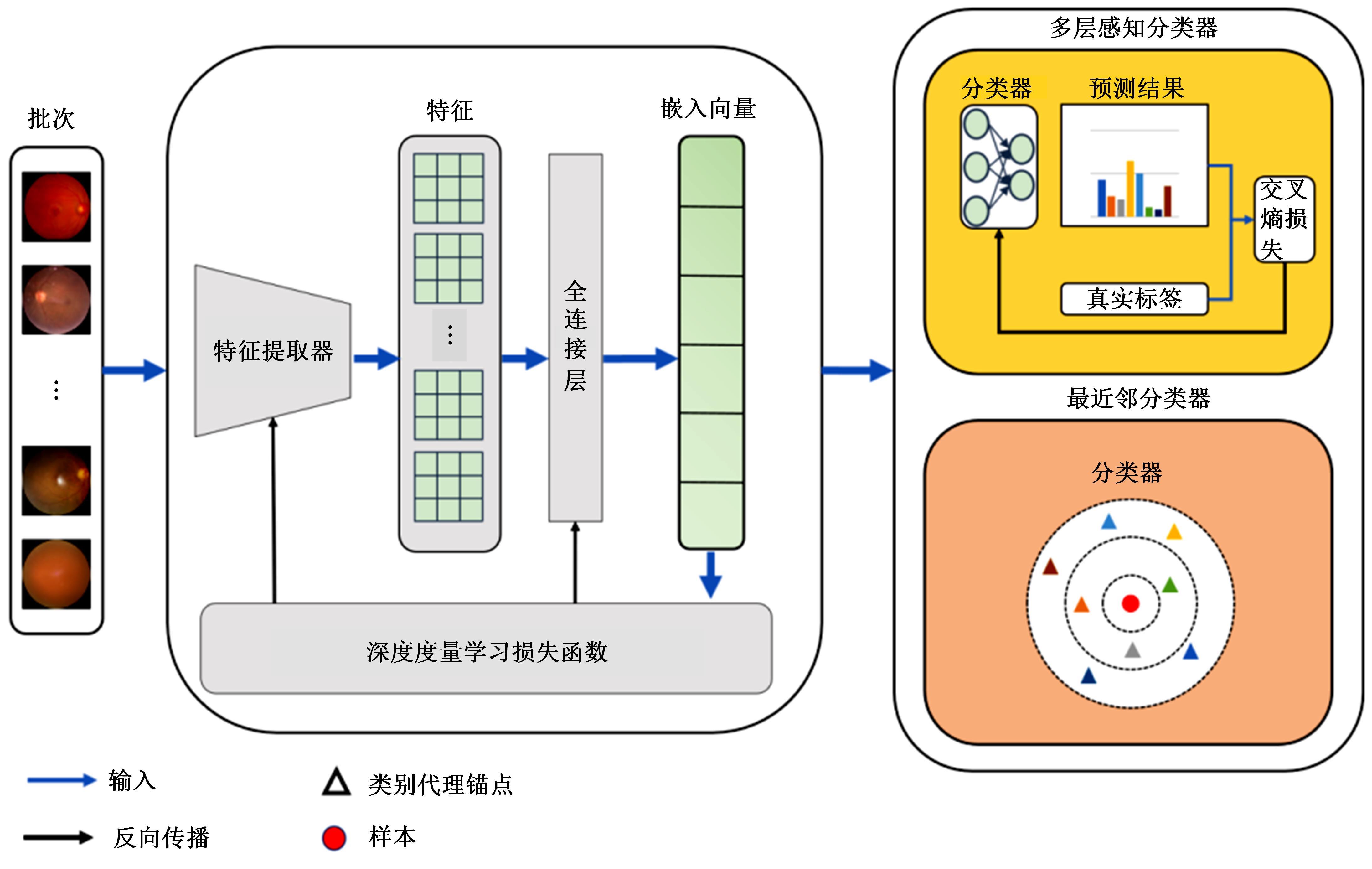
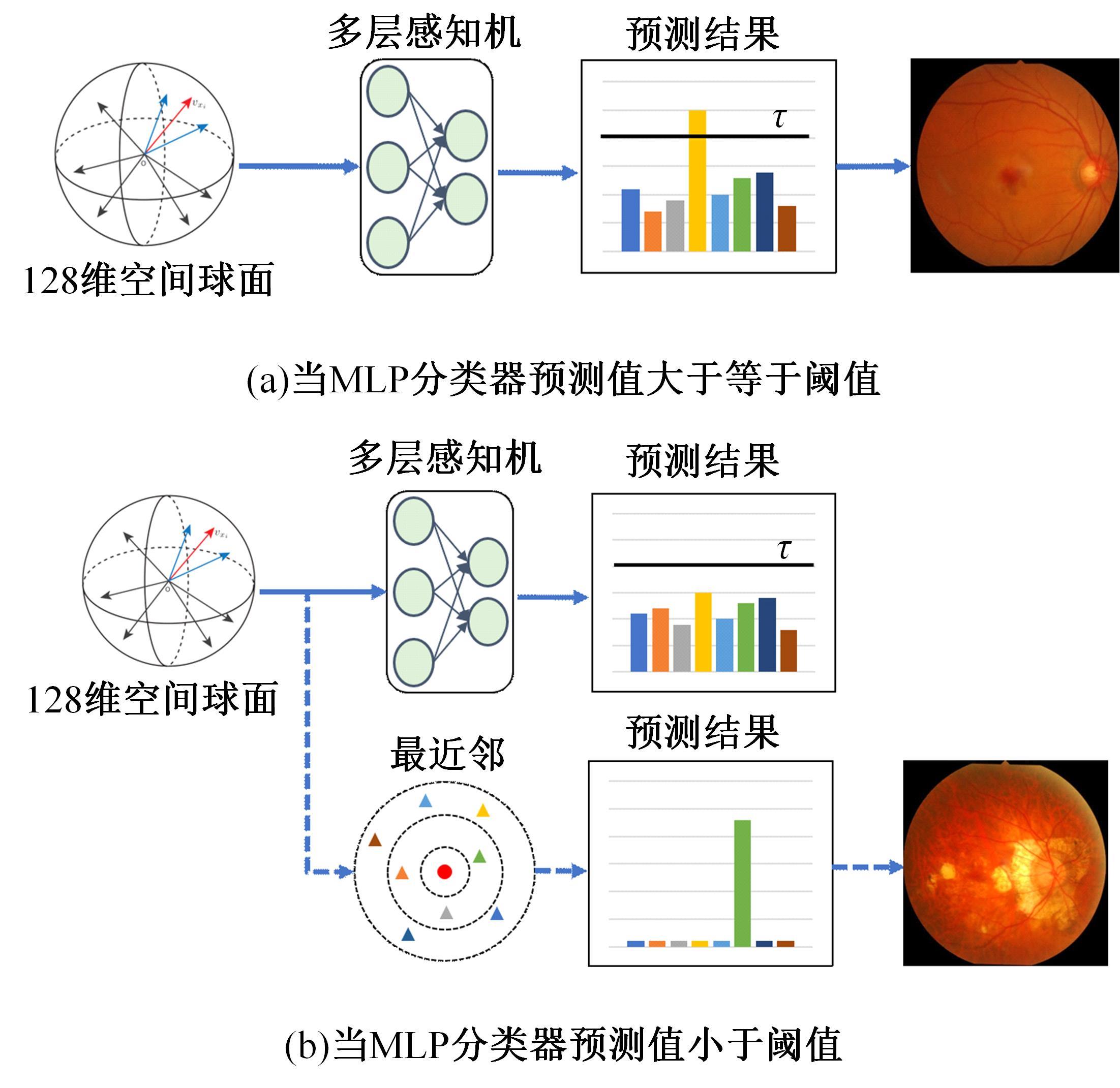
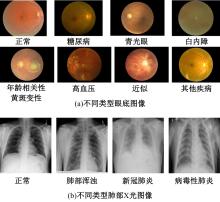
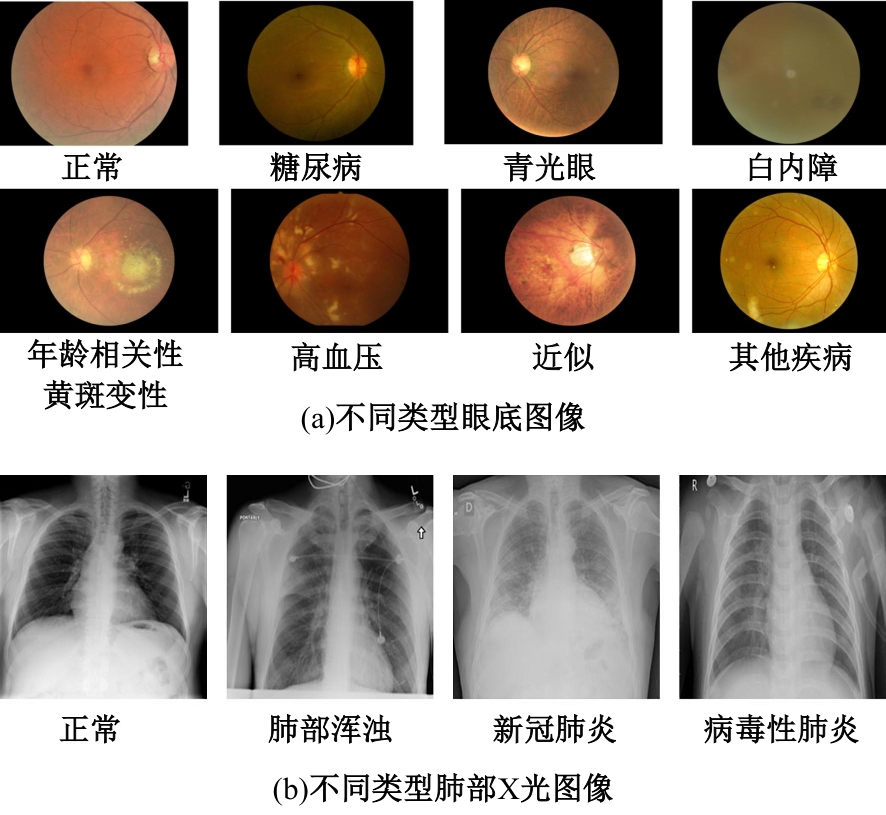
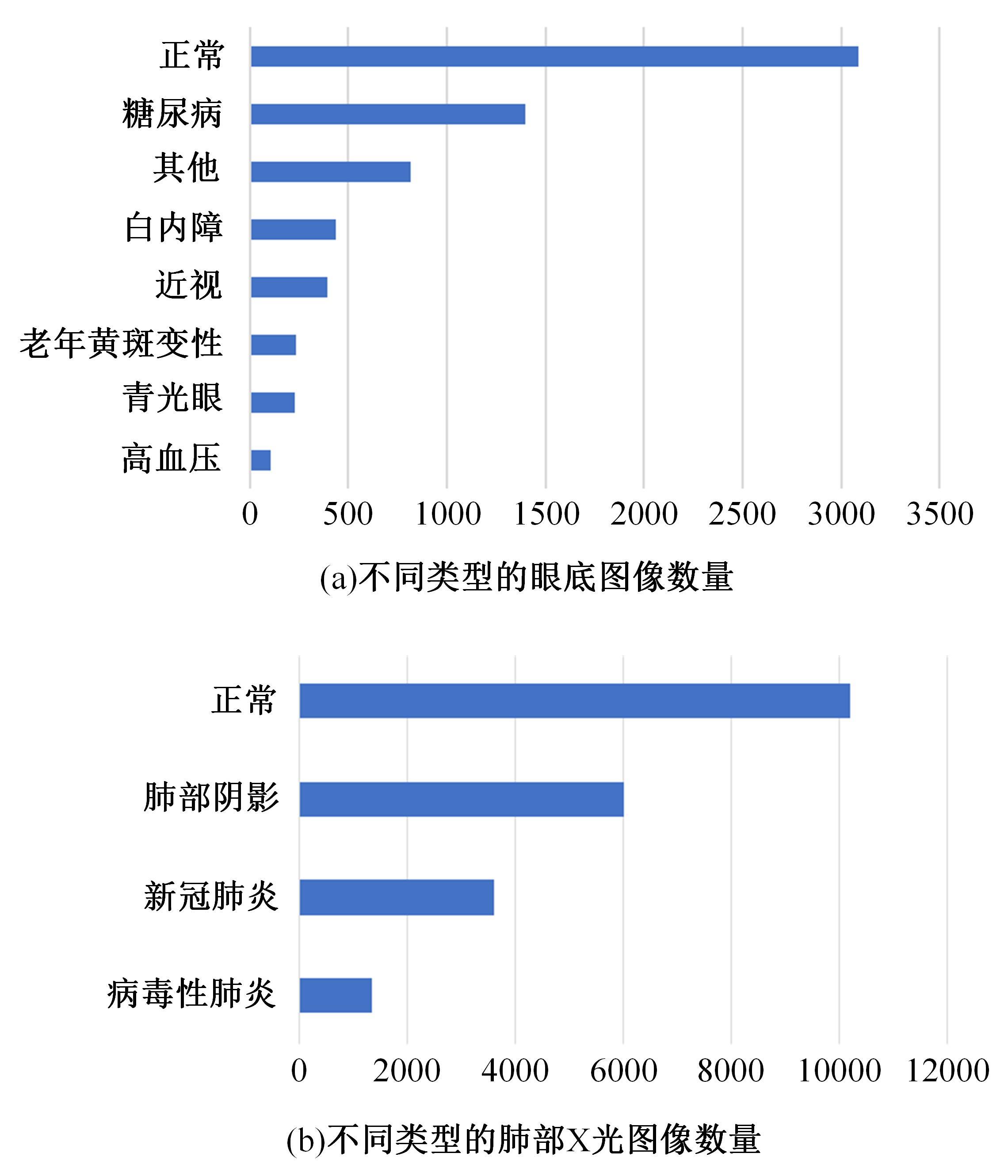
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 2122-2130.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230991
Previous Articles Next Articles
Unbalanced image classification algorithm based on fine⁃grained analysis
Ping-ping LIU1,2( ),Wen-li SHANG3,Xiao-yu XIE1,Xiao-kang YANG3
),Wen-li SHANG3,Xiao-yu XIE1,Xiao-kang YANG3
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
3.College of Software,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
CLC Number:
- TP391
| [1] | He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| [2] | Huang Z Z, Zhang J P, Shan H M. When age-invariant face recognition meets face age synthesis: a multi-task learning framework[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2021: 7282-7291. |
| [3] | Ji R, Wen L, Zhang L, et al. Attention convolutional binary neural tree for fine-grained visual categorization[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 10468-10477. |
| [4] | Wei X S, Xie C W, Wu J, et al. Mask-CNN: localizing parts and selecting descriptors for fine-grained bird species categorization[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 76: 704-714. |
