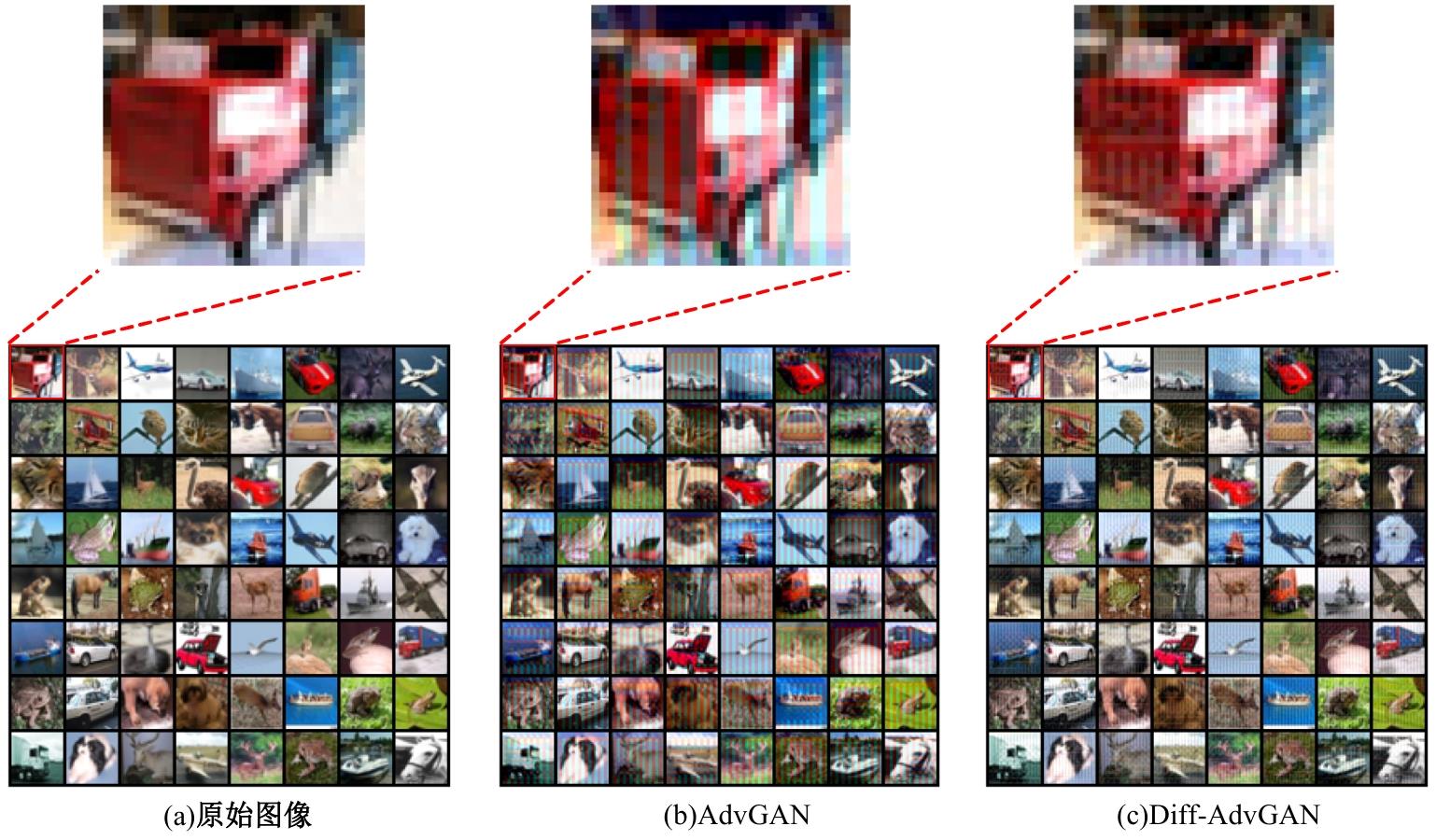
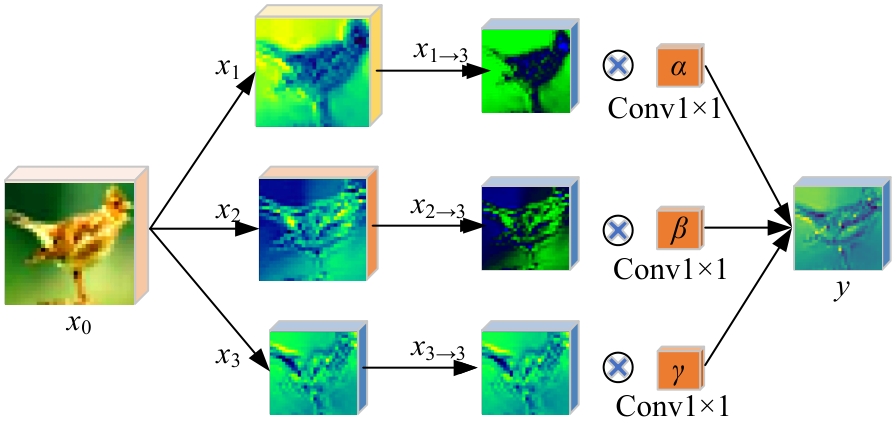
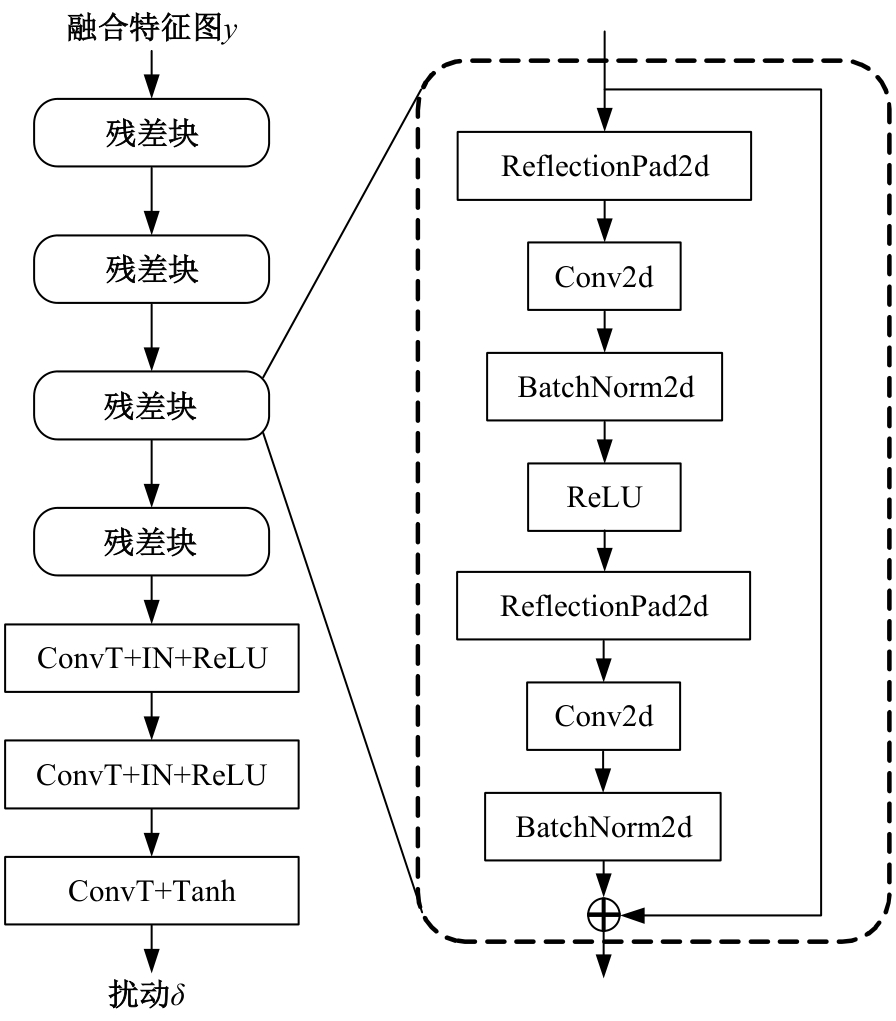
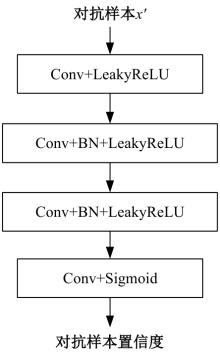
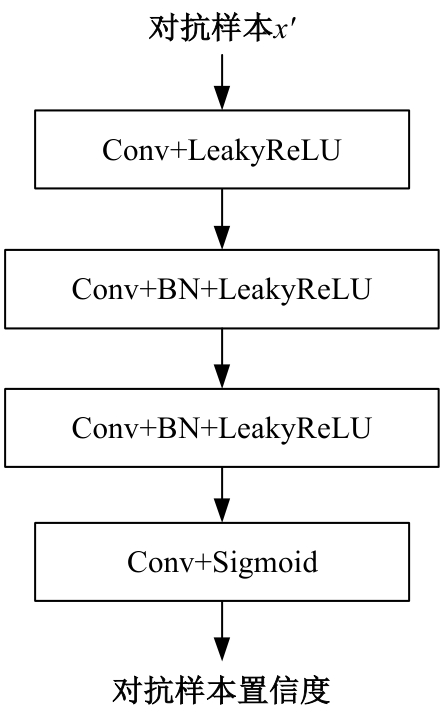
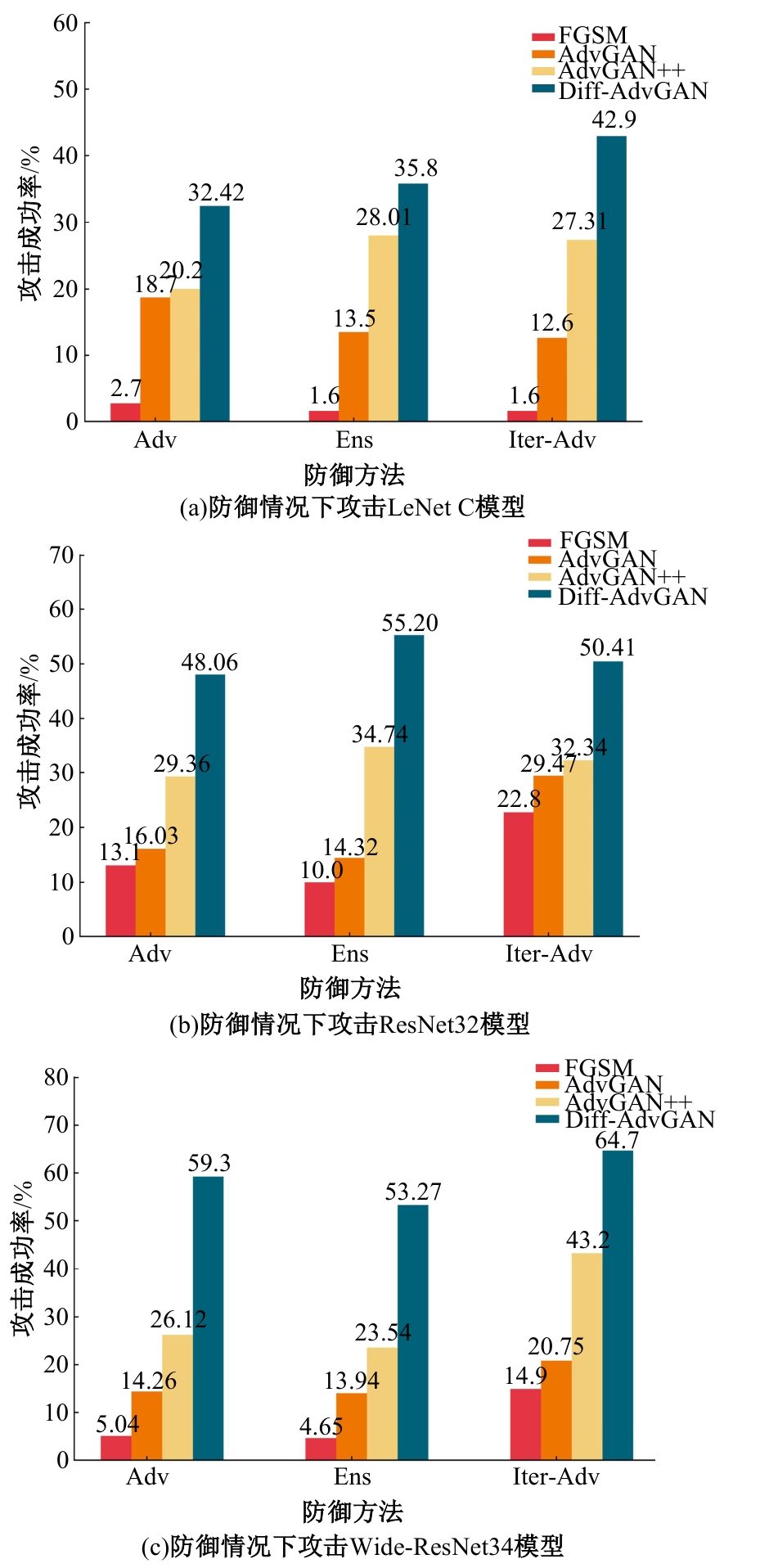
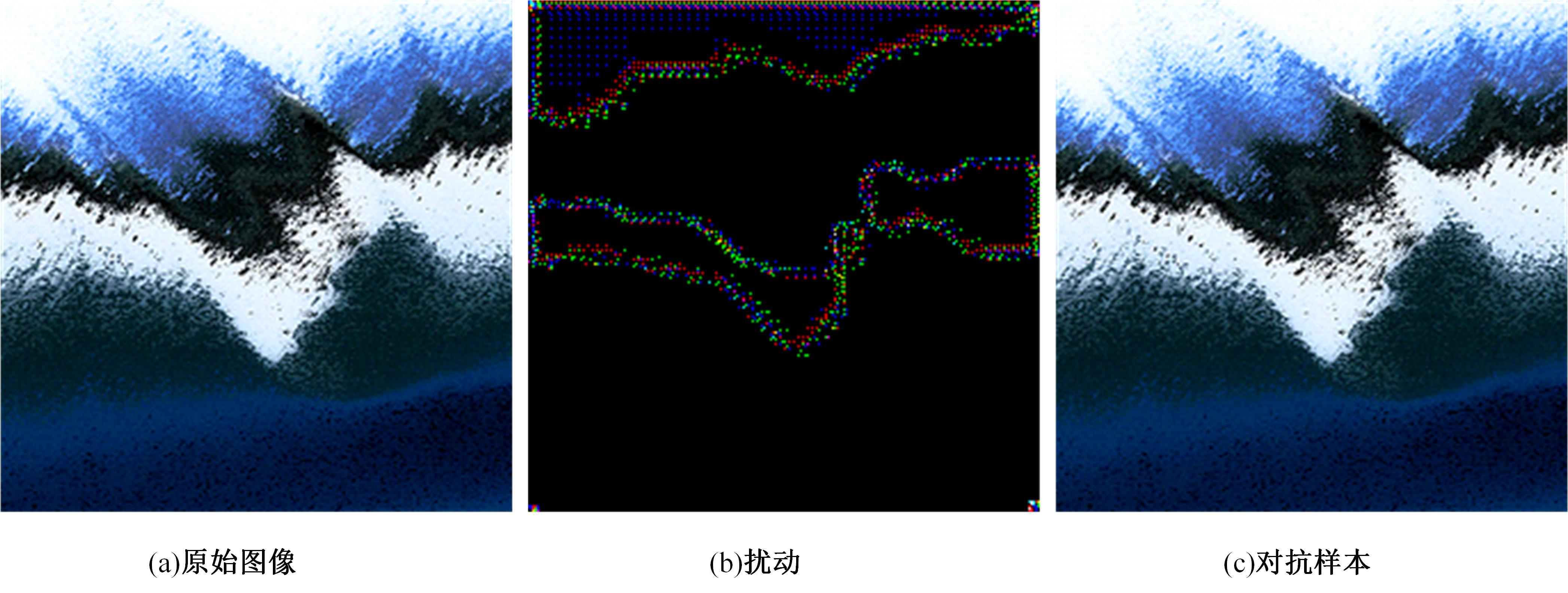
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (12): 4052-4062.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240555
Image adversarial examples generation based on Diff⁃AdvGAN
Hong ZHAO( ),Yu-xuan MA,Fu-rong SONG
),Yu-xuan MA,Fu-rong SONG
- School of Computer and Communication,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
CLC Number:
- TP391
| [1] | Kim I, Baek W, Kim S. Spatially attentive output layer for image classification[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Los Alamitos, CA, USA, 2020: 9533-9542. |
| [2] | Boutros F, Damer N, Kirchbuchner F, et al. Elasticface: Elastic margin loss for deep face recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2022: 1578-1587. |
| [3] | Hausler S, Garg S, Xu M, et al. Patch-netvlad: Multi-scale fusion of locally-global descriptors for place recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Los Alamitos, CA, USA, 2021: 14141-14152. |
