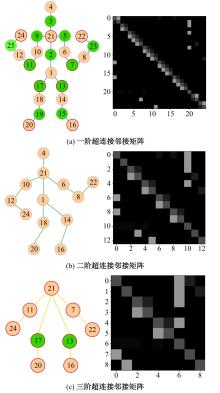
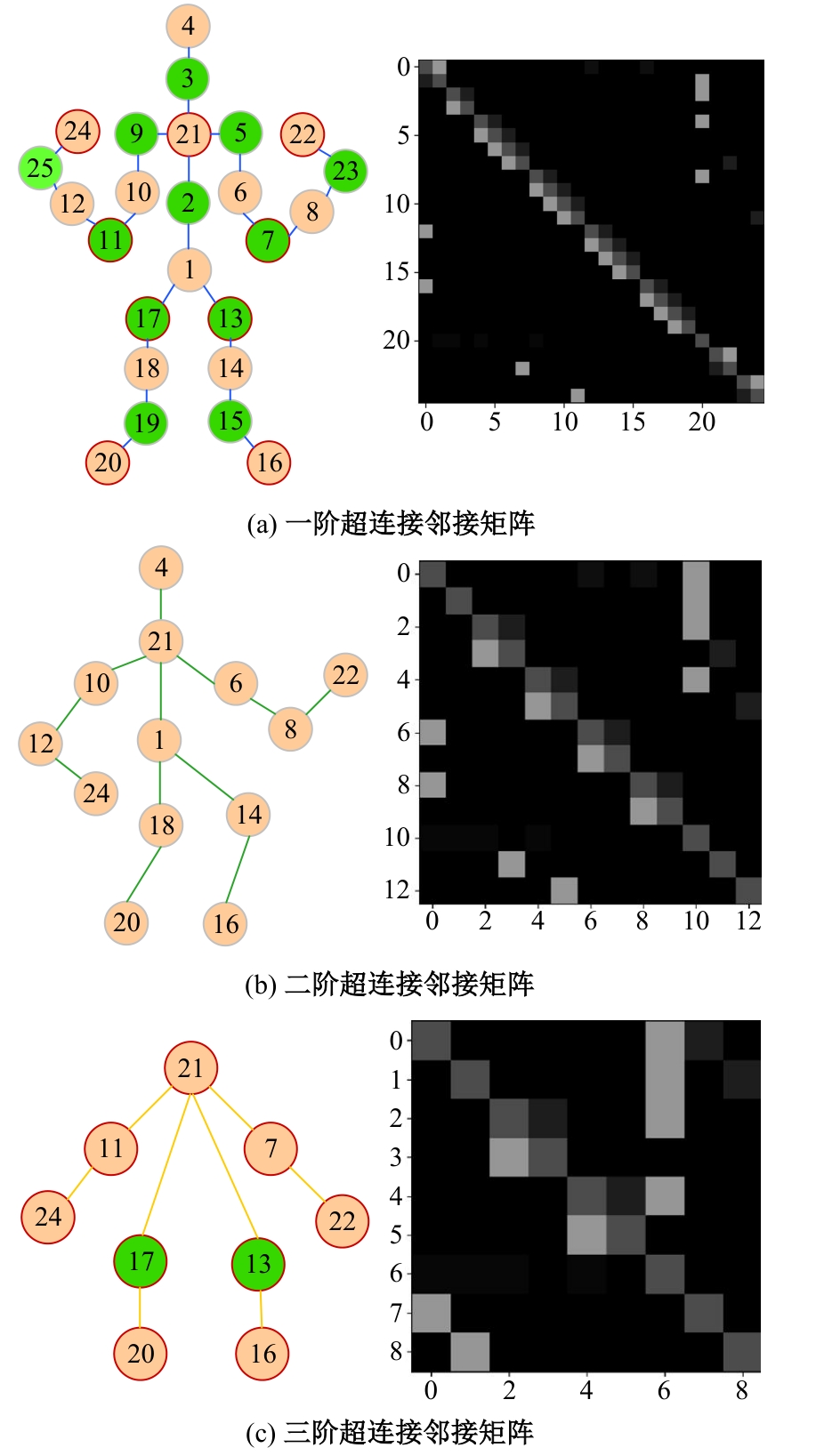
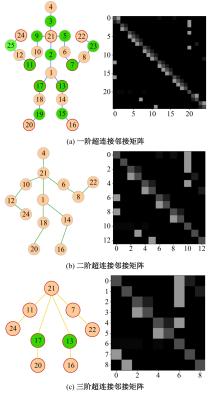
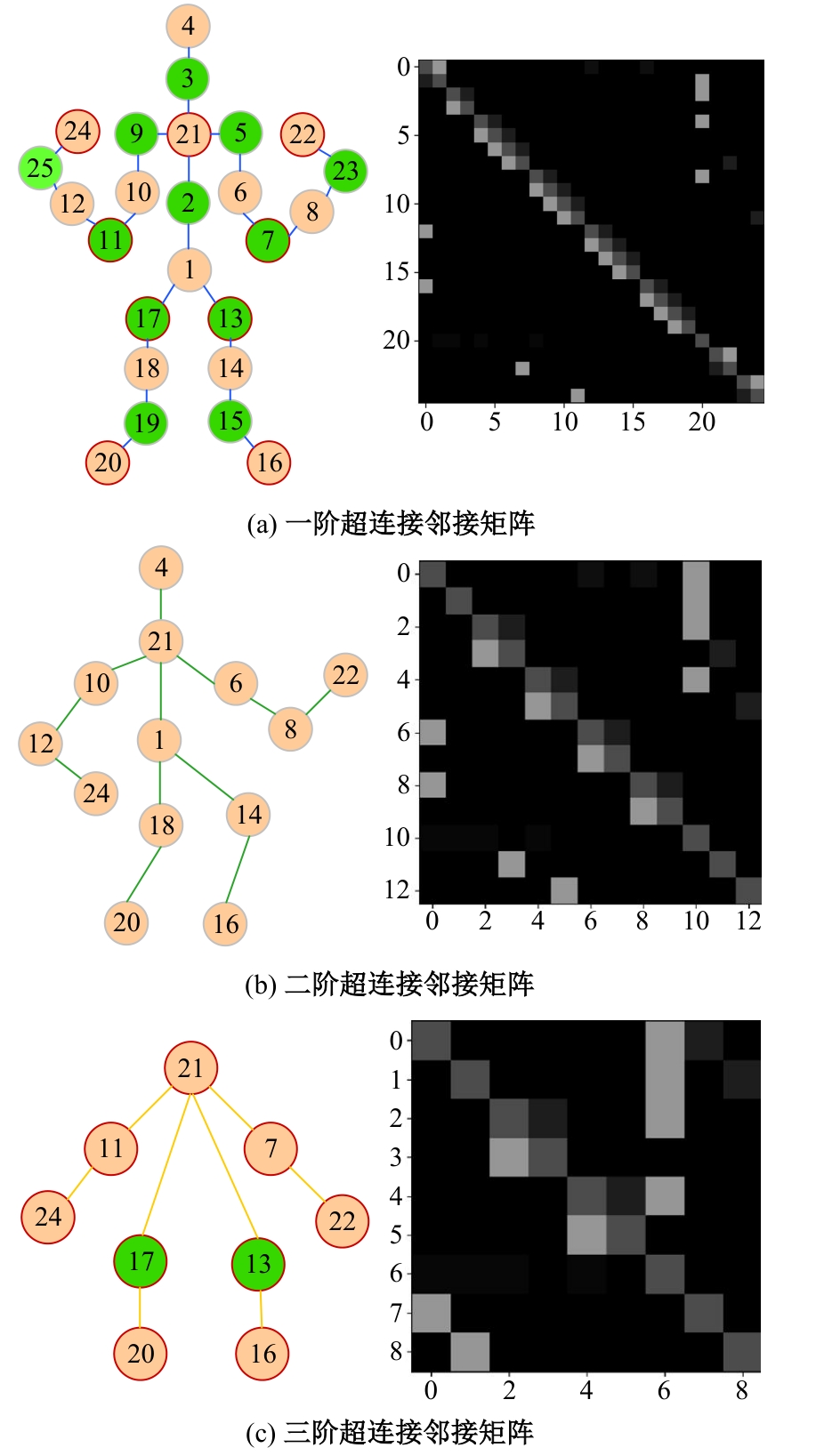
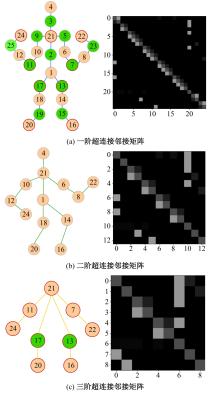
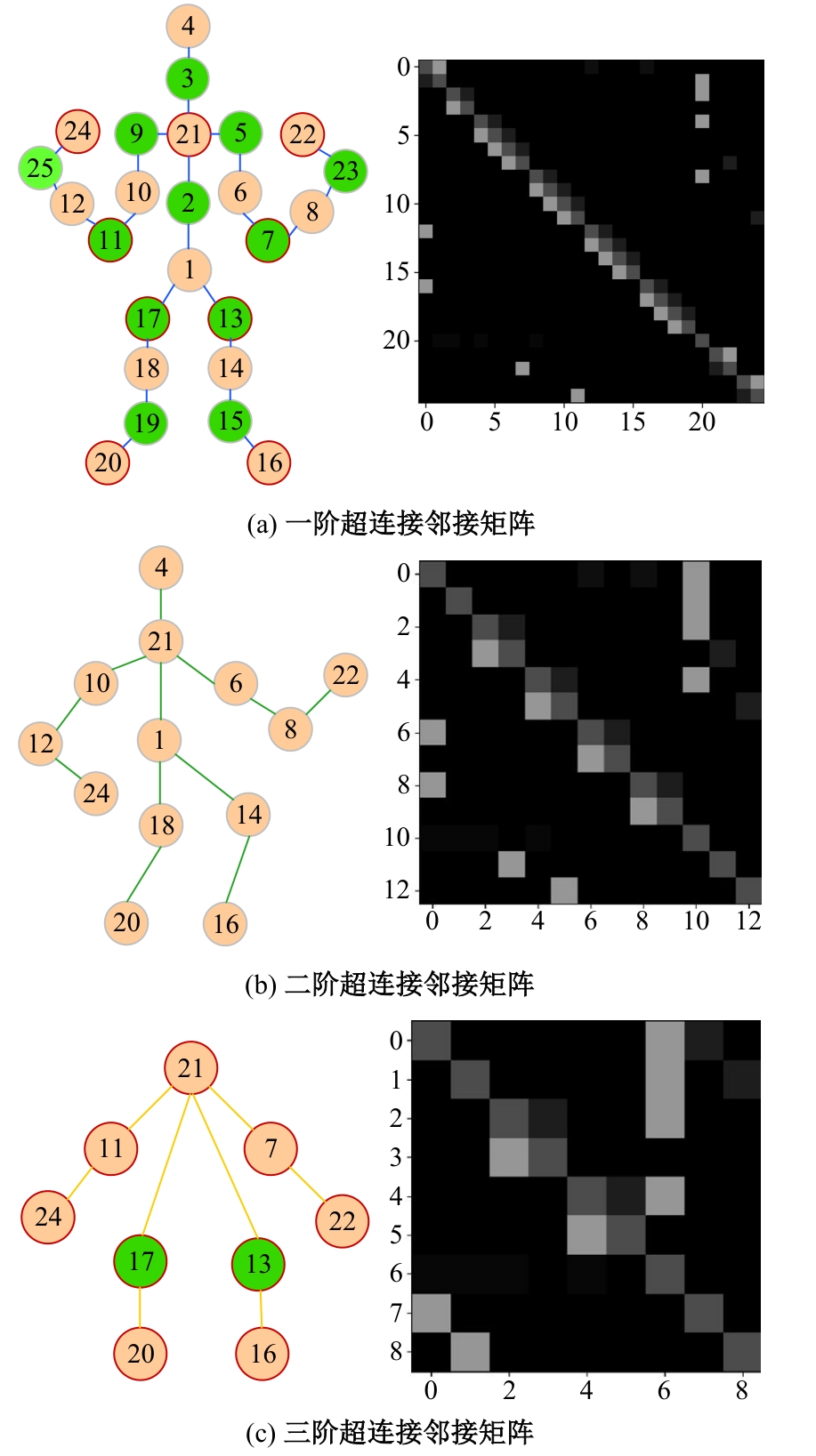
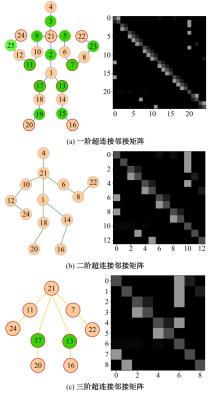
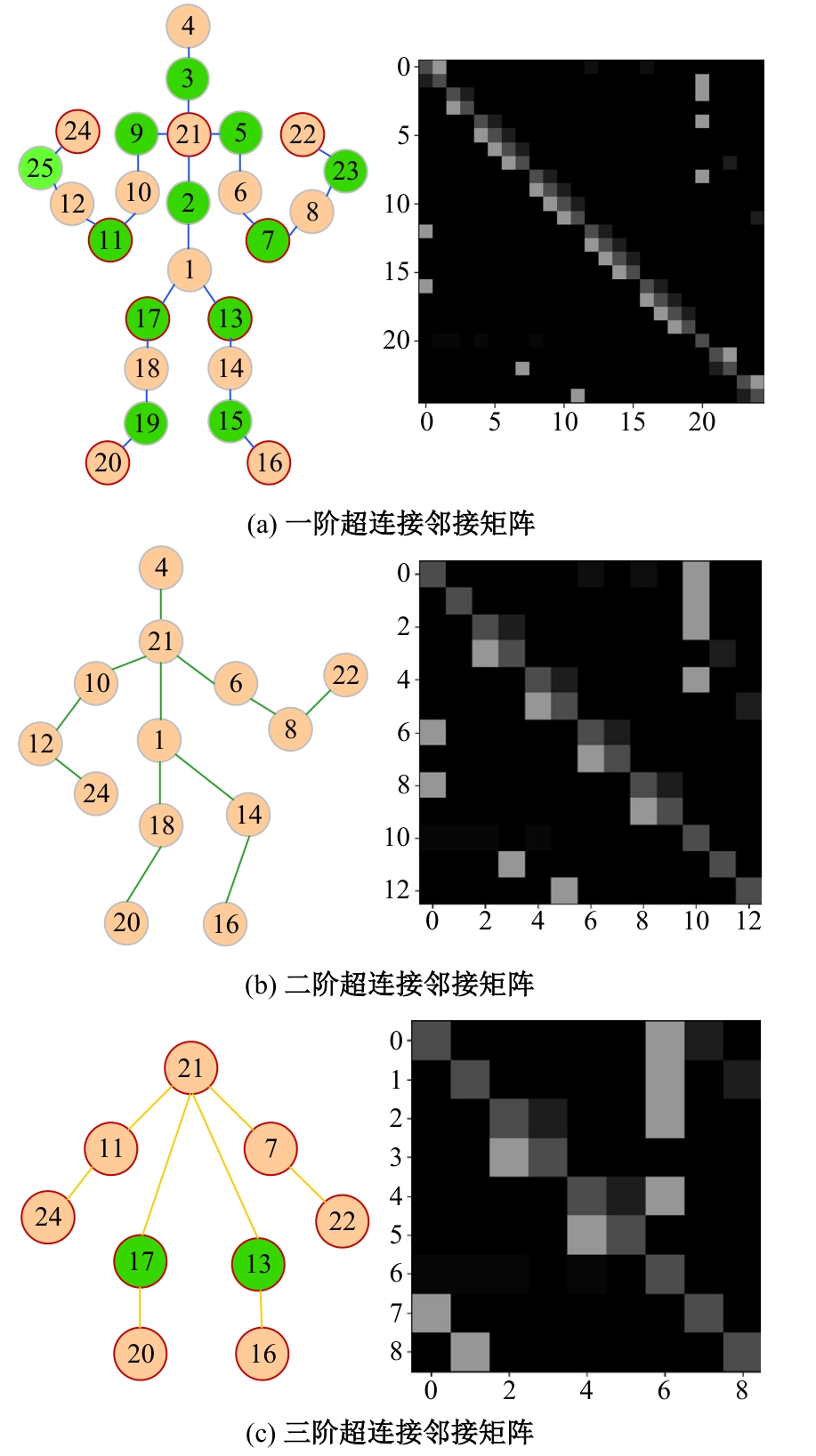
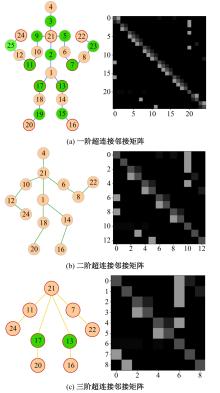
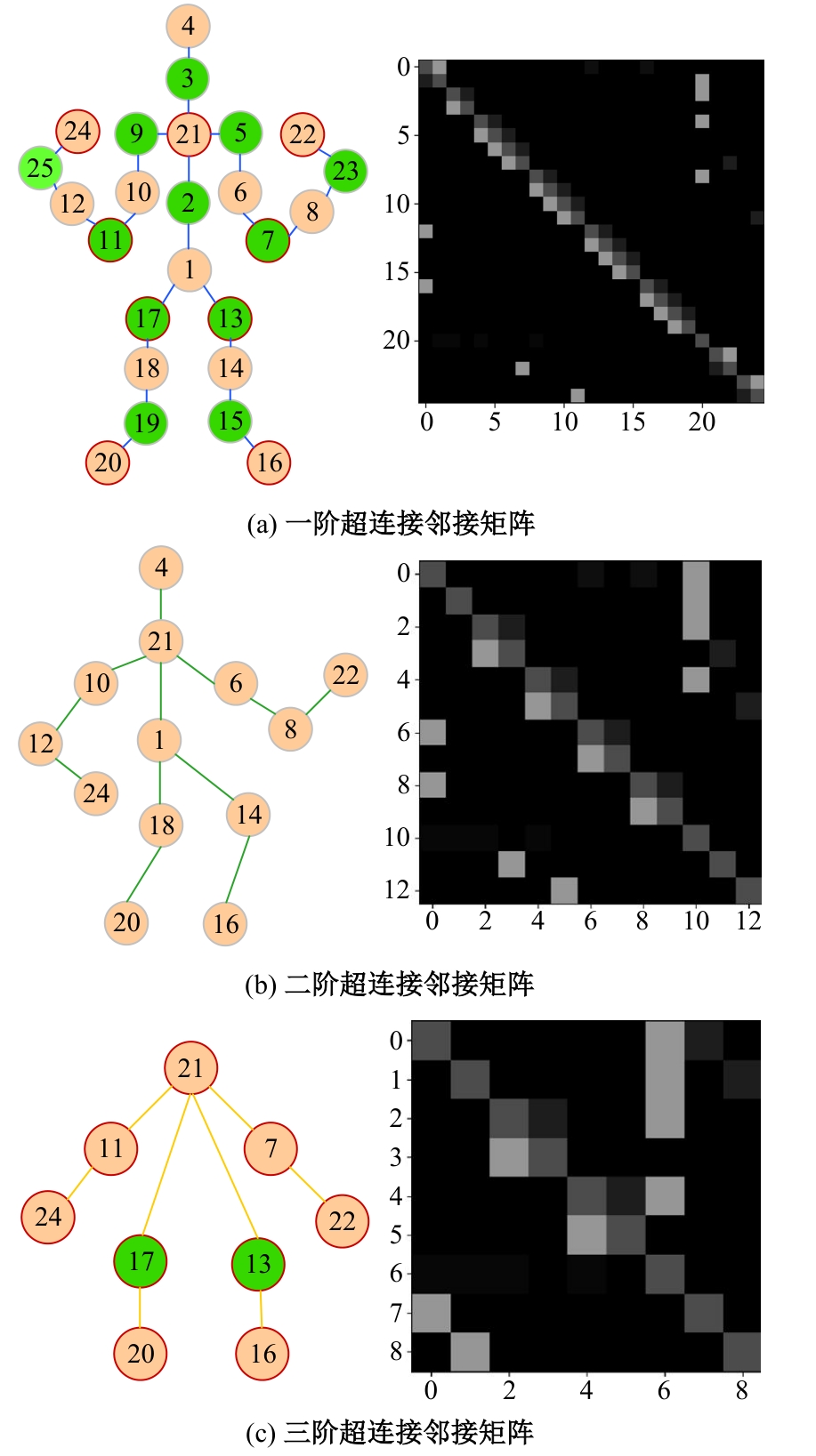
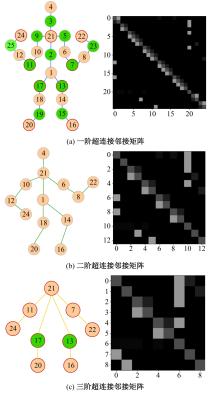
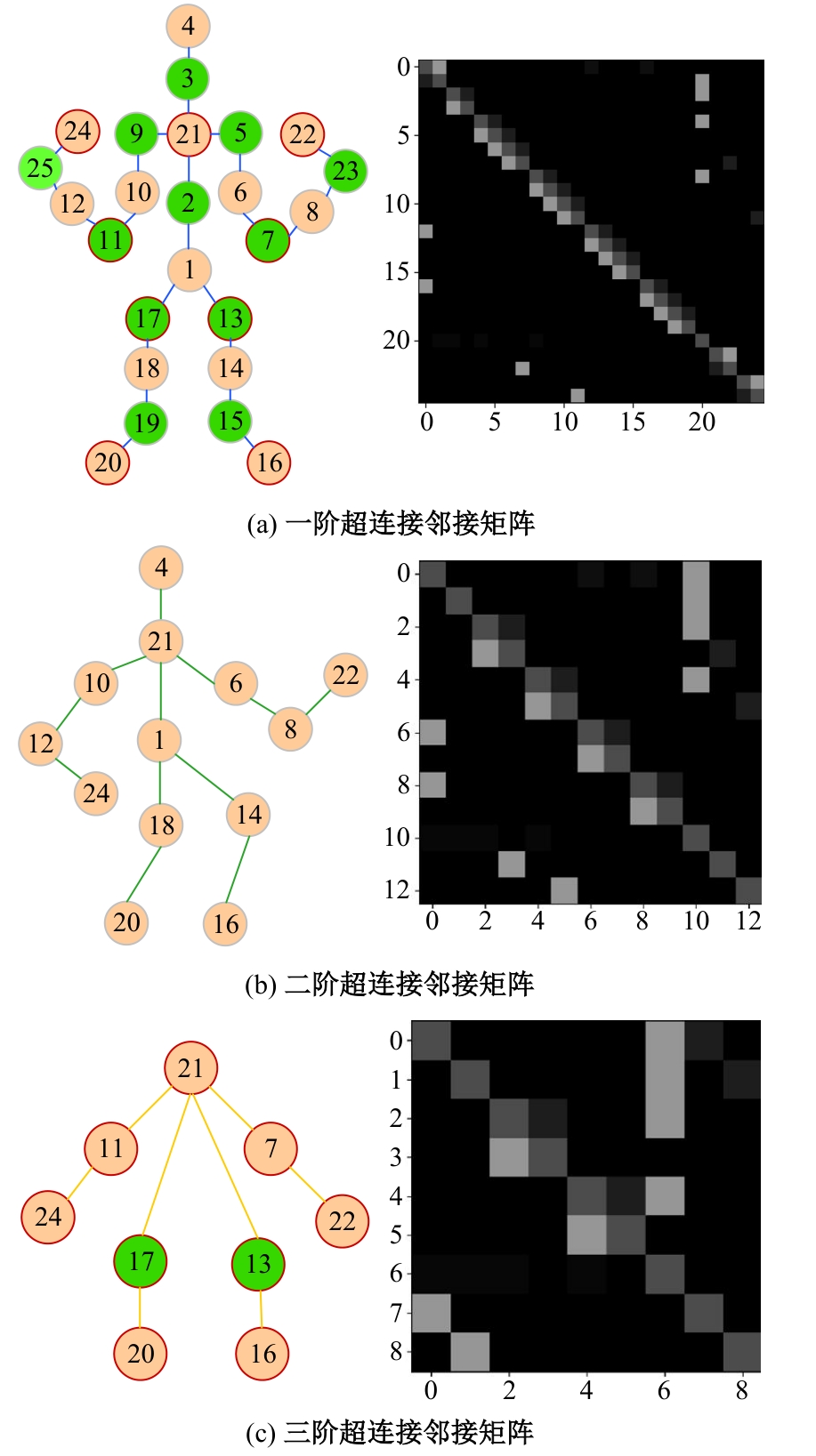
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (2): 731-740.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230440
Previous Articles Next Articles
Skeleton-based action recognition based on hyper-connected graph convolutional network
Yi CAO1,2( ),Yu XIA1,2,Qing-yuan GAO1,2,Pei-tao YE1,2,Fan YE1,2
),Yu XIA1,2,Qing-yuan GAO1,2,Pei-tao YE1,2,Fan YE1,2
- 1.School of Mechanical Engineering,Jiangnan University,Wuxi 214122,China
2.Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Food Manufacturing Equipment and Technology,Jiangnan University,Wuxi 214122,China
CLC Number:
- TP391.41
| 1 | Aggarwal J K, Ryoo M S. Human activity analysis: a review[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2011, 43(3): 16-28. |
| 2 | 钟忺, 王灿, 卢炎生, 等. 基于ISA网络的视频人体行为分类识别[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 47(2): 103-108. |
| Zhong Xian, Wang Can, Lu Yan-sheng, et al. Video human behavior recognition based on ISA network model[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(2): 103-108. | |
| 3 | 曹毅, 刘晨, 黄子龙, 等. 一种基于DenseNet网络与帧差法特征输入的人体行为识别方法[P]. 中国专利: ZL201910332644.3, 2023-04-07. |
| 4 | 詹健浩, 吴鸿伟, 周成祖, 等. 基于深度学习的行为识别多模态融合方法综述[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2023, 32(1): 41-49. |
| Zhan Jian-hao, Wu Hong-wei, Zhou Cheng-zu, et al. Survey on multi-modality fusion methods for action recognition based on deep learning[J]. Computer Systems & Applications, 2023, 32(1): 41-49. | |
| 5 | 刘云, 薛盼盼, 李辉, 等. 基于深度学习的节点行为识别综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(6): 1789-1802. |
| Liu Yun, Xue Pan-pan, Li Hui, et al. A review of action recognition using joints based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(6): 1789-1802. | |