| [5] | Zheng H, Fu J, Zha Z J, et al. Learning deep bilinear transformation for fine-grained image representation[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2019, 32: No.03621. |
| [6] | Chang D, Ding Y, Xie J, et al. The devil is in the channels: Mutual-channel loss for fine-grained image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 4683-4695. |
| [7] | Bera A, Wharton Z, Liu Y, et al. SR-GNN: spatial relation-aware graph neural network for fine-grained image categorization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 6017-6031. |
| [8] | Sundgaard J V, Harte J, Bray P, et al. Deep metric learning for otitis media classification[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2021, 71: No.102034. |
| [9] | Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale[J/OL].[2023-08-11]. |
| [10] | Guo H, Wang S. Long-tailed multi-label visual recognition by collaborative training on uniform and re-balanced samplings[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2021: 15089-15098. |
| [11] | Movshovitz-Attias Y, Toshev A, Leung T K, et al. No fuss distance metric learning using proxies[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Hawaii, USA, 2017: 360-368. |
| [12] | Wang X, Han X, Huang W, et al. Multi-similarity loss with general pair weighting for deep metric learning[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Los Angeles, USA, 2019: 5022-5030. |
| [13] | International Competition on Ocular Disease Intelligent Recognition[EB/OL]. [2021-11-18]. |