| [4] | Szegedy C, Zaremba W, Sutskever I, et al. Intriguing properties of neural networks[C]∥2nd International Conference on Learning Representations, Banff, AB, Canada, 2014: 23-41. |
| [5] | 吉顺慧, 胡黎明, 张鹏程, 等. 基于稀疏扰动的对抗样本生成方法[J]. 软件学报, 2023, 34(9): 4003-4017. |
| Ji Shun-hui, Hu Li-ming, Zhang Peng-cheng, et al. Adversarial example generation method based on sparse perturbation[J]. Journal of Software, 2023, 34(9): 4003-4017. | |
| [6] | Goodfellow I J, Shlens J, Szegedy C. Explaining and harnessing adversarial examples[J/OL]. [2025-05-01]. |
| [7] | Kurakin A, Goodfellow I J, Bengio S. Adversarial examples in the physical world[C]∥5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 2017: 1-14. |
| [8] | Carlini N, Wagner D. Towards evaluating the robustness of neural networks[C]∥2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Jose, CA, USA, 2017: 39-57. |
| [9] | Baluja S, Fischer I. Adversarial transformation networks: learning to generate adversarial examples[J/OL]. [2025-05-01]. |
| [10] | Zhao Z L, Dua D, Singh S. Generating natural adversarial examples[C]∥6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2018: 1-15. |
