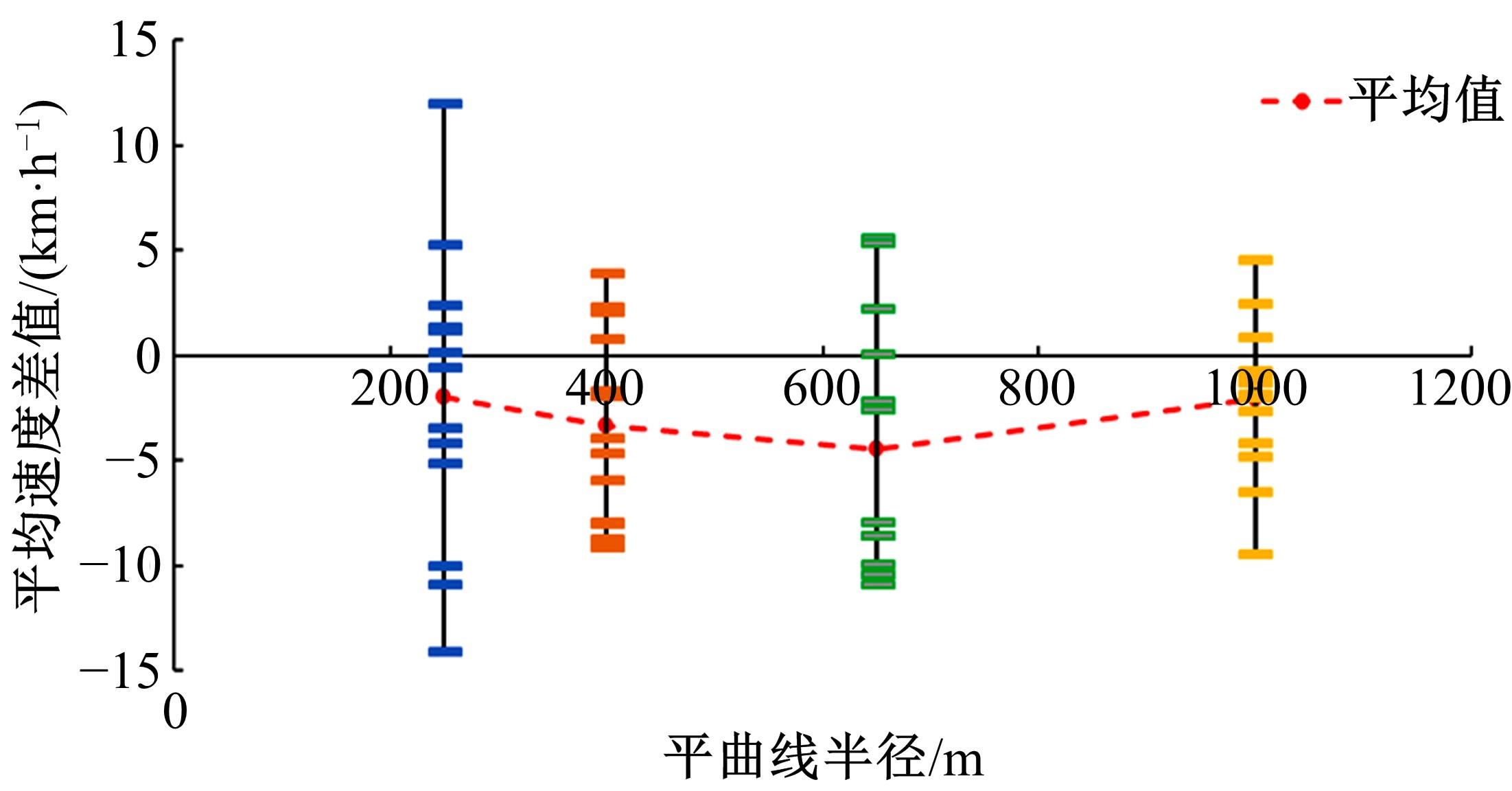
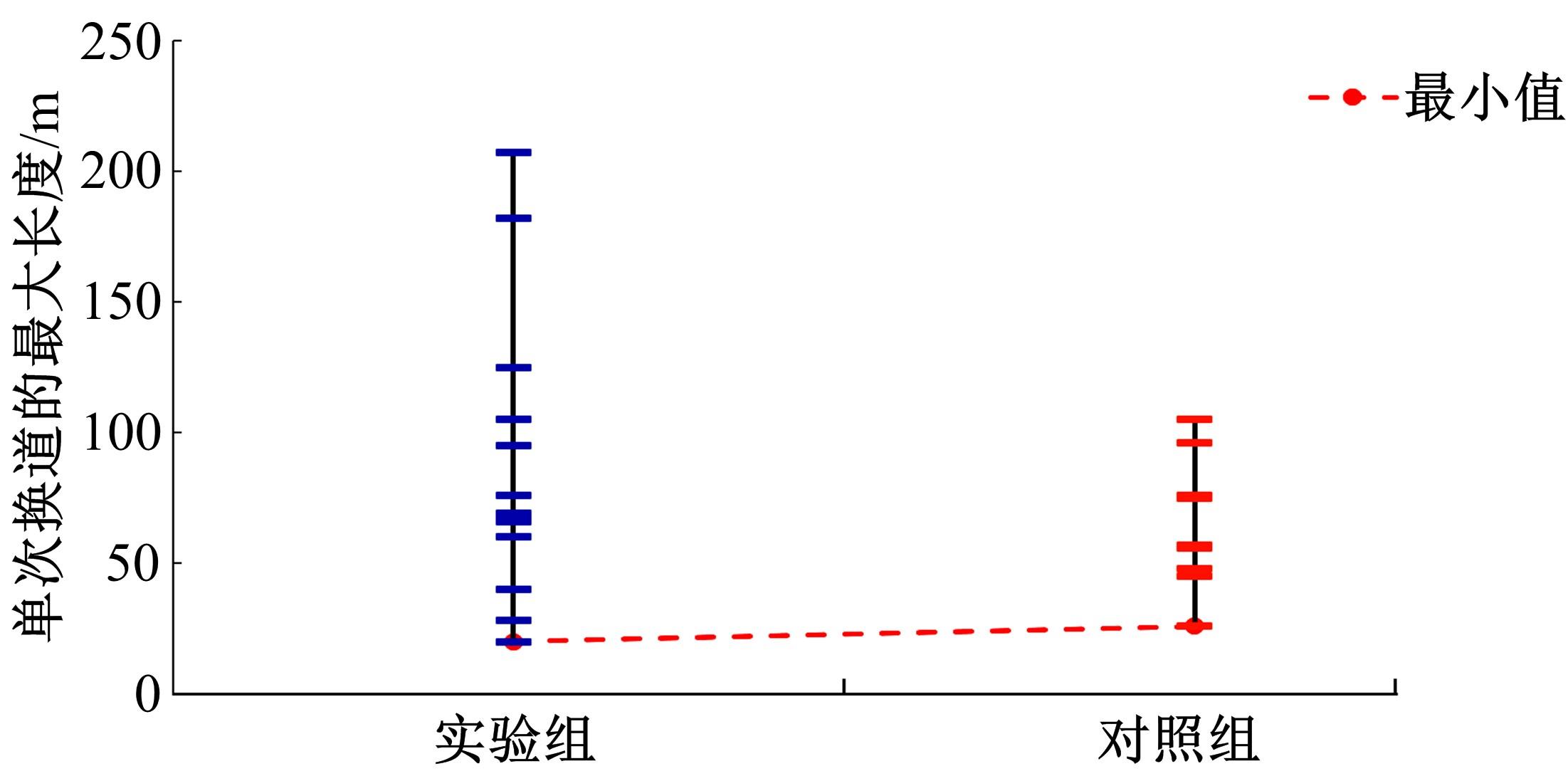
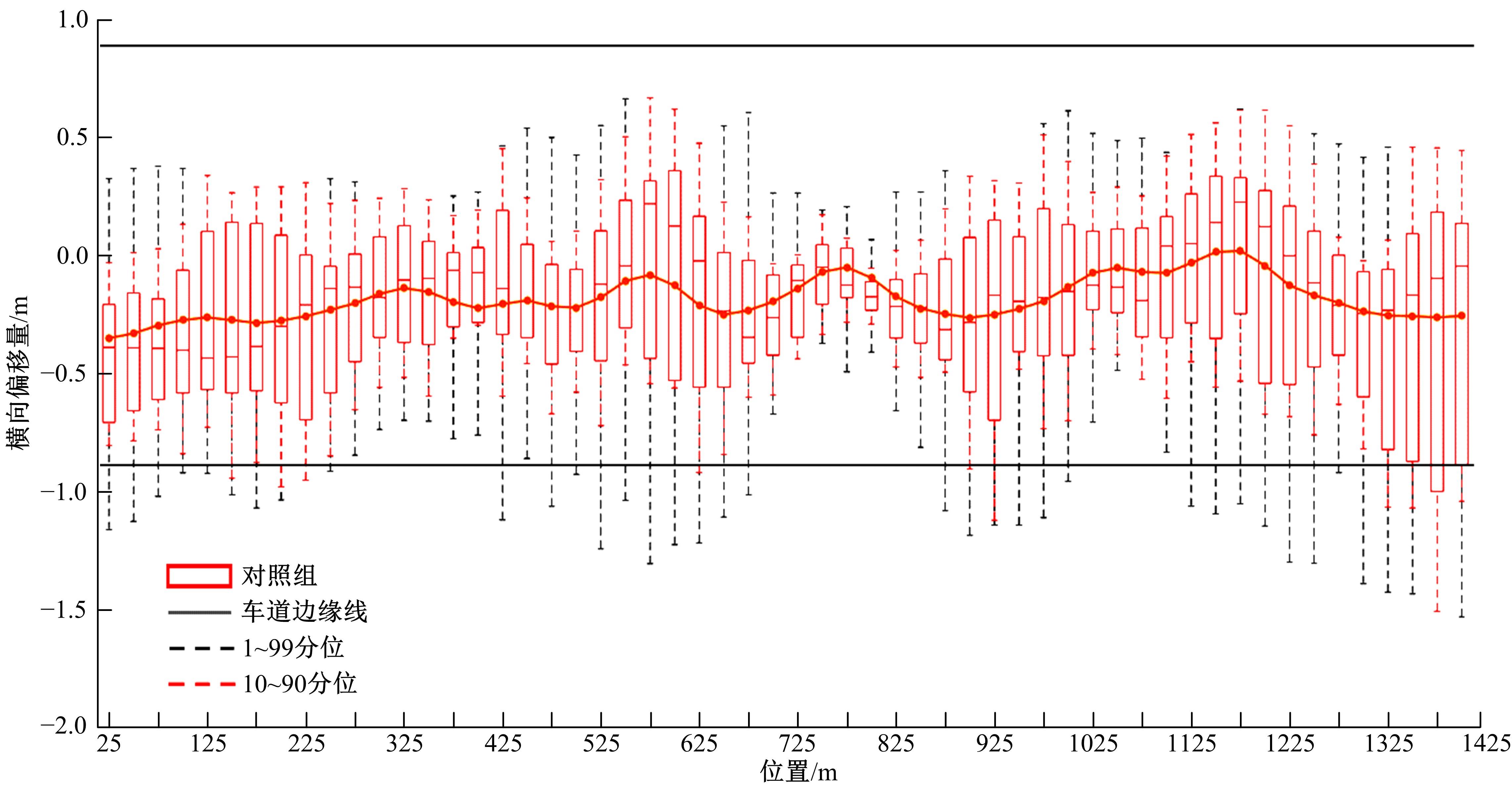
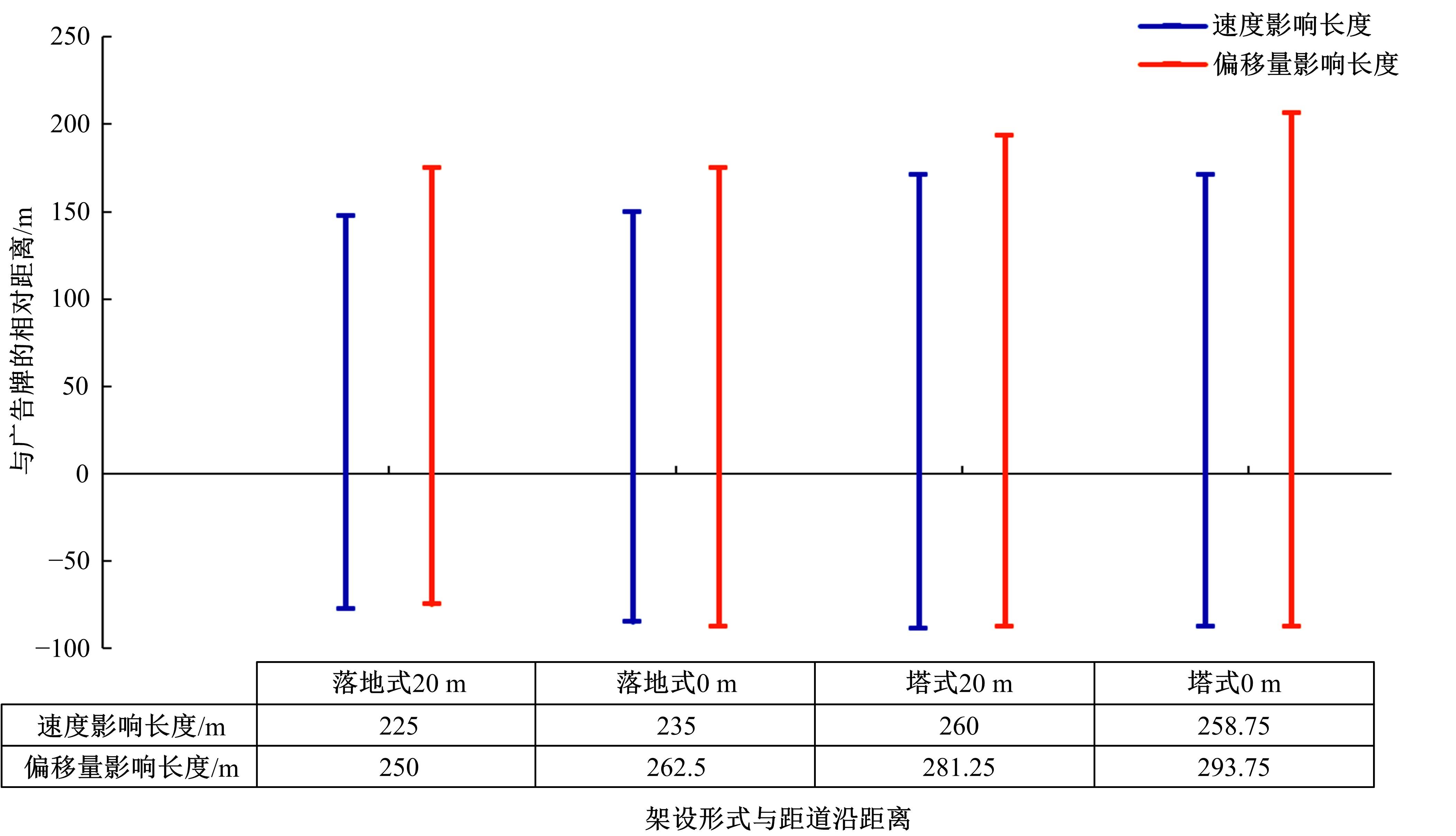
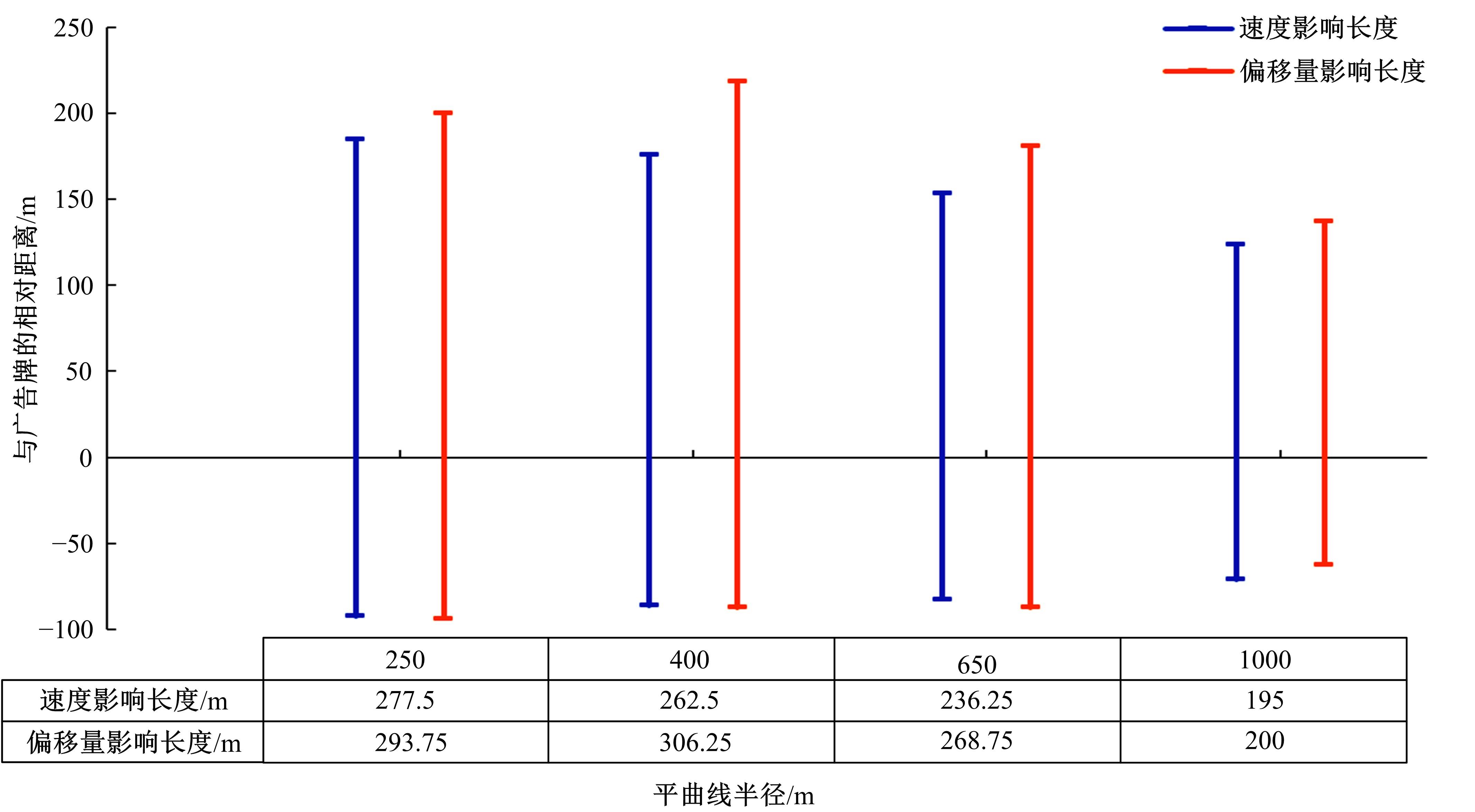
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (5): 1345-1354.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20210927
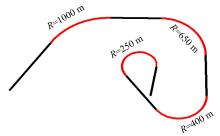
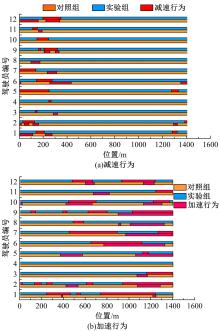
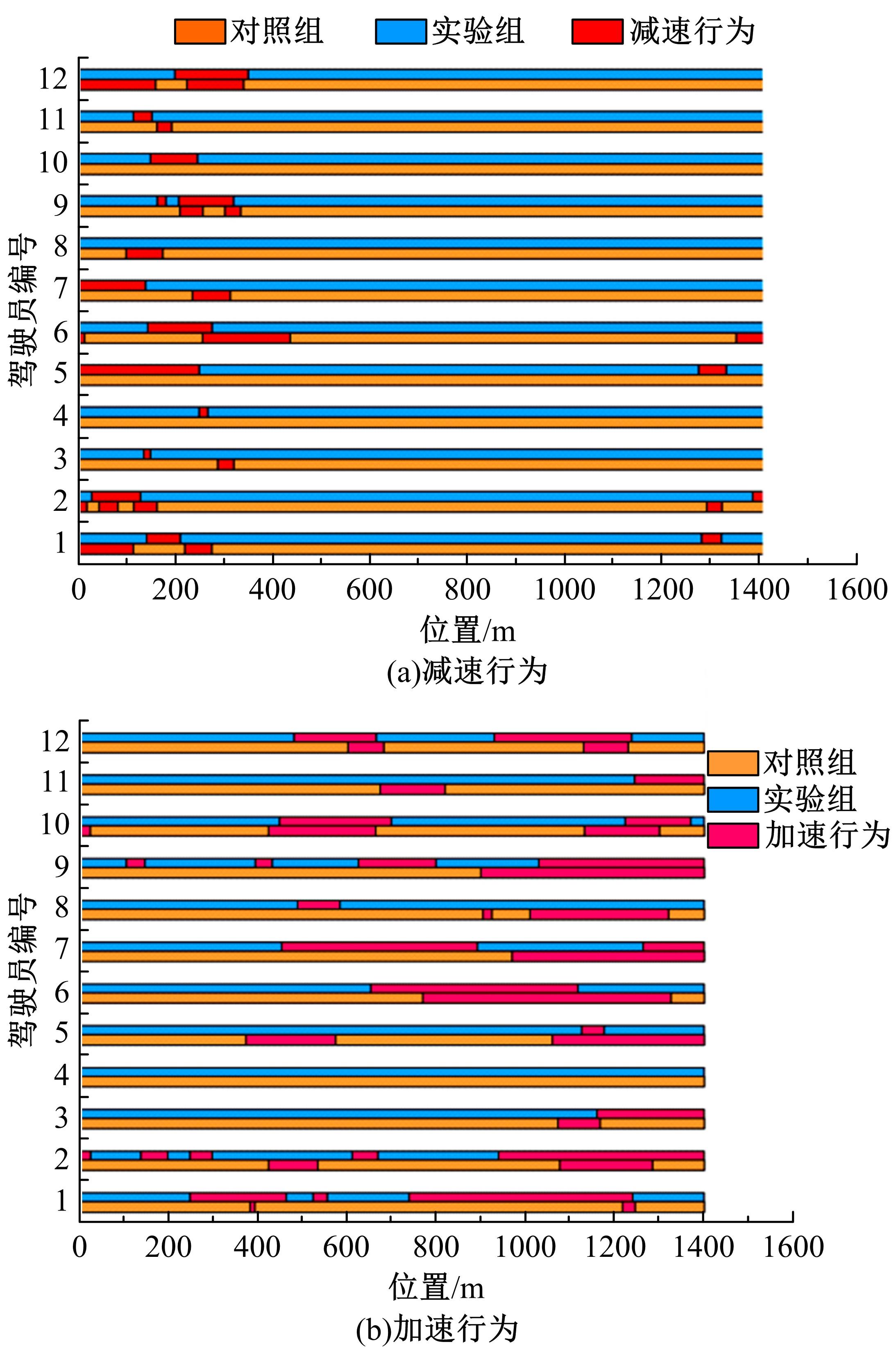
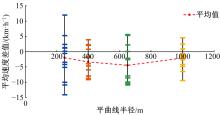
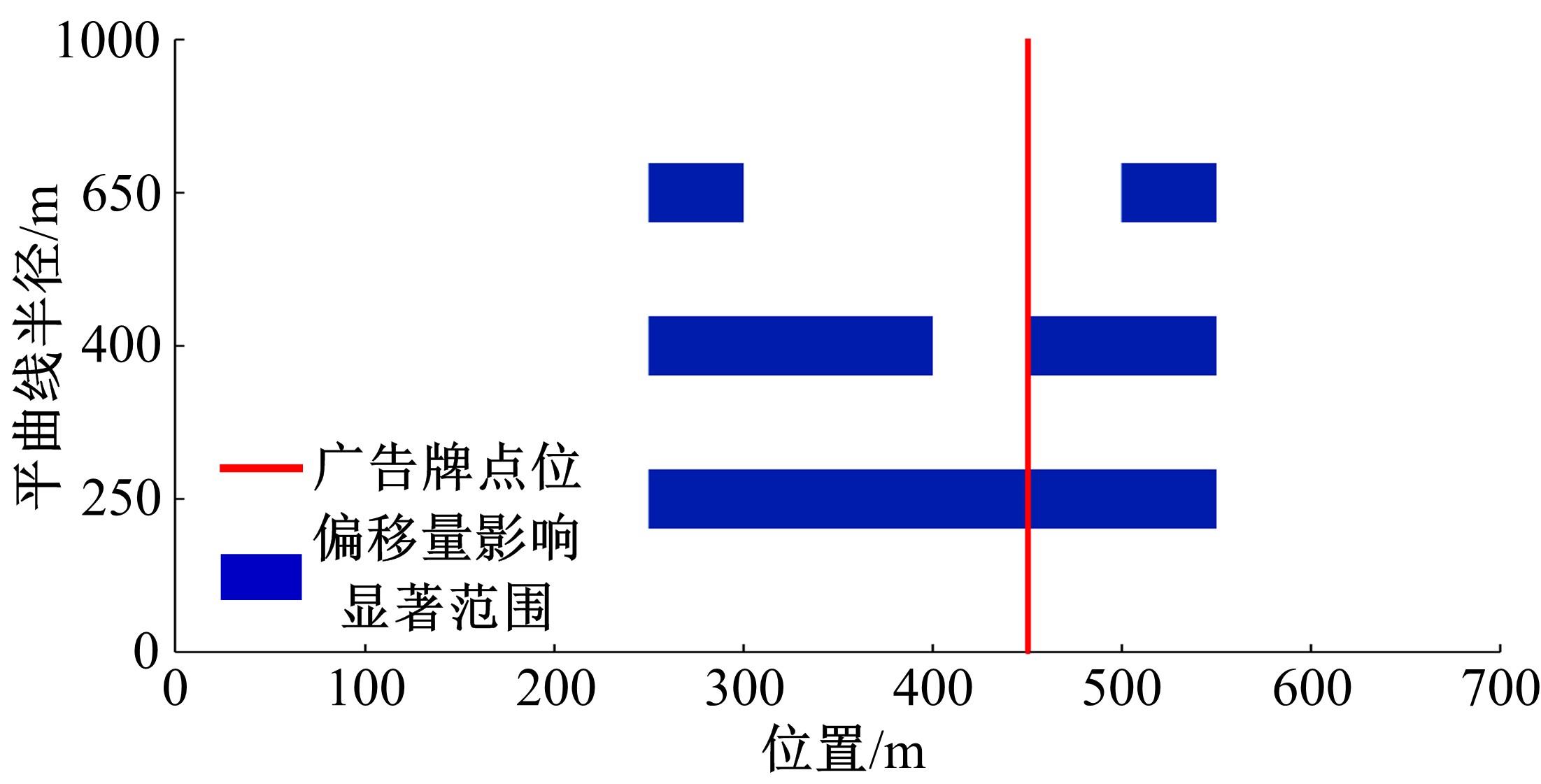
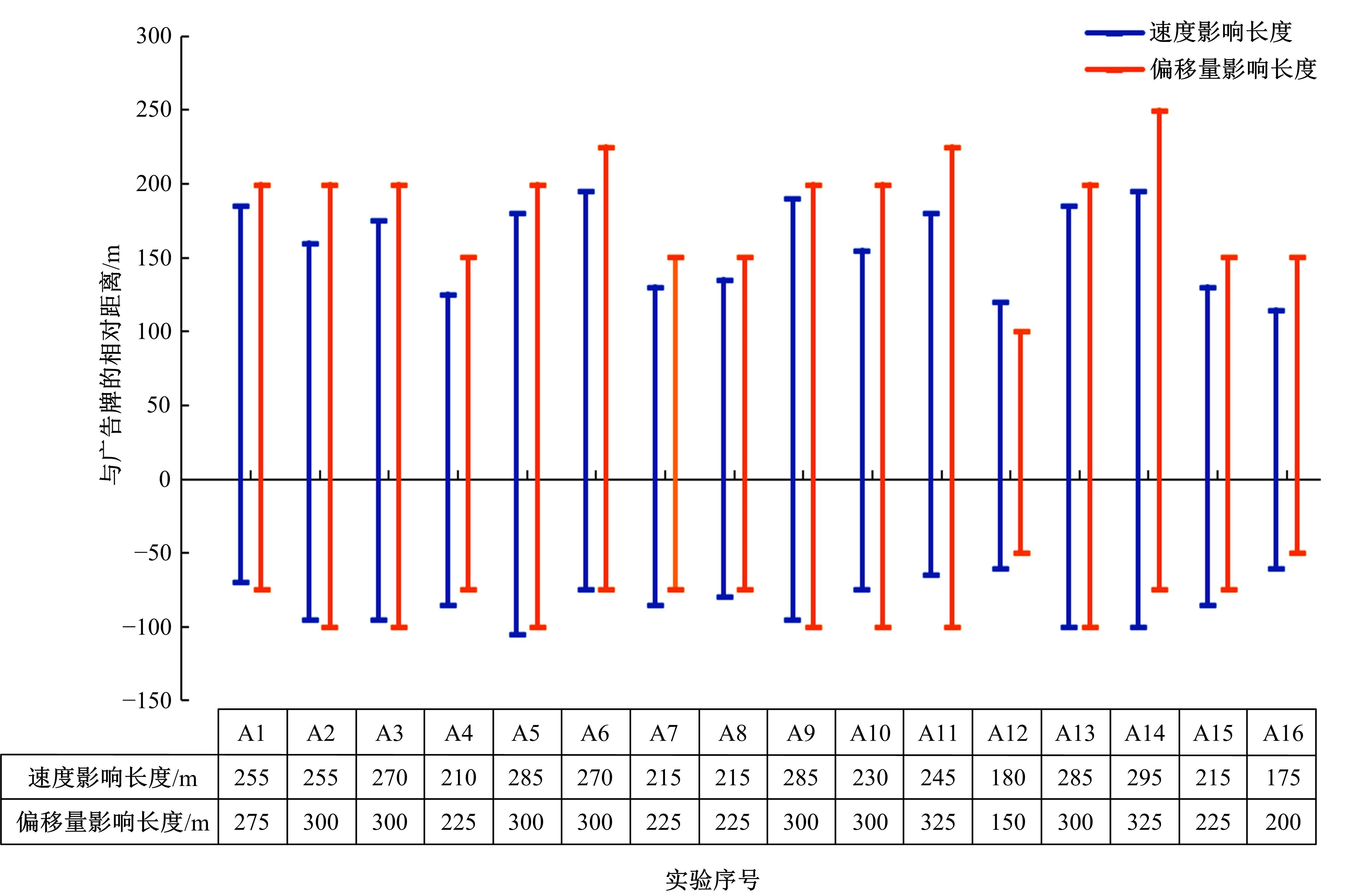
Analysis on driving behaviors on flat curved sections of highways with advertising signs
Can-can SONG1( ),Di-fei JING2,Jun-feng XIE3,Ke-xin KANG4
),Di-fei JING2,Jun-feng XIE3,Ke-xin KANG4
- 1.School of Civil Engineering,Shanghai Normal University,Shanghai 201418,China
2.The Key Laboratory of Road and Traffic Engineering,Ministry of Education,Tongji University Shanghai 201804,China
3.Chongqing Zhilang Consulting Co. ,Ltd. ,Chongqing 400014,China
