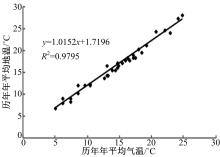
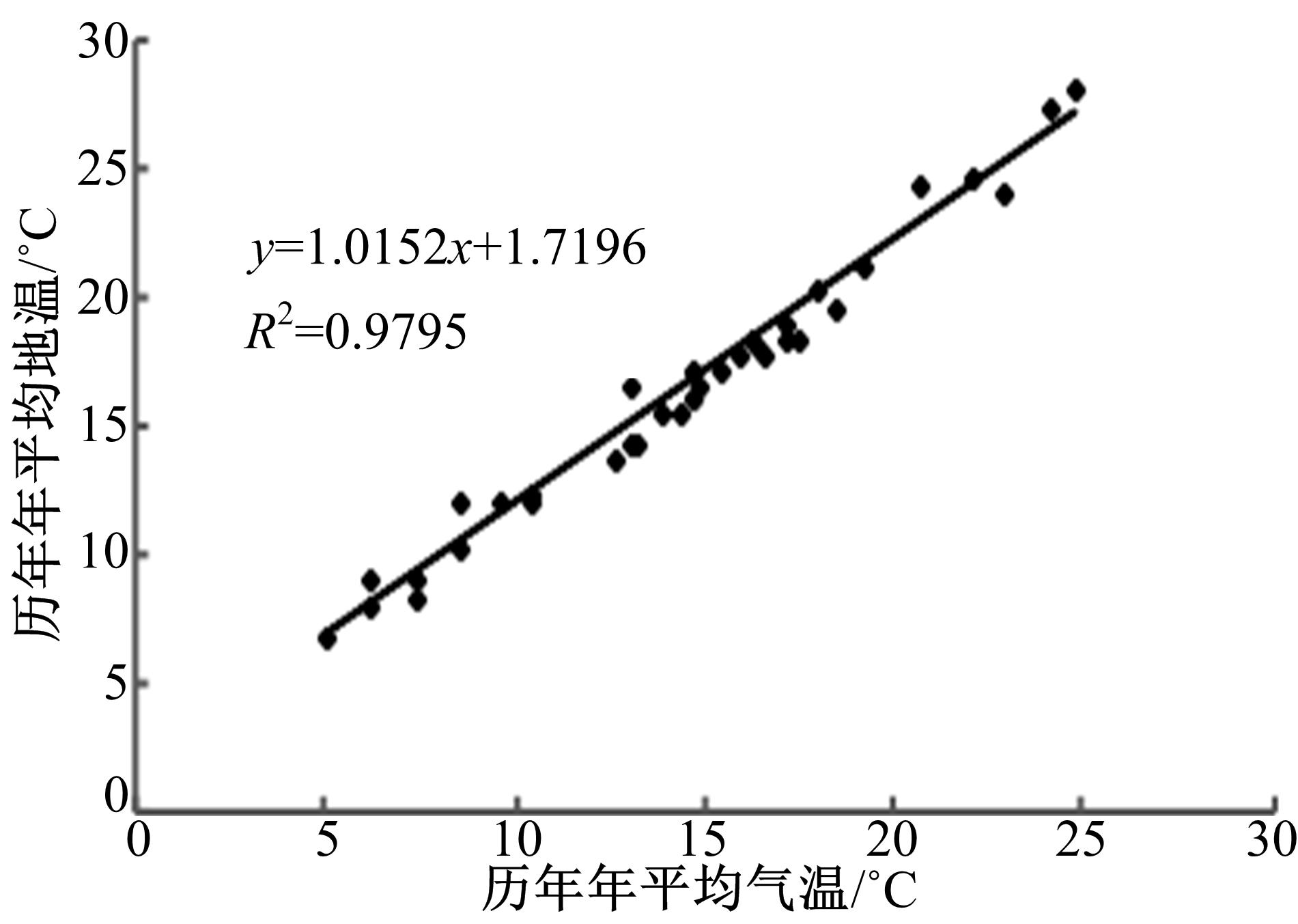
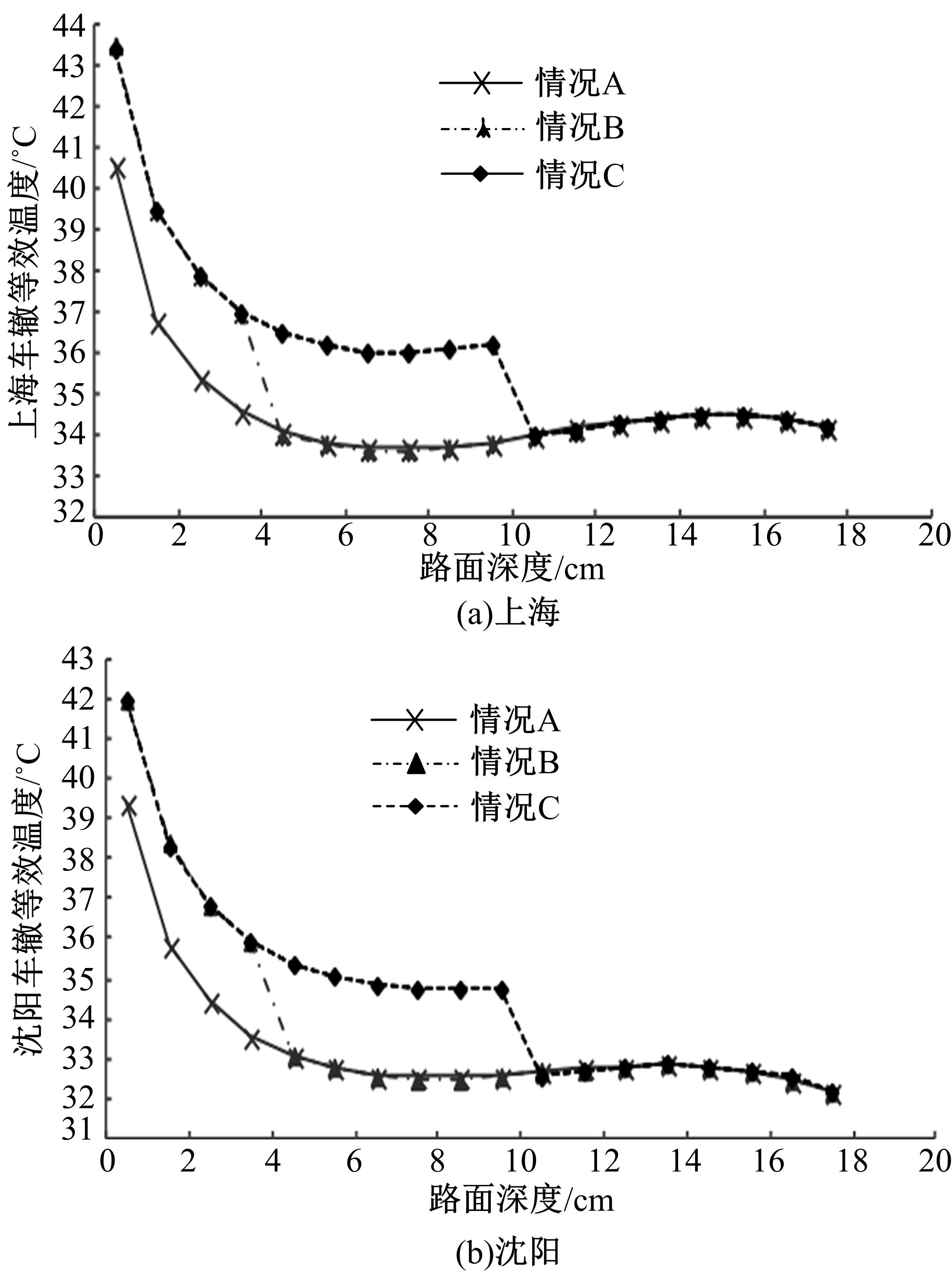
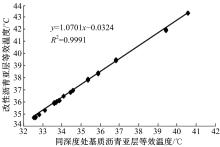
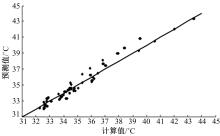
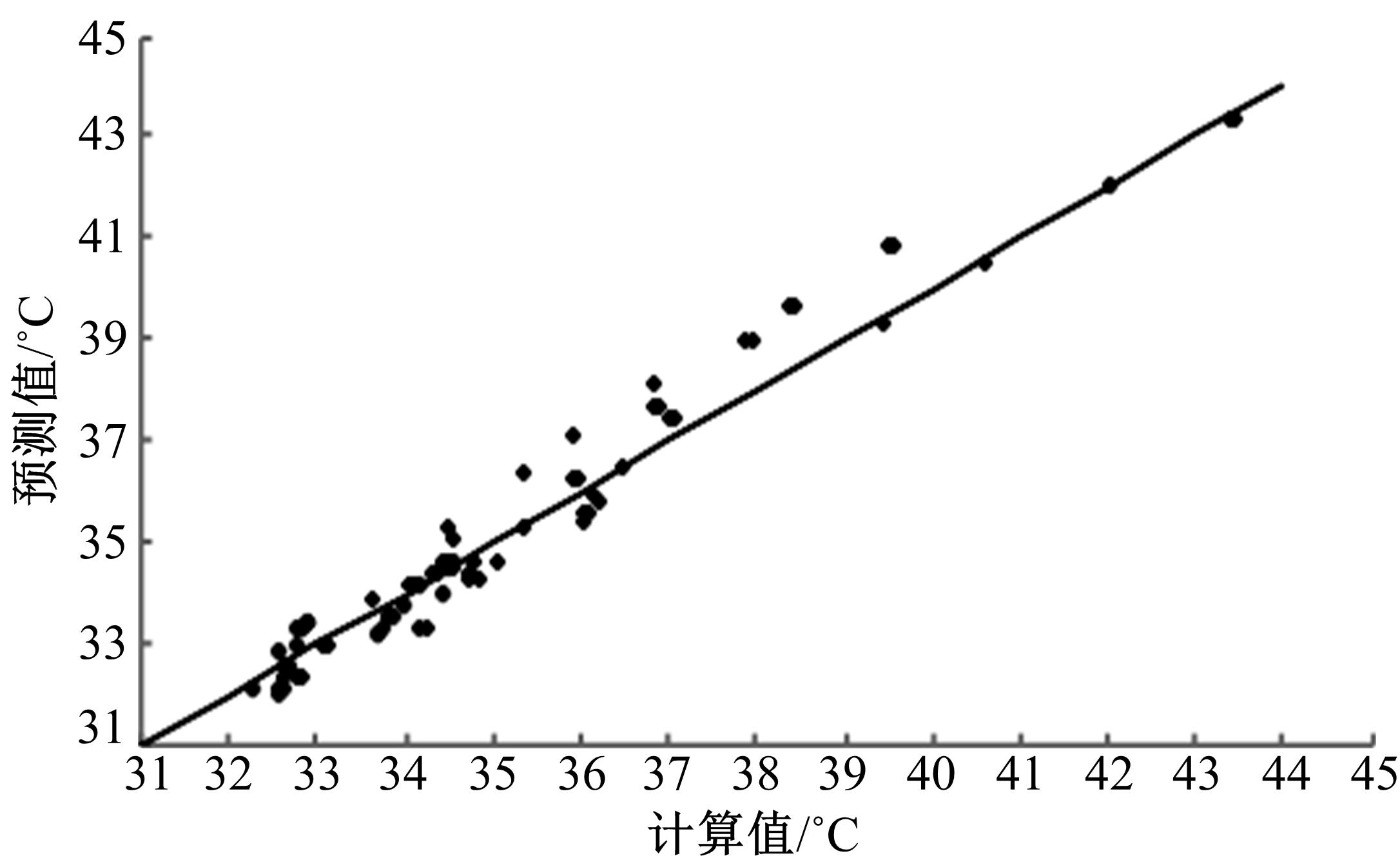
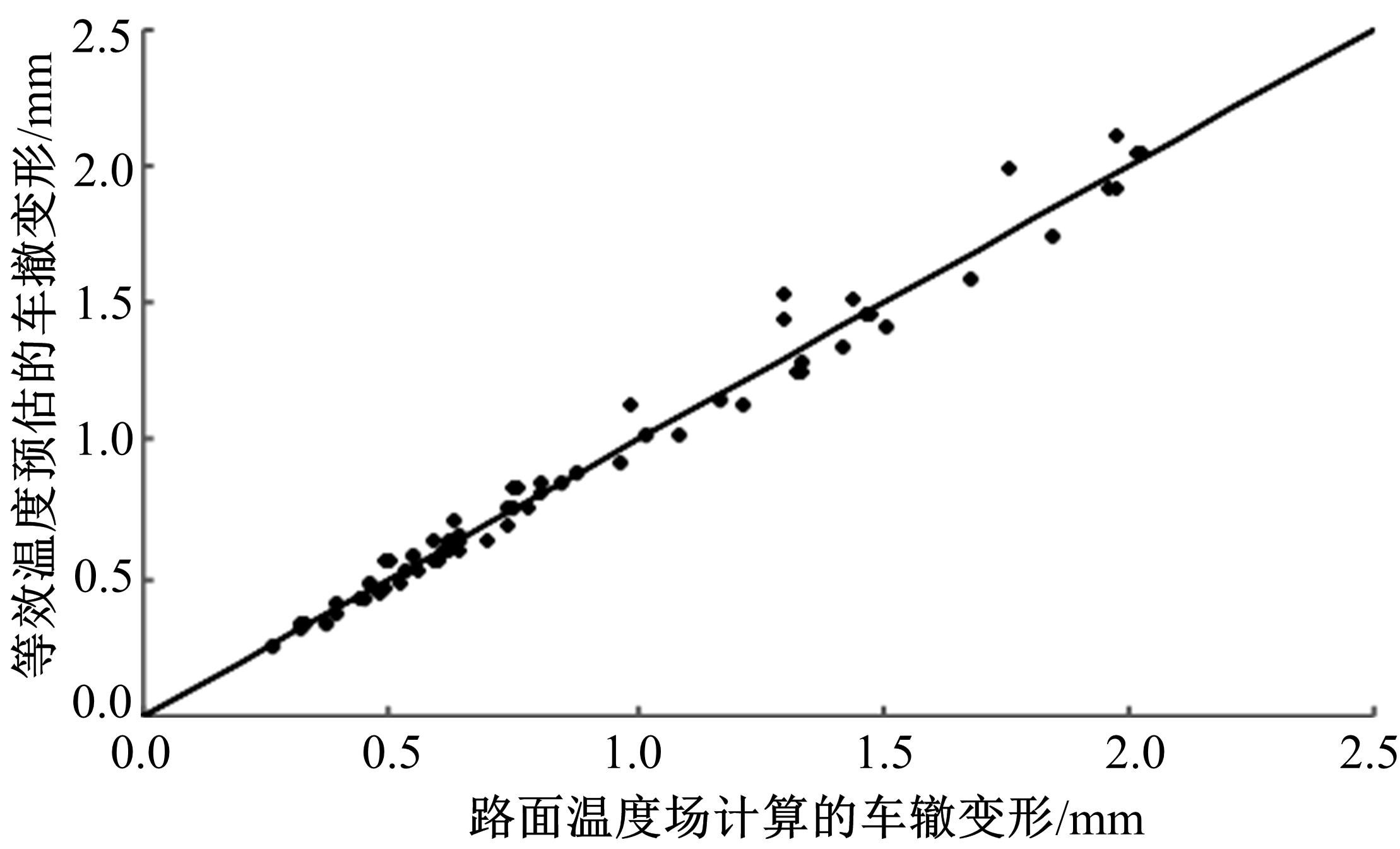
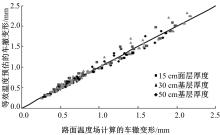
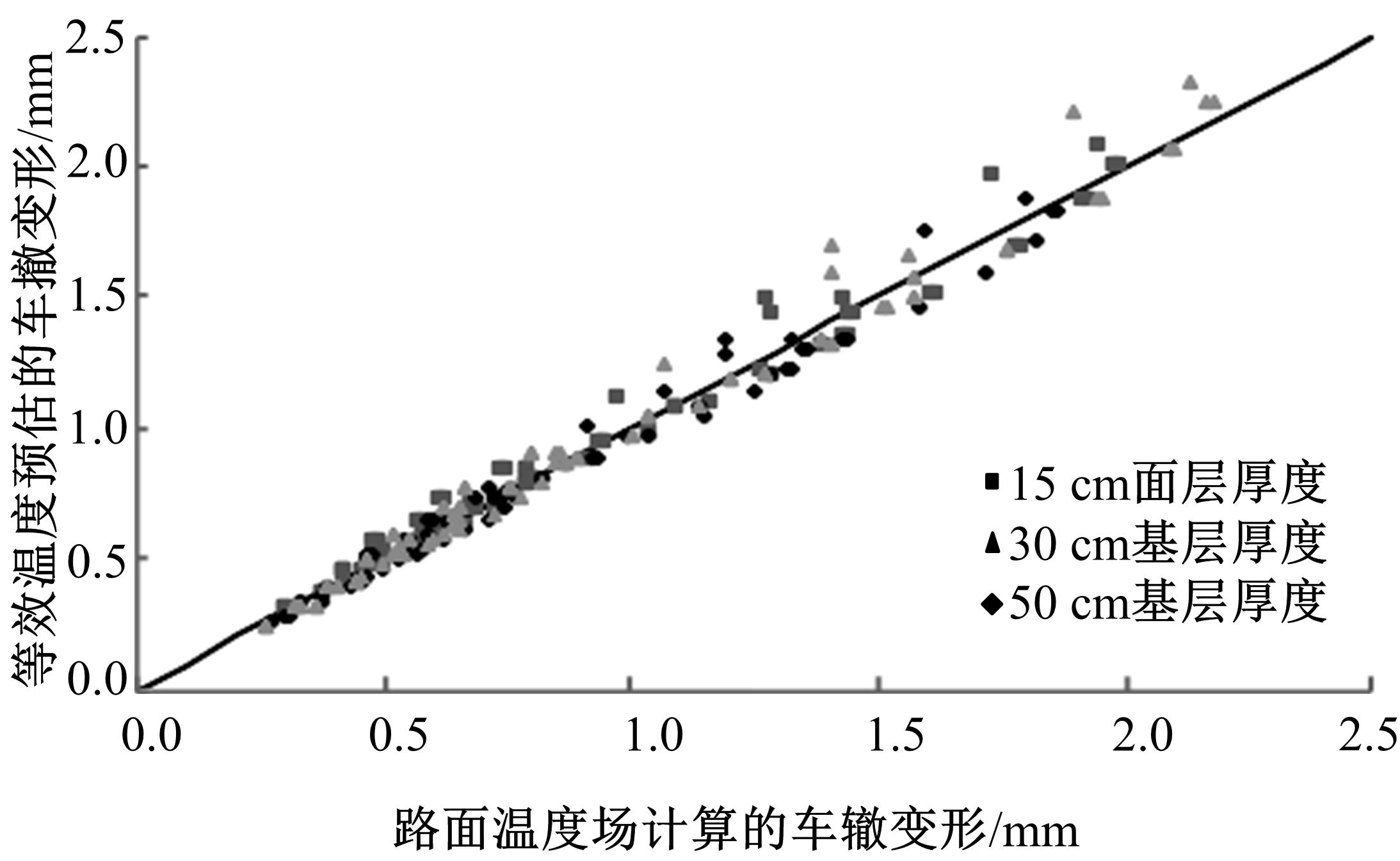
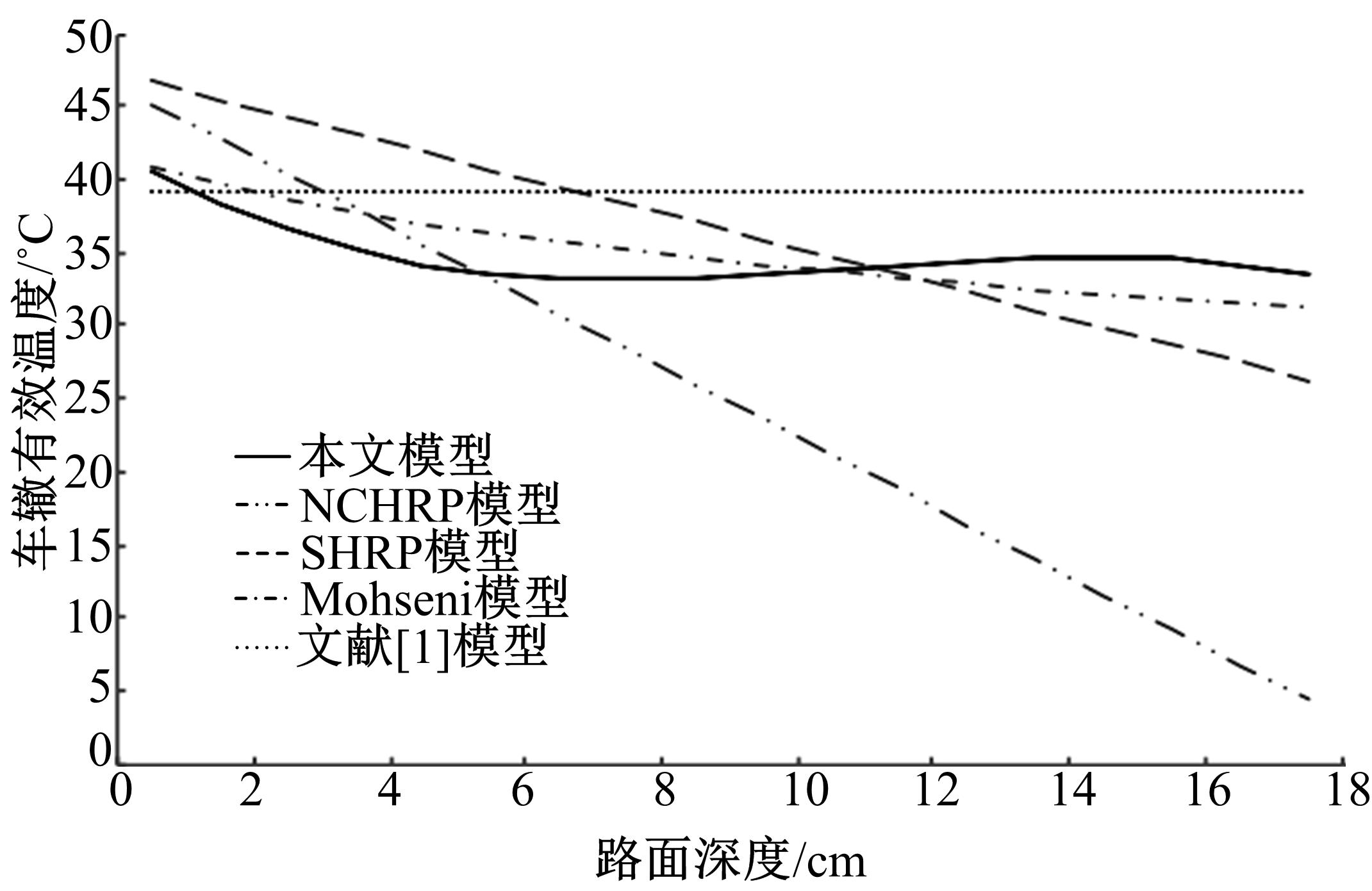
