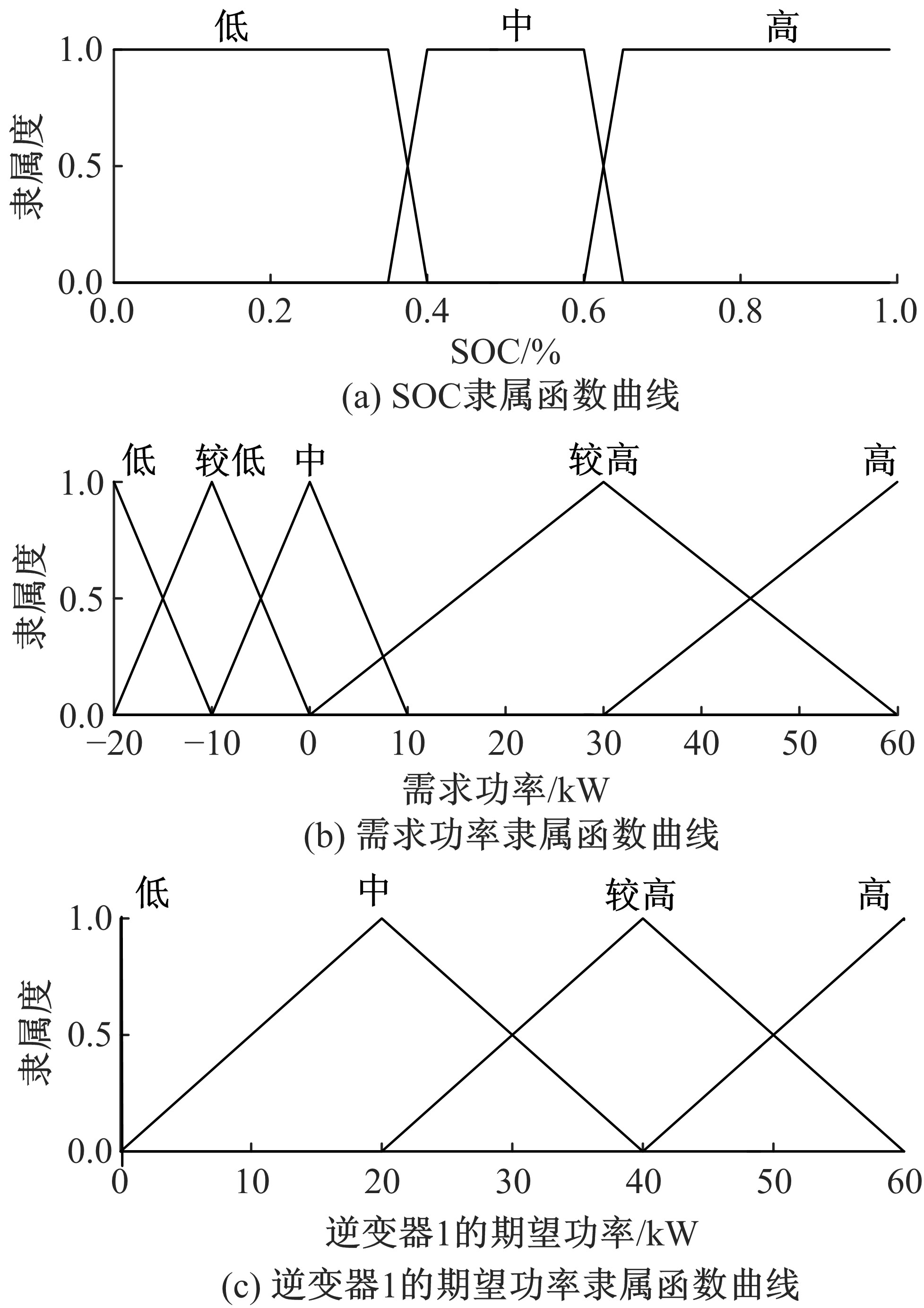
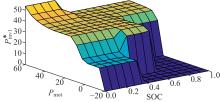
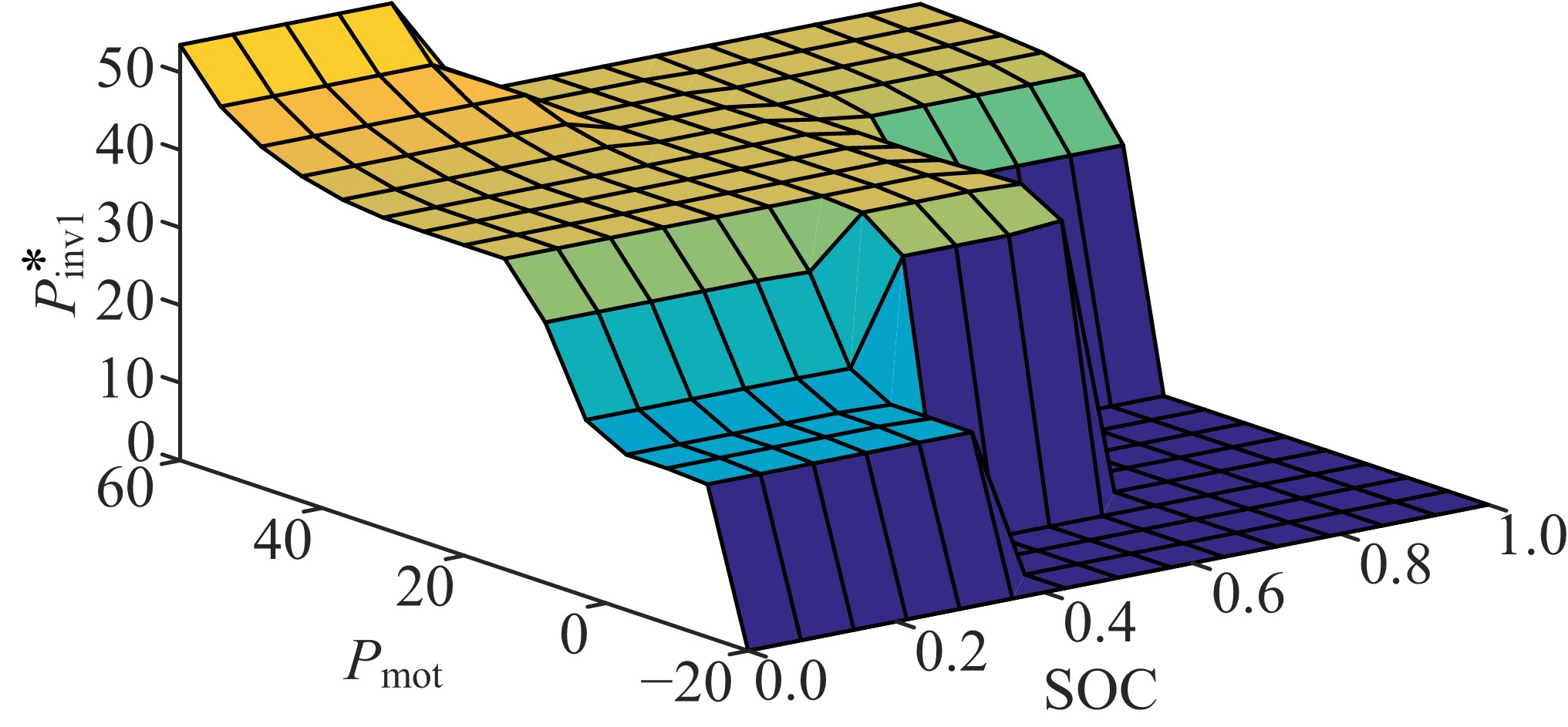
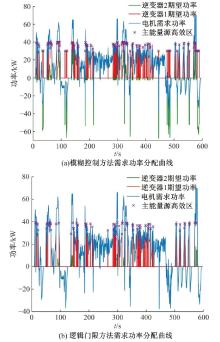
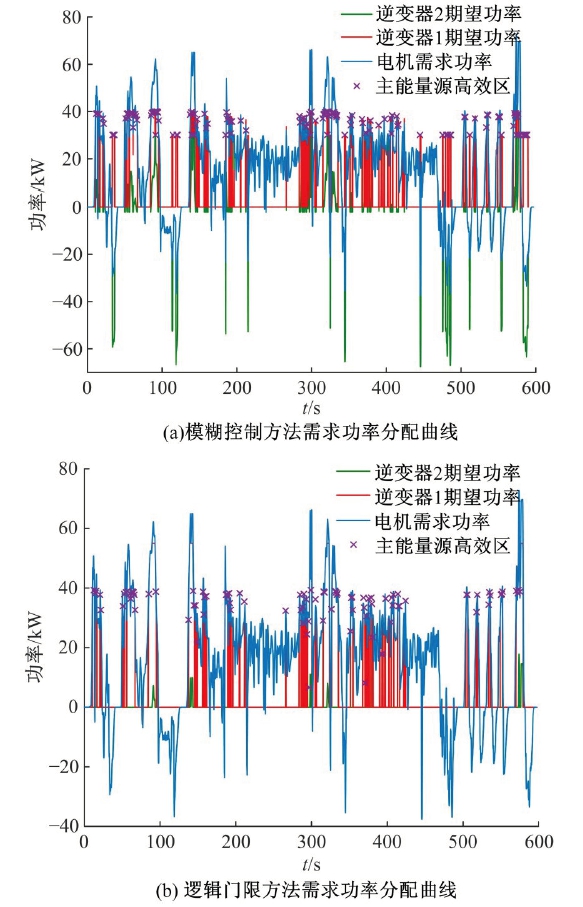
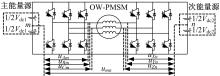
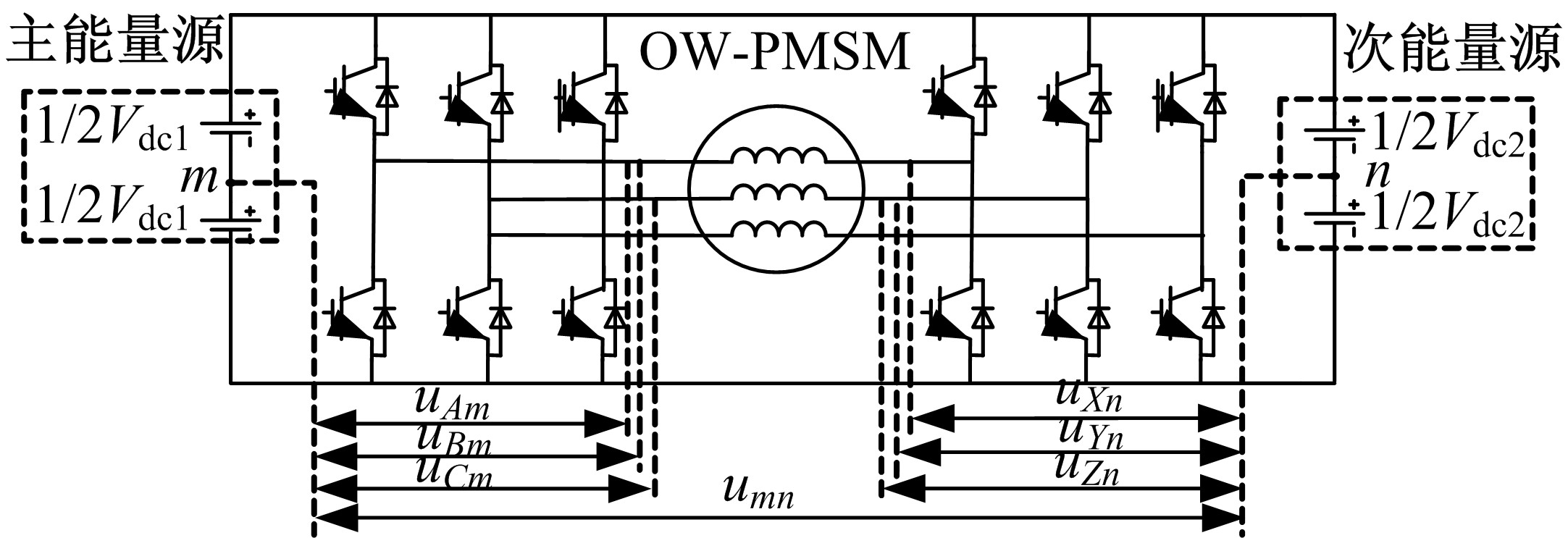
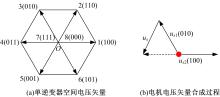
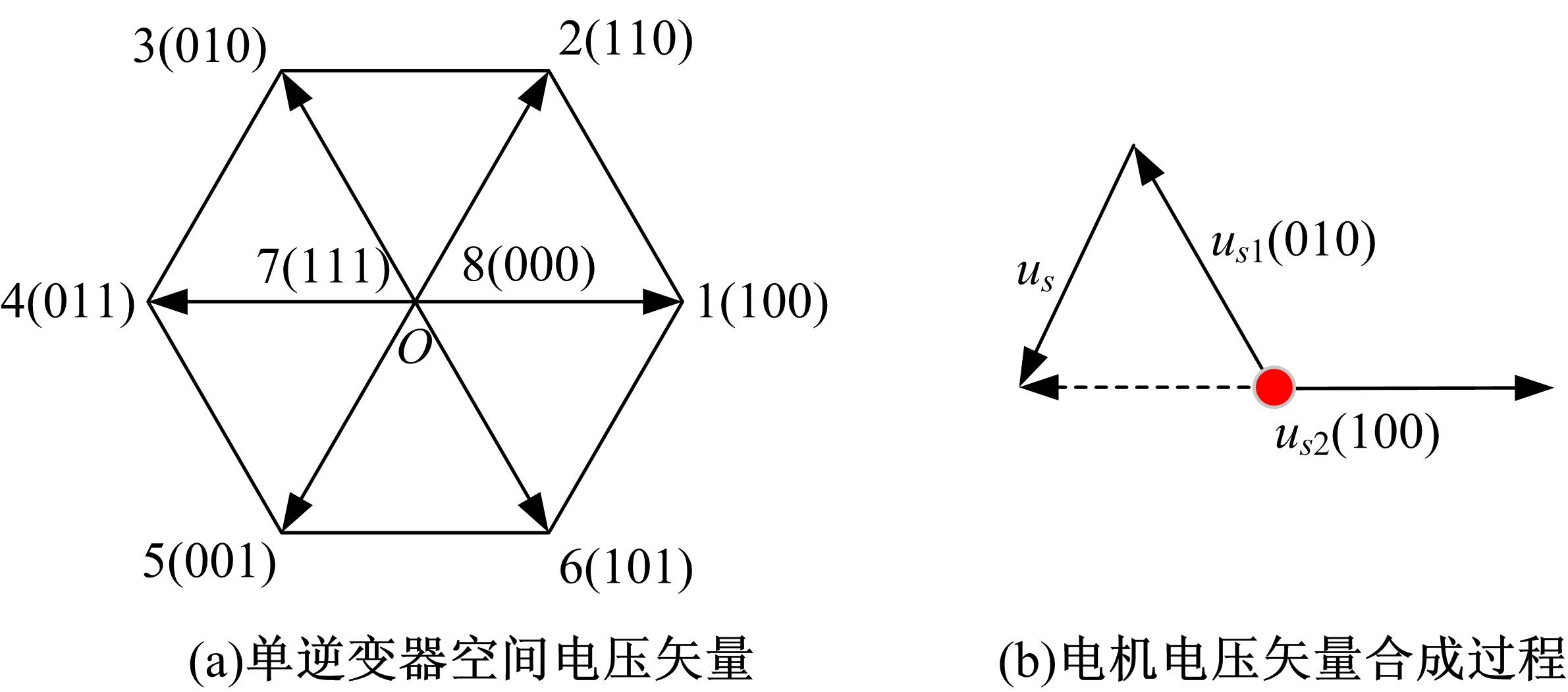
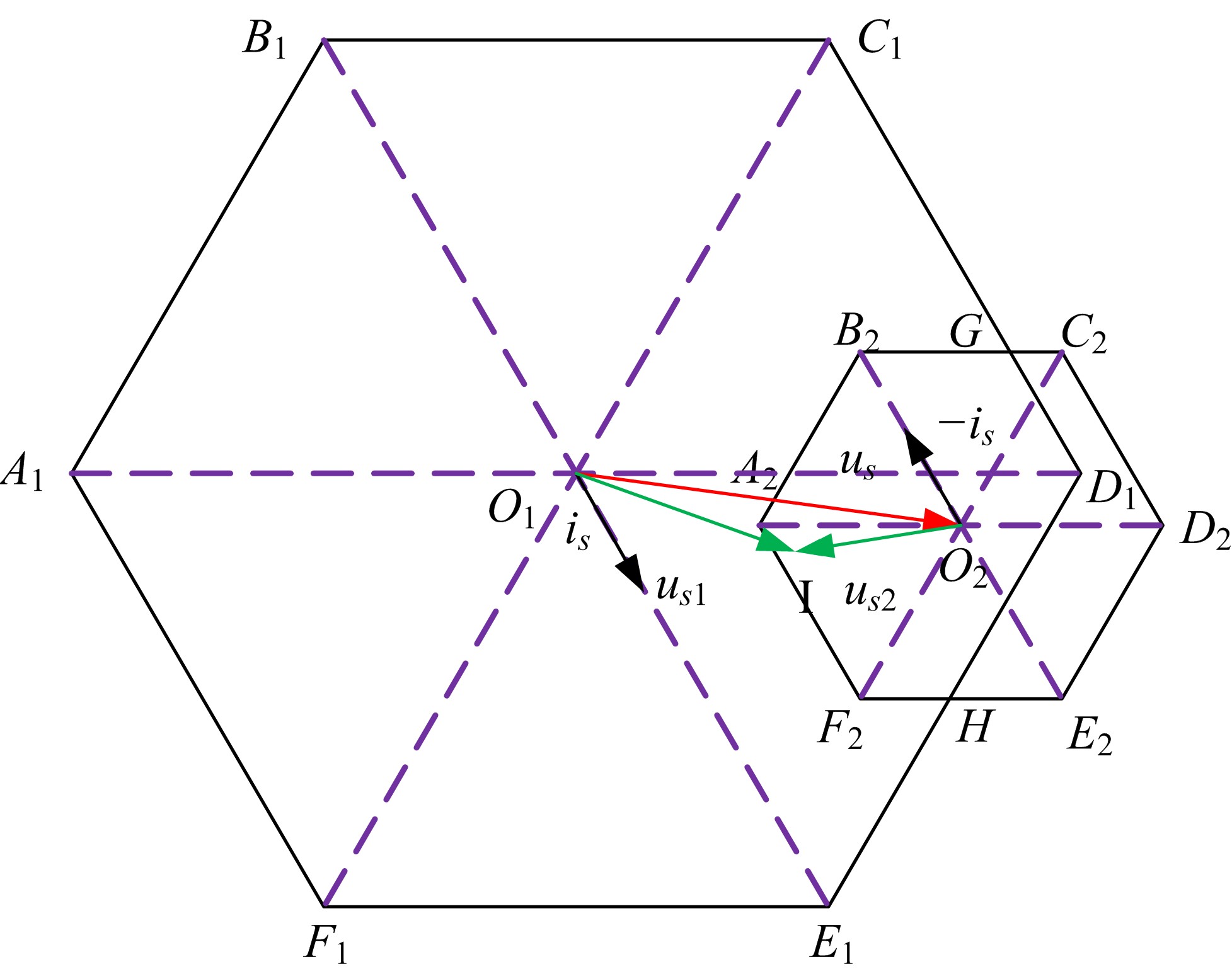
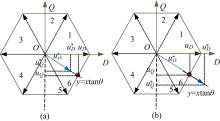
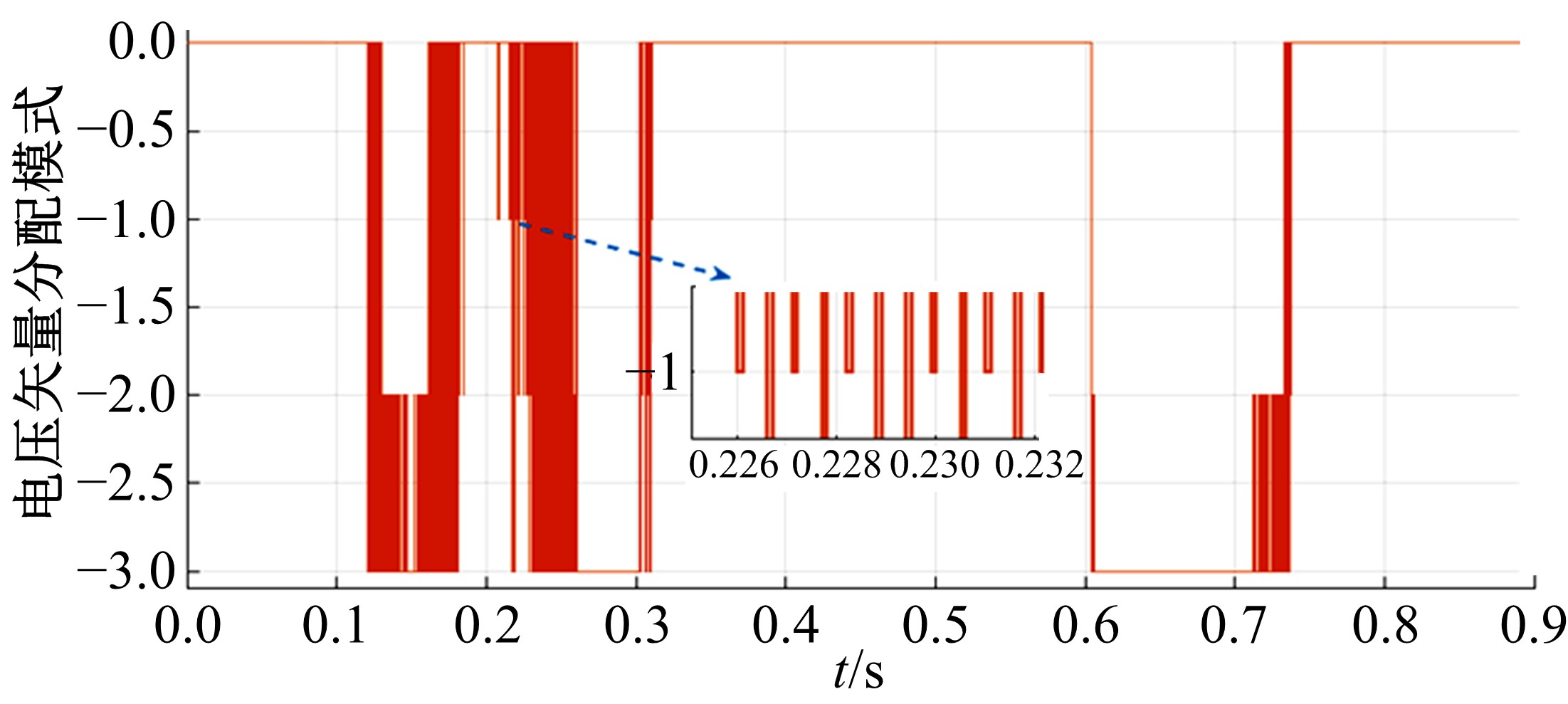
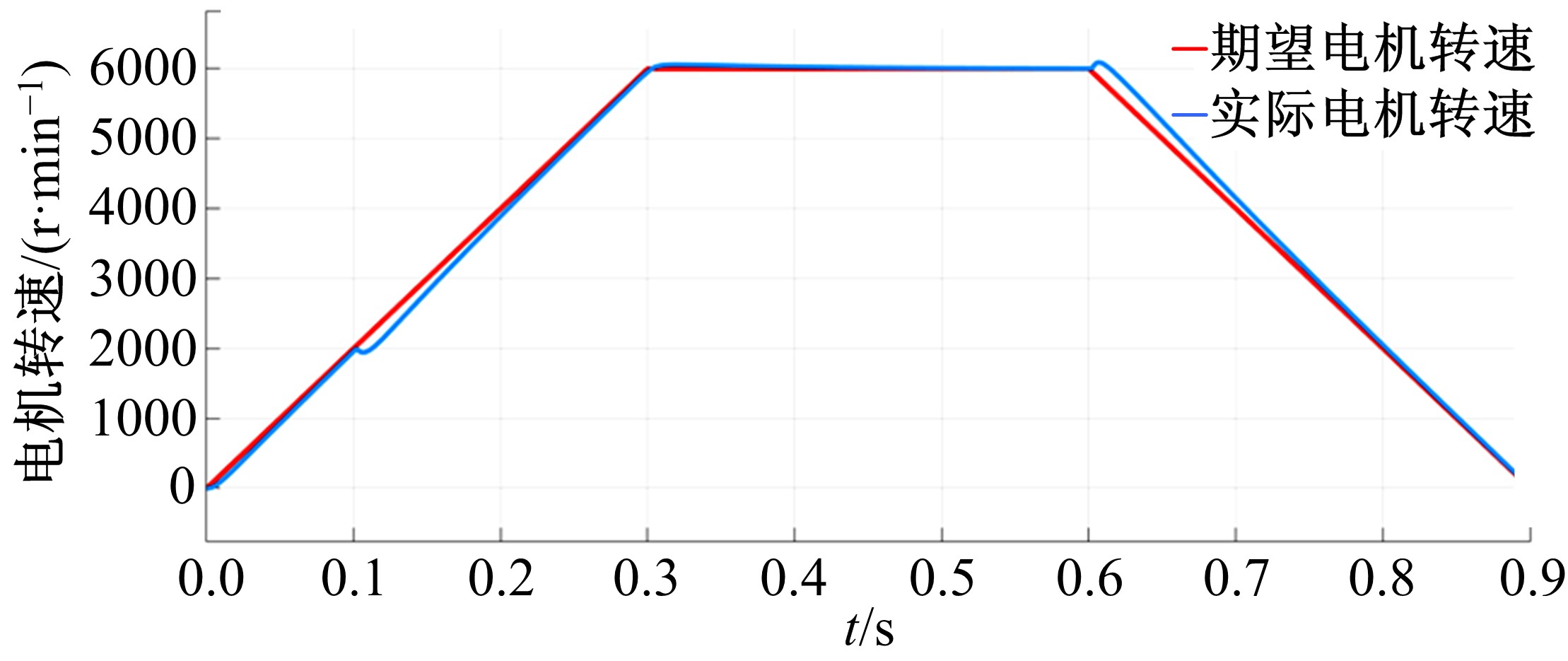
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 72-82.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190955
Previous Articles Next Articles
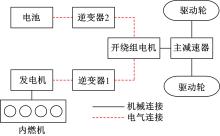
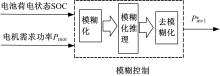
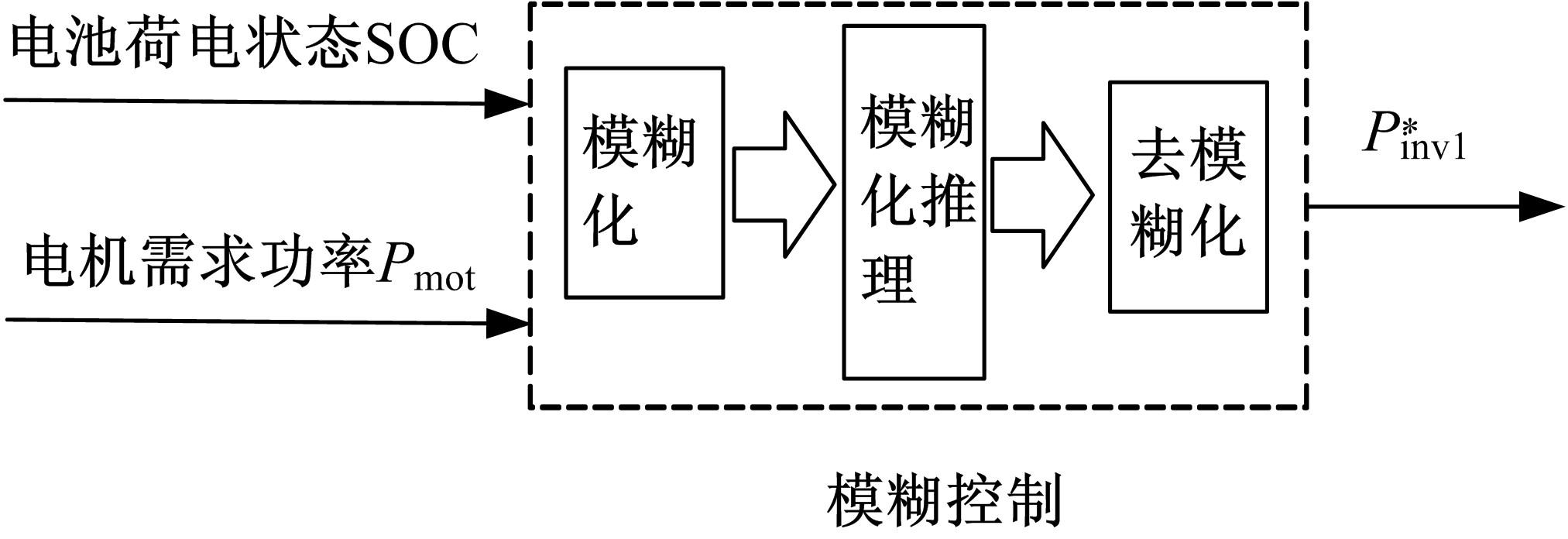
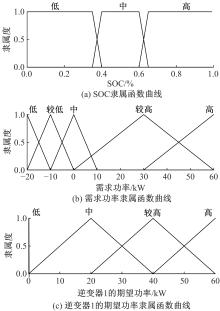
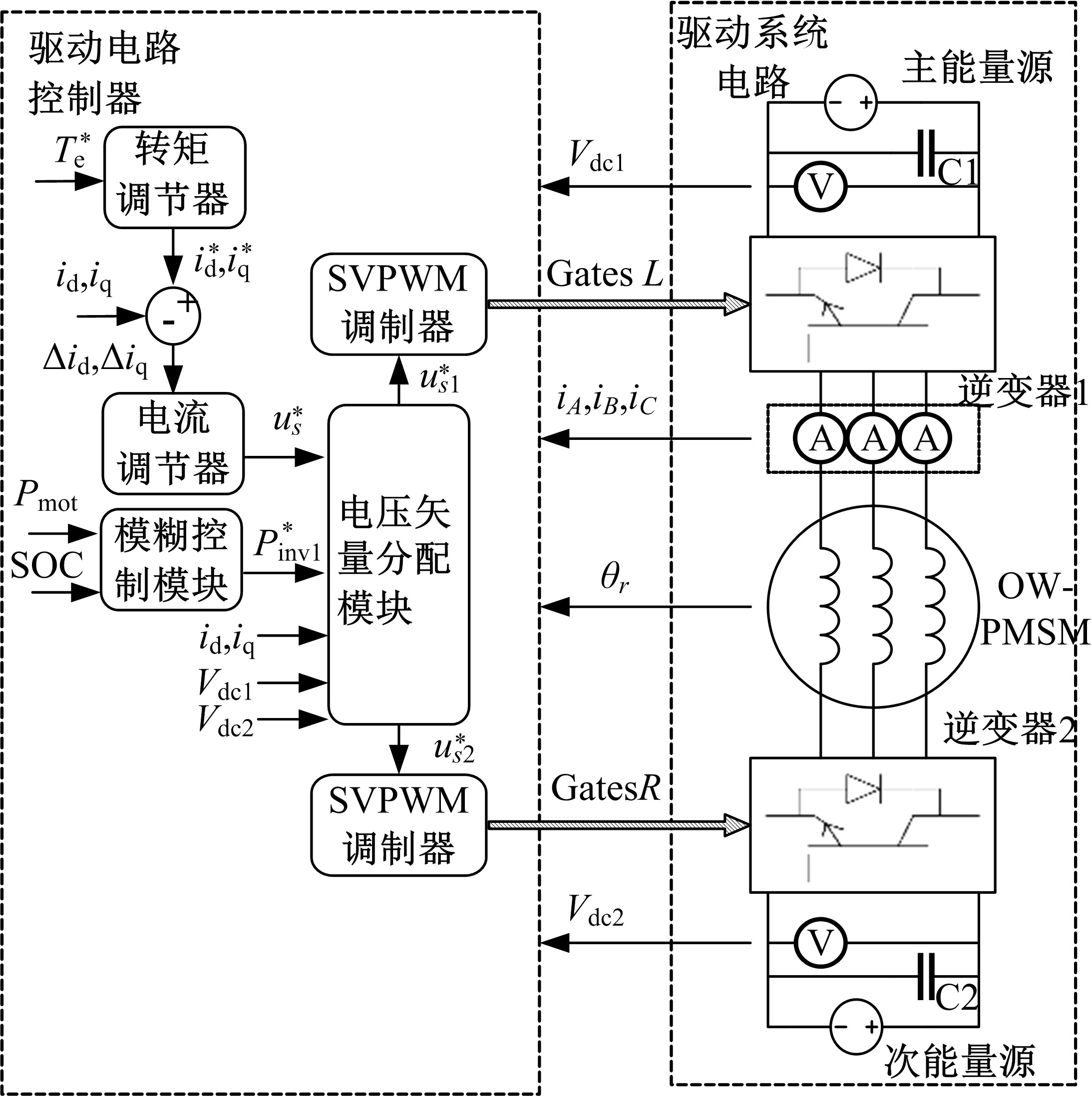
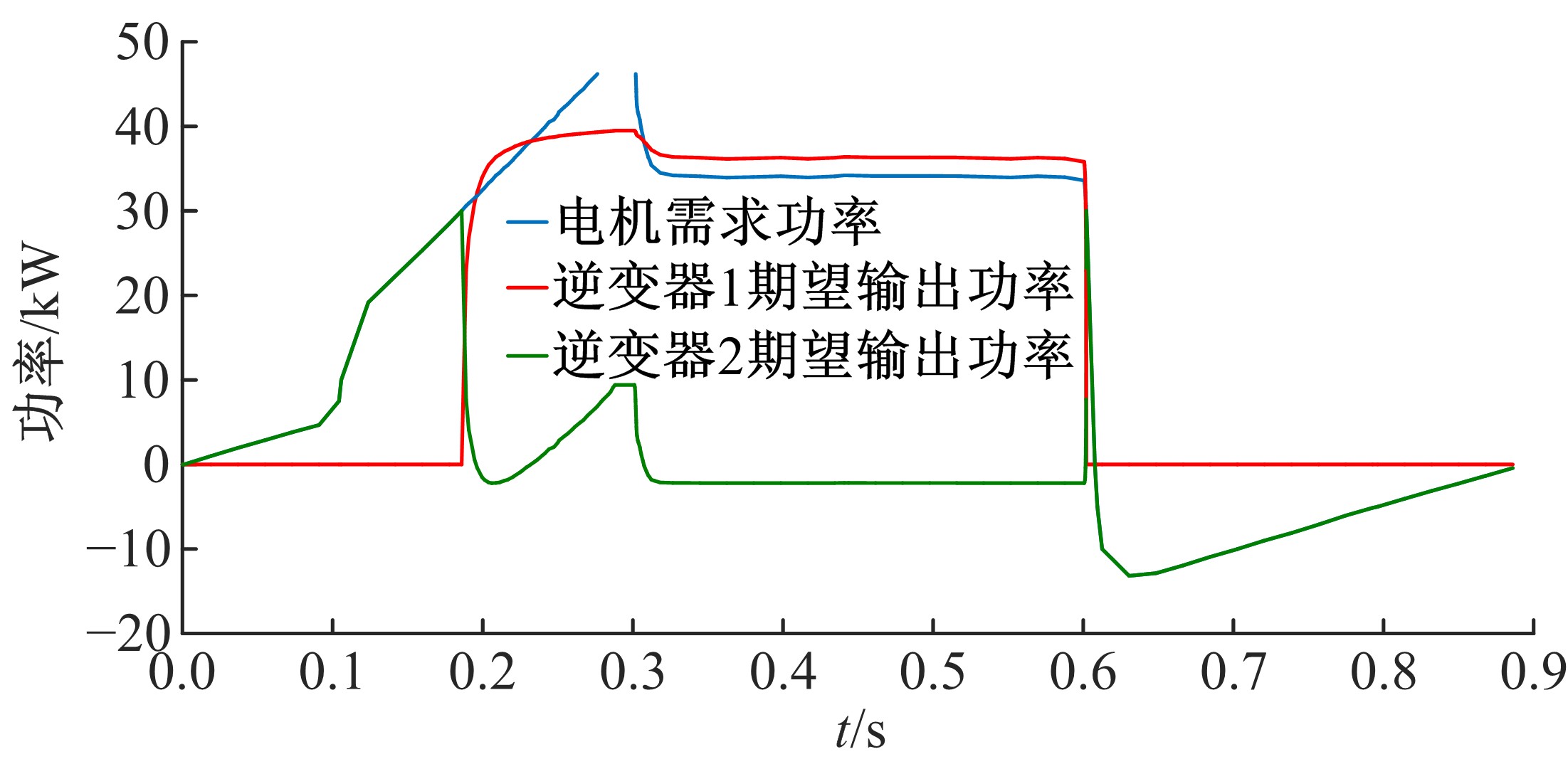
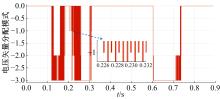
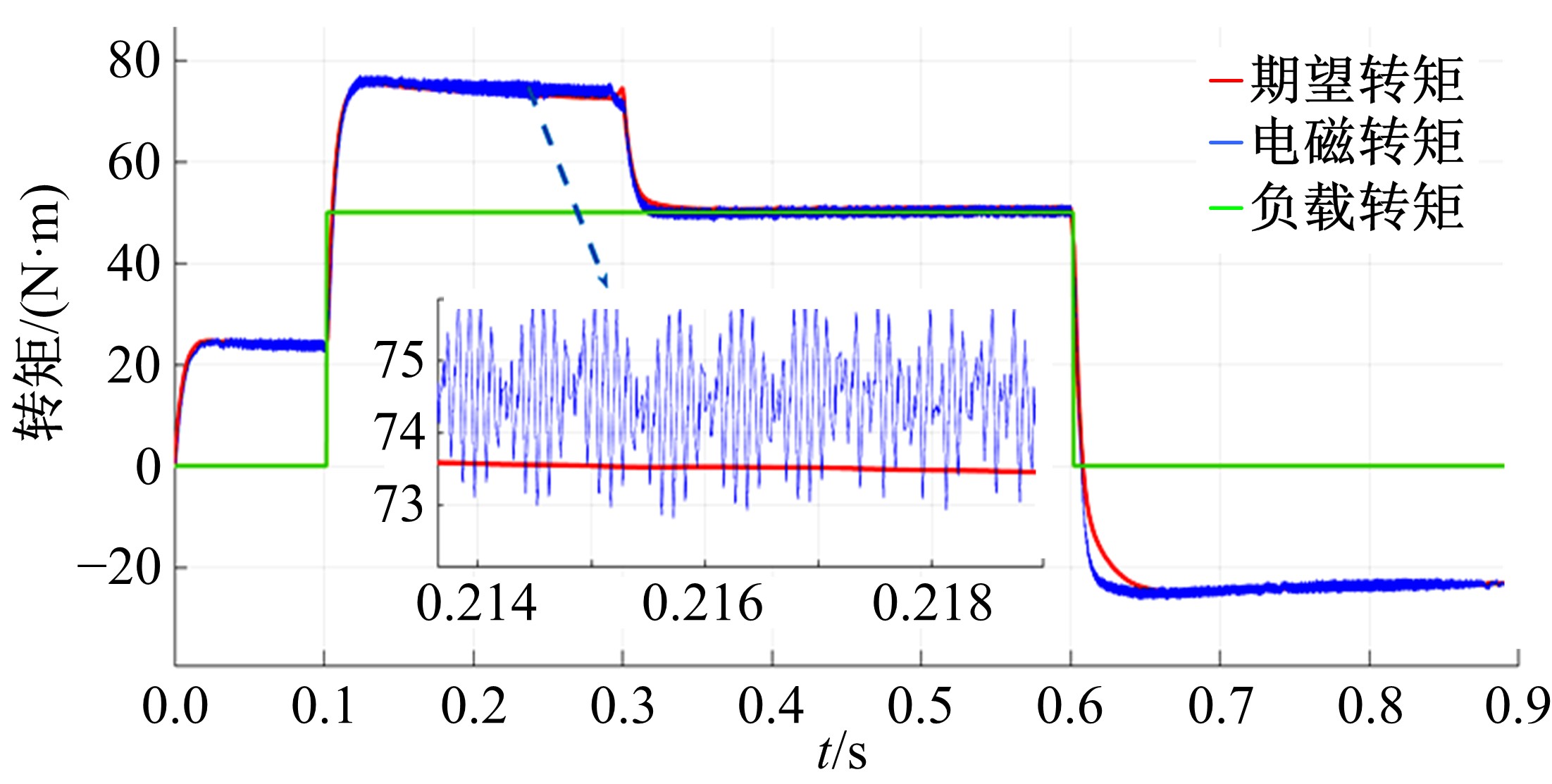
Powertrain configuration and power distribution of extended electric vehicle based on open winding motor
