Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (12): 2964-2970.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20211001
Previous Articles Next Articles
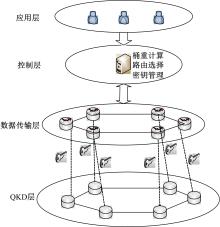
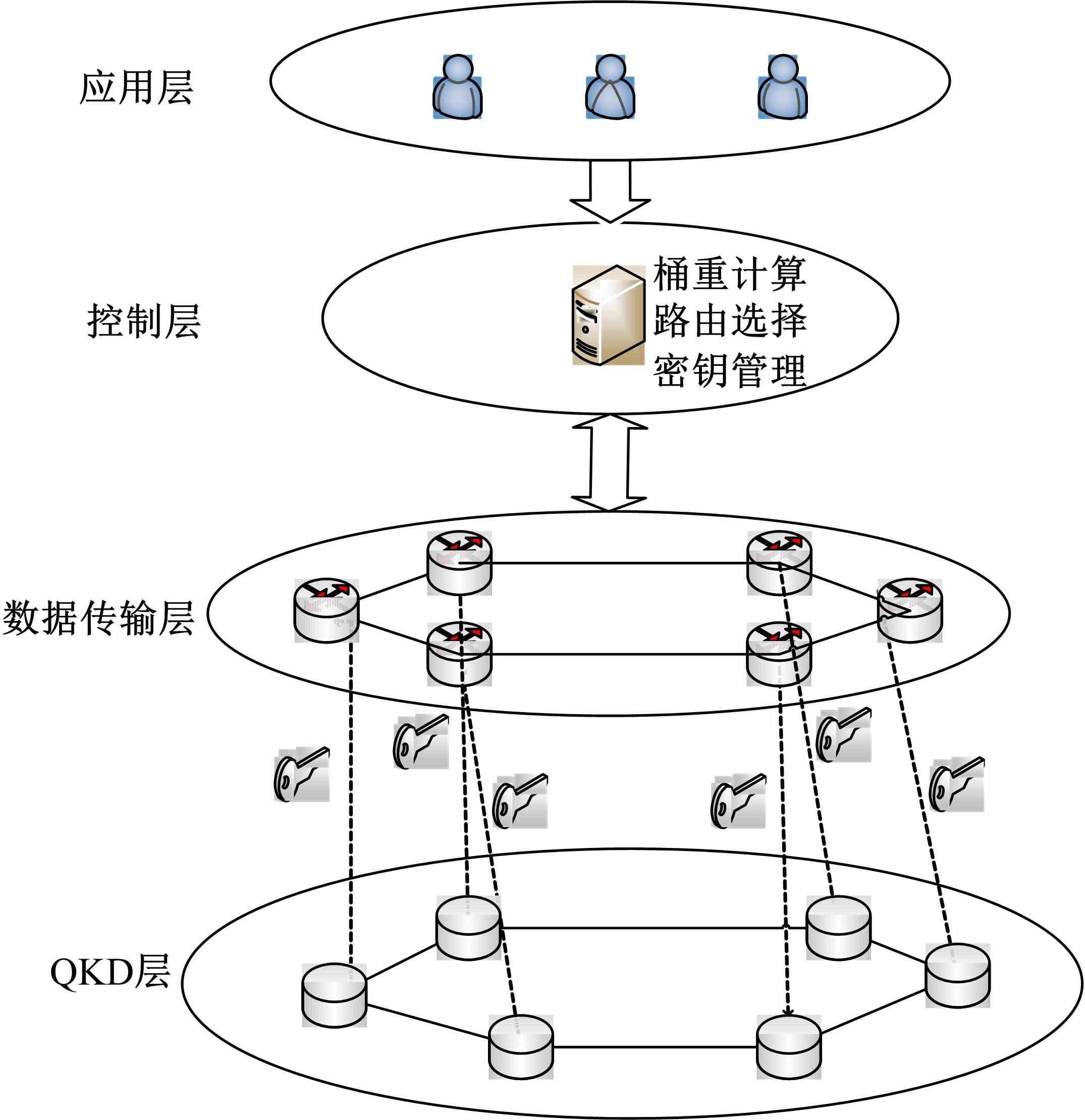
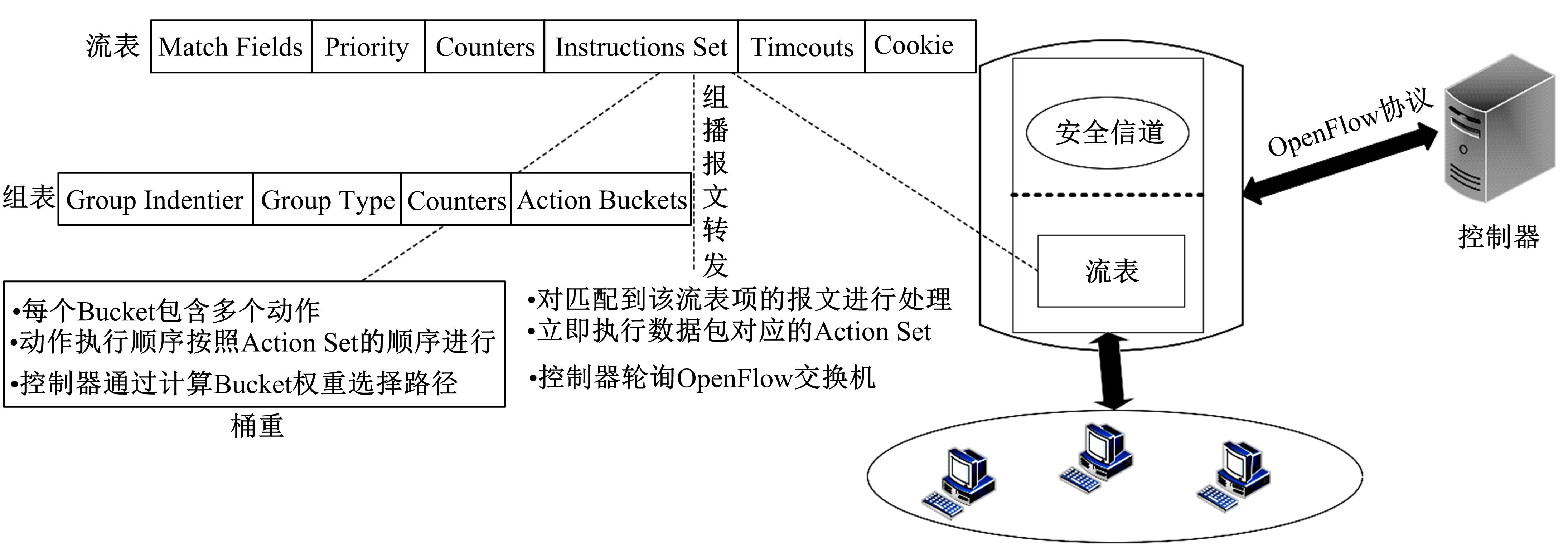
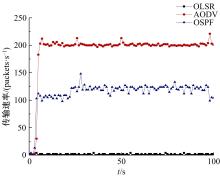
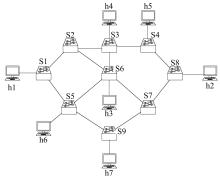
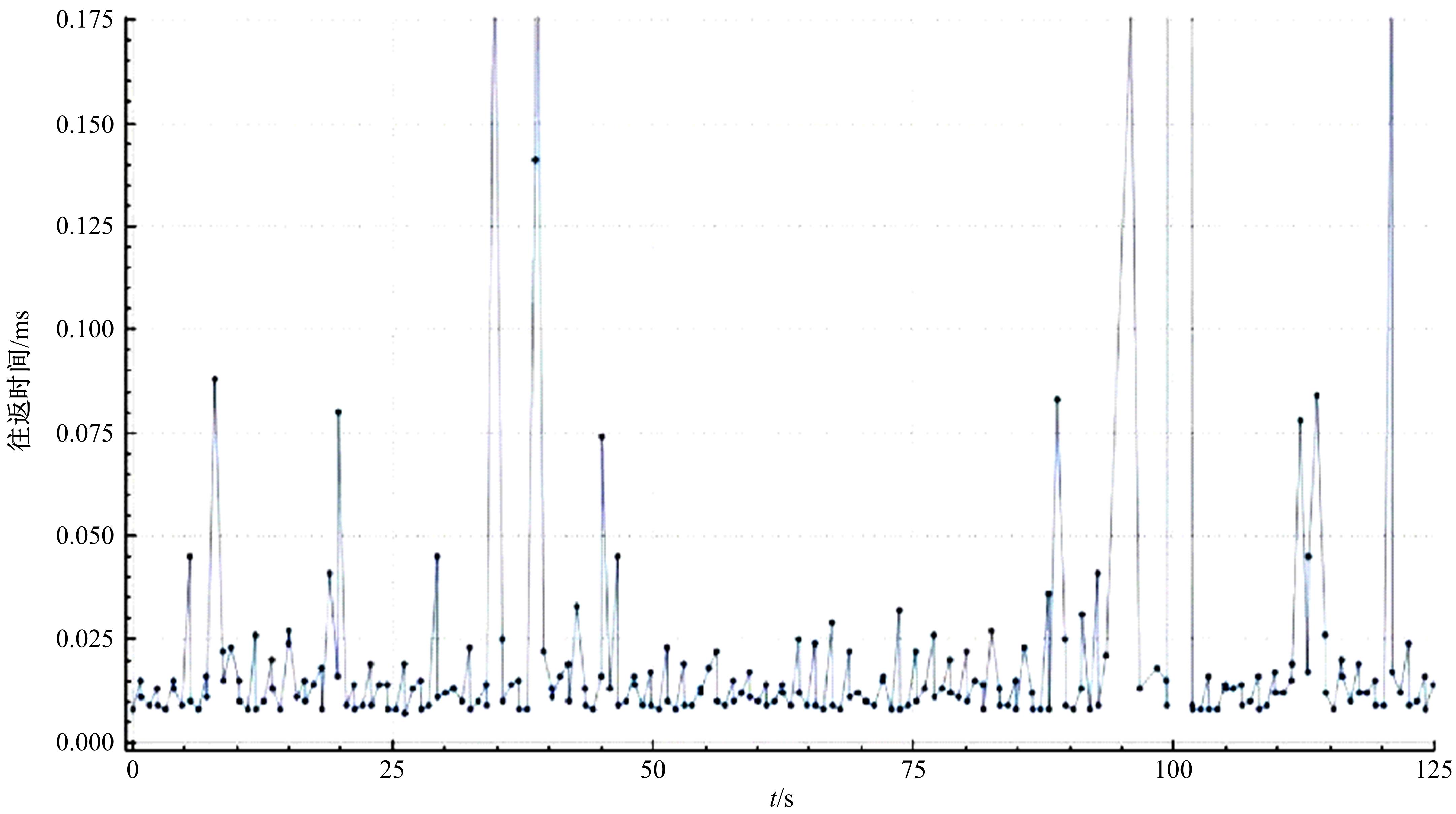
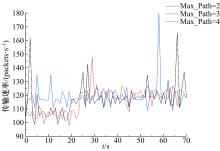
Routing method for quantum key distribution networks based on bucket weight computation
Lin BI1,2( ),Shuo FANG1,2,Xiao-qiang DI2,3
),Shuo FANG1,2,Xiao-qiang DI2,3
- 1.School of Computer Science and Technology,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130012,China
2.Jilin Province Key Laboratory of Network and Information Security,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130012,China
3.Information Center,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130012,China
CLC Number:
- TP393
| 1 | Poppe A, Peev M, Maurhart O. Outline of the SECOQC quantum-key-distribution network in Vienna[J]. International Journal of Quantum Information, 2008, 6(2): 209-218. |
