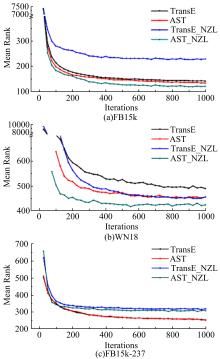
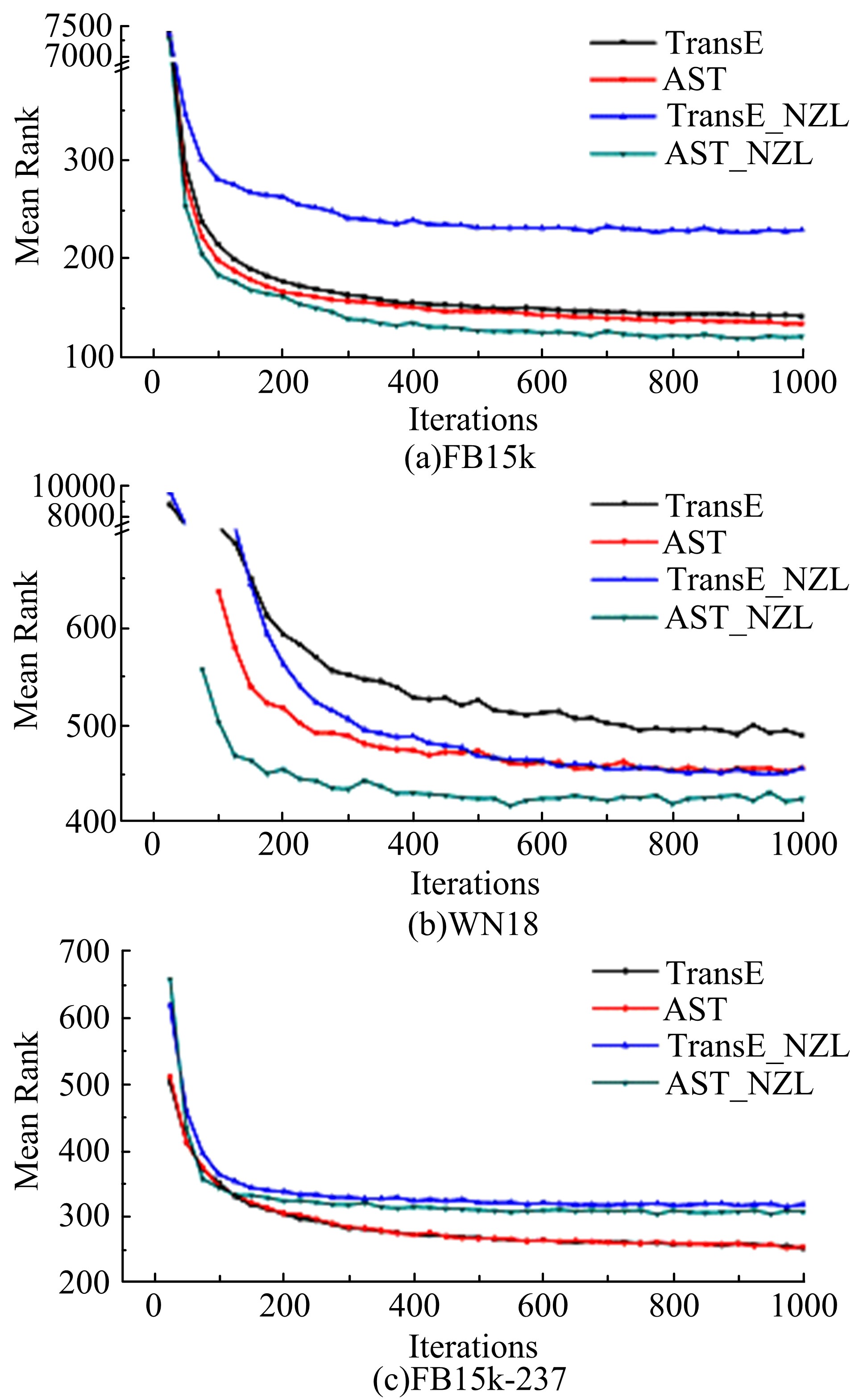
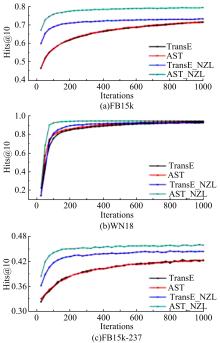
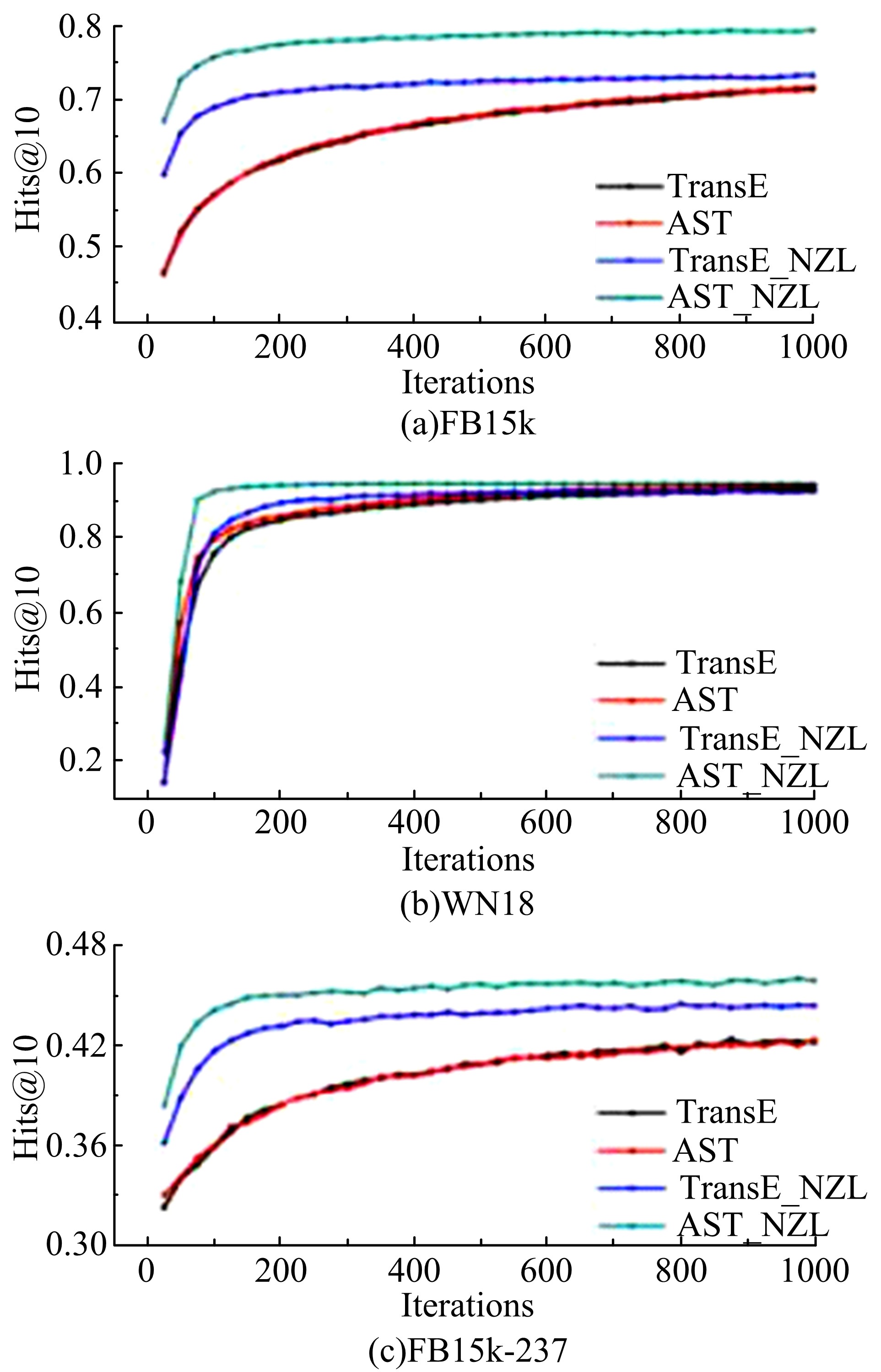
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 685-691.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180791
Knowledge graph embedding with adaptive sampling
Dan-tong OUYANG1,2( ),Cong MA1,2,Jing-pei LEI1,2(
),Cong MA1,2,Jing-pei LEI1,2( ),Sha-sha FENG1,2
),Sha-sha FENG1,2
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
2.Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
CLC Number:
- TP391
| 1 | Bollacker K, Evans C, Paritosh P, et al. Freebase:a collaboratively created graph database for structuring human knowledge[C]∥ Proceedings of the SIGMOD Conference, Vancouver, Canada, 2008: 1247- 1250. |
| 2 | Miller G A. WordNet: a lexical database for English[J]. Communications of the Acm, 1995, 38( 11): 39- 41. |
| 3 | Lehmann J, Isele R, Jakob M, et al. DBpedia-a large-scale, multilingual knowledge base extracted from wikipedia[J]. Semantic Web, 2015, 6( 2): 167- 195. |
| 4 | Daiber J, Jakob M, Hokamp C, et al. Improving efficiency and accuracy in multilingual entity extraction[C]∥ Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Semantic Systems, Graz, Austria, 2013: 121- 124. |
| 5 | Zhang Y, Dai H, Kozareva Z, et al. Variational reasoning for question answering with knowledge graph[C]∥ Proceedings of the 32nd AAAI, New Orleans, 2018: 6069- 6076. |
| 6 | Wang Q, Mao Z, Wang B, et al. Knowledge graph embedding: a survey of approaches and applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2017, 29( 12), 2724- 2743. |
| 7 | 刘知远, 孙茂松, 林衍凯, 等. 知识表示学习研究进展[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2016, 53( 2): 247- 261. |
| Liu Zhi-yuan, Sun Mao-song, Lin Yan-kai, et al. Knowledge representation learning: a review[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2016, 53 ( 2): 247- 261. | |
| 8 | Bordes A, Usunier N, Garcia-Duran A, et al. Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data[C]∥ Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing System, Lake Tahoe, 2013: 2787- 2795. |
| 9 | Wang Z, Zhang J, Feng J, et al. Knowledge graph embedding by translating on hyperplanes[C]∥ Proceedings of the 28th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Québec City, Canada, 2014: 1112- 1119. |
