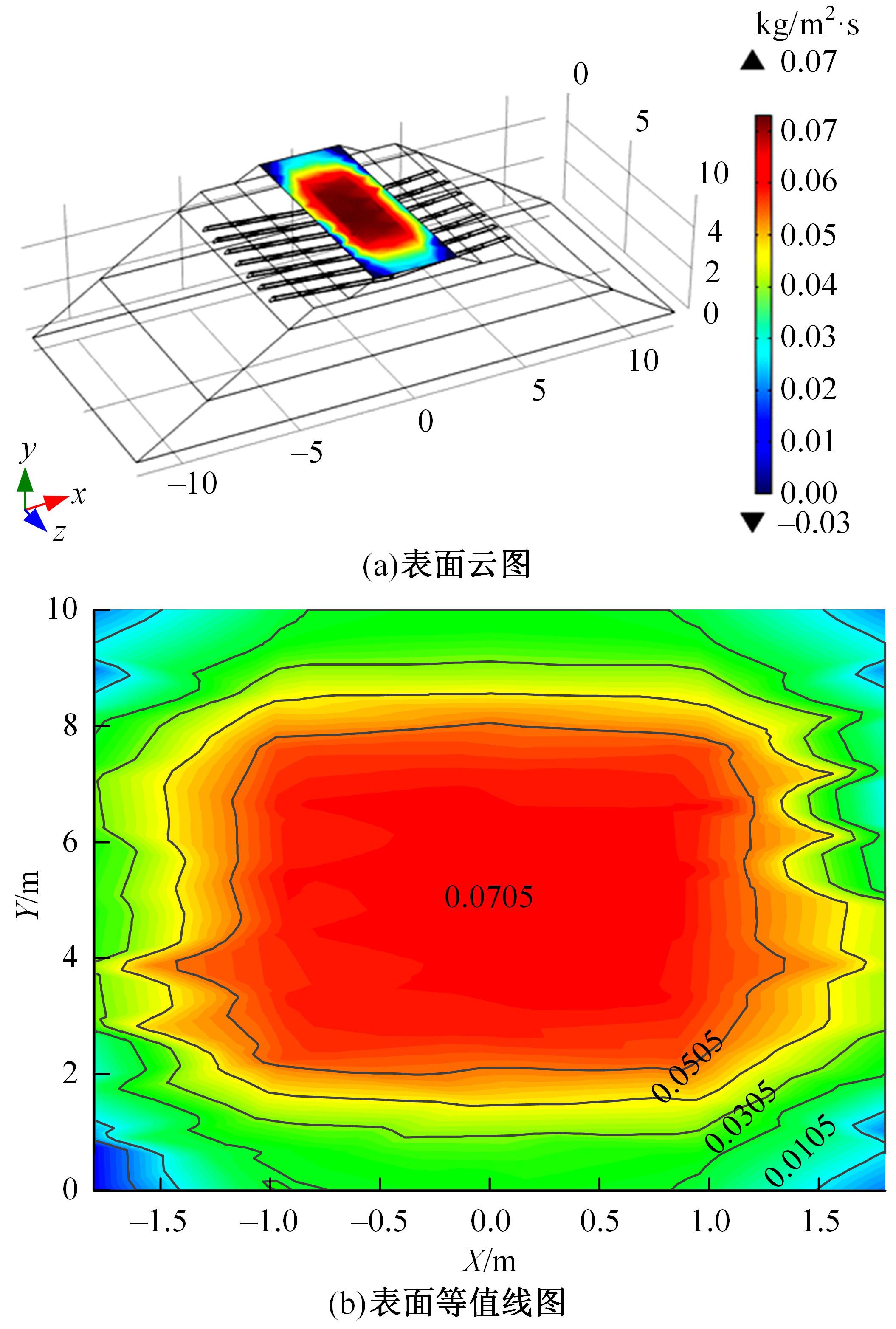
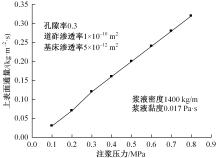
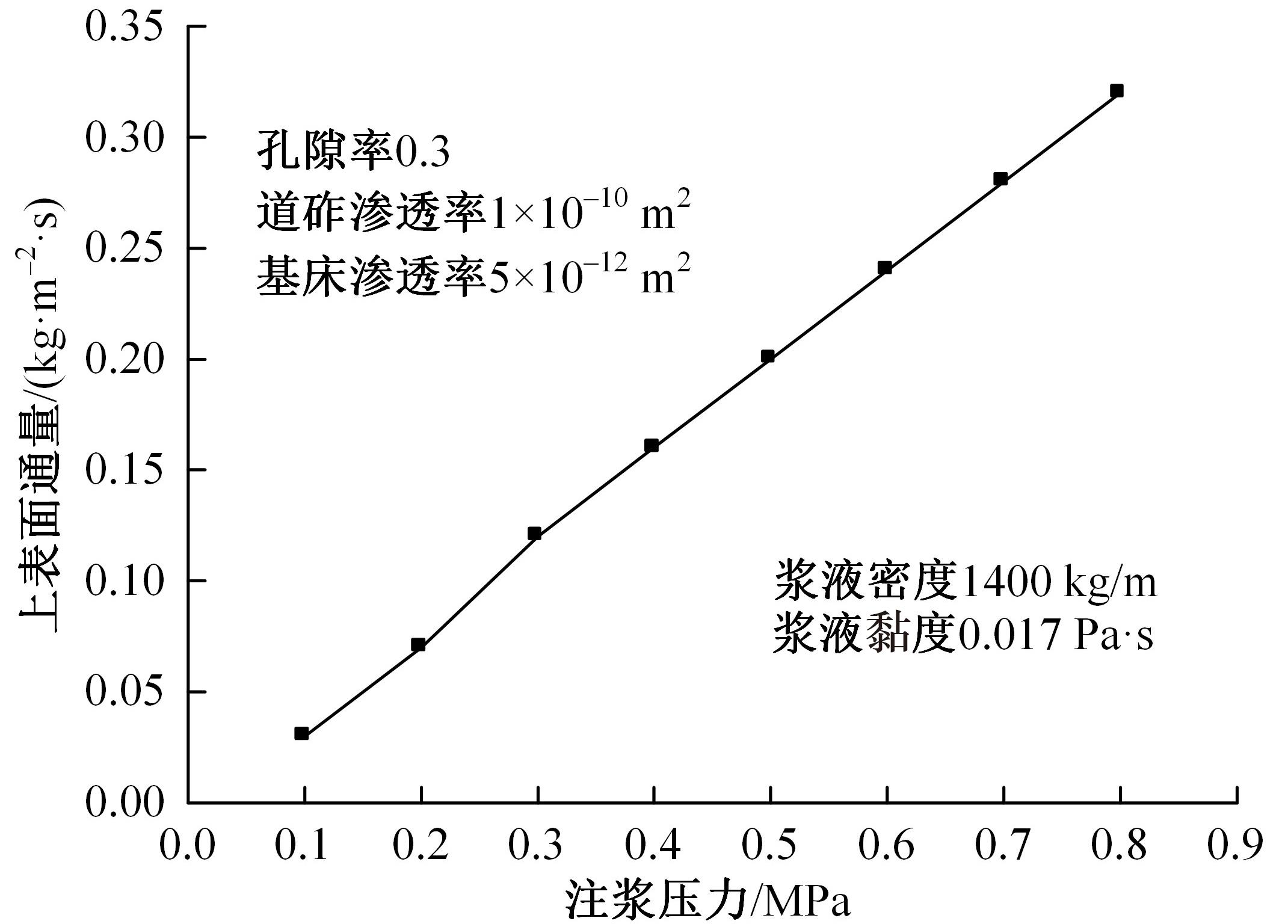
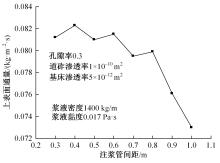
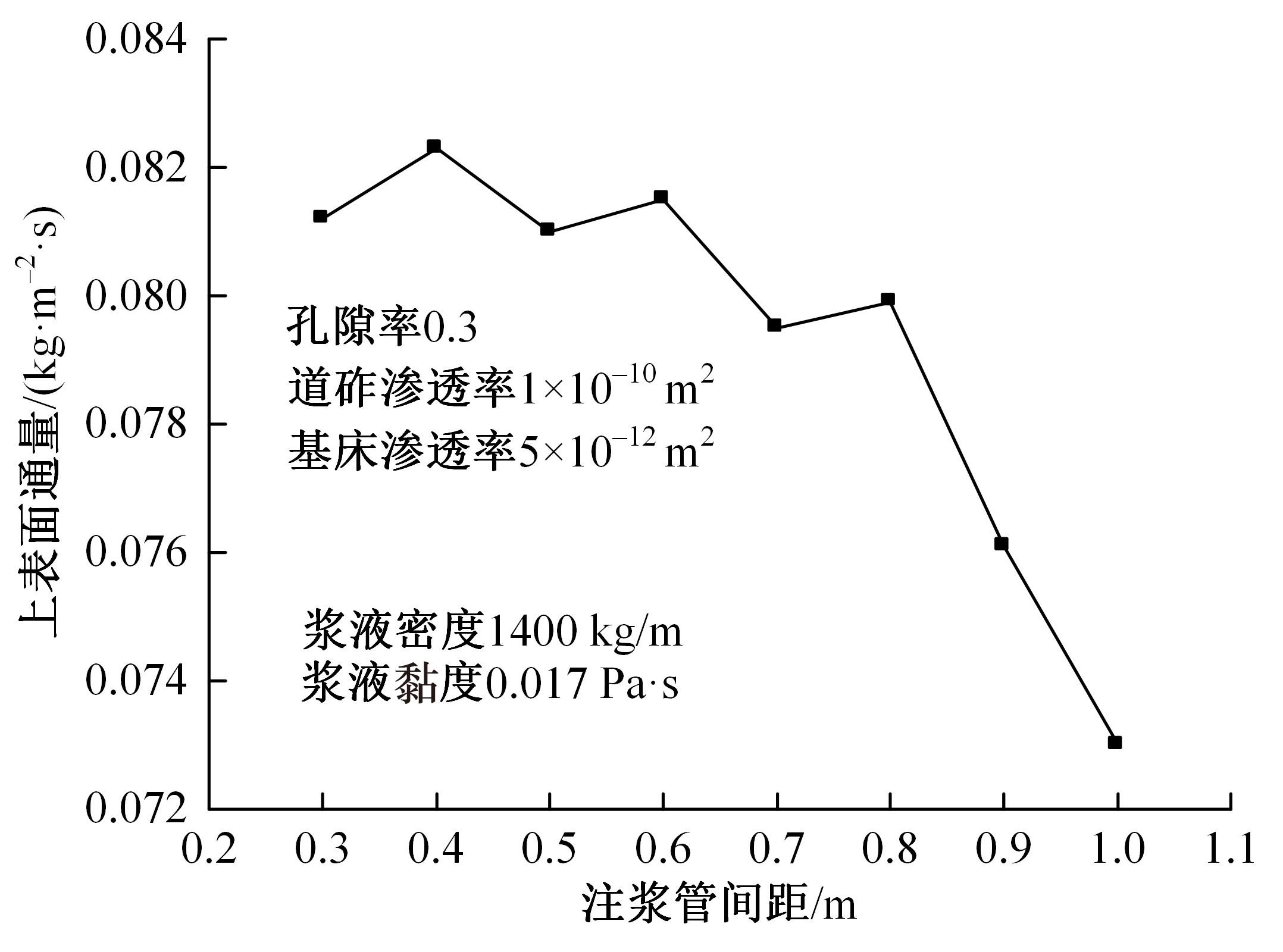
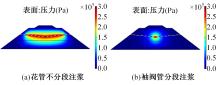
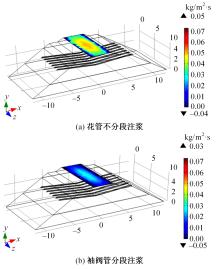
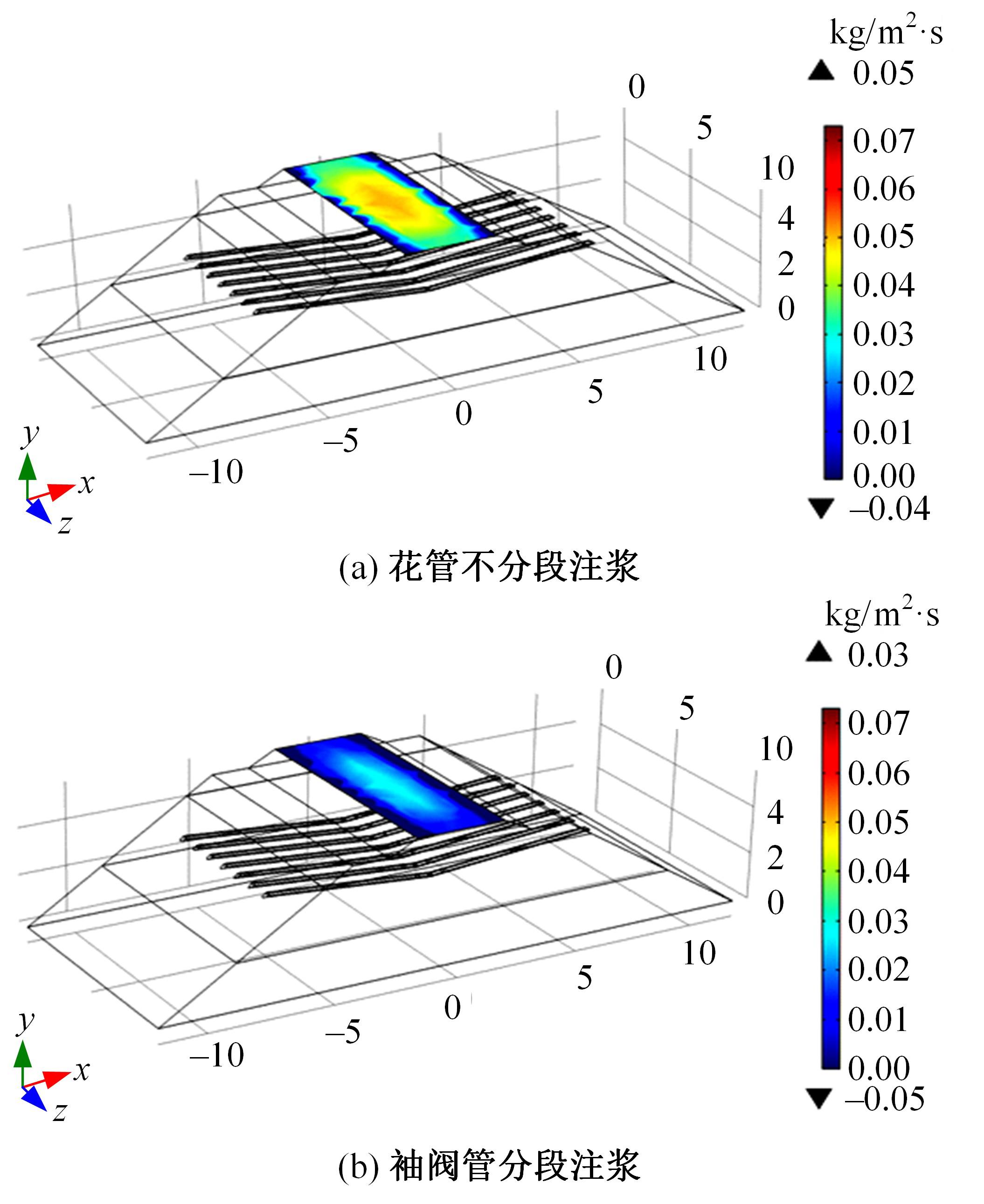
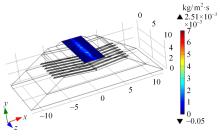
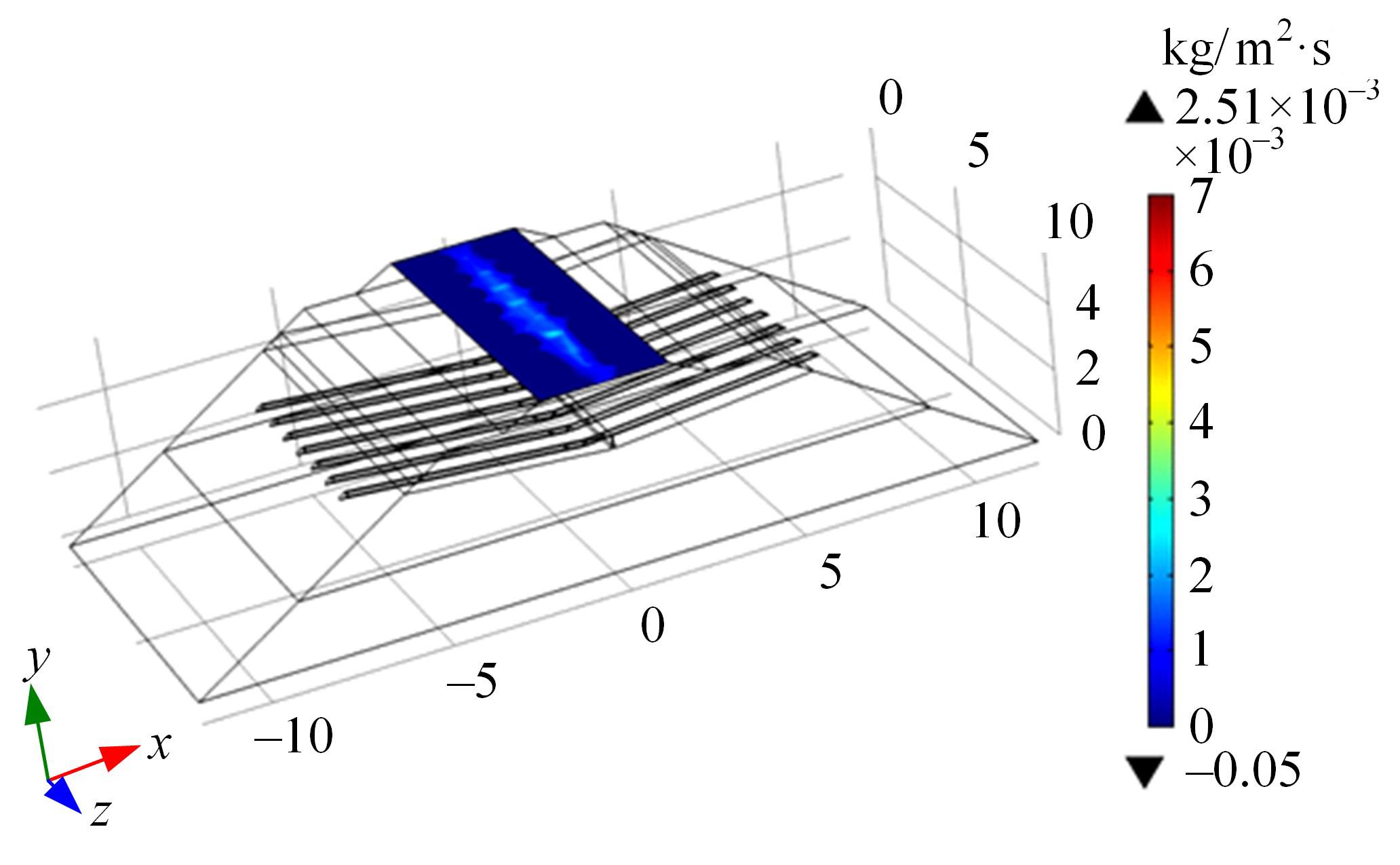
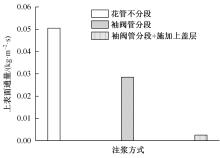
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 506-515.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220342
Analysis and control of mud spillover in high⁃speed railway ballast⁃track subgrade caused by grouting
Xiao HAN1,2,3( ),Xian-zhang LING1,2,3(
),Xian-zhang LING1,2,3( ),Shuang TIAN1,2,3,Sheng-yi CONG1,2,3
),Shuang TIAN1,2,3,Sheng-yi CONG1,2,3
- 1.College of Civil Engineering,Harbin Institute of Technology,Harbin 150090,China
2.Chongqing Research Institute,Harbin Institute of Technology,Chongqing 401135,China
3.Heilongjiang Research Center for Rail Transit Engineering in Cold Regions,Harbin 150090,China
CLC Number:
- U215.7
| 1 | 张小炳. 高速铁路列车停站方案与运行图协同优化理论与方法[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学交通运输与物流学院, 2018. |
