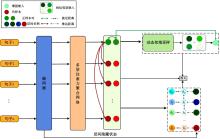
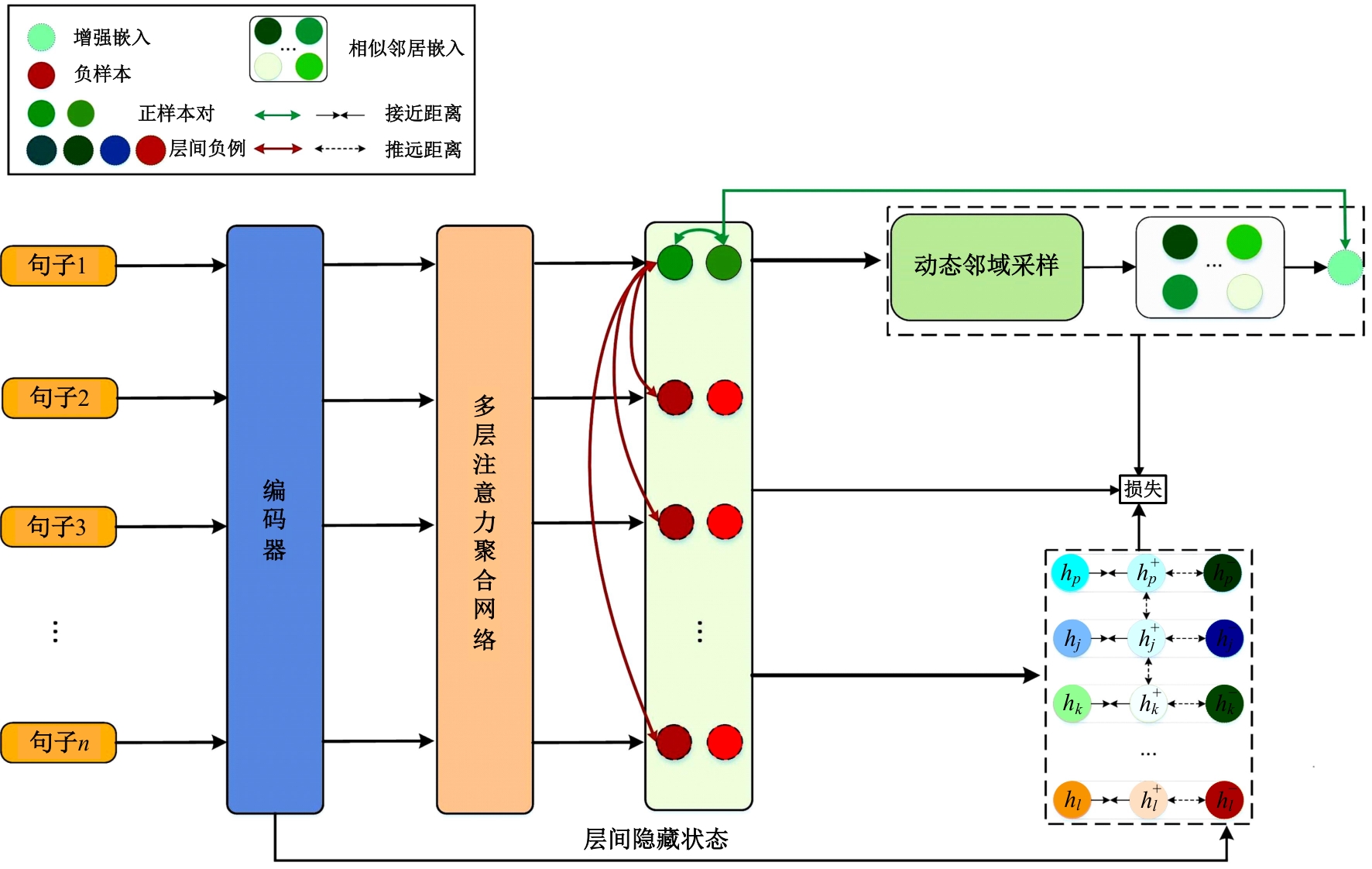
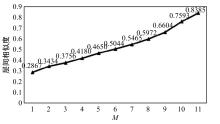
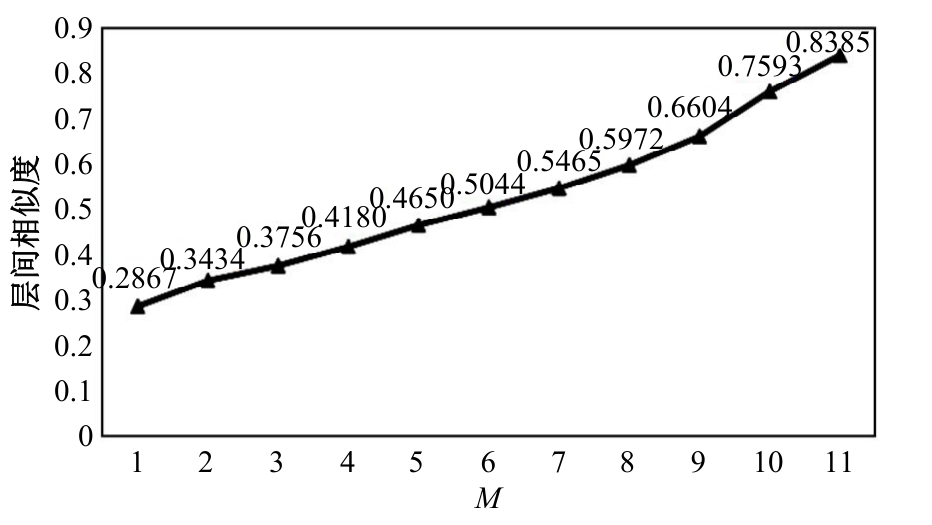
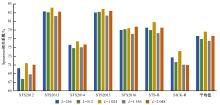
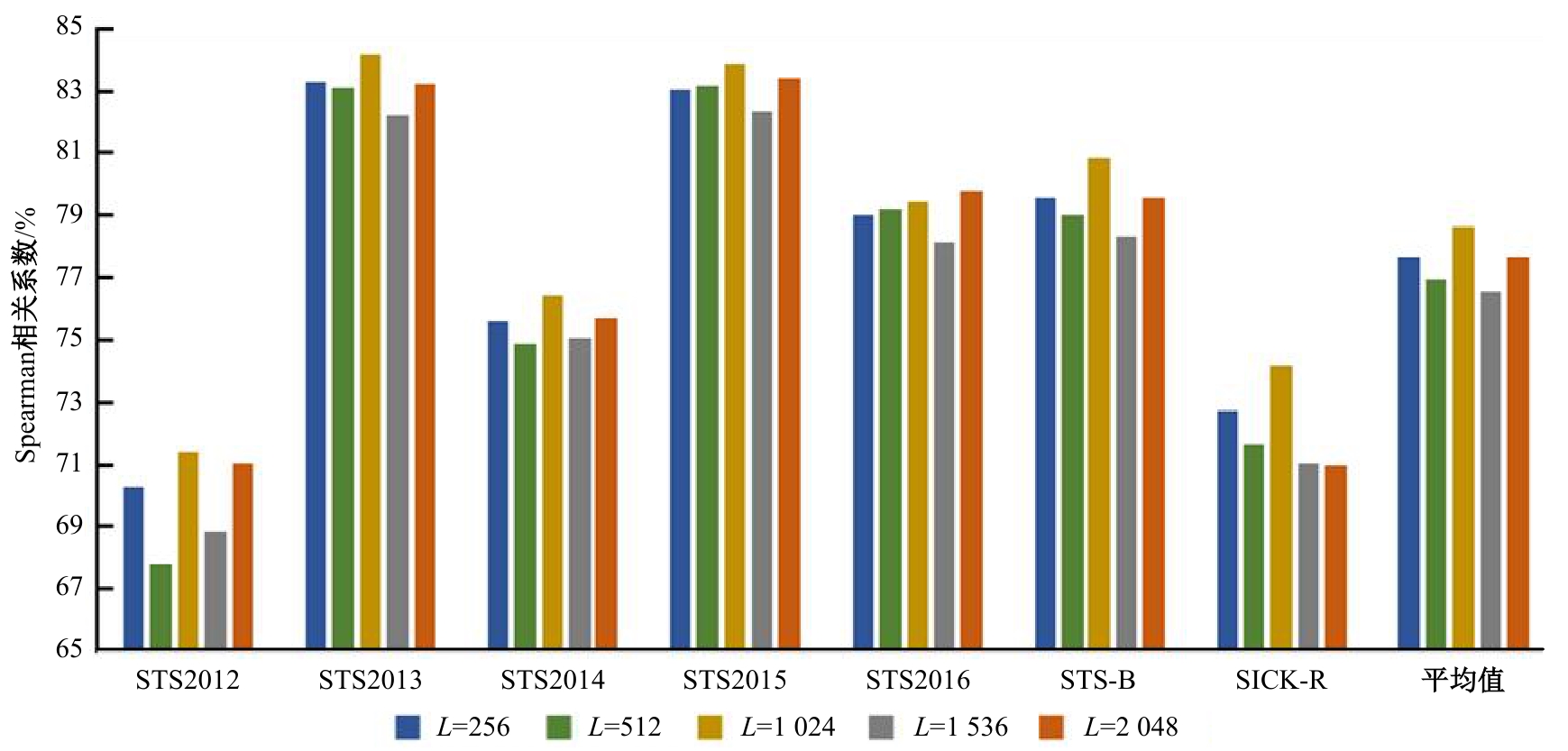
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (11): 3705-3714.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240237
Semantic similarity model based on augmented positives and interlayer negatives
Xiao-Dong CAI( ),Ye-yang HUANG,Li-fang DONG
),Ye-yang HUANG,Li-fang DONG
- School of Information and Communication,Guilin University of Electronic Technology,Guilin 541004,China
CLC Number:
- TP391.1
| [1] | Cer D, Diab M, Agirre E, et al. SemEval-2017 task 1: semantic textual similarity multilingual and crosslingual focused evaluation[C]∥Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2017: 1-14. |
| [2] | Radford A, Narasimhar K. Improving language understanding by GenerativePre-Training[EB/OL].(2018-06-11)[2023-12-11].. |
| [3] | Devlin J, Chang M W, Lee K, et al. BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[C] ∥Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2019: 4171-4186. |
| [4] | Liu Y H, Ott M, Goyal N, et al. RoBERTa: a robustly optimized BERT pretrainingapproach[EB/OL]. (2019-07-26)[2023-12-11].. |
| [5] | Yang Z L, Dai Z H, Yang Y M, et al. XLNet: generalized autogressive pretraining for language understanding[C] ∥Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: NeurIPS, 2019: 5753-5763. |
| [6] | Li B H, Zhou H, et al. On the sentenceembeddings from pre-trained language models[C]∥Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2020:9119-9130. |
| [7] | Reimers N, Gureuych, I. Sentence-BERT: sentence embeddings using siamese BERT-networks[C]∥Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2019: 3982-3992. |
