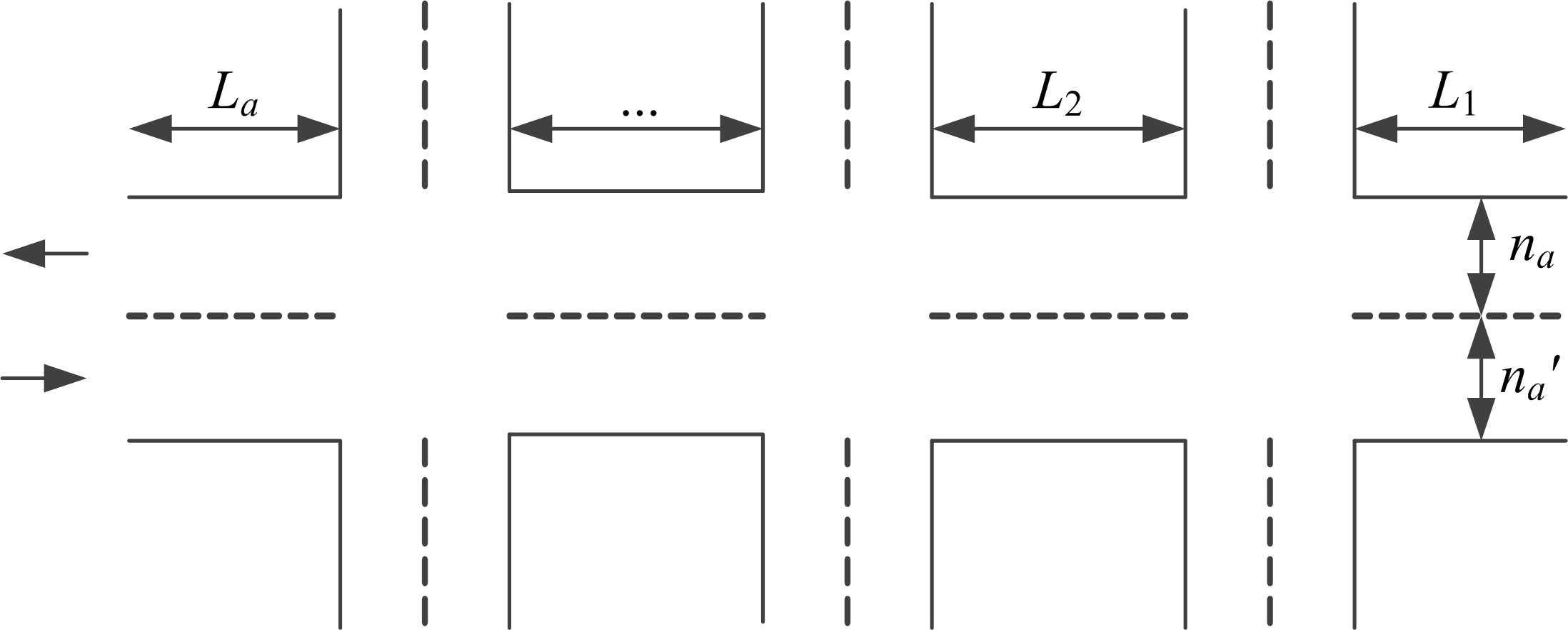
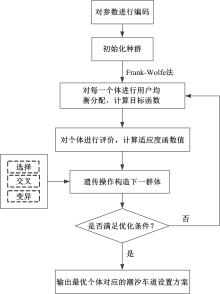
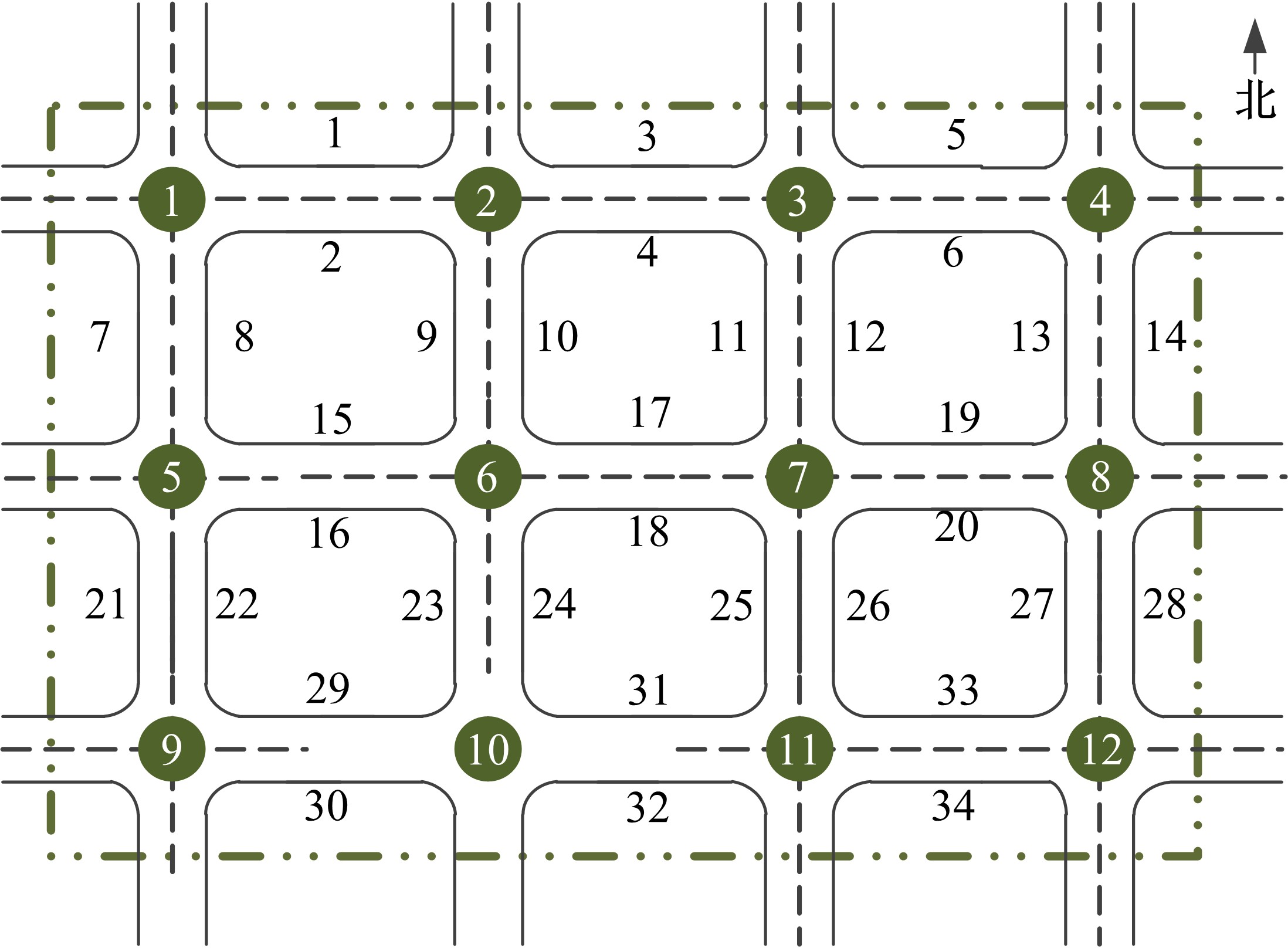
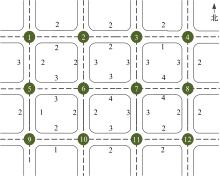
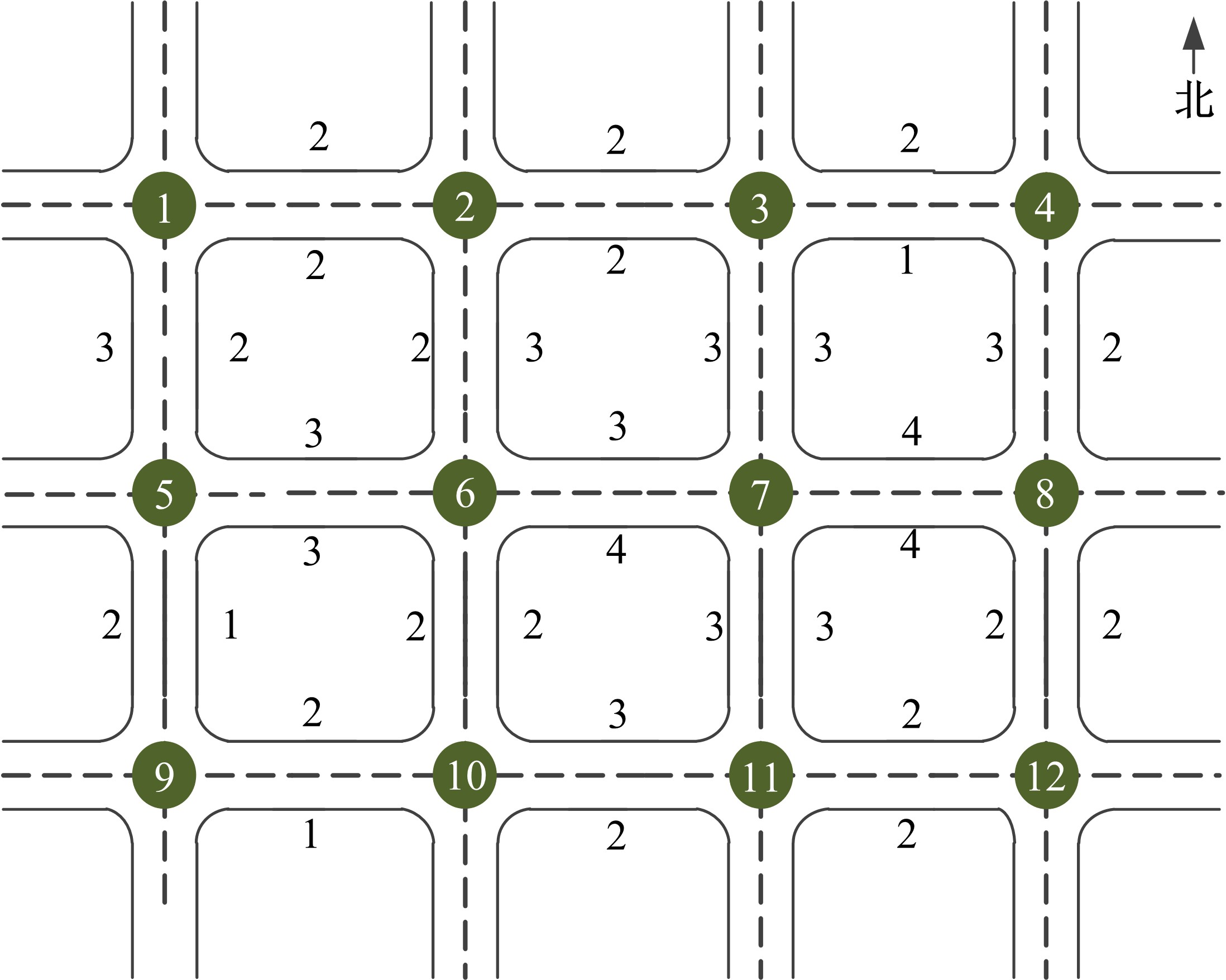
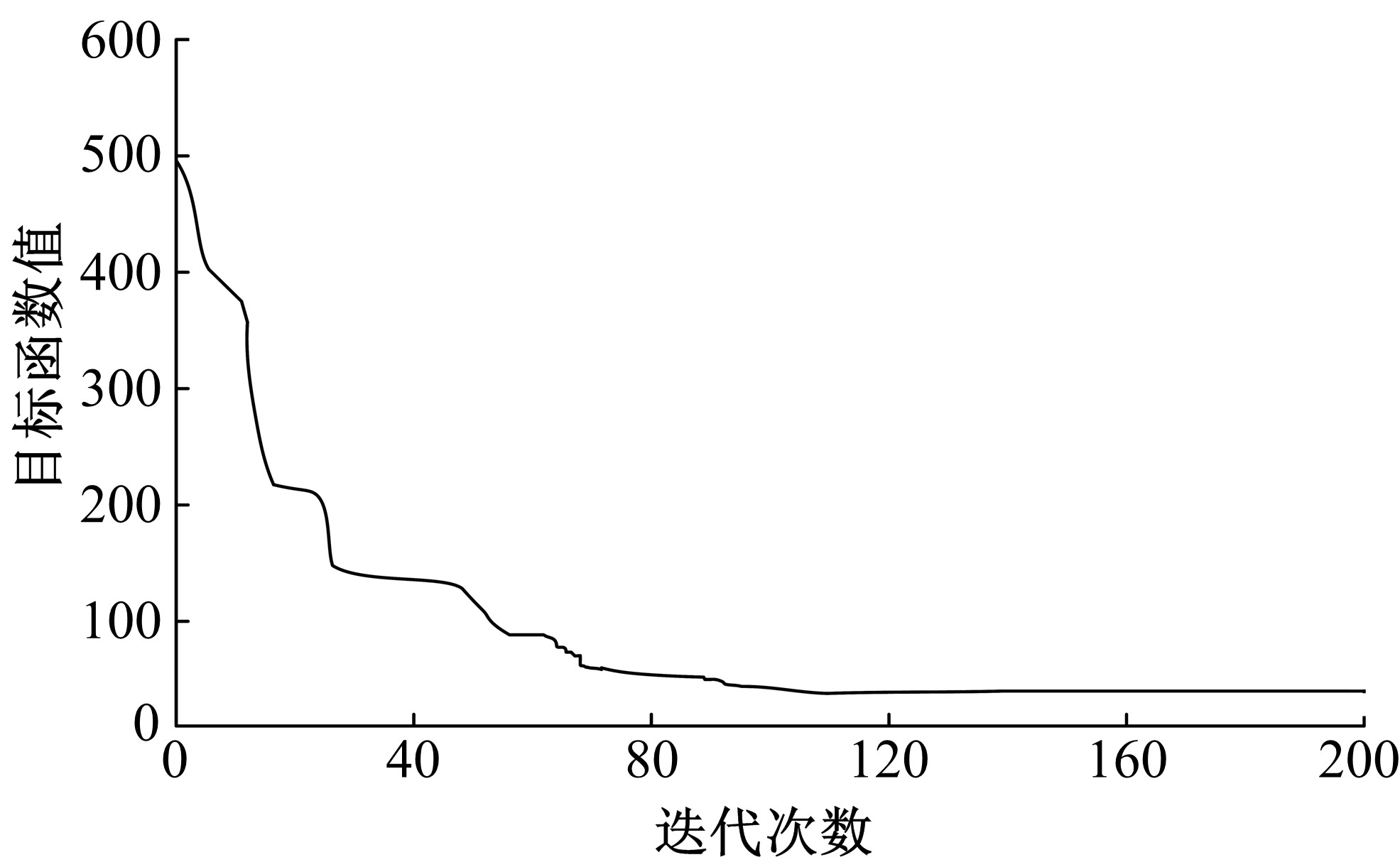
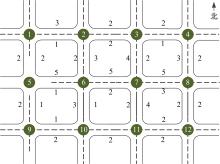
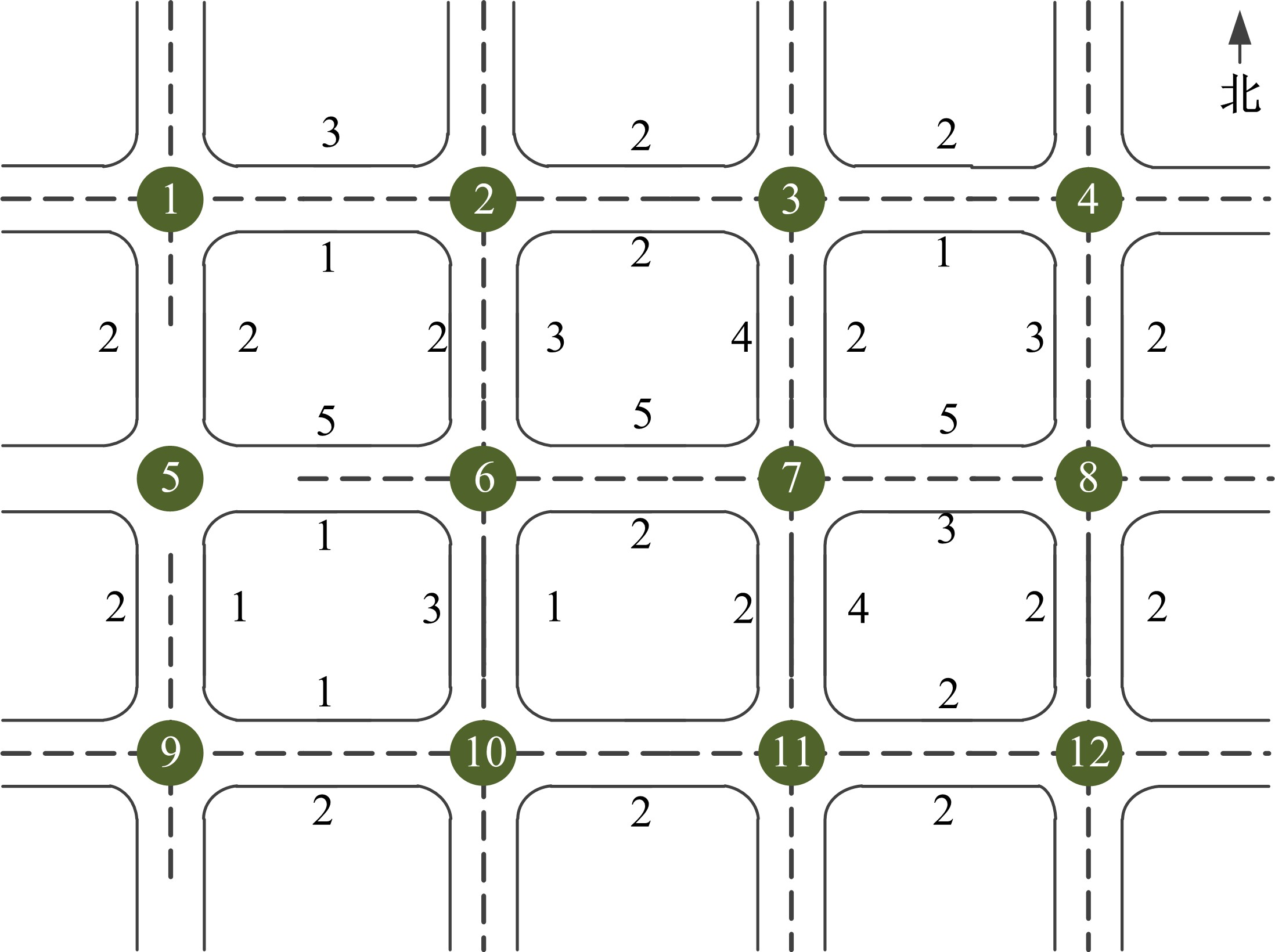
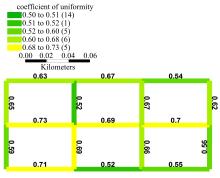
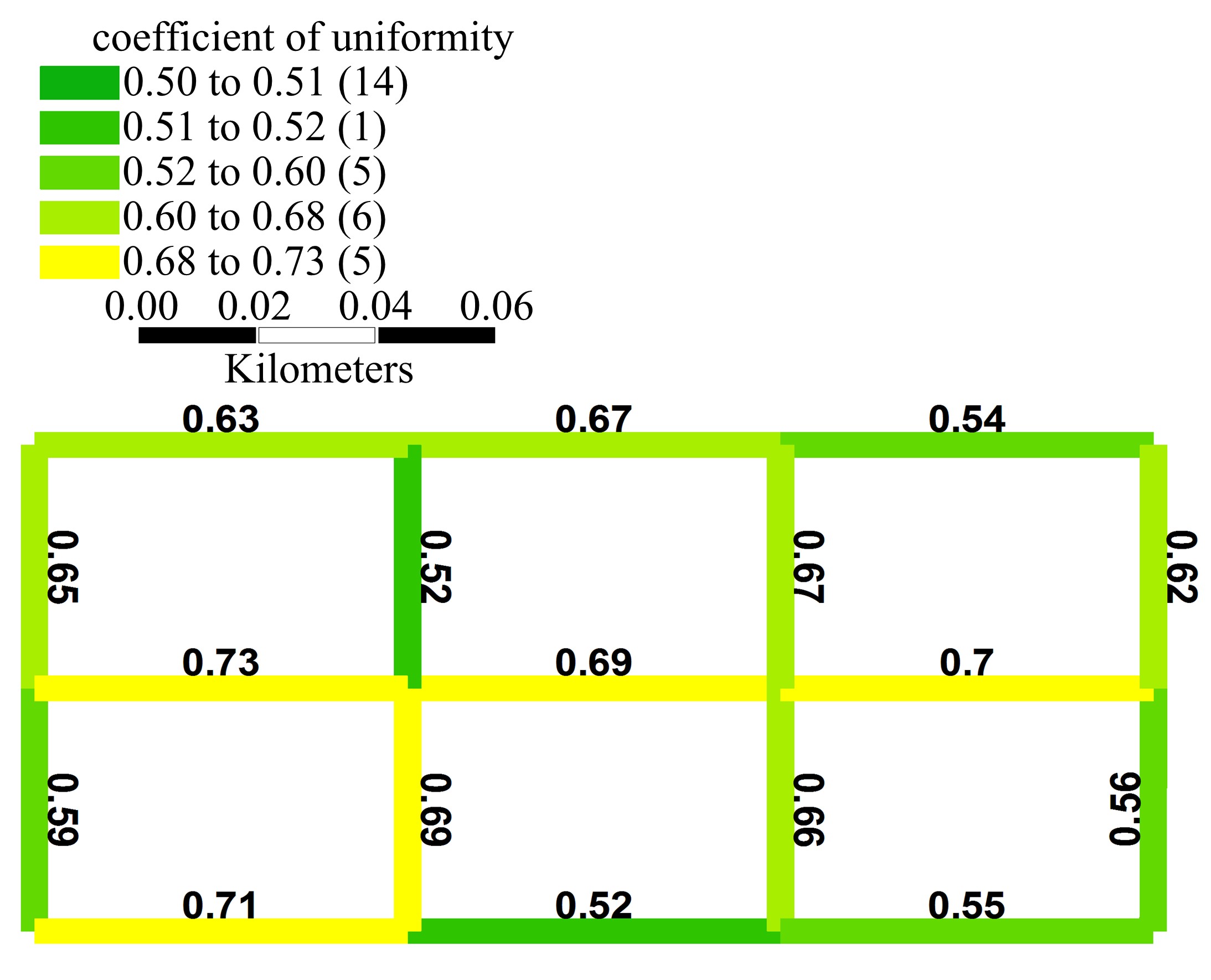
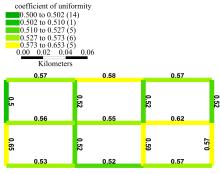
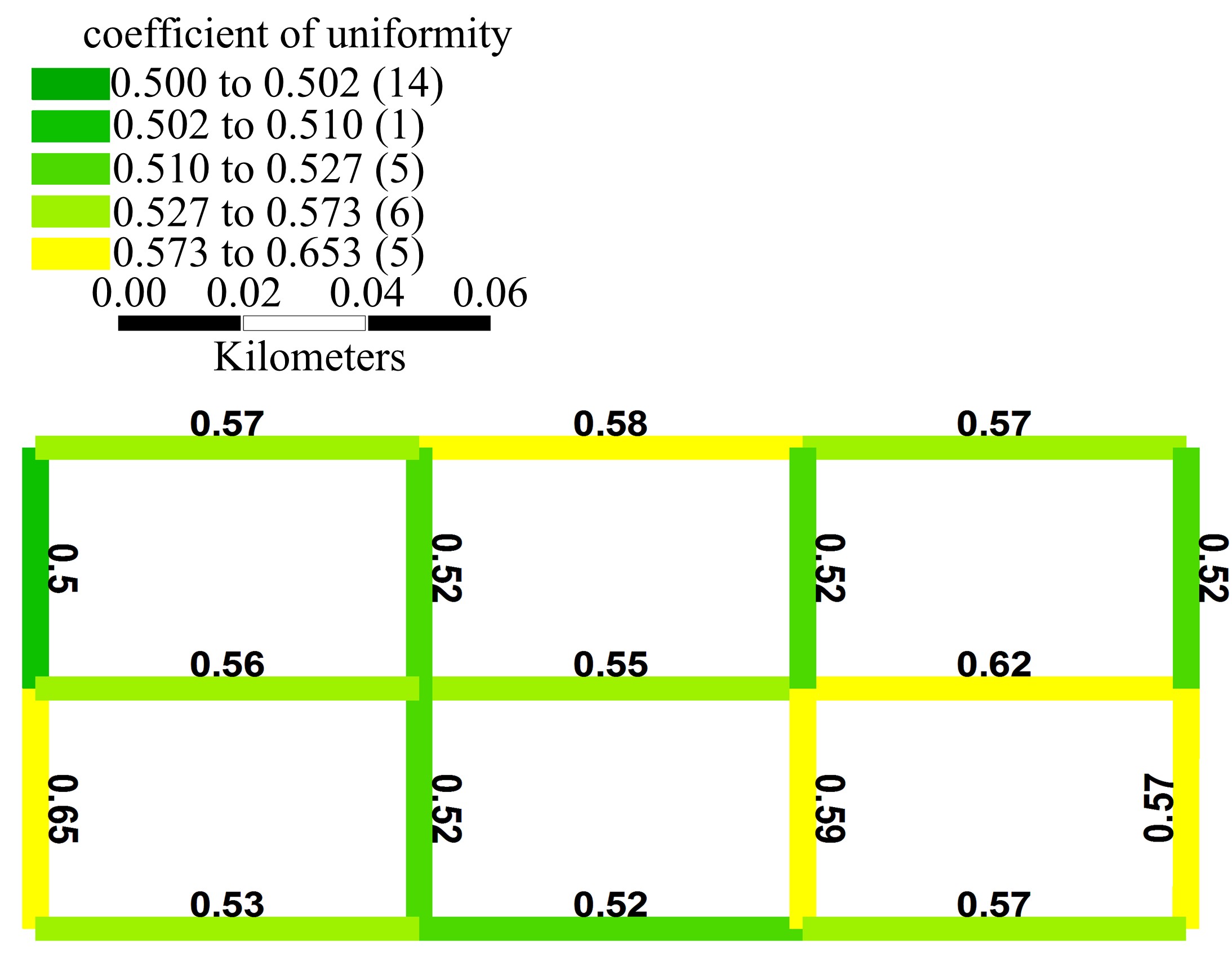
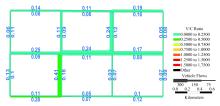
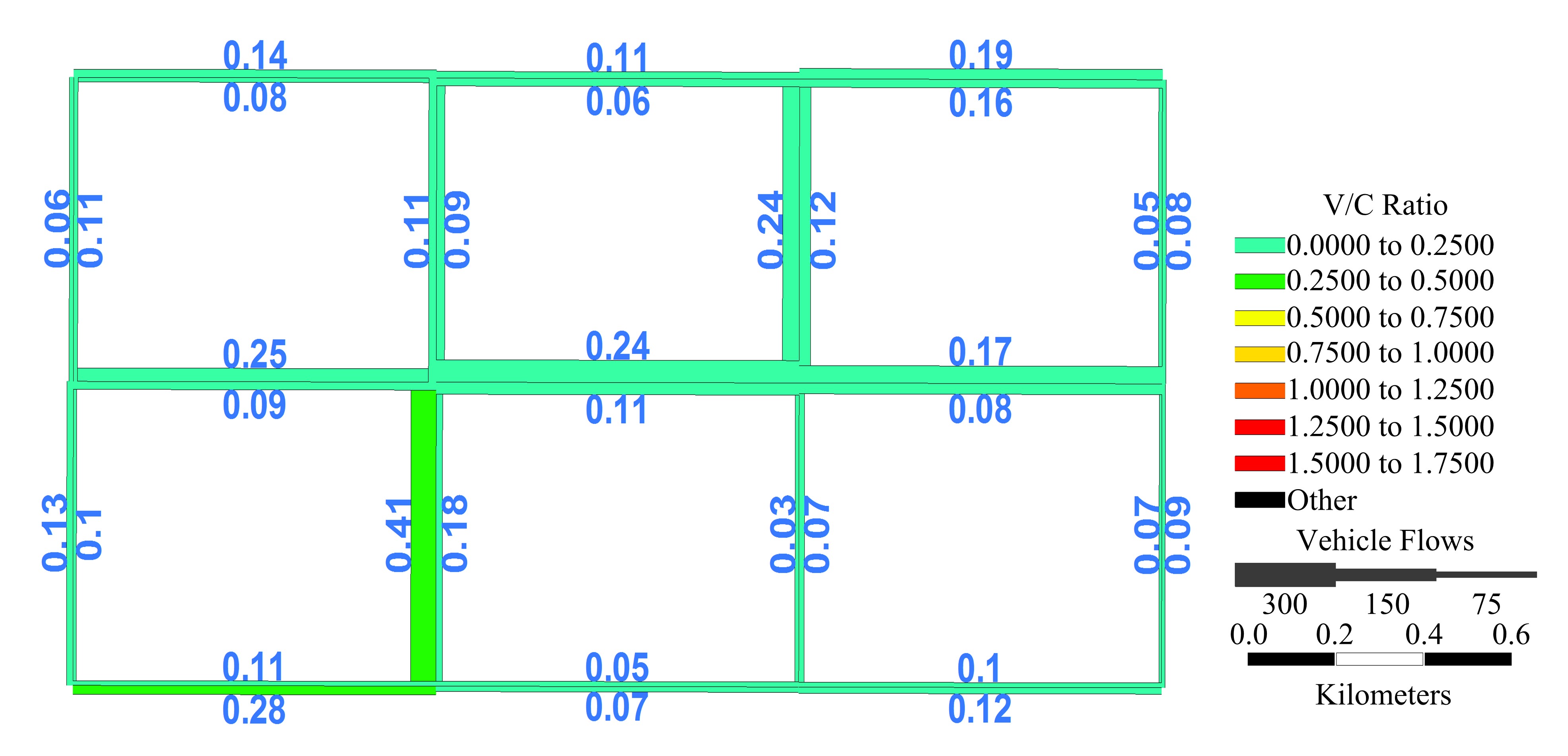
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 535-542.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180790
Bi-level programming model for optimization design of tidal lane
Hong-fei JIA( ),Xin-ru DING,Li-li YANG(
),Xin-ru DING,Li-li YANG( )
)
- College of Transportation, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
CLC Number:
- U491.5
| 1 | 刘鹏, 刘英舜. 潮汐式交通特性分析及应对措施研究[J]. 交通科技与经济, 2011, 13(3): 92-94. |
| Liu Peng, Liu Ying-shun. Study on characters of tidal transpotation and relieve meatures[J]. Technology & Economy in Areas of Communications, 2011, 13(3): 92-94. | |