| Zhang Xiao-bing. Theory and method of collaborative optimization of stopping scheme and running diagram ofhigh-speed railway[D]. Chengdu: School of Transportation and Logistics, Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018. | |
| 2 | Yang Y, Tang X, Zheng H, et al. Hydraulic fracturing modeling using the enriched numerical manifold method[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2018, 53: 462-486. |
| 3 | Moon H K, Song M K. Numerical studies of groundwater flow, grouting and solute transport injointed rock mass[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 1997, 34(3/4): 206-218. |
| 4 | Lorig L J, Brady B H G, Cundall P A. Hybrid distinct element-boundary element analysis of jointed rock[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1986, 23(4): 303-312. |
| 5 | Baca R G, Arnett R C, Langford D W. Modelling fluid flow in fractured-porous rock masses by finite-element techniques[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 2010, 4(4): 337-348. |
| 6 | Eriksson M, Stille H, Andersson J. Numericalcalculationsfor prediction of grout spread withaccount for filtration and varying aperture[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology incorporating Trenchless Technology Research, 2000, 15(4): 353-364. |
| 7 | Zheng H, Liu F, Li C G. Primal mixed solution to unconfined seepage flow in porous media with numerical manifold method[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2015, 39(2): 794-808. |
| 8 | Ma G W, Wang H D, Fan L F, et al. Segmented two-phase flow analysis in fractured geological mediumbased on the numerical manifold method[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2018, 121(11): 112-129. |
| 9 | Ma G W, Wang H D, Fan L F, et al. A unified pipe-network-based numerical manifold method for simulating immiscible two-phase flow in geological media[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2018, 568: 119-134. |
| 10 | Prevost J H, Sukumar N. Faults simulations for three-dimensional reservoir-geomechanical models with theextended finite element method[J]. Journal of the Mechanics & Physics of Solids, 2016, 86(1): 1-18. |
| 11 | 王腾, 周茗如, 马连生, 等. 基于断裂理论的湿陷性黄土劈裂注浆裂纹扩展[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 47(5): 1472-1481. |
| Wang Teng, Zhou Ming-ru, Ma Lian-sheng, et al. Crack propagation of collapsible loess by split-grouting based on fracture theory[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(5): 1472-1481. | |
| 12 | 冯学钢. 高填方路基沉降处治灌浆技术的工程实践与认识[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2006(2): 334-339. |
| Feng Xue-gang. Engineering practice and understanding of high fill roadbed settlement treatmentgrouting technology [J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006(2): 334-339. | |