Liang CHU1( ),Li-jia DONG1,Nan XU1(
),Li-jia DONG1,Nan XU1( ),Li-feng ZHANG2,Yi-fan JIA1,Zhi-hua YANG1
),Li-feng ZHANG2,Yi-fan JIA1,Zhi-hua YANG1
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.SAIC MOTOR Commercial Vehicle Technical Center,Shanghai 200438,China
CLC Number:
- TM351
| 1 | 沈启平. 车用高功率密度永磁同步电机的研究[D]. 沈阳:沈阳工业大学电气工程学院, 2012. |
| Shen Qi-ping. Research on high power density permanent magnet synchronous motor for vehicle[D]. Shenyang: School of electrical engineering, Shenyang University of Technology, 2012. | |
| 2 | 韩康. 电动汽车用永磁同步电机控制系统研究[D]. 大庆:东北石油大学电气信息工程学院, 2018. |
| Han Kang. Research on permanent magnet synchronous motor control system for electric vehicle[D]. Daqing: School of Electrical Information Engineering, Northeast Petroleum University, 2018. | |
| 3 | 蔡萍, 李永岗, 赵赫. 双三相永磁同步电机在电动汽车中的应用研究[J]. 微特电机, 2019, 47(1): 59-62, 69. |
| Cai Ping, Li Yong-gang, Zhao He. The application of dual three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor in electric vehicle[J]. Small Special Electrical Machines, 2019, 47(1): 59-62, 69. | |
