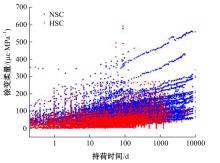
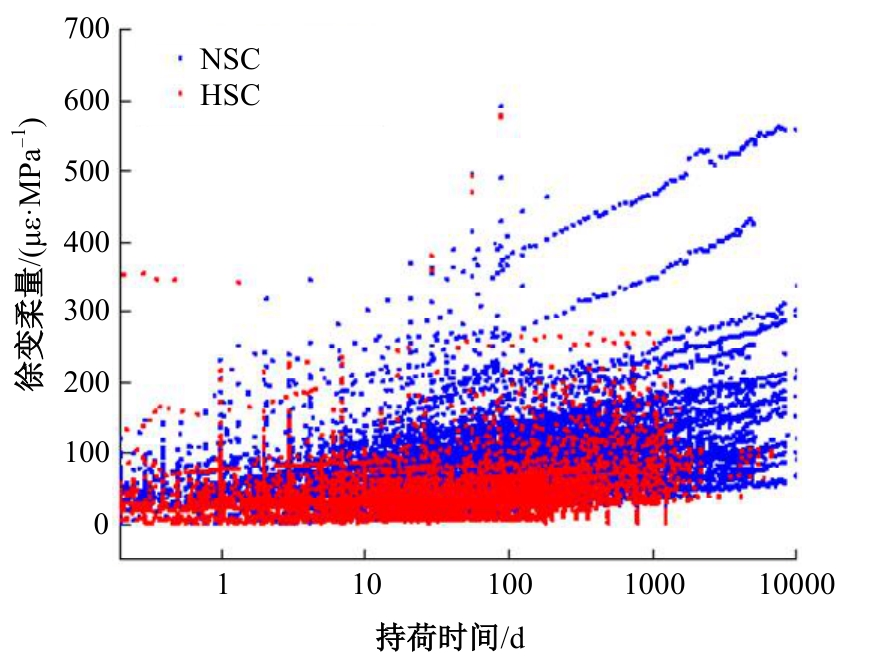
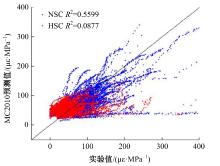
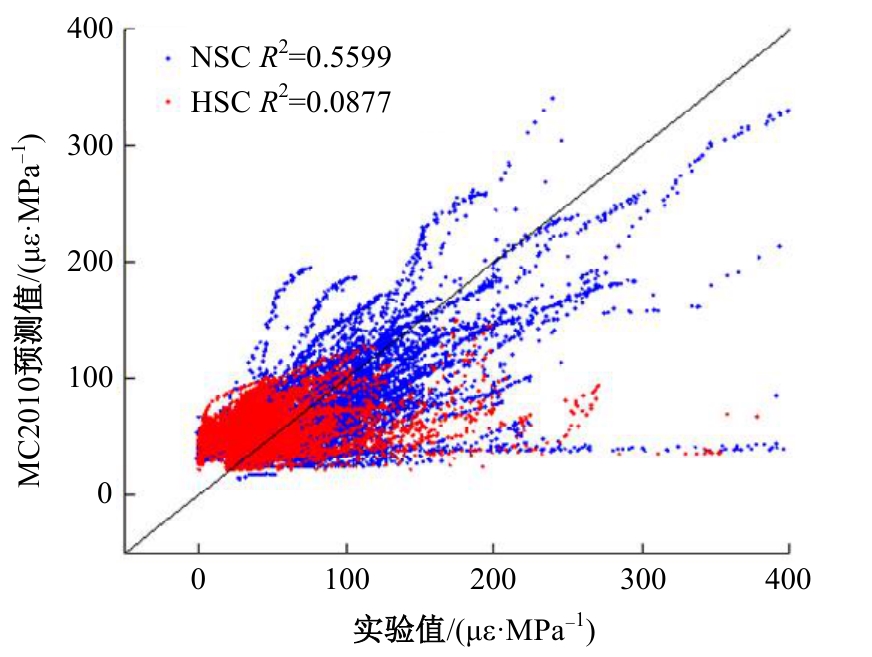
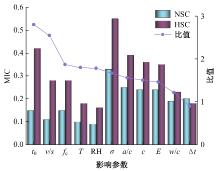
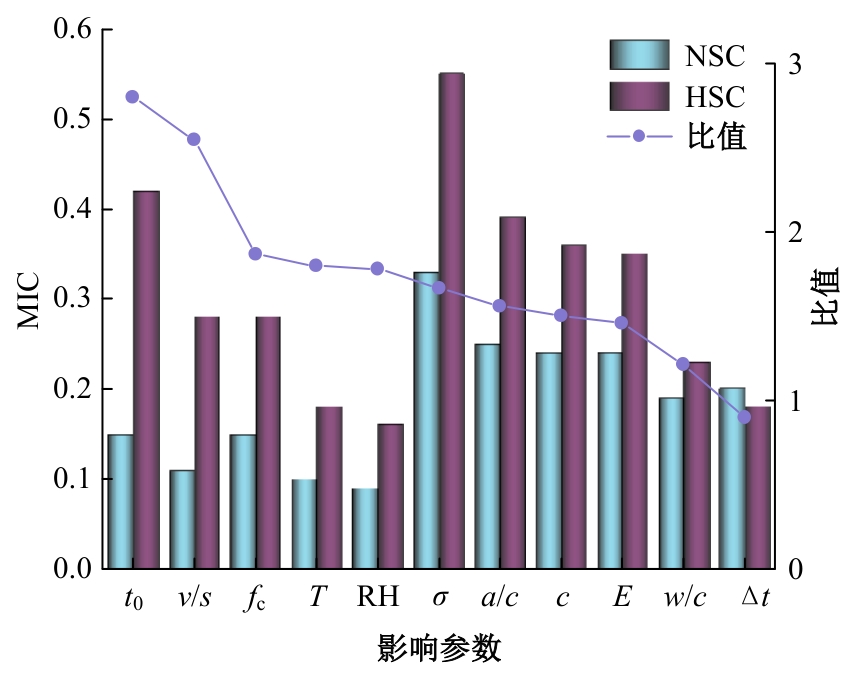
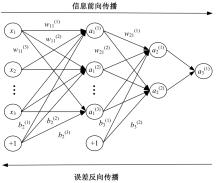
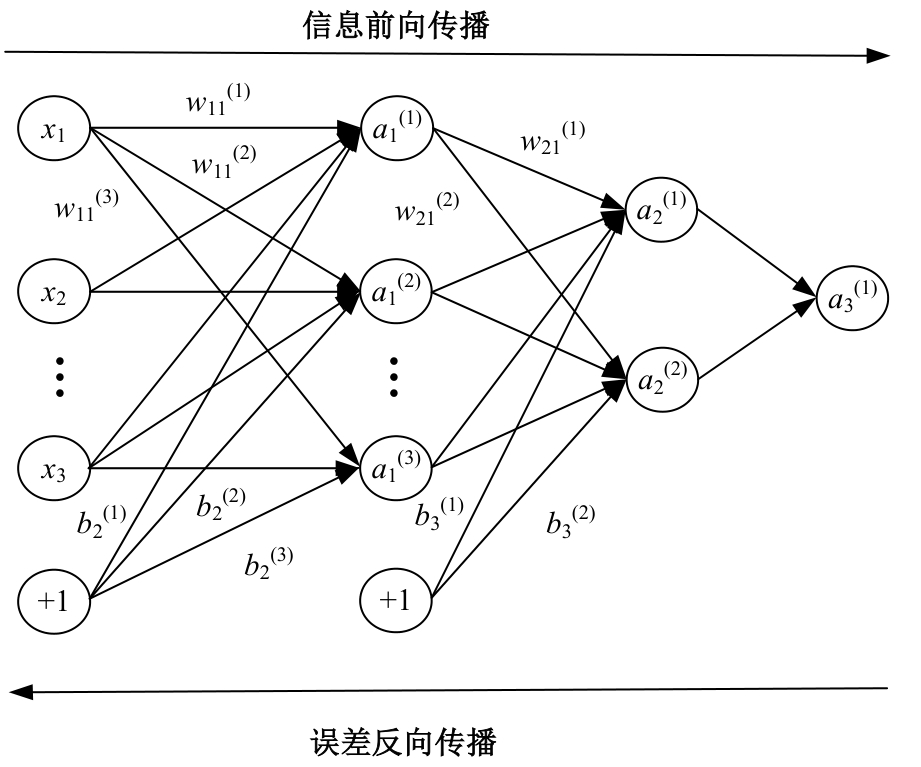
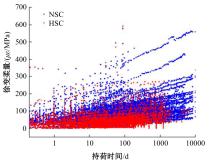
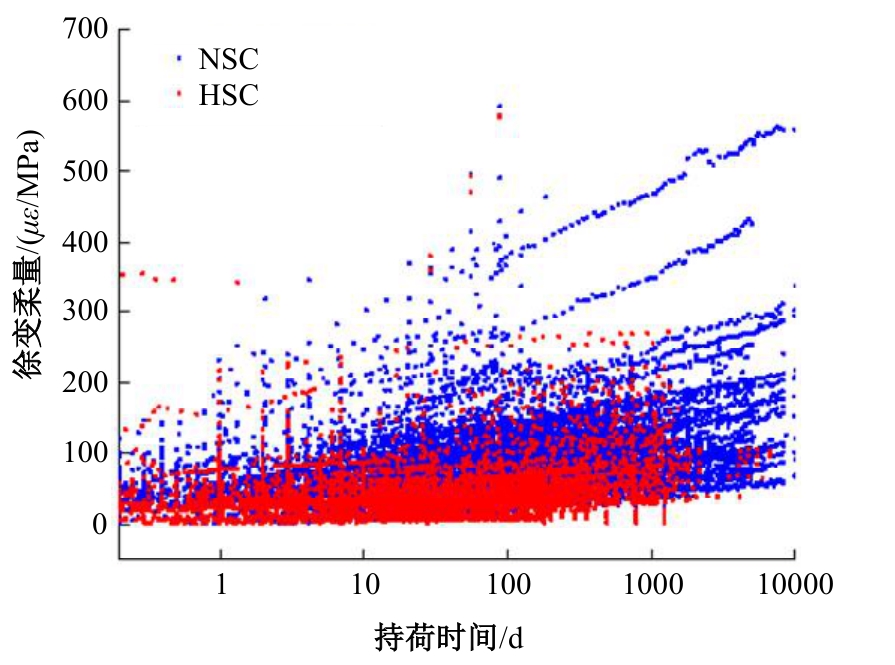
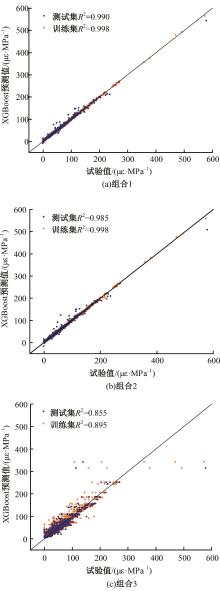
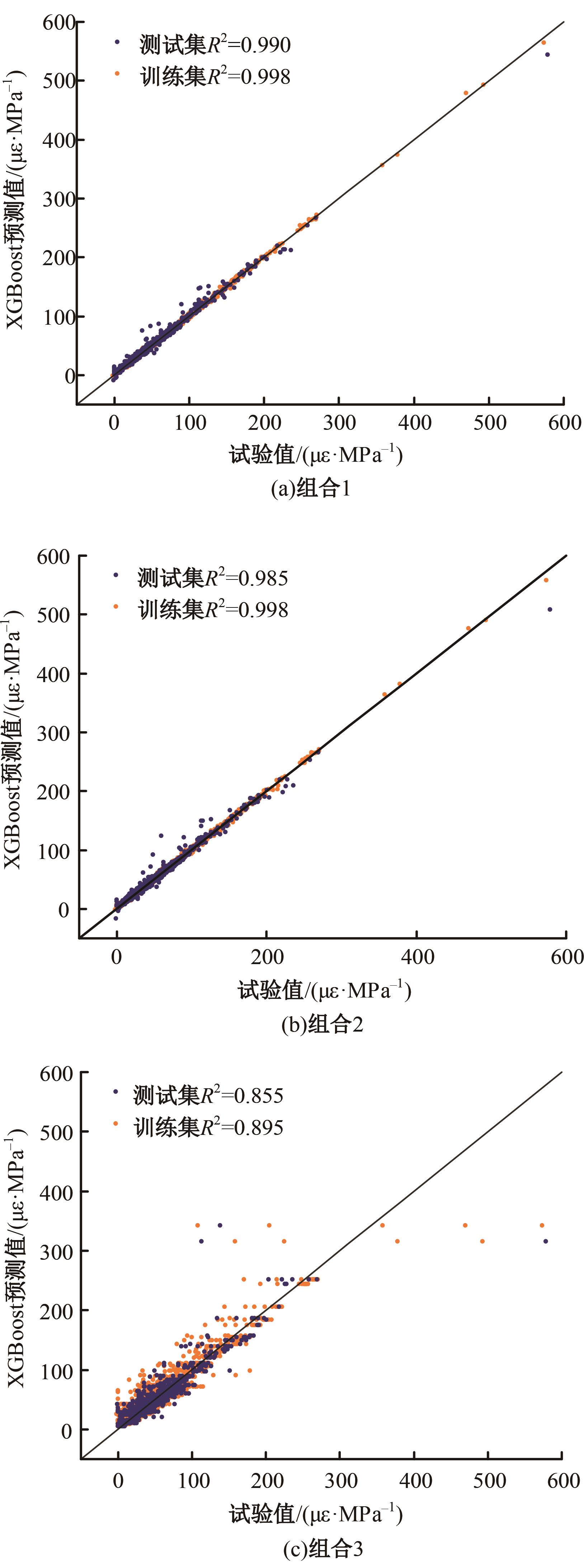
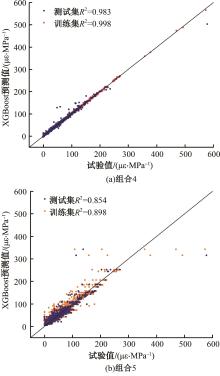
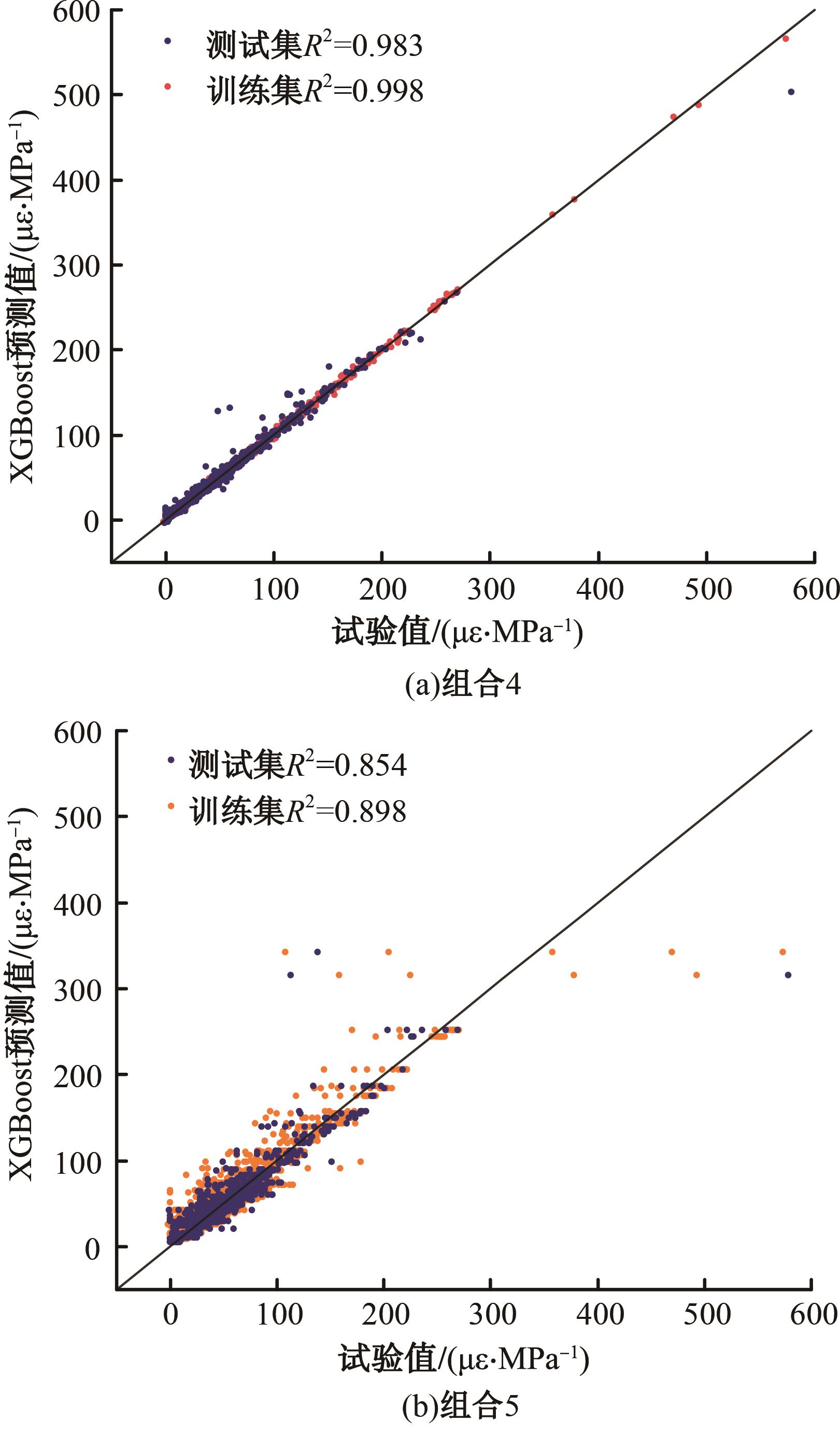
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (5): 1595-1603.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230814
Previous Articles Next Articles
Prediction of high strength concrete creep based on parametric MIC analysis and machine learning algorithm
Sheng-qi MEI1,2( ),Xiao-dong LIU2,Xing-ju WANG3,Xu-feng LI2,Teng WU2,Xiang-xu CHENG2
),Xiao-dong LIU2,Xing-ju WANG3,Xu-feng LI2,Teng WU2,Xiang-xu CHENG2
- 1.Key Laboratory of Roads and Railway Engineering Safety of Ministry of Education,Shijiazhuang 050043,China
2.School of Civil Engineering,Shijiazhuang Tiedao University,Shijiazhuang 050043,China
3.School of Traffic and Transportation,Shijiazhuang Tiedao University,Shijiazhuang 050043,China
CLC Number:
- TU17
| [1] | Vandamme M, Ulm F J. Nanogranular origin of concrete creep[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2009, 106(26): 10552-10557. |
