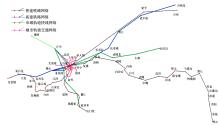
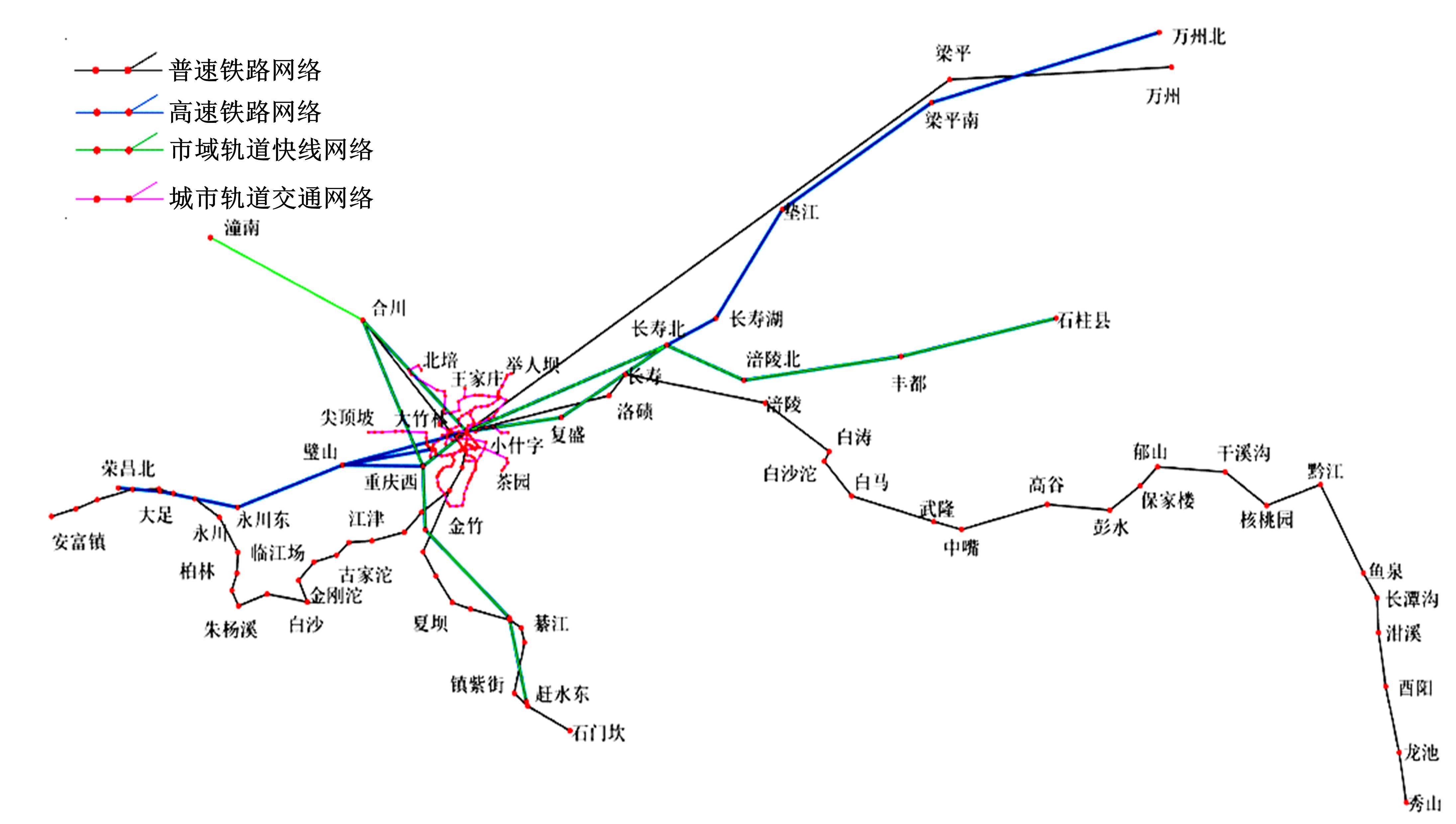
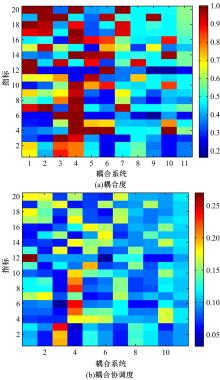
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 2040-2050.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200701
Coordination degree of multimodal rail transit network
Feng XUE1,2( ),Chuan-lei HE3,Qian HUANG4,Jian LUO5(
),Chuan-lei HE3,Qian HUANG4,Jian LUO5( )
)
- 1.School of Transportation and Logistics,Southwest Jiaotong University,Chengdu 611756,China
2.National United Engineering Laboratory of Integrated and Intelligent Transportation,Southwest Jiaotong University,Chengdu 611756,China
3.China Railway First Survey and Design Institute Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Xi'an 710043,China
4.China Railway Xi'an Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Xi'an 710054,China
5.School of Automobile and Transportation,Xihua University,Chengdu 610039,China
CLC Number:
- U113
| 1 | Erdős P, Rényi A. On the evolution of random graphs[J]. Publ Math Inst Hung Acad Sci, 1960, 5(1): 343-347. |
| 2 | Watts D J, Strogatz S H. Collective dynamics of small world networks[J]. Nature, 1998, 393(6684):440-442. |
| 3 | Barabási A L, Albert R. Emergence of scaling in random networks[J]. Science, 2011, 286(15):509-512. |
| 4 | 方锦清, 汪小帆, 郑志刚, 等. 一门崭新的交叉科学: 网络科学(上)[J]. 物理学进展, 2007, 27(3): 239-343. |
| Fang Jin-qing, Wang Xiao-fan, Zheng Zhi-gang, et al. New interdisciplinary science: network science(I)[J]. Progress in Physics, 2007, 27(3):239-343. | |
| 5 | Amaral L A N, Scala A, Barthélémy M, et al. Classes of small-world networks[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2000, 97(21):11149-11152. |
| 6 | Sienkiewicz J, Holyst J A. Public transport systems in Poland: from Bialystok to Zielona Gora by bus and tram using universal statistics of complex networks[J]. Acta Physica Polonica, 2005, 36(5): 1771-1778. |
| 7 | Lämmer S, Gehlsen B, Helbing D. Scaling laws in the spatial structure of urban road networks[J]. Physica A Statistical Mechanics & Its Applications, 2006, 363(1): 89-95. |
| 8 | 张晋, 梁青槐, 贺晓彤. 北京市地铁网络拓扑结构复杂性研究[J]. 北京交通大学学报, 2013, 37(6): 78-84. |
| Zhang Jin, Liang Qing-huai, He Xiao-tong. Study on the complexity of Beijing metro network[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2013, 37(6): 78-84. | |
| 9 | 包云, 刘军, 李婷. 中国铁路旅客列车服务网络性质研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2012, 34(12): 8-15. |
| Bao Yun, Liu Jun, Li Ting. Properties of Chinese railway passenger train service network[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2012, 34(12): 8-15. | |
| 10 | 宗跃光, 陈眉舞, 杨伟, 等. 基于复杂网络理论的城市交通网络结构特征[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2009, 39(4): 910-915. |
| Zong Yue-guang, Chen Mei-wu, Yang Wei, et al. Structure characteristic of urban composite traffic net‐work based on complex network theory[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2009, 39(4): 910-915. | |
| 11 | 卫振林, 甘杨杰, 赵鹏. 城市复合交通网络的若干特性研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2015, 15(1): 106-111. |
| Wei Zhen-lin, Gan Yang-jie, Zhao Peng. Characteristic research of urban complex traffic network[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2015, 15(1): 106-111. | |
