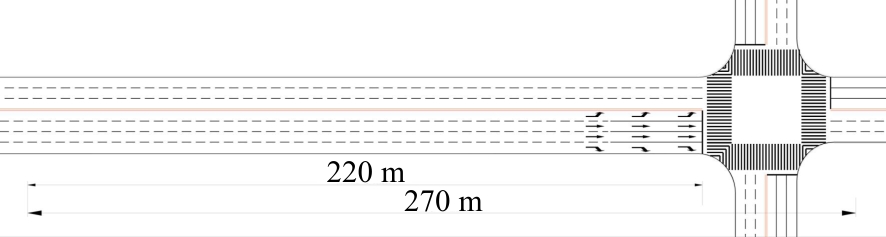
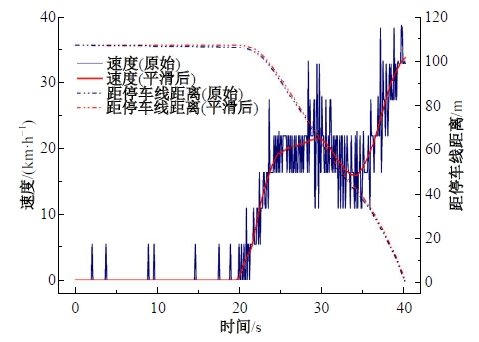
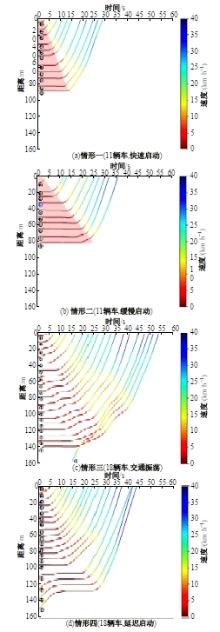
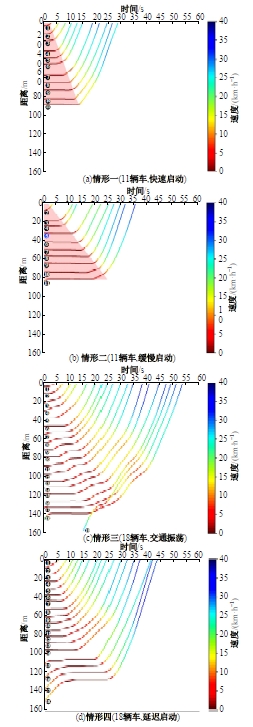
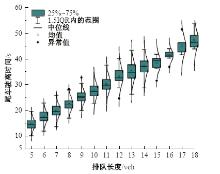
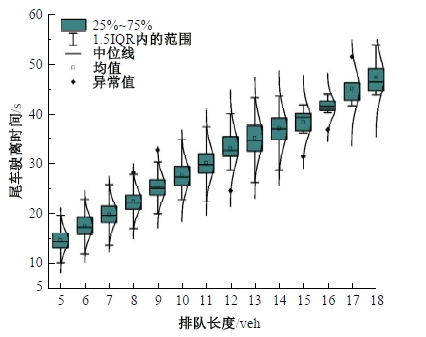
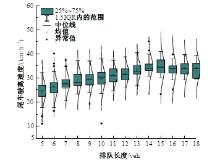
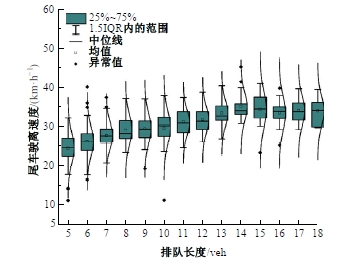
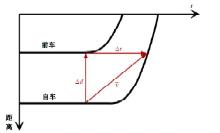
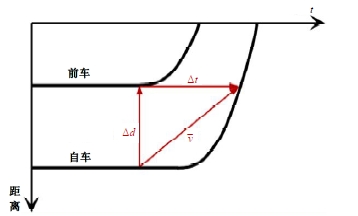
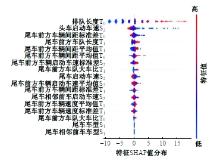
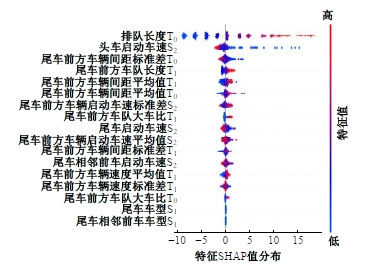
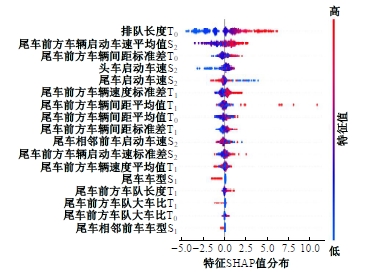
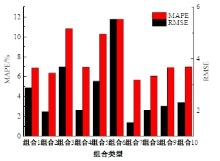
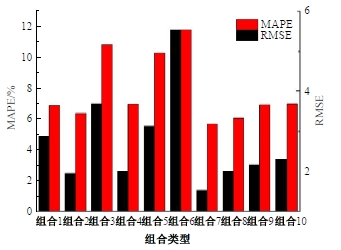
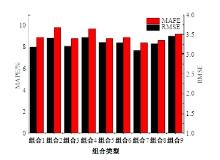
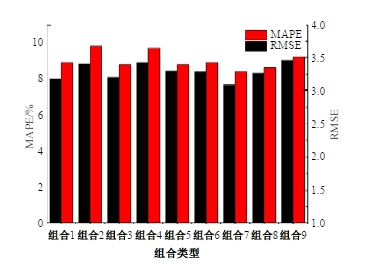
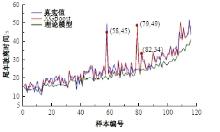
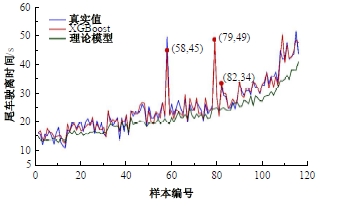
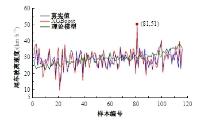
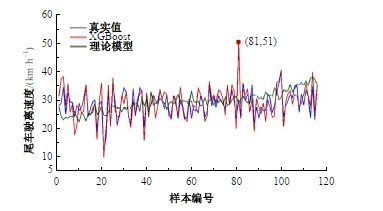
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 1275-1286.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230784
Previous Articles Next Articles
Data-driven prediction of departure state for tail vehicles in queues at signalized intersections
Kai-ming LU1,2( ),Yan-yan CHEN1,2,Yao TONG1,2,Jian ZHANG1,2,Yong-xing LI1,2(
),Yan-yan CHEN1,2,Yao TONG1,2,Jian ZHANG1,2,Yong-xing LI1,2( ),Ying LUO1,2
),Ying LUO1,2
- 1.School of Urban Transportation,Urban Construction Department,Beijing University of Technology,Beijing 100124,China
2.Beijing Key Laboratory of Traffic Engineering,Beijing University of Technology,Beijing 100124,China
CLC Number:
- U491.1
| [1] | 徐洪峰, 王殿海. BRT优先控制交叉口的机动车相位固定最小绿灯时间计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2009, 39(): 92-97. |
| Xu Hong-feng, Wang Dian-hai. Absolute minimum green calculation for vehicle phase at signalized intersections with bus rapid transit signal priority[J].Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition),2009, 39(Sup.1): 92-97. | |
| [2] | 刘东波, 沈莉潇, 代磊磊, 等. 基于多目标雷达数据的单点交通信号控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(10): 2456-2465. |
| Liu Dong-bo, Shen Li-xiao, Dai Lei-lei, et al. Traffic signal control method at isolated intersections based on multi-target radar data[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(10): 2456-2465. | |
| [3] | 刘显贵, 王晖年, 洪经纬, 等. 网联环境下信号交叉口车速控制策略及优化[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息. 2021, 21(2): 82-90. |
| Liu Xian-gui, Wang Hui-nian, Hong Jing-wei, et al. Traffic speed control strategy and optimization at signalized intersections under connected environment [J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2021, 21(2): 82-90. | |