| [14] | Rahman T, Khandakar A, Qiblawey Y, et al. Exploring the effect of image enhancement techniques on COVID-19 detection using chest X-ray images[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine,2021,132:No.104319. |
| [15] | Wang J, Yang L, Huo Z, et al. Multi-label classification of fundus images with efficientnet[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 212499-212508. |
| [16] | Lin J, Cai Q, Lin M. Multi-label classification of fundus images with graph convolutional network and self-supervised learning[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2021, 28: 454-458. |
| [17] | Li Z, Xu M, Yang X, et al. Multi-label fundus image classification using attention mechanisms and feature fusion[J]. Micromachines, 2022, 13(6): No.947. |
| [18] | Yang X, Yi S. Multi-classification of fundus diseases based on DSRA-CNN[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2022, 77: No.103763. |
| [19] | Afshar P, Heidarian S, Naderkhani F, et al. Covid-caps: a capsule network-based framework for identification of COVID-19 cases from X-ray images[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2020, 138: 638-643. |
| [20] | Panahi A, Askari M R, Akrami M, et al. Deep residual neural network for COVID-19 detection from chest X-ray images[J]. SN Computer Science, 2022, 3(2): No.169. |
| [1] | Jian WANG,Chen-wei JIA. Trajectory prediction model for intelligent connected vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1963-1972. |