| 12 | 薛锋, 何传磊, 黄倩. 成都地铁网络的关键节点识别方法及性能分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(1): 93-99. |
| Xue Feng, He Chuan-lei, Huang Qian. Key node identification of Chengdu metro network and network performance analysis[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(1):93-99. | |
| 13 | 林鹏飞, 翁剑成, 付宇, 等. 基于刷卡数据的轨道交通加权网络结构特征[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020, 50(3): 956-962. |
| Lin Peng-fei, Weng Jian-cheng, Fu Yu, et al. Structure characteristics of rail transit weighted network based on smart card data[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020,50(3):956-962. | |
| 14 | 姜磊, 柏玲, 吴玉鸣. 中国省域经济、资源与环境协调分析——兼论三系统耦合公式及其扩展形式[J]. 自然资源学报, 2017, 32(5): 788-799. |
| Jiang Lei, Bai Ling, Wu Yu-ming. Coupling and coordinating degrees of provincial economy, resources and environment in China[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2017, 32(5):788-799. | |
| 15 | Tang Z. An integrated approach to evaluating the coupling coordination between tourism and the environment[J]. Tourism Management, 2015, 46: 11-19. |
| 16 | 黄文成, 帅斌, 庞璐, 等.基于耦合协调度的道路危险品运输系统风险评价[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2016, 26(6): 117-122. |
| Huang Wen-cheng, Bin Shuai, Pang Lu, et al. Research on coupling coordination degree based method for assessing risk in road dangerous goods transport system[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2016, 26(6):117-122. | |
| 17 | 薛锋, 袁野. 基于耦合协调度模型的综合运输体系支撑力研究[J]. 交通运输工程与信息学报, 2018, 16(1): 24-31. |
| Xue Feng, Yuan Ye. Research on the supporting capability of comprehensive transportation systems using coupling coordinate model[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information, 2018, 16(1):24-31. | |
| 18 | 徐凤, 朱金福, 杨文东. 高铁-民航复合网络的构建及网络拓扑特性分析[J]. 复杂系统与复杂性科学, 2013, 10(3): 1-11. |
| Xu Feng, Zhu Jin-fu, Yang Wen-dong. Construction of high-speed railway and airline compound network and the analysis of its network topology characteristics[J]. Complex Systems and Complexity Science, 2013, 10(3): 1-11. | |
| 19 | 杨捷. 基于复杂网络的伏牛山区路网与县域经济协调发展研究[D]. 开封:河南大学环境与规划学院, 2019. |
| Yang Jie. Research on coordinated development of the road network and the county economy of Funiu mountain area based on complex network[D]. Kaifeng: College of Environment and Planning, Henan University, 2019. | |
| 20 | 蒋洁滢. 区域轨道交通综合运能匹配评价方法研究[J].中国铁路, 2019, 57(9): 90-94. |
| Jiang Jie-ying. Research on evaluation methods of comprehensive transport capacity matching for regional rail transit[J]. China Railway, 2019, 57(9):90-94. | |
| 21 | 南天伟. 铁路综合客运枢纽衔接方式运营匹配性评价及优化[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学交通运输学院, 2015. |
| Tian-wei Nan. Study on the evaluation and optimization scheme for passengers'transfer modes in railway transport hub[D]. Beijing: School of Traffic and Transportation, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2015. | |
| 22 | 陈小鸿, 周翔, 乔瑛瑶. 多层次轨道交通网络与多尺度空间协同优化——以上海都市圈为例[J]. 城市交通, 2017, 15(1): 20-30, 37. |
| Chen Xiao-hong, Zhou Xiang, Qiao Ying-yao. Coordination and optimization of multilevel rail transit network and multi-scale spatial layout: a case study of Shanghai metropolitan area[J]. Urban Transport of China, 2017, 15(1): 20-30, 37. | |
| 23 | 赵国堂, 周诗广. 我国市域铁路发展现状及未来展望[J].中国铁路, 2018,57(8):1-10. |