4.Guizhou Transportation Planning,Survey,Design and Research Institute Co. ,Ltd. ,Guiyang 550009,China
CLC Number:
- U491
| 1 | Andreassen D C. Traffic accidents and advertising signs[J]. Australian Road Research, 1985, 15(2): 103-105. |
| 2 | Ady R W. An investigation of the relationship between illuminated advertising signs and expressway accidents[J]. Traffic Safety Research Review, 1967, 11(3): 9-11. |
| 3 | Young M, Mahfoud J, Stanton N, et al. Conflicts of interest: the implications of roadside advertising for driver attention[J]. Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 2009, 12(5): 381-388. |
| 4 | Divekar G, Pradhan A, Pollatsek A, et al. Effect of external distractions: behavior and vehicle control of novice and experienced drivers evaluated[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2012, 2321(1): 15-22. |
| 5 | Hudák M, Madleňák R. The research of driver distraction by visual smog on selected road stretch in slovakia[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2017, 178: 472-479. |
| 6 | 王红.基于眼动仪的高速公路广告牌对安全驾驶影响的研究[D].西安: 长安大学汽车学院, 2007. |
| Wang Hong. Research on the influence of advertising signs on driving safety on freeways based on eye tracker[D]. Xi'an: School of Automobile, Chang'an University, 2007. | |
| 7 | 冯忠祥, 刘静, 杜姗姗.高速公路广告牌对驾驶员视觉影响研究[J].公路交通科技, 2009, 26(3): 144-147. |
| Feng Zhong-xiang, Liu Jing, Du Shan-shan. Research on influence of advertisements on drivers' vision in expressway[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2009, 26(3): 144-147. | |
| 8 | 罗青山.高速公路广告牌背景色彩对驾驶员注视特性的影响分析[J].公路交通技术, 2016(5): 124-126. |
| Luo Qing-shan. Analysis to influence by background color of ads plates on highway to fixation characteristics of drivers[J]. Technology of Highway and Transport, 2016(5): 124-126. | |
| 9 | 李智强, 高颖, 万冲.高速公路广告牌距指示牌距离对驾驶员的影响分析[J].交通标准化, 2013(15): 11-13. |
| Li Zhi-qiang, Gao Ying, Wan Chong. Influence of distance between expressway billboard and indication board on driver[J]. Transportation Standardization, 2013(15): 11-13. | |