| [11] | Arjovsky M, Chintala S, Bottou L. Wasserstein generative adversarial networks[C]∥Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, NSW, Australia:, 2017: 214-223. |
| [12] | Zhang W J. Generating adversarial examples in one shot with image-to-image translation GAN[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 151103-151119. |
| [13] | Xiao C W, Li B, Zhu J Y, et al. Generating adversarial examples with adversarial networks[C]∥Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 3905-3911. |
| [14] | 黄帅娜, 李玉祥, 毛岳恒, 等. 基于集成advGAN的黑盒迁移对抗攻击[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(10): 2391-2398. |
| Huang Shuai-na, Li Yu-xiang, Mao Yue-heng, et al. Black-box transferable adversarial attacks based on ensemble advGAN[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(10): 2391-2398. | |
| [15] | 刘悦文, 孙子文. 抵御对抗攻击的生成对抗网络IWSN入侵检测模型[J]. 江苏大学学报: 自然科学版, 2025, 46(5): 562-569. |
| Liu Yue-wen, Sun Zi-wen. Intrusion detection model based on generative adversarial networks in IWSN against adversarial attacks[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University (Natural Science Edition), 2025, 46(5): 562-569. | |
| [16] | Jandial S, Mangla P, Varshney S, et al. AdvGAN++: harnessing latent layers for adversary generation[C]∥2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop, Los Alamitos, CA, USA, 2019: 2045-2048. |
| [17] | Singh J, Gould S, Zheng L. High-fidelity guided image synthesis with latent diffusion models[C]∥2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2023: 5997-6006. |
| [18] | Podell D, English Z, Lacey K, et al. SDXL: improving latent diffusion models for high-resolution image synthesis[J/OL]. [2024-05-03]. |
| [19] | Dai X L, Liang K S, Xiao B. AdvDiff: generating unrestricted adversarial examples using diffusion models[J/OL]. [2024-05-03]. |
| [20] | Chen X Q, Gao X T, Zhao J J, et al. Advdiffuser: Natural adversarial example synthesis with diffusion models[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2023: 4562-4572. |
| [21] | Liu D C, Wang X J, Peng C L, et al. Adv-diffusion: Imperceptible adversarial face identity attack via latent diffusion model[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2024, 38(4): 3585-3593. |