| [2] | 黄永辉, 刘爱荣, 傅继阳, 等.高强钢管高强混凝土徐变特性试验研究[J]. 工程力学, 2021,38(8): 204-212. |
| Huang Yong-hui, Liu Ai-rong, Fu Ji-yang, et al. Experimental study on the creep characteristics of high-strength concrete filled high-strength steel tube [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2021, 38(8): 204-212. | |
| [3] | 柯敏勇, 刘海祥, 陈松.桥用高强混凝土双轴徐变试验研究[J].建筑结构学报,2012, 33(6): 116-122. |
| Ke Min-yong, Liu Hai-xiang, Chen Song. Biaxial creep experiment for high strength concrete in bridge engineering [J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2012, 33(6): 116-122. | |
| [4] | Le Roy R, Le Maou F, Torrenti J M. Long term basic creep behavior of high performance concrete: data and modelling[J]. Materials and Structures, 2017, 50(1): 1-11. |
| [5] | ACI Committee 209.209R1-92: Prediction of creep, shrinkage and temperature effects in concrete structures. manual of concrete practice part 1 [S/OL]. [1992-01-03]. |
| [6] | Betonbau. Fib model code for concrete structures 2010[J]. Ernst Shon, 2013: 97834336. |
| [7] | Gardner N J, Lockman M J. Design provisions for drying shrinkage and creep of normal strength concrete [J]. ACI Materials Journal, 2001, 98(2): 159-167. |
| [8] | Bažant Z P, Baweja S. Creep and shrinkage prediction model for analysis and design of concrete structures: model B3[J]. Materials and Structures, 1995, 28(6): 357-365. |