| 2 | Stone P, Fajardo D, Hausknecht M, et al. Dynamic lane reversal in traffic management[J]. International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2014, 263(4): 1929-1934. |
| 3 | 刘恋. 可变车道优化控制研究[D]. 大连: 大连交通大学交通运输工程学院, 2014. |
| Liu Lian. The reseach on optimal control of variable lane[D]. Dalian: School of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, Dalian Jiaotong University, 2014. | |
| 4 | 崔凯. 左转逆向可变车道的优化设计与控制策略[D]. 山东: 山东大学控制科学与工程学院, 2017. |
| Cui Kai. Optimal design and control strategy of left-turn reverse variable lane[D]. Shandong: Department of Control Science and Engineering, Shandong University, 2017. | |
| 5 | Habibollah N, Ali E, Hamed A. Estimation of the logit model for the online contra flow problem[J]. Transport, 2010, 25(4): 433-441. |
| 6 | Matthew H, Au T C, Stone P. Dynamic lane teversal in yraffic management[J]. IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2011, 16(7): 1929-1934. |
| 7 | 高瑞, 龙建成. 基于可变车道优化的交通网络设计问题[J]. 合肥工业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 38(11): 1446-1450. |
| Gao Rui, Long Jian-cheng. A Transportation network design problem with optimization of variable lanes[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science), 2015, 38(11): 1446-1450. | |