| [8] | Gao T Y, Yao X C, Chen D Q. SimCSE: simple contrastive learning of sentence embeddings[C]∥Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2021: 6894-6910. |
| [9] | Wu X, Gao C C, Zang L J, et al. ESimCSE: enhanced sample building method for contrastive learning of unsupervised sentence embedding[C]∥Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Computational Linguistics. New York: ACM Press,2022:3898-3907. |
| [10] | Zhang Y H, Zhu H J, Wang Y L, et al. A contrastive framework for learning sentence representations from pairwise and triple-wise perspective in angular space[C]∥Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg, PA: CAL, 2022: 4892–4903. |
| [11] | Chuang Y S, Dangovski R, Luo H Y, et al. DiffCSE: difference-based contrastive learning for sentence embeddings[C]∥Proceedings of the 2022 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2023: 4207-4218. |
| [12] | Liu J D, Liu J H, Wang Q F, et al. RankCSE: unsupervised sentence representations learning via learning to rank[C]∥Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2023: 13785-13802. |
| [13] | Wang H, Li Y G, Huang Z, et al. SNCSE: contrastive learning for unsupervised sentence embedding with soft negative samples[C]∥International Conference on Intelligent Computing. New York, USA: ICIC, 2023: 419-431. |
| [14] | He H L, Zhang J L, Lan Z Z, et al.Instance smoothed contrastive learning for unsupervised sentence embedding[C]∥Proceedings of the Thirty-Seventh AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Washington, DC: AAAI Press, 2023: 12863-12871. |
| [15] | Robinson J, Chuang C Y, Sra S, et al. Contrastive learning with hard negative samples[C]∥9th International Conference on Learning Representations. Virtual, 2021: joshr17. |
| [16] | Wu X, Gao C C, Su Y P, et al.Smoothed contrastive learning for unsupervised sentence embedding[C]∥Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Computational Linguistics. New York, USA: ICCL, 2022: 4902-4906. |