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2018, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (6): 1703-1711.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20170520
Previous Articles Next Articles
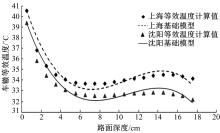
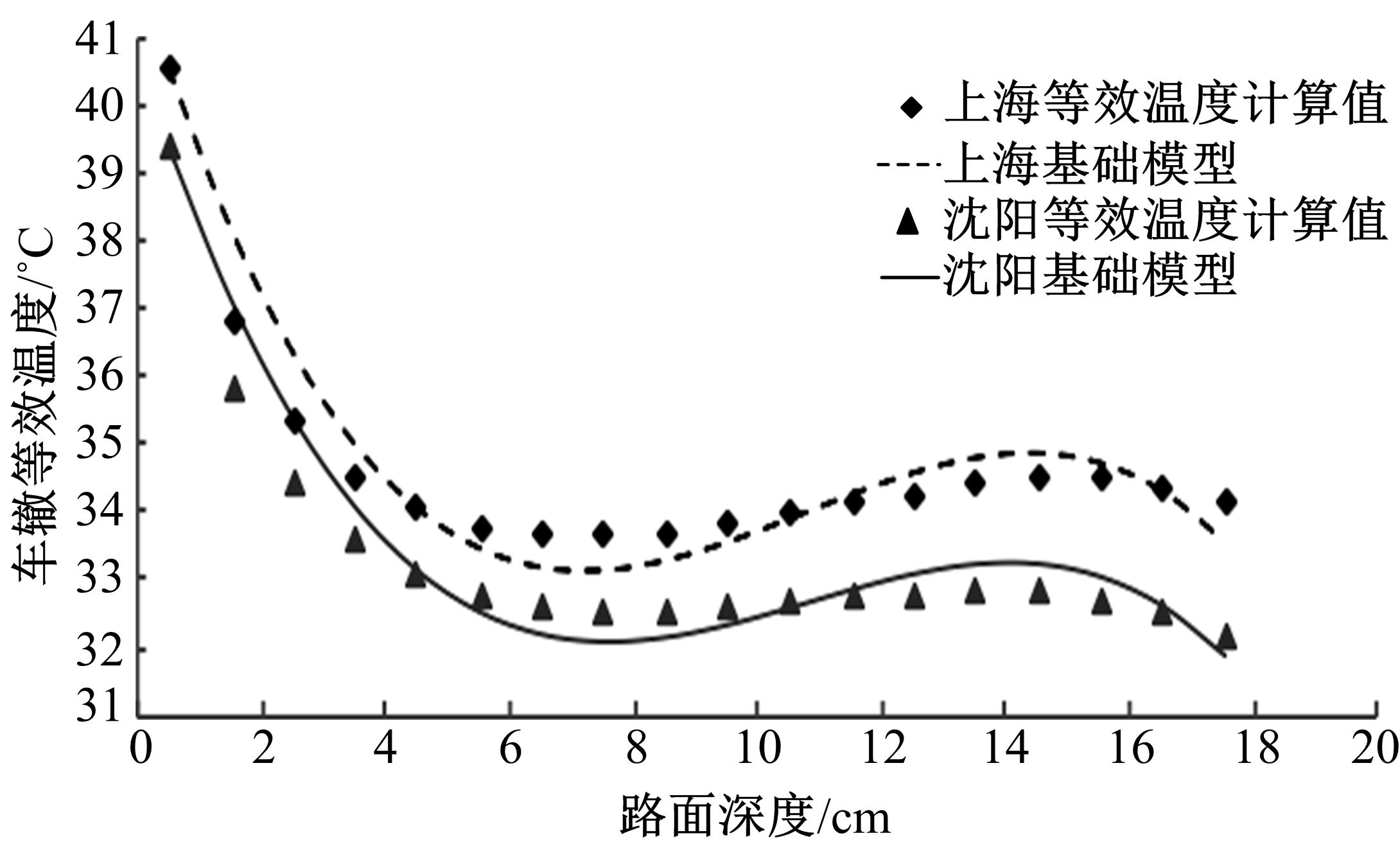
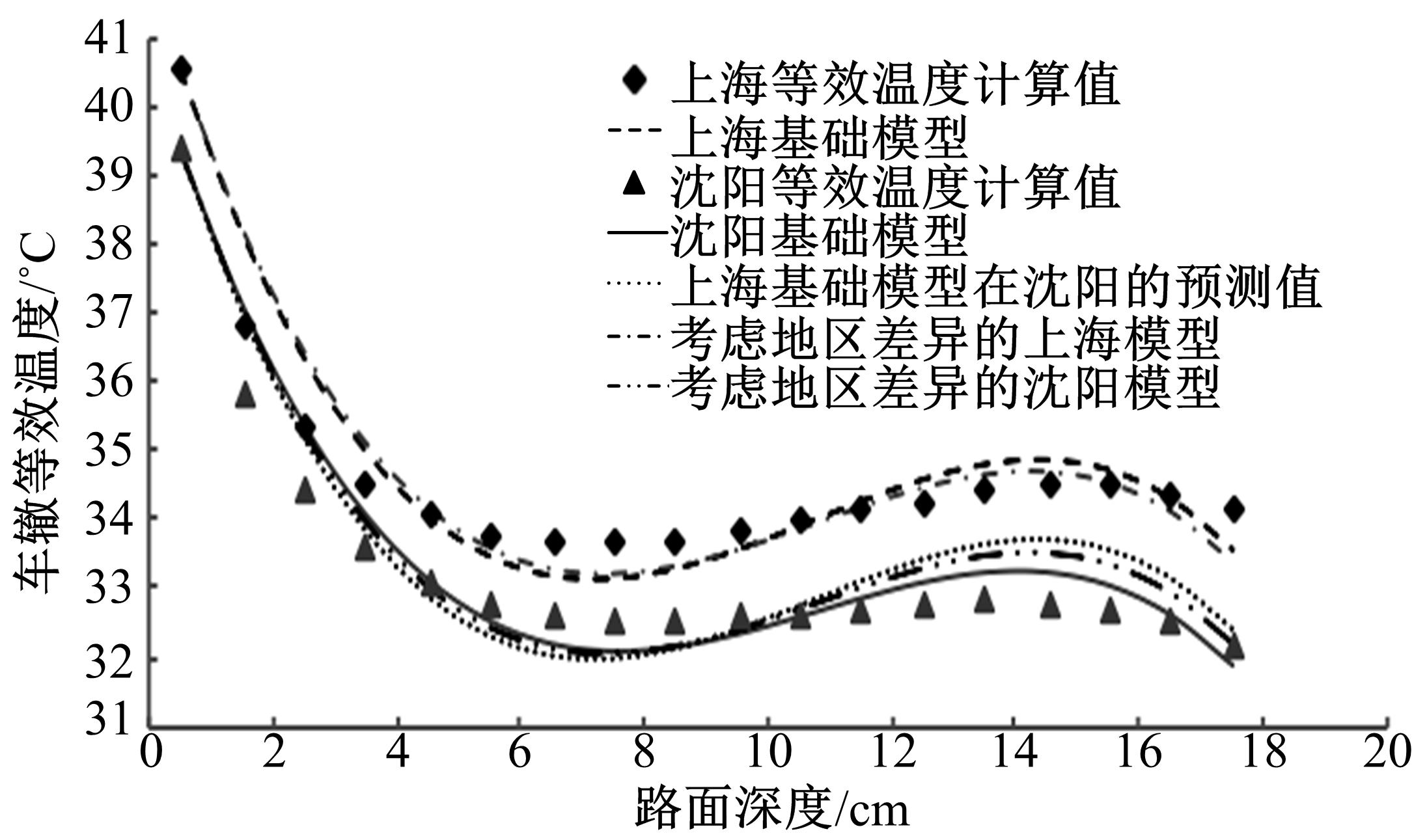
Prediction model on rutting equivalent temperature for asphalt pavement at different depth
LI Yi( ),LIU Li-ping,SUN Li-jun(
),LIU Li-ping,SUN Li-jun( )
)