| 4 | Kumar K V P, Kumar T V. An effective four-level Voltage switching state algorithm for direct torque controlled open end winding induction motor drive by using two two-level inverters[J]. Electric Power Components & Systems, 2017, 45(19): 2175-2187. |
| 5 | Kunisetti V P K, Kodumur Meesala R E, Thippiripati V K. Improvised predictive torque control strategy for an open end winding induction motor drive fed with four-level inversion using normalized weighted sum model[J]. IET Power Electronics, 2018, 11(5): 808-816. |
| 6 | Vinod B R, Baiju M R, Shiny G. Five level inverter fed space vector based direct torque control of open-end winding induction motor drive[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2018, 33(3):1392-1401. |
| 7 | Sandulescu P, Meinguet F, Kestelyn X, et al. Control strategies for open-end winding drives operating in the flux-weakening region[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2014, 29(9): 4829-4842. |
| 8 | Vinod B R, Baiju M R, Shiny G. Five level inverter fed space vector based direct torque control of open-end winding induction motor drive[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2018, 33(3):1392-1401. |
| 9 | 周文志. 混合逆变器开绕组永磁同步电机容错控制技术研究[D]. 杭州:浙江大学电气学院, 2016. |
| Zhou Wen-zhi. Fault-tolerant control technology of hybrid inverter open-winding permanent magnet synchronous motor [D]. Hangzhou:School of Electrical Engineering, Zhejiang University, 2016. | |
| 10 | 赵克, 安群涛, 孙力. 容错逆变器PMSM无位置传感器控制系统[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2010, 14(4): 25-30. |
| Zhao Ke, An Qun-tao, Sun Li. Fault tolerant inverter PMSM position sensorless control system[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2010, 14(4): 25-30. | |
| 11 | Park J S, Nam K. Dual inverter strategy for high speed operation of HEV permanent magnet synchronous motor[C]∥IEEE Industry Applications Conference Forty-First IAS Annual Meeting, Tampa, FL, USA, 2006: 488-494. |
| 12 | Priestley M, Fletcher J E, Tan C. Space-vector PWM technique for five-phase open-end winding PMSM drive operating in the over-modulation region[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(9): 6816-6827. |
| 13 | 林斌. 混合逆变器开绕组永磁同步电机驱动系统研究[D]. 杭州:浙江大学电气工程学院, 2015. |