| 13 | 崔凯, 许鹏飞, 黄井镜, 等. 土遗址裂隙注浆-土界面粘结构性能干旱环境耐久性对比[J/OL]. [2023-11-25]. |
| Cui Kai, Xu Peng-fei, Huang Jing-jing, et al. Comparison of grain-soil interface bonding properties in soil site fracture grouting in drought environment[J/OL]. [2023-11-25]. | |
| 14 | 朱登元, 管延华, 刘惠忠, 等. 袖阀管劈裂注浆加固粉土路基实验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2012, 34(8): 1425-1431. |
| Zhu Deng-yuan, Guan Yan-hua, Liu Hui-zhong, et al. Experimental study on strengthening silty subgrade with sleeve valve tube split grouting[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2012, 34(8): 1425-1431. | |
| 15 | 李璐, 程鹏达, 钟宝昌, 等. 黏性浆液在小孔隙多孔介质中扩散的流固耦合分析[J]. 水动力学研究与进展A辑, 2011, 26(2): 209-216. |
| Li Lu, Cheng Peng-da, Zhong Bao-chang, et al. Fluid-structure interaction analysis of viscous grout diffusion in smallporous media[J]. Advances in Hydrodynamics Research A, 2011, 26(2): 209-216. | |
| 16 | 程鹏达. 孔隙地层中粘性时变注浆浆液流动特性研究[D]. 上海: 上海大学力学与工程科学学院, 2012. |
| Cheng Peng-da. Study on flow characteristics of viscous time-varying grout in pore formation[D]. Shanghai: School of Mechanics and Engineering Science,Shanghai University, 2012. | |
| 17 | 孙培德, 杨东全, 陈奕柏. 多物理场耦合模型及数值模拟导论[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 2007. |