- The Key Laboratory of Road and Traffic Engineering, Ministry of Education, Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
CLC Number:
- U416
| [1] |
苏凯, 孙立军 . 车辙等效温度确定方法探讨[J]. 大连理工大学学报, 2006,46(增刊1):162-167.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8608.2006.z1.027 |
|
Su Kai, Sun Li-jun . Discussion of methods for determining effective temperature of rutting[J]. Journal of Dalian University of Technology, 2006,46(Sup.1):162-167.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8608.2006.z1.027 |
|
| [2] | 栗培龙, 张争奇, 王秉纲 . 考虑有效温度及荷载的沥青混凝土路面车辙等效温度研究[J]. 公路, 2011(2):6-11. |
| Li Pei-long, Zhang Zheng-qi, Wang Bing-gang . Research on rutting equivalent temperature of asphalt concrete pavement considering effective temperature and load[J]. Highway, 2011(2):6-11. | |
| [3] | 吁新华, 谈至明, 胡洪龙 , 等. 沥青面层的车辙等效温度[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2014,42(5):701-706,729. |
| Yu Xin-hua, Tan Zhi-ming, Hu Hong-long , et al. Rutting equivalent temperature for asphalt pavement[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2014,42(5):701-706,729. | |
| [4] | 孙立军 . 沥青路面结构行为学[M]. 2版. 上海: 同济大学出版社, 2013. |
| [5] |
孙立军, 秦健 . 沥青路面温度场的预估模型[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2006,34(4):480-483.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2006.04.011 |
|
Sun Li-jun, Qin Jian . Prediction model on temperature field in asphalt pavement[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2006,34(4):480-483.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2006.04.011 |
|
| [6] | Witczak M W . Effective temperature analysis for permanent deformation of asphaltic mixtures[R]. Washington DC: National Research Council, 1992. |
| [7] | Cominsky R J, Huber G A, Kennedy T W , et al. The Superpave mix design manual for new construction and overlays[R]. Washington DC: National Research Council, 1994. |
| [8] | Sotil A . Use of the dynamic modulus E * test as permanent deformation performance criteria for asphalt pavement systems [D]. Tempe: Arizona State University, 2005. |
| [9] | Monismith C L, Hicks R G, Finn F N , et al. Permanent deformation response of asphalt-aggregate mixes[R]. Washington DC:National Research Council, 1994. |
| [10] |
EI-Basyouny M, Jeong M G . Effective temperature for analysis of permanent deformation and fatigue distress on asphalt mixtures[J]. Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2009(2127):155-163.