| [22] | Liu S T, Huang D, Wang Y H. Learning spatial fusion for single-shot object detection[J/OL]. [2024-05-03]. |
| [23] | Ho J, Jain A, Abbeel P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models[J]. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2020, 33: 6840-6851. |
| [24] | Song J M, Meng C L, Ermon S. Denoising diffusion implicit models[J/OL]. [2024-05-03]. |
| [25] | Tramèr F, Kurakin A, Papernot N, et al. Ensemble adversarial training: attacks and defenses[C]∥6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2018: 1-20. |
| [26] | Madry A, Makelov A, Schmidt L, et al. Towards deep learning models resistant to adversarial attacks[C]∥6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2018: 1-23. |
| [1] | Wei LAN,Zheng ZHOU,Guan-yu WANG,Wei WANG,Miao-miao ZHANG. Intelligent fitting method for vehicle design based on machine learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(9): 2858-2863. |
| [2] | Yan PIAO,Ji-yuan KANG. RAUGAN:infrared image colorization method based on cycle generative adversarial networks [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2722-2731. |
| [3] | Guang-wen LIU,Qi-ying ZHAO,Chao WANG,Lian-yu Gao,Hua CAI,Qiang FU. Progressive recursive generative adversarial network-based single-image rain removal algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1363-1373. |
| [4] | He-shan ZHANG,Meng-wei FAN,Xin TAN,Zhan-ji ZHENG,Li-ming KOU,Jin XU. Dense small object vehicle detection in UAV aerial images using improved YOLOX [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1307-1318. |
| [5] | Yuan JI,Ya-qi YU. Optimization algorithm for speech facial video generation based on dense convolutional generative adversarial networks and keyframes [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 986-992. |
| [6] | Wei LYU,Jia-ze HAN,Jing-hui CHU,Pei-guang JING. Multi⁃modal self⁃attention network for video memorability prediction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1211-1219. |
| [7] | Le-ping LIN,Zeng-tong LU,Ning OUYANG. Face reconstruction and recognition in non⁃cooperative scenes [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(12): 2941-2946. |
| [8] | Shuai-na HUANG,Yu-xiang LI,Yue-heng MAO,Ai-ying BAN,Zhi-yong ZHANG. Black-box transferable adversarial attacks based on ensemble advGAN [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(10): 2391-2398. |
|
||