| [9] | Bažant Z P, Wendner R. RILEM draft recommendation. TC-242-MDC multi-decade creep and shrinkage of concreteL Material model and structural analysis Model B4 for creep, drying shrinkage and autogenous shrinkage of normal and high-strength concretes with multi-decad applicability[J]. Materials Structures, 2015, 48(4): 753-770. |
| [10] | Peng Y, Unluer C. Modeling the mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete using hybrid machine learning algorithms[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2023, 190: 106812. |
| [11] | Yang Z, Zhu H, Zhang B, et al. Short-term creep behaviors of seawater sea-sand coral aggregate concrete: An experimental study with rheological model and neural network[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 363: 129786. |
| [12] | Pham A D, Hoang N D, Nguyen Q T. Predicting compressive strength of high-performance concrete using metaheuristic-optimized least squares support vector regression[J]. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 2016, 30(3): No.06015002. |
| [13] | Liang M, Chang Z, Wan Z, et al. Interpretable ensemble-machine-learning models for predicting creep behavior of concrete[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2022, 125: 104295. |
| [14] | 曲广雷, 闫宗伟, 郑木莲, 等. 基于神经网络与回归分析的多孔混凝土性能预测[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2025, 55(1): 269-282. |
| Qu Guang-lei, Yan Zong-wei, Zheng Mu-lian, et al. Performance prediction of porous concrete based on neural network and regression analysis[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Editon), 2025, 55(1): 269-282. | |
| [15] | Xu J, Zhao X, Yu Y, et al. Parametric sensitivity analysis and modelling of mechanical properties of normal-and high-strength recycled aggregate concrete using grey theory, multiple nonlinear regression and artificial neural networks[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 211: 479-491. |
| [16] | Park D, Rilett L R. Forecasting freeway link travel times with a multilayer feedforward neural network[J]. Computer‐Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 1999, 14(5): 357-367. |
| [17] | Reshef D N, Reshef Y A, Finucane H K, et al. Detecting novel associations in large data sets[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6062): 1518-1524. |
| [18] | Li K, Long Y, Wang H, et al. Modeling and sensitivity analysis of concrete creep with machine learning methods[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2021, 33(8): 04021206. |
| [19] | Hubler M H, Wendner R, Bazant Z P. Comprehensive database for concrete creep and shrinkage: Analysis and recommendations for testing and recording[J]. ACI Materials Journal, 2015, 112(4): 547-558. |