| 8 | 曲大义, 曹俊业, 王进展, 等. 潮汐车道与变向车道协同优化的绿波控制方法[J]. 济南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 31(3): 208-214. |
| Qu Da-yi, Cao Jun-ye, Wang Jin-zhan, et al. Green wave control method of collaborative optimization of tidal lane and variable lane[J]. Journal of University of Jinan (Science and Technology), 2017, 31(3): 208-214. | |
| 9 | Wang J W, Wang H F, Zhang W J, et al. Evacuation planning based on the contra flow technique with consideration of evacuation priorities and traffic setup time[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligeng Transportation Systems, 2013, 14(1): 480-485. |
| 10 | Konstantinos A, Henrique S F, Rodrigo C C. Motorway tidal flow lane control[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2018, 51(9): 279-284. |
| 11 | 张鹏, 李文权, 常玉林. 可变车道的城市路网备用容量模型[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2010, 45(2): 255-260. |
| Zhang Peng, Li Wen-quan, Chang Yu-lin. Reserve capacity model for urban road network with variable lanes[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2010, 45(2): 255-260. | |
| 12 | Gao Z Y, Song Y F. A reserve capacity model of optimal signal control with user equilibrium route choice[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 2002, 36(4): 313-323. |
| 13 | NCHRP. Convertle Roadways and Lanes[R]. Washington DC: Transportation Research Board of the National Academies, 2004. |
| 14 | 王勇. 城市交通网络可变车道设置方案研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学交通运输与物流学院, 2014. |
| Wang Yong. Research for reversible lane plan in urban traffic network[D]. Chengdu: School of Transportation and Logistics, Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014. | |
| 15 | 曹俊业. 基于潮汐流特性的变向车道协同优化控制方法[D]. 青岛: 青岛理工大学机械与汽车工程学院, 2016. |
| Cao Jun-ye. Control method of variable lane cooperation based on the characteristics of tidal flow[D]. Qingdao: School of Mechanical and Aotomotive Engineering, Qingdao University of Technology, 2016. | |
| 16 | 王雄. 城市道路可变车道设置的一主二从双层规划模型与算法[D]. 长沙: 中南大学交通运输工程学院, 2013. |
| Wang Xiong. Bi-level programming model and algorithm of urban roads convertible lanes[D]. Changsha: School of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, Central South University, 2013. | |