| Sun Pei-de, Yang Dong-quan, Chen Yi-bai. Introduction to Multiple Physical Field Coupling Models and Numerical Simulation[M]. Beijing: China Science and Technology Press, 2007. | |
| 18 | 李培超, 孔祥言, 卢德唐. 饱和多孔介质流固耦合渗流的数学模型[J]. 水动力学研究与进展A辑, 2003, 18(4): 419-426. |
| Li Pei-chao, Kong Xiang-yan, Lu De-tang. A mathematical model forfluid-structure coupling seepage in saturated porous media[J]. Hydrodynamics Research and Progress Series A, 2003, 18(4): 419-426. | |
| 19 | 崔溦, 李永杰, 戚蓝, 等. 高自生热材料注浆过程多场耦合数值分析[J]. 武汉大学学报: 工学版, 2018, 51(11): 941-949. |
| Cui Wei, Li Yong-jie, Qi Lan, et al. Multi-field coupling numerical analysis of high autogenic thermal material grouting process[J]. Journal of Wuhan University (Engineering Edition), 2018, 51(11): 941-949. | |
| 20 | 王丽娜. 注浆技术在路基加固中的机理及应用研究[D].济南: 山东大学土建与水利学院, 2017. |
| Wang Li-na. Research on mechanism and application of grouting technology in roadbed reinforcement[D]. Ji'nan: School of Civil Engineering and Water Conservancy, Shandong University, 2017. | |
| 21 | . 高速铁路设计规范 [S]. |
| 22 | 张千里, 韩自力, 吕宾林. 高速铁路路基基床结构分析及设计方法[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2005, 26(6): 53-57. |
| Zhang Qian-li, Han Zi-li, Lv Bin-lin. Structural analysis anddesign method of high-speed railwaysubgrade foundation bed[J]. China Railway Science, 2005, 26(6): 53-57. | |
| 23 | . 注浆技术规程 [S]. |