| Lin Bin. Research on drive system of open-winding permanent magnet synchronous motor of hybrid inverter [D]. Hangzhou:School of Electrical Engineering, Zhejiang University, 2015. | |
| 14 | Welchko B A. A double-ended inverter system for the combined propulsion and energy management functions in hybrid vehicles with energy storage[C]∥IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Raleigh, NC, USA, 2005: 1401-1406. |
| 15 | Casadei D, Grandi G, Lega A, et al. Multilevel operation and Input power balancing for a dual two-level inverter with insulated DC sources[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2008, 44(6): 1815-1824. |
| 16 | Chu L, Jia Y F, Chen D S, et al. Research on control strategies of an open-end winding permanent magnet synchronous driving motor(OW-PMSM)-equipped dual inverter with a switchable winding mode for electric vehicles[J]. Energies, 2017, 10(5): No 616. |
| 17 | Camara M B, Gualous H, Gustin F, et al. DC/DC converter design for supercapacitor and battery power management in hybrid vehicle applications—polynomial control strategy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2010, 57(2): 587-597. |
| 18 | Listwan J, Pieńkowski K. Field-oriented control of five-phase induction motor with open-end stator winding[J]. Archives of Electrical Engineering, 2016, 65(3): 395-410. |
| [1] | WANG Li, LIU Xin-hui, WANG Xin, CHEN Jin-shi, LIANG Yi-jie. Shifting strategy of digital hydraulic transmission system for wheel loader [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 819-826. |
| [2] | WANG Wei, WANG Qing-nian, TIAN Yong-jun, WANG Ren-guang, WEN Quan. Control strategy for compound power slit hybrid electric bus based on fuzzy control [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 337-343. |
| [3] | MA Bei, ZHANG Hai-lin, ZHANG Zhao-wei, ZHONG Ming. Imperfect channel state information based D2D power allocation algorithm [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1320-1324. |
| [4] | NIE Hai-tao, LONG Ke-hui, MA Jun, ZHANG Lei, MA Xi-qiang. Face recognition based on fast scale invariant feature transform algorithm and fuzzy control [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 549-555. |