| 17 | 代磊磊, 顾金刚, 俞春俊, 等. 潮汐车道交通流特性与设置方案仿真研究[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2012, 30(1): 15-19. |
| Dai Lei-lei, Gu Jin-gang, Yu Chun-jun, et al. Traffic flow characteristics on reversible lane and its operational plan based on simulation[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2012, 30(1): 15-19. | |
| 18 | 陈雪珍. 基于双层规划的城市轨道交通接驳公交线路研究[D]. 南昌: 华东交通大学交通运输与物流学院, 2016. |
| Chen Xue-zhen. Research of urban rail transit feeder bus routes based on bi-level programming[D]. Nanchang: School of Transportation and Logistics, East China Jiaotong University, 2016. | |
| 19 | 李和成, 王宇平. 求解混合整数双层规划问题的遗传算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2009, 39(3): 781-786. |
| Li He-cheng, Wang Yu-ping. Genetic algorithms for solving mixed-integer bilevel programming problems[D]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2009, 39(3): 781-786. | |
| 20 | 董海隆. 大型市政工程施工期间交通微循环改善研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州交通大学交通运输学院, 2013. |
| Dong Hai-long. The research of transportation microcirculation improvement during the large-scale municipal construction[D]. Lanzhou: School of Traffic and Transportation, Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2013. | |
