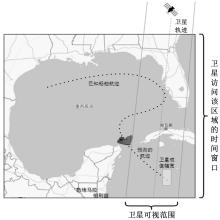
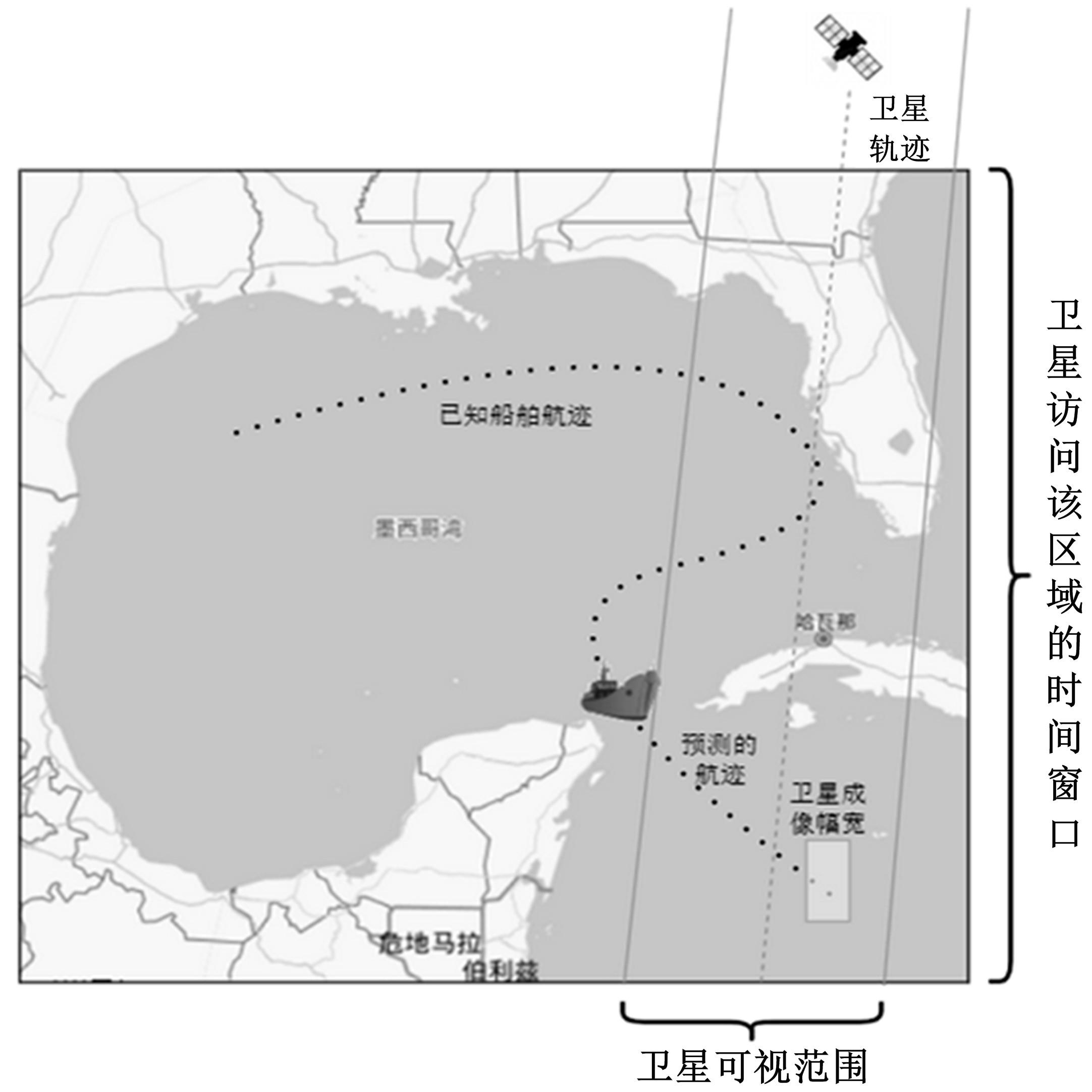
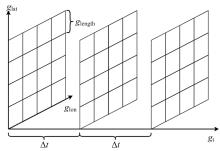
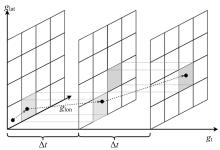
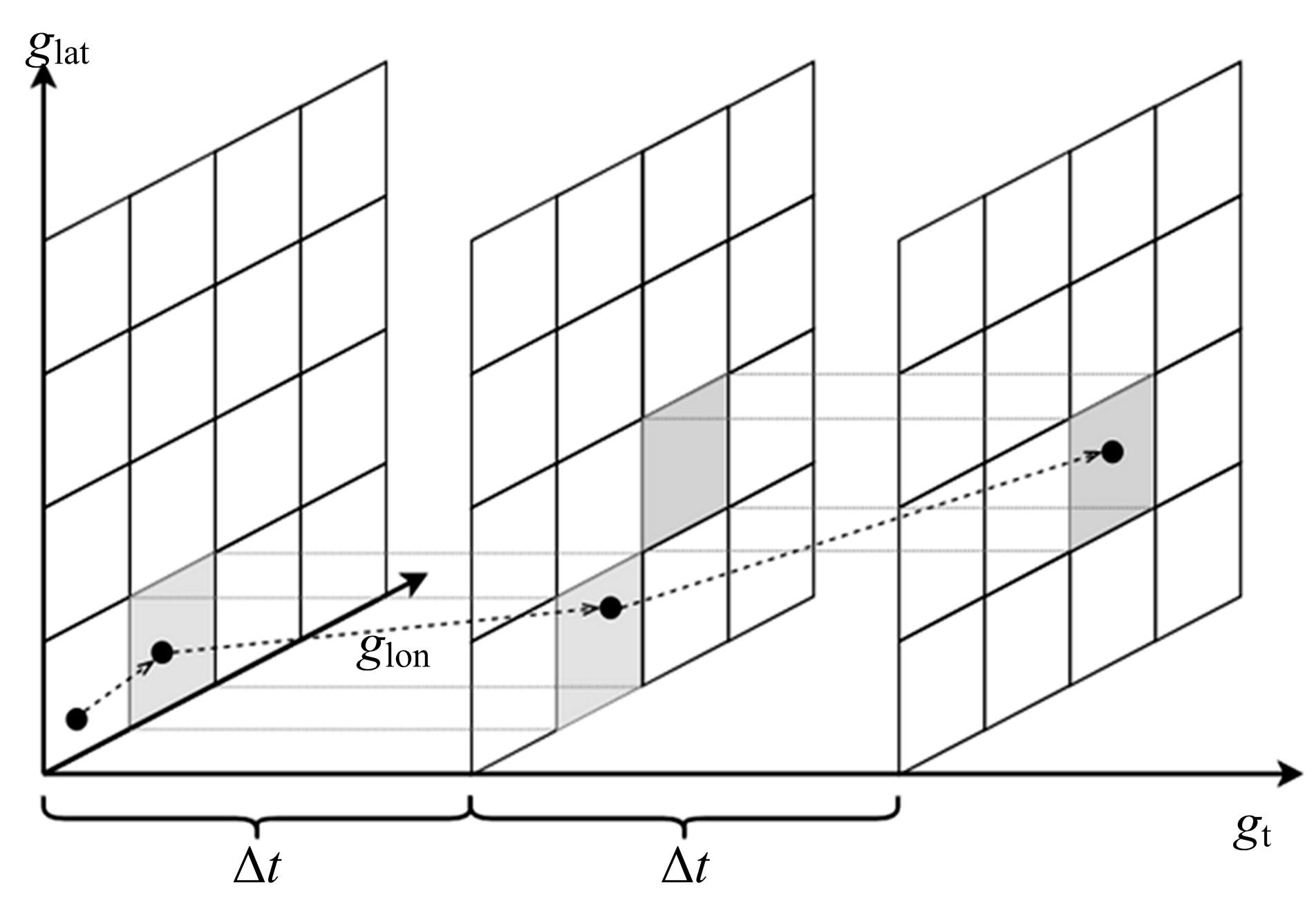
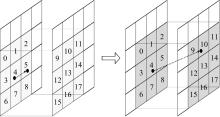
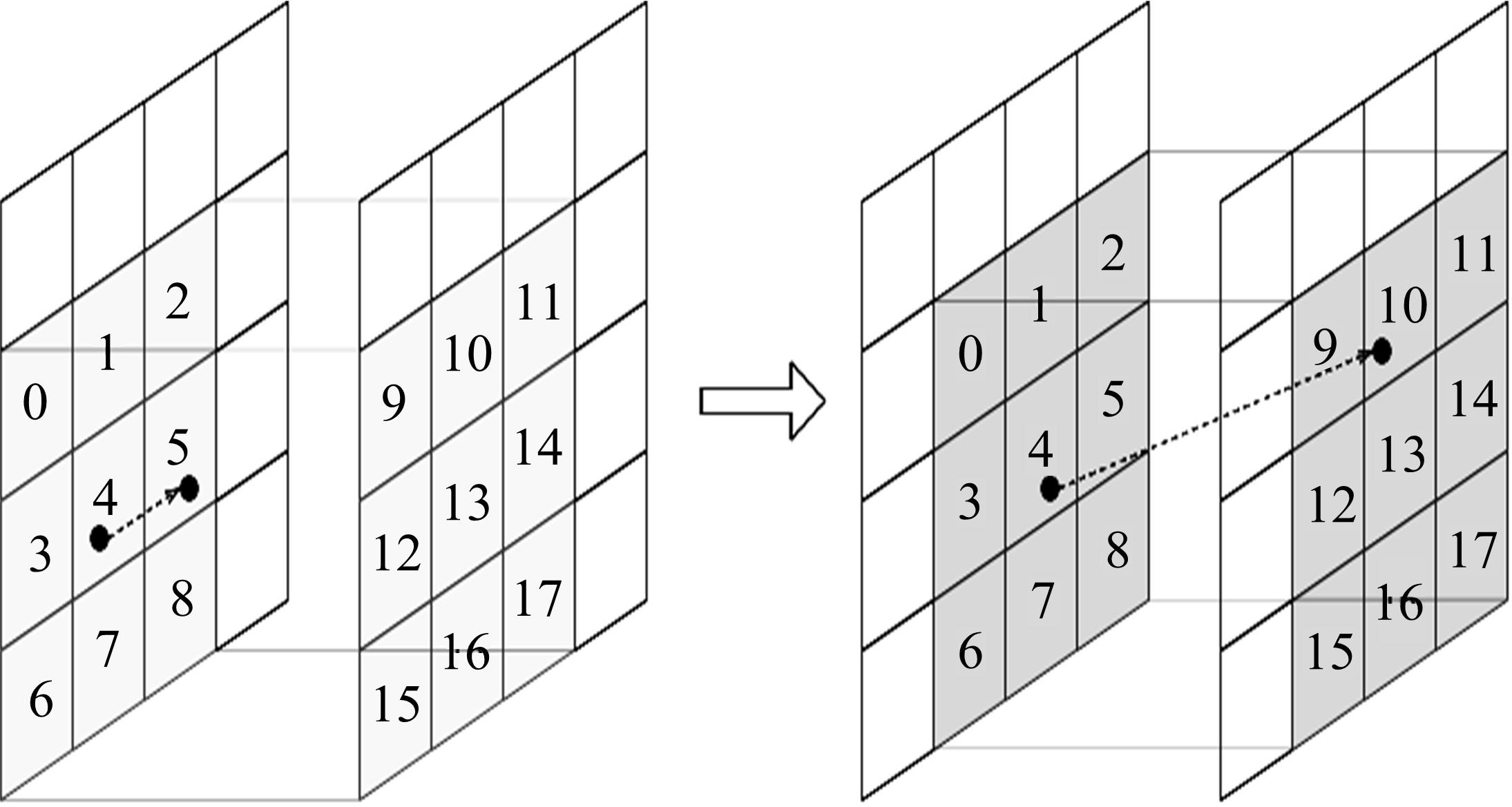
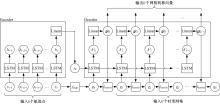