| 10 | Lin Y, Liu Z, Zhu X, et al. Learning entity and relation embeddings for knowledge graph completion[C]∥ Proceedings of the 29th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Austin, Texas, USA, 2015: 2181- 2187. |
| 11 | Ji G, He S, Xu L, et al. Knowledge graph embedding via dynamic mapping matrix[C]∥ Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Beijing, China, 2015: 687- 696. |
| 12 | Ji G, Liu K, He S, et al. Knowledge graph completion with adaptive sparse transfer matrix[C]∥ Proceedings of the 30th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, Arizona, USA, 2016: 985- 991. |
| 13 | Liu H, Wu Y, Yang Y. Analogical inference for multi-relational embeddings[C]∥ Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2017: 2168- 2178. |
| 14 | Wang P, Li S, Pan R. Incorporating GAN for negative sampling in knowledge representation learning[C]∥ Proceedings of the 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, 2018: 2005- 2012. |
| 15 | Liu H, Wu Y, Yang Y. Adaptive sampling for SGD by exploiting side information[C]∥ Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, 2016: 364- 372. |
| 16 | 刘峤, 韩明皓, 杨晓慧, 等. 基于表示学习和语义要素感知的关系推理算法[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2017, 54( 8): 1682- 1692. |
| Liu Qiao, Han Ming-hao, Yang Xiao-hui, et al. Representation learning based relational inference algorithm with semantical aspect awareness[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2017, 54( 8): 1682- 1692. |
| [1] | Yi-bin LI,Jia-min GUO,Qin ZHANG. Methods and technologies of human gait recognition [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 1-18. |
| [2] | Qian XU,Ying LI,Gang WANG. Pedestrian-vehicle detection based on deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1661-1667. |
| [3] | Wan-fu GAO,Ping ZHANG,Liang HU. Nonlinear feature selection method based on dynamic change of selected features [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1293-1300. |
| [4] | Dan⁃tong OUYANG,Jun XIAO,Yu⁃xin YE. Distant supervision for relation extraction with weakconstraints of entity pairs [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 912-919. |