| 10 | 沈一川. 高速公路广告牌对夜间驾驶视觉影响[J]. 交通世界, 2014(1): 130-131. |
| Shen Yi-chuan. The impacts of highway billboards on night visual while driving[J]. Transpo World, 2014(1): 130-131. | |
| 11 | 潘晓东, 詹嘉, 王富贵.山区公路小半径曲线加宽及安全设计研究[J].公路工程, 2007, 32(6): 4-6, 29. |
| Pan Xiao-dong, Zhen Jia, Wang Fu-gui. Research of curve widen and safe design for mountainous highway with small radius[J]. Highway Engineering, 2007, 32(6): 4-6, 29. | |
| 12 | 荆迪菲, 宋灿灿, 郭忠印, 等.高密度路网区高速公路可变信息标志版面要素组合[J].同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2021, 49(6): 853-862. |
| Jing Di-fei, Song Can-can, Guo Zhong-yin, et al. Layout elements combination optimization of variable message signs for expressways in high-density road network areas[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2021, 49(6): 853-862. | |
| 13 | 张姝玮, 郭忠印, 杨轸, 等.驾驶行为多重分形特征在驾驶疲劳检测中的应用[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(2): 557-564. |
| Zhang Wei-shu, Guo Zhong-yin, Yang Zhen, et al. Application of multi-fractal features of driving performance in driver fatigue detection[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 557-564. | |
| 14 | 李林波, 李杨, 邹亚杰.基于时依等比例风险回归模型的换道时长影响因素[J].同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2021, 49(7): 933-940. |
| Li Lin-bo, Li Yang, Zou Ya-jie. Factors affecting lane-changing duration based on time-dependent proportional-hazards regression model[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2021, 49(7): 933-940. | |
| 15 | 孙倩, 郭忠印.基于长短期记忆神经网络方法的车辆跟驰模型[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(4): 1380-1386. |
| Sun Qian, Guo Zhong-yin. Vehicle following model based on long short-term memory neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(4): 1380-1386. | |
| 16 | Wallace B. Driver distraction by advertising: genuine risk or urban myth?[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Municipal Engineer, 2003, 156(3): 185-190. |