| [20] | Tang L, Na S H. Comparison of machine learning methods for ground settlement prediction with different tunneling datasets[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2021, 13(6): 1274-1289. |
| [21] | Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Friedman J H, et al. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction[M]. New York: Springer, 2009. |
| [22] | Cortes C, Vapnik V. Support-vector networks[J]. Machine Learning, 1995, 20: 273-297. |
| [23] | Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, et al. Scikit-learn: machine learning in python[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2011, 12: 2825-2830. |
| [24] | Chen T, Guestrin C. XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system[C]∥Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 785-794. |
| [25] | Zeghal M. Modeling the creep compliance of asphalt concrete using the artificial neural network technique[C]∥GeoCongress 2008: Characterization, Monitoring, and Modeling of GeoSystems, New Orleans, USA, 2008: 910-916. |
| [1] | Xue-ping FAN,Du YANG,Jiu-yu LI,Qi-fan ZHAO,Yue-fei LIU. Dynamic prediction of bridge coupled extreme stresses produced by temperature and vehicle loads [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1588-1594. |
| [2] | Yu ZHOU,Meng LI,Sheng-kui DI,Xian-zeng SHI,Dong CHEN. Analytical solution of thrust influence line of variable section two-hinged arch and application of damage identification [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 664-672. |
| [3] | Yu-dai WANG,Bin WANG,Fu-sheng MIAO,Nan MA. Freezing and expansion response of lined channels under changes in hydrothermal coupling [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 256-268. |
| [4] | Hao JIANG,Zheng-wen ZHAO. Experiment on shear performance of RC beams strengthened with basalt fiber grid cement-based composites [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 211-220. |
| [5] | Fang-fang WEI,Li-ping LI,Qing-peng XU,You-zheng ZHAO,Jing-jing YANG. Experiment on seismic behavior of fire-fired composite shear wall with double steel plates and infill concrete after reinforcement [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 230-244. |
| [6] | Jin-quan ZHAO,Long ZHOU,Yong-gang DING,Rong-ji ZHU. Experiment on anchoring performance of spiral stirrup-corrugated pipe grout splicing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2484-2494. |
| [7] | Wei-song YANG,An ZHANG,Wei-xiao XU,Hai-sheng LI,Ke DU. Seismic performance of stiffness enhanced metal coupling beam damper [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2469-2483. |
| [8] | Qi-wu YAN,Zhong-liang ZOU. Hybrid algorithm for seismic energy-dissipated structures based on optimal placement of dampers [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2267-2274. |