| [5] | CHEN Jie, MO Wei. Adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control for crawler-type mobile manipulators [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(3): 892-898. |
| [6] | MA Xu-hui, LIU Xiao-ming, ZHANG Jin-jin. Oversaturated intersection traffic signal control method considering bus priority [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(3): 748-754. |
| [7] | DONG Bing,TIAN Yan-tao,ZHOU Chang-jiu. Fuzzy logic-based optimal control method for energy management of pure electric vehicle [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 516-525. |
| [8] | ZHAO Xiao-hui,SHA Jing-qi. Resource allocation algorithm in DF relay assisted OFDM cognitive radio systems [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(5): 1481-1487. |
| [9] | HAN Kyong-won, TIAN Yan-tao, KONG Yong-su, ZHANG Ying-hui, LI Jin-song. Adaptive decoupled sliding mode control for the ball and plate system [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(3): 718-725. |
| [10] | YE Jin-hua,LI Di,YE Feng. Dual reinforcement learning adaptive fuzzy control of wheeled mobile robot [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(3): 742-749. |
| [11] | ZHAO Xiao-hui, YANG Wei-wei, JIN Xiao-guang. Selective subcarrier relaying and power allocation algorithm for multi-relay-assisted OFDM systems [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(2): 478-484. |
| [12] | WANG Qing-nian, WANG Jun, CHEN Hui-yong, ZENG Xiao-hua, TANG Xian-zhi. Accelerating and braking intention identification in hybrid vehicle [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(2): 281-286. |
| [13] | LI Jing, YU Chun-xian. Vehicle chassis integrated control system based on fuzzy and PID [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(增刊1): 509-513. |
| [14] | MA Wen-xing, LIU Bin, LIU Chun-bao, LIU Hao. Hydrodynamic speed adjusting system and its control of wind turbine [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(05): 1276-1283. |
| [15] | SHI Yu-chen, BAI Bao-ming. Inference cancellation based on superposition modulation and adaptive power allocation [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(01): 213-217. |
|
||