| 2 | Zhang Q, Xu F, Chen Y A, et al. Large scale quantum key distribution: challenges and solutions[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(18): 24260-24273. |
| 3 | Sasaki M, Fujiwara M, Ishizuka H, et al. Field test of quantum key distribution in the tokyo qkd network[J].Optics Express, 2011, 19(11): 10387-10409. |
| 4 | Mehic M, Niemiec M, Rass S, et al. Quantum key distribution: a networking perspective[J]. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 2020; 53(5): 1-41. |
| 5 | Golden B L, DeArmon J S, Baker E K. Computational experiments with algorithms for a class of routing problems[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 1983, 10(1): 47-59. |
| 6 | Peev M, Pacher C, Alléaume R, et al. The SECOQC quantum key distribution network in Vienna[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2009, 11:075001. |
| 7 | 温浩. 量子密钥分配网络的协议和机制[D].合肥: 中国科学技术大学通信学院.2008. |
| Wen H. Protocols and mechanisms in the quantum key distribution networks[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2008. | |
| 8 | 邵凯. 多用户量子通信网络拓扑结构及路由算法研究[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学通信学院.2014. |
| Shao Kai. Research on topology and routing algorithm for multi-user quantum communication network[D]. Xianan: Xidian University. 2014. | |
| 9 | Han Q, Yu L, Zheng W, et al. A novel QKD network routing algorithm based on optical-path-switching[J]. Journal of Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, 2014, 5(1):13-19. |
| 10 | Jo E, Pan D, Liu J, et al. A simulation and emulation study of SDN-based multipath routing for fat-tree data center networks[J]. Proceedings Winter Simulation Conference, 2014: 3072-3083 |
| 11 | Mehic M, Fazio P, Rass S, et al. A novel approach to quality of service provisioning in trusted relay quantum key distribution networks[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2018(1): 168-181. |
| 12 | Cao Y, Zhao Y, Wang J, et al. Cost-efficient quantum key distribution (QKD) over WDM networks[J]. Journal of Optical Communications and Networking, 2019, 11(6): 285-298. |
| 13 | Leone H, Miller N R, Singh D, et al. QuNet: Cost vector analysis & multi-path entanglement routing in quantum networks[J]. arXiv: 2105.00418 |
| 14 | Amin R, Reisslein M, Shah N. Hybrid SDN networks: A survey of existing approaches[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(4): 3259-3306. |
| 15 | Wang Hua, Zhao Yong-li, Avishek Nag. Quantum-key-distribution (QKD) networks enabled by software-defined networks (SDN)[J]. Applied Sciences,2019, 9(10): 2081-2082. |
| 16 | Dong Kai, Zhao Yong-li, Yang Tian-cheng,et al. Tree-topology-based quantum-key-relay strategy for secure multicast services[J]. Journal of Optical Communications and Networking, 2020, 12(5): 120-132. |
| [1] | Jun SHEN,Xiao ZHOU,Zu-qin JI. Implementation of service dynamic extended network and its node system model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 2058-2068. |
| [2] | HAN Jia-wei, LIU Yan-heng, SUN Xin, SONG Li-jun. Identity-based encryption scheme based on cloud and quantum keys [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 551-557. |
| [3] | WU Jia-nan, WANG Shi-gang, WANG Xin-cheng, WEI Rong-kai, LIU Gui-xia. Influence of fiber channel stress on quantum key distribution bit error rate [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1612-1616. |
| [4] | HAN Jia-wei, LIU Yan-heng, SUN Xin, SONG Li-jun. Quantum key management algorithm based on sliding window [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 535-541. |
| [5] | CHENG Fang, TAO Hui, ZHANG Zhi-zhong, PEI Er-rong. Low delay algorithm for DTN networks based on packet exchange [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 392-395. |
|