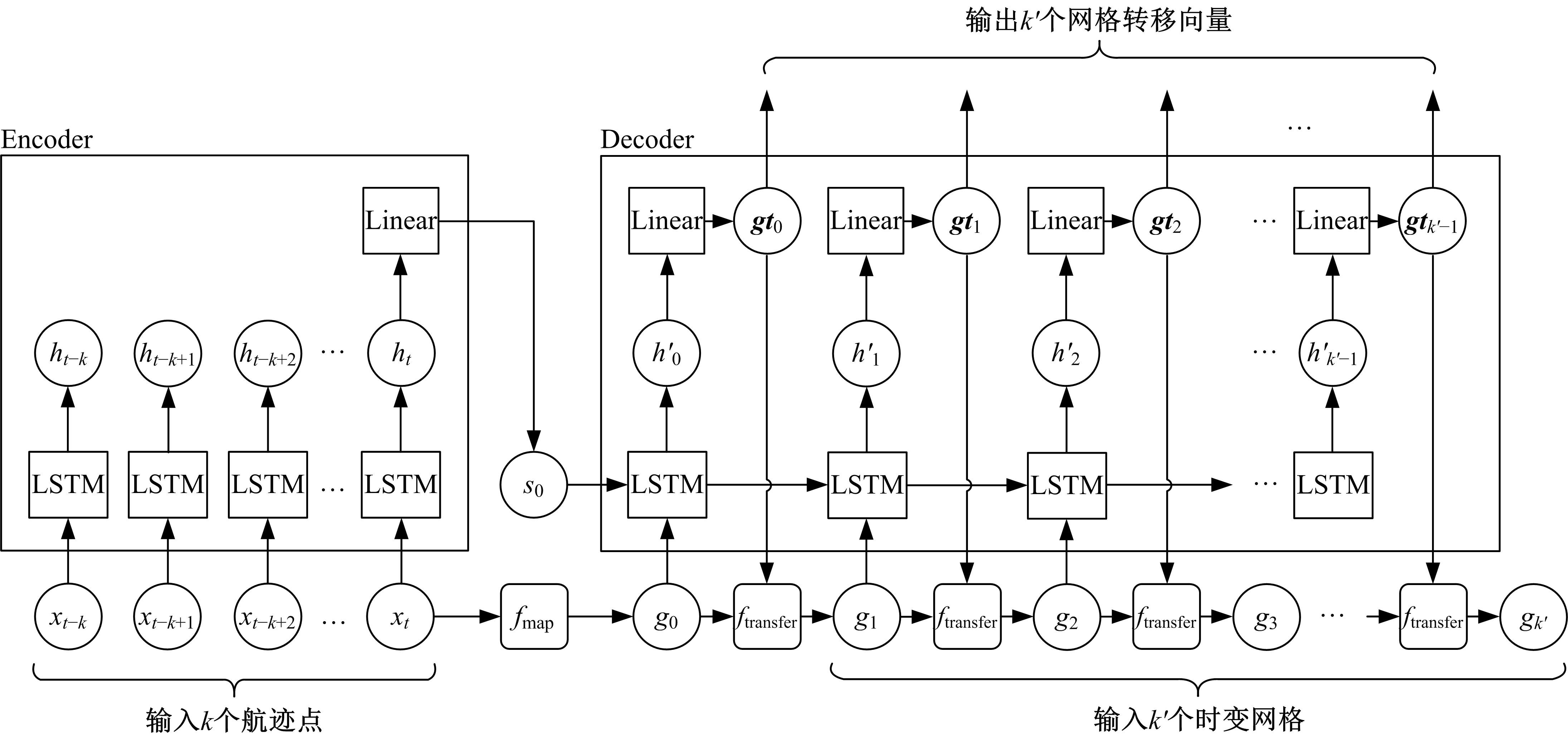
| 1 |
Paul E B, Carmine P, David A B F. Optimal search,location and tracking of surface maritime targets by a constellation of surveillance satellites[R]. Edinburgh:DSTO Information Sciences Laboratory, 2002.
|
| 2 |
王慧林,邱涤珊,马满好,等.基于先验信息的海洋移动目标卫星成像侦测任务规划[J].火力与指挥控制,2011, 36(3): 105-110.
|
|
Wang Hui-lin, Qiu Di-shan, Ma Man-hao, et al. Research on mission-planning of satellite imaging reconnaissance for ocean moving targets based on the prior information[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2011, 36(3): 105-110.
|
| 3 |
陈杰,邢利菊. 面向海洋移动目标成像侦察方法研究[J]. 计算机与数字工程, 2014, 42(3): 395-398.
|
|
Cheng Jie, Xing Li-ju. Imaging reconnaissance method facing ocean motion target[J]. Computer & Digital Engineering, 2014, 42(3): 395-398.
|
| 4 |
梅关林,冉晓旻,范亮,等. 面向移动目标的卫星传感器调度技术研究[J]. 信息工程大学学报, 2016, 17(5): 513-517.
|
|
Mei Guan-lin, Ran Xiao-min, Fan Liang, et al. Research on satellite sensor scheduling technology for moving target[J]. Journal of Information Engineering University, 2016, 17(5): 513-517.