| 6 | Si C, Chen W, Wang W, et al. An attention enhanced graph convolutional LSTM network for skeleton-based action recognition[C]∥ Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1227-1236. |
| 7 | Liu J, Wang G, Hu P, et al. Global context-aware attention LSTM networks for 3D action recognition[C]∥Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 3671-3680. |
| 8 | Shi L, Zhang Y, Cheng J, et al. Two-stream adaptive graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition[C]∥Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 12018-12027. |
| 9 | 曹毅, 刘晨, 黄子龙, 等. 时空自适应图卷积神经网络的骨架行为识别[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 48(11): 5-10. |
| Cao Yi, Liu Chen, Huang Zi-long, et al. Skeleton-based action recognition based on spatio-temporal adaptive graph convolutional neural-network[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(11): 5-10. | |
| 10 | Xing Y, Zhu J, Li Y, et al. An improved spatial temporal graph convolutional network for robust skeleton-based action recognition[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2023, 53: 4592-4608. |
| 11 | 曹毅, 吴伟官, 李平, 等. 基于时空特征增强图卷积网络的骨架行为识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(8): 3022-3031. |
| Cao Yi, Wu Wei-guan, Li Ping, et al. Skeleton-based action recognition based on spatio-temporal feature enhanced graph convolutional network[J]. Journal of Electronics and Information, 2023, 45(8): 3022-3031. | |
| 12 | Ding C, Wen S, Ding W, et al. Temporal segment graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 110: 104675. |
| 13 | Alsarhan T, Ali U, Lu H. Enhanced discriminative graph convolutional network with adaptive temporal modelling for skeleton-based action recognition[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2022, 216: 103348. |
| 14 | Yang H, Yan D, Zhang L, et al. Feedback graph convolutional network for skeleton-based action recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 164-175. |
| 15 | Cheng K, Zhang Y, He X, et al. Skeleton-based action recognition with shift graph convolutional network[C]∥Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 180-189. |