| [17] | Kim T, Yoo K M, Lee S G. Self-guided contrastive learning for BERT sentence representations[C]∥Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2021: 2528-2540. |
| [18] | Oh D, Kim Y J, Lee H D, et al.Don't judge a language model by its last layer: contrastive learning with layer-wise attention pooling[C]∥Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Computational Linguistics. New York, USA: ICCL, 2022: 4585-4592. |
| [19] | Deng J H, Wan F Q, Yang T, et al. Clustering-aware negative sampling for unsupervised sentence representation[C] ∥Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2023: 8713-8729. |
| [1] | Xiu-hui WANG,Yong-bo XU. Chinese named entity recognition algorithm with soft attention mask embedding [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2026, 56(1): 231-238. |
| [2] | Hong-bin WANG,Hao-dong TANG,Yan-tuan XIAN,Bo LIU,Xin-liang GU. Knowledge graph alignment based on entity reliable path and semantic aggregates [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(11): 3673-3685. |
| [3] | Jing-shu YUAN,Wu LI,Xing-yu ZHAO,Man YUAN. Semantic matching model based on BERTGAT-Contrastive [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2383-2392. |
| [4] | You-wei WANG,Ao LIU,Li-zhou FENG. New method for text sentiment classification based on knowledge distillation and comment time [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1664-1674. |
| [5] | Jun-jie LIU,Jia-yi Dong,Yong YANG,Dan LIU,Fu-heng QU,Yan-chang LYU. Analysis of factors associated with online learning performance of students based on HM-OLS stepwise regression model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3755-3762. |
| [6] | Liu LIU,Kun DING,Shan-shan LIU,Ming LIU. Event detection method as machine reading comprehension [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 533-539. |