| [2] | Xiang-jiu CHE,Yu-peng SUN. Graph node classification algorithm based on similarity random walk aggregation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2069-2075. |
| [3] | Feng-feng ZHOU,Zhe GUO,Yu-si FAN. Feature representation algorithm for imbalanced classification of multi⁃omics cancer data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2089-2096. |
| [4] | Hai-peng CHEN,Shi-bo ZHANG,Ying-da LYU. Multi⁃scale context⁃aware and boundary⁃guided image manipulation detection method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2114-2121. |
| [5] | Zi-hao SHEN,Yong-sheng GAO,Hui WANG,Pei-qian LIU,Kun LIU. Deep deterministic policy gradient caching method for privacy protection in Internet of Vehicles [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1638-1647. |
| [6] | You-wei WANG,Ao LIU,Li-zhou FENG. New method for text sentiment classification based on knowledge distillation and comment time [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1664-1674. |
| [7] | Hong-wei ZHAO,Ming-zhu ZHOU,Ping-ping LIU,Qiu-zhan ZHOU. Medical image segmentation based on confident learning and collaborative training [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1675-1681. |
| [8] | Yue HOU,Jin-song GUO,Wei LIN,Di ZHANG,Yue WU,Xin ZHANG. Multi-view video speed extraction method that can be segmented across lane demarcation lines [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1692-1704. |
| [9] | Jun WANG,Chang-fu SI,Kai-peng WANG,Qiang FU. Intrusion detection method based on ensemble learning and feature selection by PSO-GA [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1396-1405. |
| [10] | Tao XU,Shuai-di KONG,Cai-hua LIU,Shi LI. Overview of heterogeneous confidential computing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 755-770. |
| [11] | Meng-xue ZHAO,Xiang-jiu CHE,Huan XU,Quan-le LIU. A method for generating proposals of medical image based on prior knowledge optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 722-730. |
| [12] | Xiao-dong CAI,Qing-song ZHOU,Yan-yan ZHANG,Yun XUE. Social recommendation based on global capture of dynamic, static and relational features [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 700-708. |
| [13] | Xiang-jiu CHE,Yu-ning WU,Quan-le LIU. A weighted isomorphic graph classification algorithm based on causal feature learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 681-686. |
| [14] | Xiao-ran GUO,Tie-jun WANG,Yue YAN. Entity relationship extraction method based on local attention and local remote supervision [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 307-315. |
| [15] | Hao WANG,Bin ZHAO,Guo-hua LIU. Temporal and motion enhancement for video action recognition [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 339-346. |
|