| [4] | 杨澜, 赵祥模, 吴国垣, 等. 智能网联汽车协同生态驾驶策略综述[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2020, 20(5): 58-72. |
| Yang Lan, Zhao Xiang-mo, Wu Guo-yuan, et al. A review of collaborative eco-driving strategies for intelligent connected vehicles[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering,2020, 20(5): 58-72. | |
| [5] | Luo Q, Yuan J, Chen X, et al. Analyzing start-up time headway distribution characteristics at signalized intersections[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2019, 535: No.122348. |
| [6] | Mondal S, Gupta A. Discharge characteristics analysis of queued-up vehicles at signal-controlled intersections under heterogeneous traffic conditions[J]. International Journal of Civil Engineering, 2019, 17(5): 619-628. |
| [7] | Jin X, Zhang Y, Wang F, et al. Departure headways at signalized intersections: a log-normal distribution model approach[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies,2009, 17(3): 318-327. |
| [8] | 唐克双, 董可然, 黄志荣, 等. 信号交叉口排队消散特性实证对比[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 43(11): 1689-1695. |
| Tang Ke-shuang, Dong Ke-ran, Huang Zhi-rong, et al. Empirical comparison of queuing dissipation characteristics at signalized intersections[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2015, 43(11): 1689-1695. | |
| [9] | Zhan X, Li R, Ukkusuri S V. Lane-based real-time queue length estimation using license plate recognition data[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies,2015, 57: 85-102. |
| [10] | Mei Y, Gu W, Chung E C S, et al. A Bayesian approach for estimating vehicle queue lengths at signalized intersections using probe vehicle data[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2019, 109: 233-249. |
| [11] | 谈超鹏, 姚佳蓉, 唐克双. 基于抽样车辆轨迹数据的信号控制交叉口排队长度分布估计[J]. 中国公路学报. 2021, 34(11): 282-295. |
| Tan Chao-peng, Yao Jia-rong, Tang Ke-shuang. Queue length distribution estimation at signalized intersections based on sampled vehicle trajectory data[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport,2021, 34(11): 282-295. | |
| [12] | He X, Liu H X, Liu X. Optimal vehicle speed trajectory on a signalized arterial with consideration of queue[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies,2015, 61: 106-120. |
| [13] | Wu L, Ci Y, Wang Y, et al. Fuel consumption at the oversaturated signalized intersection considering queue effects: a case study in Harbin, China[J]. Energy, 2020, 192: No.116654. |