|
| 5 |
Li J F, Geng-xi Y Z, Yao F, et al.Using multiple satellites to search for maritime moving targets based on reinforcement learning[J].Journal of Donghua University(English Edition), 2016, 33(5): 749-754.
|
| 6 |
张海龙,夏维,胡笑旋,等. 面向多障碍物海面卫星搜索动目标方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(10): 2256-2262.
|
|
Zhang Hai-long, Xia Wei, Hu Xiao-xuan, et al. Method for moving targets search by satellites on multi-obstacle sea[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(10): 2256-2262.
|
| 7 |
夏忠,张海龙,靳鹏.基于信息融合的多星搜索动目标问题[J].火力与指挥控制, 2020, 45(7): 20-25, 30.
|
|
Xia Zhong, Zhang Hai-long, Jin Peng. Research on moving target problem of multi-satellite search based on information fusion[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2020, 45(7): 20-25, 30.
|
| 8 |
Qiao S, Shen D, Wang X, et al. A self-adaptive parameter selection trajectory prediction approach via hidden markov models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2015, 16(1):284-296.
|
| 9 |
Rong H, Teixeira A P, Soares C G. Ship trajectory uncertainty prediction based on a Gaussian process model[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 182(15): 499-511.
|
| 10 |
Liang Y, Zhang H. Ship track prediction based on ais data and pso optimized LSTM network[J]. International Core Journal of Engineering, 2020, 6(5): 23-33.
|
| 11 |
胡玉可,夏维,胡笑旋,等.基于循环神经网络的船舶航迹预测[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2020, 42(4): 871-877.
|
|
Hu Yu-ke, Xia Wei, Hu Xiao-xuan, et al. Vessel trajectory prediction based on recurrent neural network[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020,42(4):871-877.
|
| 12 |
Duc-Duy N, Chan L V, Muhammad I A. Vessel trajectory prediction using sequence-to-sequence models over spatial grid[C]∥The 12th ACM International Conference, New Zealand, 2018: 258-261.
|
| 13 |
游兰,韩雪薇,何正伟,等.基于改进Seq2Seq的短时AIS轨迹序列预测模型[J]. 计算机科学, 2020, 47(9): 169-174.
|
|
You Lan, Han Xue-wei, He Zheng-wei, et al. Improved sequence-to-sequence model for short-term vessel trajectory prediction using AIS data streams[J]. Computer Science, 2020, 47(9): 169-174.
|
| 14 |
夏永泉,黄海鹏,王兵,等.一种基于改进的无监督深度学习自编码方法[J]. 科技通报, 2018, 34(7):183-187.
|
|
Xia Yong-quan, Huang Hai-peng, Wang Bing, et al. Self-encoding method based on improved unsupervised deep learning[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2018, 34(7): 183-187.
|
| 15 |
Sutskever I, Vinyals O, Le Q V. Sequence to Sequence Learning with Neural Networks[C/OL]∥[2021-03-15].
|
| 16 |
徐谦,李颖,王刚.基于深度学习图像语义分割的机器人环境感知[J].吉林大学学报:工学版, 2019, 49(1): 248-260.
|
|
Xu Qian, Li Ying, Wang Gang. Robotic environment sensing based on semantic segmentation by deep learning[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(1): 248-260.
|
| 17 |
Sepp Hochreiter, Technische Universität München, Fakultät für Informatik, et al. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735-1780.
|
| 18 |
刘畅. 船舶自动识别系统(AIS)关键技术研究[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学通信与信息系统, 2013.
|
|
Liu Chang. Study of key technology of automatic identification system(AIS)[D].Dalian: Communication and Information Systems, Dalian Maritime University, 2013.
|
| 19 |
伊恩,约书亚,亚伦.深度学习[M].北京: 人民邮电出版社, 2017.
|
| 20 |
赵宏伟,刘晓涵,张媛,等.基于关键点注意力和通道注意力的服装分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020, 50(5): 1765-1770.
|
|
Zhao Hong-wei, Liu Xiao-han, Zhang Yuan, et al. Clothing classification algorithm based on landmark attention and channel attention[J].Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1765-1770.
|
| 21 |
冯荣强,赵磊,杨勇,等.计及电价和Attention机制的LSTM短期负荷预测模型[J].科技通报, 2020, 36(11): 57-62, 68.
|
|
Feng Rong-qiang, Zhao Lei, Yang Yong, et al. LSTM-Short-term load forecasting model considering electricity price and attention mechanism[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2020, 36(11): 57-62, 68.
|