| [9] | Feng-guo JIANG,Yu-ming ZHOU,Li-li BAI,Shuang LIANG. Improved krill algorithm and its application in structural optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2256-2266. |
| [10] | Guang-tai ZHANG,Cheng-xiao ZHOU,Shi-tuo LIU. Restoring force model of fiber lithium slag concrete column in saline soil environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1944-1957. |
| [11] | Yan-song DIAO,Yi-jian REN,Yuan-qiang YANG,Ling-yun ZHAO,Xiu-li LIU,Yun LIU. Experimental on seismic performance of replaceable splicing steel beam-column joints with friction energy dissipation components [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1643-1656. |
| [12] | Xue-ping FAN,Yue-fei LIU. Bridge extreme stress dynamic prediction based on improved Gaussian mixed particle filter new algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1038-1044. |
| [13] | Yi-fan LIU,Zhi-wei MIAO,Chen SHEN,Xiang-dong GENG. Evaluation of mechanical properties of non-uniform corroded rebars based on Monte Carlo method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1007-1015. |
| [14] | Xue-ping FAN,Heng ZHOU,Yue-fei LIU. Time⁃variant reliability analysis of bridge members based on Gaussian Copula⁃Bayesian dynamic models [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 485-493. |
| [15] | Hai-xu YANG,Yue GUO,Hai-biao WANG,Yi HU. Bending performance of cold-formed thin-walled steel-glulam composite beams [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3513-3525. |
|