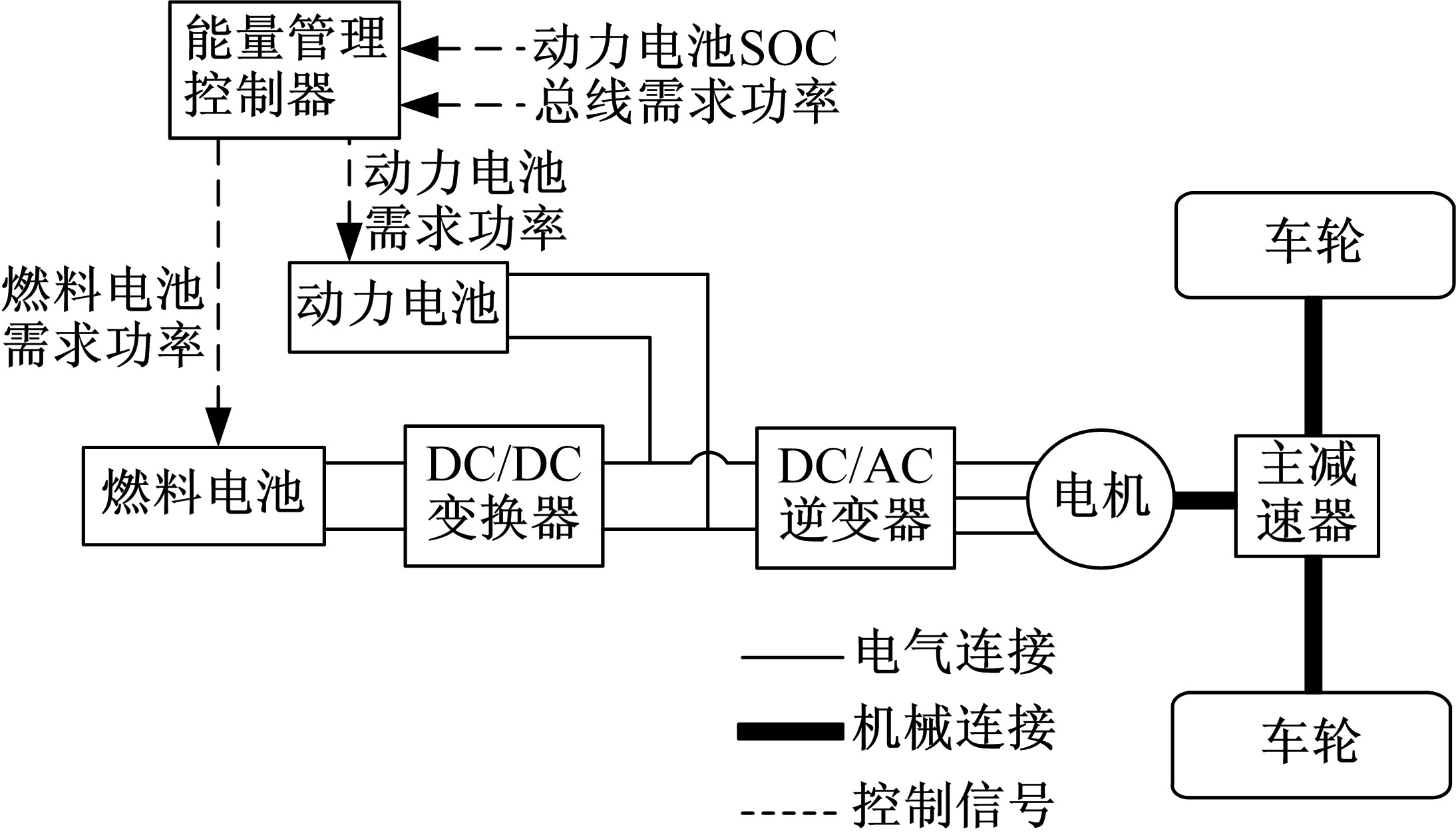
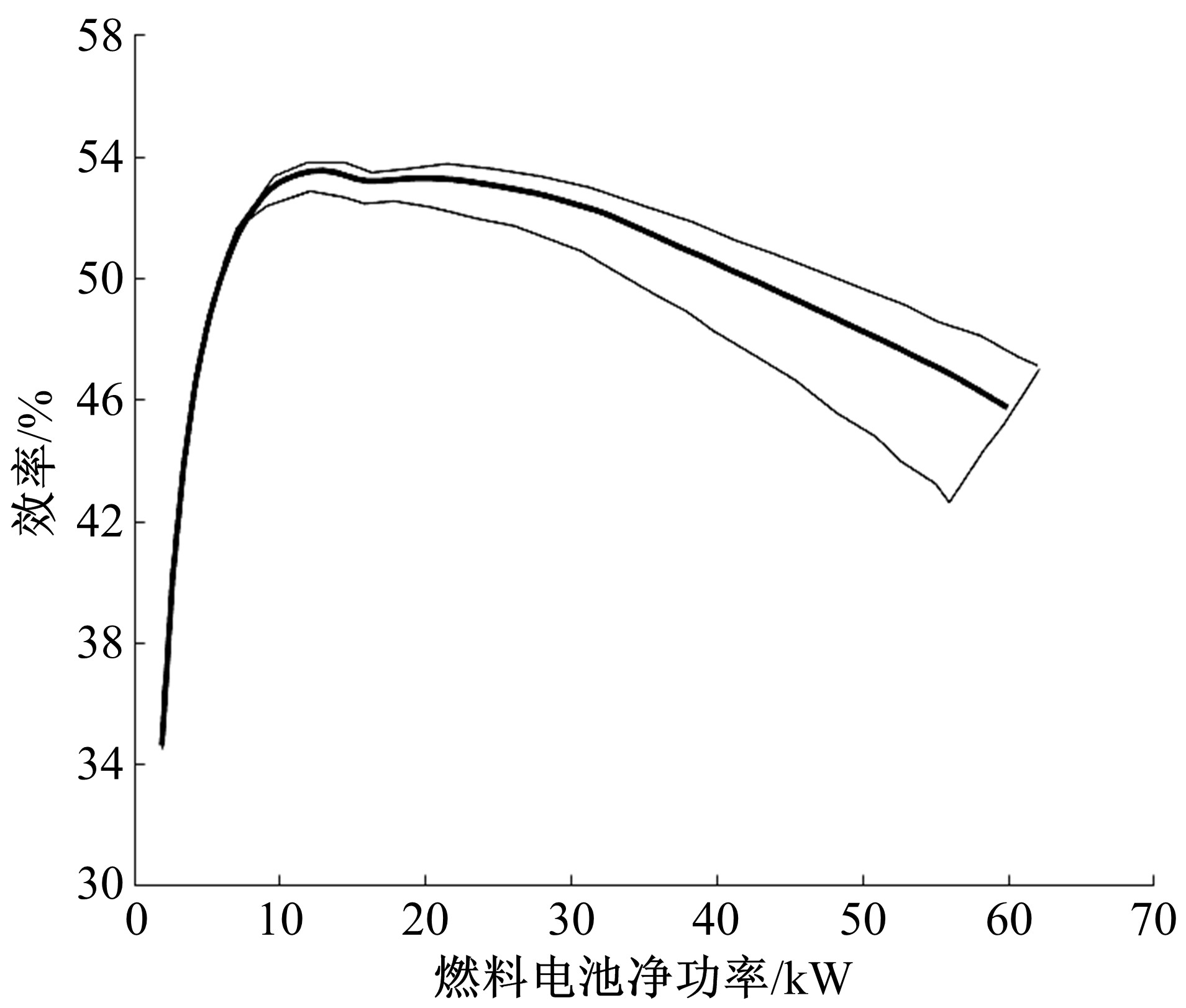
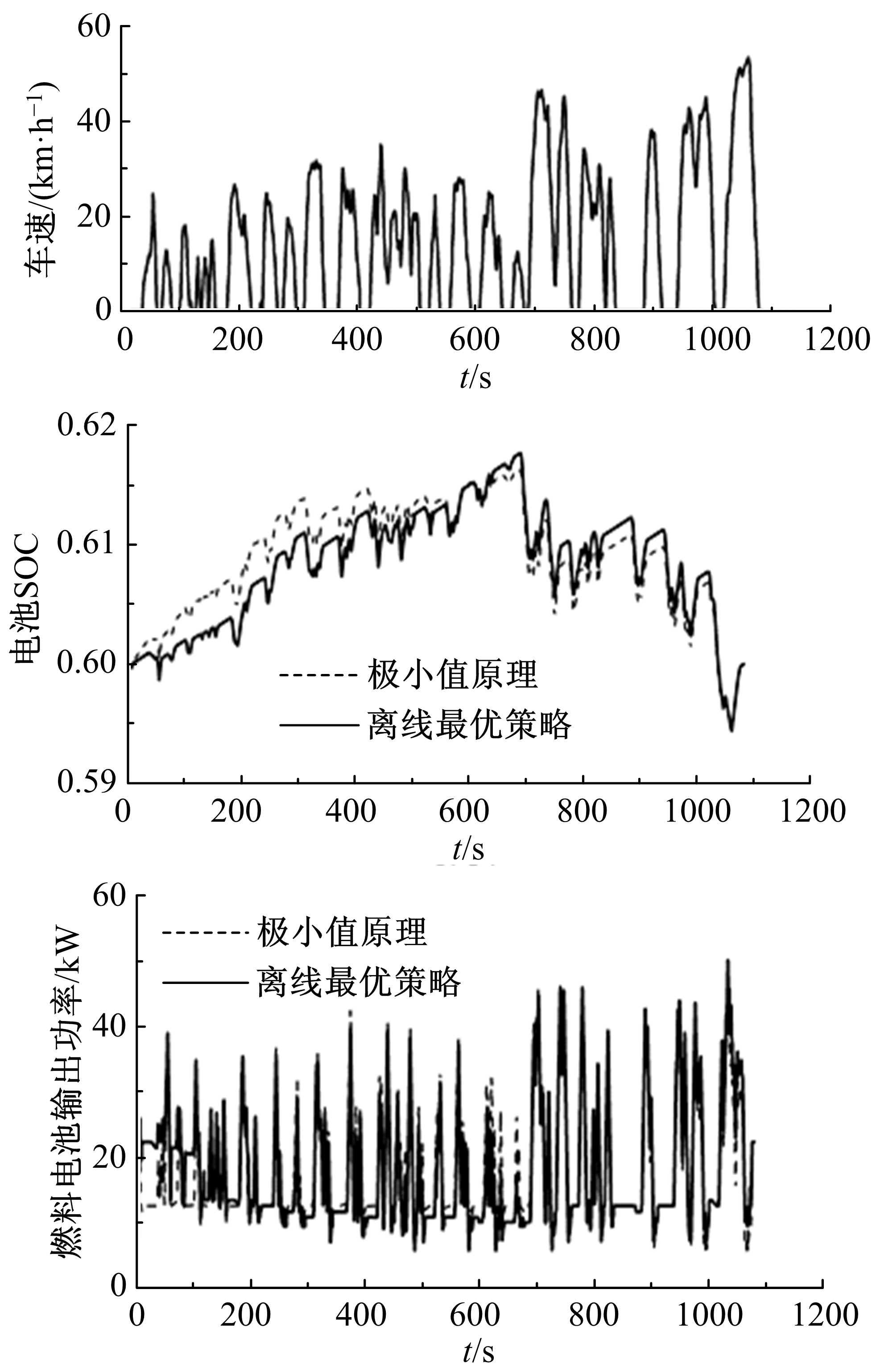
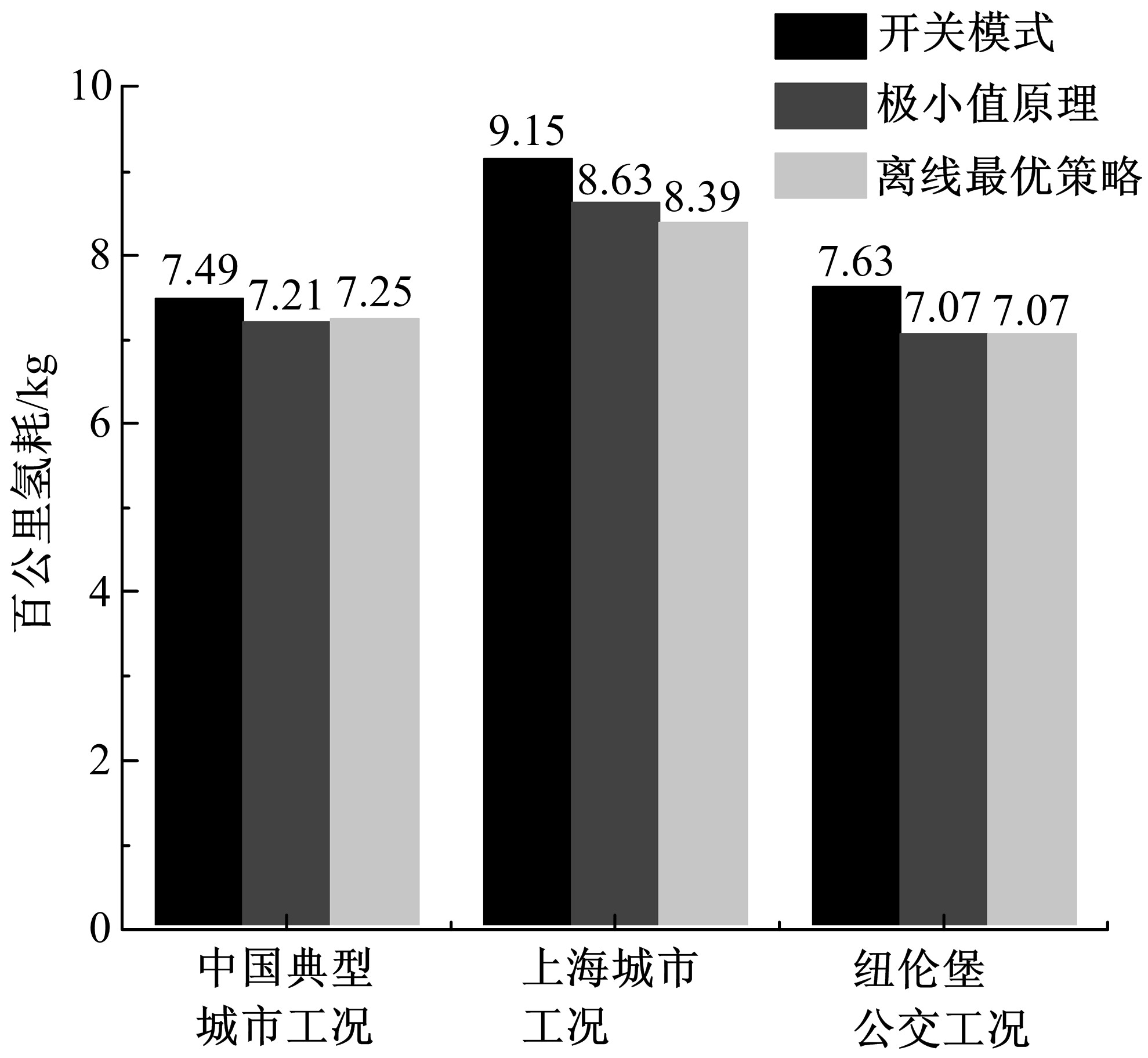
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 36-43.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180966
Previous Articles Next Articles
Energy management strategy of fuel cell bus based on Pontryagin′s minimum principle
Zhe WANG1,2( ),Yi XIE1,2,Peng-fei ZANG1,2,Yao WANG1,2
),Yi XIE1,2,Peng-fei ZANG1,2,Yao WANG1,2
- 1. School of Automotive Studies, Tongji University, Shanghai 201804, China
2. Clean Energy Automotive Engineering Center, Tongji University, Shanghai 201804, China
CLC Number:
- U461.8
| 1 | 衣宝廉, 侯明. 车用燃料电池耐久性的解决策略[J]. 汽车安全与节能学报, 2011, 2(2): 91-100. |
| Yi Bao-lian, Hou Ming. Solutions for the durability of fuel cells in vehicle applications[J]. Journal of Automotive Safety and Energy, 2011, 2(2): 91-100. | |
| 2 | 张来云. 增程式燃料电池汽车动力系统匹配及能量管理策略研究[D]. 上海:华东理工大学机械与动力工程学院, 2016. |
| Zhang Lai-yun. The power system matching and energy management strategy research of fuel cell range extender electric vehicle[D]. Shanghai: College of Mechanical and Power Engineering,East China University of Science and Technology, 2016. | |
| 3 | 谢星, 周苏, 王廷宏, 等. 基于Cruise/Simulink的车用燃料电池/蓄电池混合动力的能量管理策略仿真[J]. 汽车工程, 2010, 32(5): 373-378. |