| [5] | GU Hai-jun, TIAN Ya-qian, CUI Ying. Intelligent interactive agent for home service [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1578-1585. |
| [6] | DONG Sa, LIU Da-you, OUYANG Ruo-chuan, ZHU Yun-gang, LI Li-na. Logistic regression classification in networked data with heterophily based on second-order Markov assumption [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1571-1577. |
| [7] | WANG Xu, OUYANG Ji-hong, CHEN Gui-fen. Measurement of graph similarity based on vertical dimension sequence dynamic time warping method [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1199-1205. |
| [8] | ZHANG Hao, ZHAN Meng-ping, GUO Liu-xiang, LI Zhi, LIU Yuan-ning, ZHANG Chun-he, CHANG Hao-wu, WANG Zhi-qiang. Human exogenous plant miRNA cross-kingdom regulatory modeling based on high-throughout data [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1206-1213. |
| [9] | LI Xiong-fei, FENG Ting-ting, LUO Shi, ZHANG Xiao-li. Automatic music composition algorithm based on recurrent neural network [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 866-873. |
| [10] | LIU Jie, ZHANG Ping, GAO Wan-fu. Feature selection method based on conditional relevance [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 874-881. |
| [11] | HUANG Lan, JI Lin-ying, YAO Gang, ZHAI Rui-feng, BAI Tian. Construction of disease-symptom semantic net for misdiagnosis prompt [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 859-865. |
| [12] | WANG Xu, OUYANG Ji-hong, CHEN Gui-fen. Heuristic algorithm of all common subsequences of multiple sequences for measuring multiple graphs similarity [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 526-532. |
| [13] | LIU Xue-juan, YUAN Jia-bin, XU Juan, DUAN Bo-jia. Quantum k-means algorithm [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 539-544. |
| [14] | YANG Xin, XIA Si-jun, LIU Dong-xue, FEI Shu-min, HU Yin-ji. Target tracking based on improved accelerated gradient under tracking-learning-detection framework [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 533-538. |
| [15] | LI Jia-fei, SUN Xiao-yu. Clustering method for uncertain data based on spectral decomposition [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1604-1611. |
|
||