doi: 10.3141/2127-18 |
| [11] | Moulthrop J, Witczak M W . A performance-related specification for hot-mix asphalt[R]. Washington DC: Transportation Research Board of the National Academies, 2011. |
| [12] | Mohseni A, Azari H. Effective temperature for permanent deformation testing of asphalt mixtures [C]//International Society of Asphalt Pavements, Raleigh, North Carolina, 2014: 1501-1511. |
| [13] | Witczak M W, Andrei D, Houston W N . Guide for mechanistic-empirical design of new and rehabilitated pavement structures[R]. Washington DC: Transportation Research Board of the National Academies, 2004. |
| [14] |
秦健, 孙立军 . 沥青路面温度场的分布规律[J]. 公路交通科技, 2006,23(8):18-21.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2006.08.005 |
|
Qin Jian, Sun Li-jun . Study on asphalt pavement temperature field distribution pattern[J]. Journal on Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2006,23(8):18-21.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2006.08.005 |
|
| [15] | Barber E S. Calculation of maximum pavement temperatures from weather reports [C]//Highway Research Board, Washington DC, 1957: 1-8. |
| [1] | Xiao⁃ming HUANG,Qing⁃qing CAO,Xiu⁃yu LIU,Jia⁃ying CHEN,Xing⁃lin ZHOU. Simulation of vehicle braking performance on rainy daysbased on pavement surface fractal friction theory [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 757-765. |
| [2] | Jing WANG,Xiang LYU,Xiao⁃long QU,Chun⁃ling ZHONG,Yun⁃long ZHANG. Analysis of relationship between subgrade soil shear strength and chemical and minerals component [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 766-772. |
| [3] | ZANG Guo-shuai, SUN Li-jun. Method based on inertial point for setting depth to rigid layer [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1037-1044. |
| [4] | NIAN Teng-fei, LI Ping, LIN Mei. Micro-morphology and gray entropy analysis of asphalt characteristics functional groups and rheological parameters under freeze-thaw cycles [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1045-1054. |
| [5] | GONG Ya-feng, SHEN Yang-fan, TAN Guo-jin, HAN Chun-peng, HE Yu-long. Unconfined compressive strength of fiber soil with different porosity [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 712-719. |
| [6] | CHENG Yong-chun, BI Hai-peng, MA Gui-rong, GONG Ya-feng, TIAN Zhen-hong, LYU Ze-hua, XU Zhi-shu. Pavement performance of nano materials-basalt fiber compound modified asphalt binder [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 460-465. |
| [7] | ZHANG Yang-peng, WEI Hai-bin, JIA Jiang-kun, CHEN Zhao. Numerical evaluation on application of roadbed with composite cold resistance layer inseasonal frozen area [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 121-126. |
| [8] | JI Wen-yu, LI Wang-wang, GUO Min-long, WANG Jue. Experimentation and calculation methods of prestressed RPC-NC composite beam deflection [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 129-136. |
| [9] | MA Ye, NI Ying-sheng, XU Dong, DIAO Bo. External prestressed strengthening based on analysis of spatial grid model [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 137-147. |
| [10] | LUO Rong, ZENG Zhe, ZHANG De-run, FENG Guang-le, DONG Hua-jun. Moisture stability evaluation of asphalt mixture based on film pressure model of Wilhelmy plate method [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1753-1759. |
| [11] | NI Ying-sheng, MA Ye, XU Dong, LI Jin-kai. Space mesh analysis method for shear lag effect of cable-stayed bridge with corrugated steel webs [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1453-1464. |
| [12] | ZHENG Chuan-feng, MA Zhuang, GUO Xue-dong, ZHANG Ting, LYU Dan, Qin Yong. Coupling effect of the macro and micro characteristics of mineral powder on the low-temperature performance of asphalt mortar [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1465-1471. |
| [13] | YU Tian-lai, ZHENG Bin-shuang, LI Hai-sheng, TANG Ze-rui, ZHAO Yun-peng. Analyses of defects and causes of steel-plastic compound reinforced retaining wall [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1082-1093. |
| [14] | CAI Yang, FU Wei, TAO Ze-feng, CHEN Kang-wei. Influence analysis of geotextile on reducing traffic induced reflective cracking using extended finite element model [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 765-770. |
| [15] | LIU Han-bing, ZHANG Hu-zhu, WANG Jing. Effect of dehydration on shear strength properties of compacted clayey soil [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 446-451. |
|