| Xie Xing, Zhou Su, Wang Ting-hong, et, al. A Simulation on energy management strategy for the power system of a fuel cell/battery HEV based on Cruise/Simulink[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2010, 32(5): 373-378. | |
| 4 | 李熙, 谢勇波, 宋超,等. 基于T-S模糊控制的燃料电池客车能量管理策略及仿真分析[J]. 客车技术与研究, 2017, 39(4): 5-8, 39. |
| Li Xi, Xie Yong-bo, Song Chao, et al. Management strategy and simulation analysis on fuel cell bus energy based on T-S fuzzy control[J]. Bus & Coach Technology and Research, 2017, 39(4): 5-8, 39. | |
| 5 | Ahn H S, Lee N S. Power distribution control law for FCHEV-a fuzzy logic-based approach[C]∥International Conference on Control and Automation, Budapest, Hungary, 2005. |
| 6 | 徐陈锋. 基于自适应模糊策略的燃料电池车混合动力系统控制[D]. 杭州:浙江大学控制科学与工程学院, 2017.Xu Chen-feng. Adaptive fuzzy control for power management of fuel-cell-battery hybrid vehicles[D]. Hangzhou:College of Control Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, 2017. |
| 7 | Fletcher T, Thring R, Watkinson M. An energy management strategy to concurrently optimise fuel consumption & PEM fuel cell lifetime in a hybrid vehicle[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(46): 21503-21515. |
| 8 | 张炳力, 代康伟, 赵韩, 等. 基于随机动态规划的燃料电池城市客车能量管理策略优化[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2008, 20(17): 4664-4667. |
| Zhang Bing-li, Dai Kang-wei, Zhao Han, et al. Optimized energy management strategy for fuel cell city bus based on stochastic dynamic programming[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2008, 20(17): 4664-4667. | |