| 16 | Li C, Zhong Q, Xie D, et al. Co-occurrence feature learning from skeleton data for action recognition and detection with hierarchical aggregation[C]∥Proceedings of International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 786-792. |
| 17 | Tae S K, Austin R. Interpretable 3D human action analysis with temporal convolutional networks[C]∥ Proceedings of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, New York, USA, 2017: 1623-1631. |
| 18 | Zhang P, Lan C, Zeng W, et al. Semantics-guided neural networks for efficient skeleton-based human action recognition[C]∥Proceedings of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1109-1118. |
| 19 | Henaff M, Bruna J, Le C Y. Deep convolutional networks on graph structured data[J/OL]. [2023-04-15]. arXiv Preprint arXiv: . |
| 20 | 曹毅, 夏宇, 高清源, 等. 基于动态时序多维自适应图卷积网络的骨架行为识别方法[P]. 中国专利: ZL115661861A, 2022-01-31. |
| 21 | Li C, Zhou A, Yao A. Omni-dimensional dynamic convolution[J/OL]. [2023-04-16]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2209.07947v1. |
| 22 | Amir S, Liu J, Ng T T, et al. NTU RGB+D: a large scale dataset for 3d human activity analysis[C]∥ Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New York, USA, 2016: 1010-1019. |
| 23 | Liu J, Shahroudy A, Perez M, et al. NTU RGB+D 120: a large-scale benchmark for 3D human activity understanding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(10): 2684-2701. |
| [1] | Pei-guang JING,Yu-dou TIAN,Shao-chu WANG,Yun LI,Yu-ting SU. Traffic flow prediction algorithm based on dynamic diffusion graph convolution [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1582-1592. |
| [2] | Fu-heng QU,Yue-tao PAN,Yong YANG,Ya-ting HU,Jian-fei SONG,Cheng-yu WEI. An efficient global K-means clustering algorithm based on weighted space partitioning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1393-1400. |
| [3] | Shuai-shuai SUN,Chun-xiao FENG,Liang ZHANG. Path planning for multimodal quadruped robots based on discrete sampling [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1120-1128. |
| [4] | Zhi-gang JIN,Ren-jun SU,Xiao-fang ZHAO. Psychological assessment method based on heterogeneous graph network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1078-1085. |