| 24 | 凌贤长, 官宏宇, 王成举. 黏土浆液固化剂的技术性能与工程中的应用[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2005, 3(): 40-41. |
| Ling Xian-zhang, Guan Hong-yu, Wang Cheng-ju. Technical performance and engineering application of clay grout curing agent[J]. South-to-north WaterDiversion and Water Science and Technology, 2005, 3(Sup.1): 40-41. | |
| 25 | 凌贤长, 蔡德所, 朱新永, 等. 特种粘土固化浆液研制及其工程应用成套技术[Z]. 2004. |
| 26 | 张玉石. 特种粘土固化浆液扩散性与可注性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学土木工程学院, 2006. |
| Zhang Yu-shi. Study on diffusivity and injectivity of special clay solidified grout[D]. Harbin: School of Civil Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, 2006. |
| [1] | Ce LIANG,Fu-lei HUANG,Ji-cai LIANG,Yi LI. Numerical simulation on deformation of protective beam with “日”-shaped section during rotary draw bending [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3397-3403. |
| [2] | Yong-hui SHANG,Lin-rong XU,Zhao-feng CHEN. Consolidation characteristics and influencing factors of rigid pile-raft foundation of high-speed railway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1588-1597. |
| [3] | Liu ZHANG,Xiao-yi ZHENG,Fan ZHANG,Yu ZHAO,Shu-yang ZHAO. Structural optimization design of large tolerance and multi⁃flexibility lens subassembly [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 478-485. |
| [4] | Yin-ping LI,Tian-xu JIN,Li LIU. Design and dynamic characteristic simulation of pantograph⁃catenary continuous energy system for pure electric LHD [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 454-463. |
| [5] | Wei-min ZHUANG,Hong-da SHI,Dong-xuan XIE,Guan-nan YANG. Thickness distribution of adhesive layer in dissimilar clinch⁃adhesive hybrid joint with steel and aluminum alloy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 100-106. |
| [6] | ZHOU Jie, LUO Yan, WANG Xun, WANG Hui, LI Yang, TAO Ya-ping. Multi-objective optimization of stamping forming process of head based on response surface model [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 205-212. |
| [7] | CHENG Qiang, ZHANG Zhen-dong, GUO Hui, XIE Nai-liu. Electro-magnetic-thermal coupling of GDI injector [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(3): 806-813. |
| [8] | LI Guo-fa, HAN Ming-zuo, SHAN Cui-yun, LIU Jia. Finite element simulation and experiment of magneto-rheological torque servo device [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(05): 1284-1289. |
| [9] | WANG Jing, WANG Dian-Hai, QU Zhao-Wei. Prediction method of highway induced passenger flow volume adapting ChangchunJilin high speed railway project [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(06): 1518-1522. |
|
||