| 9 | Zheng C H, Xu G Q, Park Y I, et al. Prolonging fuel cell stack lifetime based on Pontryagin's minimum principle in fuel cell hybrid vehicles and its economic influence evaluation[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 248: 533-544. |
| 10 | Chen H, Pei P, Song M. Lifetime prediction and the economic lifetime of proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 142: 154-163. |
| 11 | Pei P, Chang Q, Tang T. A quick evaluating method for automotive fuel cell lifetime[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2008, 33(14): 3829-3836. |
| 12 | Pei P, Yuan X, Li P, et al. Lifetime evaluating and the effects of operation conditions on automotive fuel cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2010, 23(1): 66-71. |
| 13 | Pei P, Chen H. Main factors affecting the lifetime of proton exchange membrane fuel cells in vehicle applications: a review[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 125: 60-75. |
| [1] | Fang-wu MA,Hong-yu LIANG,Ying ZHAO,Meng YANG,Yong-feng PU. Multi⁃objective crashworthiness optimization design of concave triangles cell structure with negative Poisson′s ratio [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 29-35. |
| [2] | Kong-hui GUO,Shi-qing HUANG,Hai-dong WU. In⁃plane dynamic tire model for high⁃frequency excitation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 19-28. |
| [3] | Xin CHEN,Xin-jian RUAN,Ming LI,Ning WANG,Jia-ning WANG,Kai-xuan PAN. Application of modified discrete scheme based onlarge eddy simulation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1756-1763. |
| [4] | Fang-wu MA,Li-wei NI,Liang WU,Jia-hong NIE,Guang-jian XU. Position and attitude closed loop control of wheel⁃leggedall terrain mobile robot [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1745-1755. |
| [5] | Li-qiang JIN, Duan-yang TIAN, Hao TIAN, Meng-meng LIU. Brake force assistant technology for vehicle electronicstability control system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1764-1776. |
| [6] | Yang WANG,Zhan⁃shuai SONG,Kong⁃hui GUO,Ye ZHUANG. Measurement of inertial parameters of rotating inertia rig [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1795-1801. |
| [7] | Wei-min ZHUANG,Yang LIU,Peng-yue WANG,Hong-da SHI,Ji-shuan XU. Simulation on peeling failure of self⁃piercing riveted joints insteel and aluminum alloy dissimilar sheets [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1826-1835. |
| [8] | Jie LI, Wen-cui GUO, Qi ZHAO, Sheng-feng GU. Road roughness identification based on vehicle responses [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1810-1817. |