| 21 | 祁宏生, 王殿海, 宋现敏. 路网交通状态平衡控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2012, 42(5): 1185-1190. |
| Qi Hong-sheng, Wang Dian-hai, Song Xian-min. Balanced control method for road network traffic state[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2012, 42(5): 1185-1190. |
| [1] | Yuan-li GU, Yuan ZHANG, Xiao-ping RUI, Wen-qi LU, Meng LI, Shuo WANG. Short⁃term traffic flow prediction based on LSSVMoptimized by immune algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1852-1857. |
| [2] | Yi-ming BIE,Kai JIANG,Ru-ru TANG,Lin-hong WANG,Xin-yu XIONG. Time of interval partition for traffic control at isolated intersection considering impacts of plan transition [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1844-1851. |
| [3] | Fu-chun JIA,Xian-jie MENG,Yu-long LEI. Optimal design of two degrees of freedom dynamic vibration absorber based on multi-objective genetic algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1969-1976. |
| [4] | Guo-zhu CHENG, Si-he FENG, Tian-jun FENG. Setting condition of on⁃street parking space occupied vehicle lane [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1858-1864. |
| [5] | Fang-wu MA,Lu HAN,Yang ZHOU,Shi-ying WANG,Yong-feng PU. Multi material optimal design of vehicle product using polylactic acid composites [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1385-1391. |
| [6] | Quan LIANG,Jian-cheng WENG,Wei ZHOU,Jian RONG. Stability identification of public transport commute passengers based on association rules [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1484-1491. |
| [7] | Hai-bo LONG,Jia-qi YANG,Xue-yu ZHAO. Optimizing vehicles allocation of multimodal coordinated freight transport based on transshipment delay risks [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1492-1499. |
| [8] | Wen⁃jing WU,Run⁃chao CHEN,Hong⁃fei JIA,Qing⁃yu LUO,Di SUN. Collaborative control method of vehicles in U⁃turn zone under environment of cooperative vehicle infrastructure system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1100-1106. |
| [9] | Hong⁃zhi WANG,Fang⁃da JIANG,Ming⁃yue ZHOU. Power allocation of cognitive radio system based on genetic particle swarm optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1363-1368. |