| [5] | Jing-peng GAO,Guo-xuan WANG,Lu GAO. LSTM⁃MADDPG multi⁃agent cooperative decision algorithm based on asynchronous collaborative update [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(3): 797-806. |
| [6] | Liu LIU,Kun DING,Shan-shan LIU,Ming LIU. Event detection method as machine reading comprehension [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 533-539. |
| [7] | Jian LI,Qi XIONG,Ya-ting HU,Kong-yu LIU. Chinese named entity recognition method based on Transformer and hidden Markov model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1427-1434. |
| [8] | Chun-hui LIU,Si-chang WANG,Ce ZHENG,Xiu-lian CHEN,Chun-lei HAO. Obstacle avoidance planning algorithm for indoor navigation robot based on deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3558-3564. |
| [9] | Tian BAI,Ming-wei XU,Si-ming LIU,Ji-an ZHANG,Zhe WANG. Dispute focus identification of pleading text based on deep neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [10] | Sheng-sheng WANG,Lin-yan JIANG,Yong-bo YANG. Transfer learning of medical image segmentation based on optimal transport feature selection [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1626-1638. |
| [11] | Hao-yu TIAN,Xin MA,Yi-bin LI. Skeleton-based abnormal gait recognition: a survey [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(4): 725-737. |
| [12] | Yong LIU,Lei XU,Chu-han ZHANG. Deep reinforcement learning model for text games [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 666-674. |
| [13] | Xiu-fang WANG,Shuang SUN,Chun-yang DING. Real⁃time detection of embedded bearing faults based on 1D⁃RSCNN [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 310-317. |
| [14] | Jing-pei LEI,Dan-tong OUYANG,Li-ming ZHANG. Relation domain and range completion method based on knowledge graph embedding [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(1): 154-161. |
| [15] | Zhi-hua LI,Ye-chao ZHANG,Guo-hua ZHAN. Realtime mosaic and visualization of 3D underwater acoustic seabed topography [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(1): 180-186. |
|
||