| [9] | Bai-chao CHEN,Meng ZOU,Zhao-long DANG,Han HUANG,Yang JIA,Rui-yang SHI,Jian-qiao LI. Experiment on pressure⁃sinkage for mesh wheels of CE⁃3lunar rover on lunar regolith [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1836-1843. |
| [10] | Ren HE,Kun TU. Electromagnetic brake with changed⁃temperature air gap width [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1777-1785. |
| [11] | Qiao-bin LIU,Wen-ku SHI,Zhi-yong CHEN,Lian-meng LUO,Zhi-yong SU,Kai-jun HUANG. Parameter estimation of mixed reliability model based on kernel density optimal grouping and gravity search algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1818-1825. |
| [12] | Xin GUAN,Hao JIN,Chun-guang DUAN,Ping-ping LU. Estimation of lateral slope of vehicle driving road [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1802-1809. |
| [13] | Ting YAN,Lin YANG,Liang CHEN. AMT shift actuator adaptive intelligent control strategy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1441-1450. |
| [14] | Fang-wu MA,Lu HAN,Yang ZHOU,Shi-ying WANG,Yong-feng PU. Multi material optimal design of vehicle product using polylactic acid composites [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1385-1391. |
| [15] | Bo ZHANG,Jian-wei ZHANG,Kong-hui GUO,Hai-tao DING,Hong-qing CHU. Current control of permanent magnet synchronous motor for road feeling simulation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1405-1413. |
|
||