| [10] | Zhao⁃wei QU,Zhao⁃tian PAN,Yong⁃heng CHEN,Peng⁃fei TAO,Di SUN. Car⁃following model with improving safety distance based on optimal velocity model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1092-1099. |
| [11] | Lei CHEN,Jiang⁃feng WANG,Yuan⁃li GU,Xue⁃dong YAN. Multi⁃source traffic data fusion algorithm based onmind evolutionary algorithm optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 705-713. |
| [12] | Qiang TU,Lin CHENG,Fen LIN,Chao SUN. Finding shortest path considering traveler′s risk attitude [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 720-726. |
| [13] | Ning⁃bo CAO,Li⁃ying ZHAO,Zhao⁃wei QU,Yong⁃heng CHEN,Qiao⁃wen BAI,Xiao⁃lei DENG. Social force model considering bi⁃direction pedestrian slipstreaming behavior [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 688-694. |
| [14] | Chao⁃ying YIN,Chun⁃fu SHAO,Xiao⁃quan WANG. Influence of urban built environment on car commuting considering parking availability [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 714-719. |
| [15] | Qiao⁃wen BAI,Zhao⁃wei QU,Yong⁃heng CHEN,Shuai XIONG,Chu⁃qing TAO. Modeling on trajectories of through vehicles with an unprotected left⁃turn phase under non⁃strict priority [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 673-679. |
|
||