| [1] | Jin LI,Yu-tong SUN,Xiao-zhong WEI,Yu-ling JIAO. Design of bus priority signal considering flexible lane setting [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 448-456. |
| [2] | Shao-bo JI,Yang LI,Meng LI,Shi-bin SU,Xiao-long MA,Shao-qing HE,Guo-rui JIA,Yong CHENG. Influence of driving behavior on energy consumption of pure electric shared vehicles [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(4): 754-763. |
| [3] | Jin XU,Cun-shu PAN,Jing-hou FU,Jun LIU,Dan-qi WANG. Speed behavior characteristic on typical driving scenarios and along switched scenarios [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1331-1341. |
| [4] | Ping WAN,Chao-zhong WU,Xiao-feng MA. Discriminating threshold of driving anger intensity based on driving behavior features by ROC curve analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 121-131. |
| [5] | Liang JIANG,Yi HE. Risky driving behavior and influencing factors analysis for electric two⁃wheeler [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1107-1113. |
| [6] | XU Hong-feng, GAO Shuang-shuang, ZHENG Qi-ming, ZHANG Kun. Hybrid dynamic lane operation at signalized intersection [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 430-439. |
| [7] | WAN Ping, WU Chao-zhong, LIN Ying-zi, MA Xiao-feng. Driving anger detection based on multivariate time series features of driving behavior [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1426-1435. |
| [8] | WANG Hai-wei, WEN Hui-ying, LIU Min. Experimental evaluation of nighttime driver's physiological characteristics in driving simulator [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 420-428. |
| [9] | GUO Ying-shi, FU Rui, ZHAO Kai, MA Yong, YUAN Wei. Evaluation and test of real-time identification models of driver's lane change intention [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 1836-1844. |
| [10] | JIANG Gui-yan, LIU Bin, SUI Xiao-yan, MA Ming-fang. Real time information collection of passenger flow in public transportation based on bus IC card charging system [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1076-1082. |
| [11] | LI Shi-wu, XU Yi, SUN Wen-cai, WANG Lin-hong, GUO Meng-zhu, CHAI Meng. Pupil diameter based construction conflict self-feedback discrimination method [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 418-425. |
| [12] | ZHAO Shu-zhi, LIANG Shi-dong, MA Ming-hui, LIU Hua-sheng, ZHU Yong-gang. Real-time queue length estimation at signalized intersection [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 85-91. |
| [13] | ZHANG Bo, WANG Wen-jun, WEE Minkooc, CHENG Bo. Detection handheld phone use by driver based on machine vision [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1688-1695. |
| [14] | WANG Zhe, YANG Bai-ting, LIU Xin, LIU Qun, SONG Xian-min. Discriminant analysis of driving decisions based on fuzzy clustering [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1414-1419. |
| [15] | ZHU Jin-cheng, XIAO Feng, SHUAI Bin, LIU Xiao-bo. Impact and feasibility of charging taxis in pricing zone [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(1): 89-96. |
|
||