| Zhao Guo-tang, Zhou Shi-guang. Today and future of suburban railway in china[J]. China Railway, 2018, 57(8):1-10. |
| [1] | Rong QIAN,Ru ZHANG,Ke-jun ZHANG,Xin JIN,Shi-liang GE,Sheng JIANG. Capsule graph neural network based on global and local features fusion [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 1048-1054. |
| [2] | Bo PENG,Yuan-yuan ZHANG,Yu-ting WANG,Ju TANG,Ji-ming XIE. Automatic traffic state recognition from videos based on auto⁃encoder and classifiers [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 886-892. |
| [3] | Dian-hai WANG,Xin-yi SHEN,Xiao-qin LUO,Sheng JIN. Offset optimization with minimum average vehicle delay [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 511-523. |
| [4] | Xian-min SONG,Ming-ye ZHANG,Zhen-jian LI,Xin WANG,Ya-nan ZHANG. Setting of dynamic bus lane and its simulation analysis and evaluation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1677-1686. |
| [5] | Hong-fei JIA,Xin-ru DING,Li-li YANG. Bi-level programming model for optimization design of tidal lane [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 535-542. |
| [6] | Chao-ying YIN,Chun-fu SHAO,Xiao-quan WANG,Zhi-hua XIONG. Influence of built environment on commuting mode choice considering spatial heterogeneity [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 543-548. |
| [7] | Da-wei ZHANG,Hai-tao ZHU. An optimization⁃based evacuation model considering pedestrian heterogeneity [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 549-556. |
| [8] | Yuan-li GU, Yuan ZHANG, Xiao-ping RUI, Wen-qi LU, Meng LI, Shuo WANG. Short⁃term traffic flow prediction based on LSSVMoptimized by immune algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1852-1857. |
| [9] | Yi-ming BIE,Kai JIANG,Ru-ru TANG,Lin-hong WANG,Xin-yu XIONG. Time of interval partition for traffic control at isolated intersection considering impacts of plan transition [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1844-1851. |
| [10] | Guo-zhu CHENG, Si-he FENG, Tian-jun FENG. Setting condition of on⁃street parking space occupied vehicle lane [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1858-1864. |
| [11] | Quan LIANG,Jian-cheng WENG,Wei ZHOU,Jian RONG. Stability identification of public transport commute passengers based on association rules [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1484-1491. |
| [12] | Hai-bo LONG,Jia-qi YANG,Xue-yu ZHAO. Optimizing vehicles allocation of multimodal coordinated freight transport based on transshipment delay risks [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1492-1499. |
| [13] | Wen⁃jing WU,Run⁃chao CHEN,Hong⁃fei JIA,Qing⁃yu LUO,Di SUN. Collaborative control method of vehicles in U⁃turn zone under environment of cooperative vehicle infrastructure system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1100-1106. |
| [14] | Zhao⁃wei QU,Zhao⁃tian PAN,Yong⁃heng CHEN,Peng⁃fei TAO,Di SUN. Car⁃following model with improving safety distance based on optimal velocity model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1092-1099. |
| [15] | Lei CHEN,Jiang⁃feng WANG,Yuan⁃li GU,Xue⁃dong YAN. Multi⁃source traffic data fusion algorithm based onmind evolutionary algorithm optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 705-713. |
|
||