| [7] | Yue-lin CHEN,Zhu-cheng GAO,Xiao-dong CAI. Long text semantic matching model based on BERT and dense composite network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(1): 232-239. |
| [8] | Yue-kun MA,Yi-feng HAO. Fast recognition method of short text named entities considering feature sparsity [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3529-3535. |
| [9] | Xiang-jiu CHE,Huan XU,Ming-yang PAN,Quan-le LIU. Two-stage learning algorithm for biomedical named entity recognition [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2380-2387. |
| [10] | Ya-hui ZHAO,Fei-yu LI,Rong-yi CUI,Guo-zhe JIN,Zhen-guo ZHANG,De LI,Xiao-feng JIN. Korean⁃Chinese translation quality estimation based on cross⁃lingual pretraining model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2371-2379. |
| [11] | Jian LI,Qi XIONG,Ya-ting HU,Kong-yu LIU. Chinese named entity recognition method based on Transformer and hidden Markov model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1427-1434. |
| [12] | Tian BAI,Ming-wei XU,Si-ming LIU,Ji-an ZHANG,Zhe WANG. Dispute focus identification of pleading text based on deep neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [13] | Wen-jun WANG,Yin-feng YU. Automatic completion algorithm for missing links in nowledge graph considering data sparsity [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1428-1433. |
| [14] | Dong-ming SUN,Liang HU,Yong-heng XING,Feng WANG. Text fusion based internet of things service recommendation for trigger⁃action programming pattern [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2182-2189. |
| [15] | Ya-hui ZHAO,Fei-yang YANG,Zhen-guo ZHANG,Rong-yi CUI. Korean text structure discovery based on reinforcement learning and attention mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1387-1395. |
|
||