| [14] | Yang H, Rakha H, Ala M V. Eco-cooperative adaptive cruise control at signalized intersections considering queue effects[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,2017, 18(6): 1575-1585. |
| [15] | Dong H, Zhuang W, Chen B, et al. Enhanced eco-approach control of connected electric vehicles at signalized intersection with queue discharge prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(6): 5457-5469. |
| [16] | Dong H, Zhuang W, Yin G, et al. Energy-optimal velocity planning for connected electric vehicles at signalized intersection with queue prediction[C]∥IEEE ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics(AIM), Boston, USA, 2020: 238-243. |
| [17] | Ye F, Hao P, Qi X, et al. Prediction-based eco-approach and departure at signalized intersections with speed forecasting on preceding vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 20(4): 1378-1389. |
| [18] | 徐洪峰, 郑明明, 李克平. 机动车相位固定最小绿灯时间计算方法[J]. 公路交通科技, 2008(5): 105-110. |
| Xu Hong-Feng, Zheng Ming-ming, Li Ke-ping.Absolute minimum green time calculation for vehicle phase[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Developmen, 2008(5): 105-110. | |
| [19] | Elefteriadou L. The highway capacity manual 6th edition: a guide for multimodal mobility analysis[J]. Institute of Transportation Engineers. 2016, 86(4): 14-18. |
| [20] | 罗小芹, 王殿海, 金盛. 面向混合交通的感应式交通信号控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2019, 49(3): 695-704. |
| Luo Xiao-qin, Wang Dian-hai, Jin Sheng. Traffic signal actuated control at isolated intersections for heterogeneous traffic[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 695-704. | |
| [21] | Shi X P, Wong Y D, Li M Z F, et al. A feature learning approach based on XGBoost for driving assessment and risk prediction[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2019, 129: 170-179. |
| [22] | Shi R, Xu X, Li J, et al. Prediction and analysis of train arrival delay based on XGBoost and Bayesian optimization[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2021, 109:No. 107538. |
| [23] | 魏田正, 魏雯, 李海梅, 等. 基于XGBoost算法的危险场景驾驶行为模式分析及安全评估[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2022, 40(5): 53-60. |
| Wei Tian-zheng, Wei Wen, Li Hai-mei, et al. An analysis of driving behavior model and safety assessment under risky scenarios based on an XGBoost algorithm[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2022, 40(5): 53-60. | |
| [24] | 赵晓华, 亓航, 姚莹, 等. 基于可解释机器学习框架的快速路立交出口风险预测及致因解析[J]. 东南大学学报:自然科学版, 2022, 52(1): 152-161. |
| Zhao Xiao-hua, Qi Hang, Yao Ying, et al. Risk prediction and causation analysis of expressway interchange exits based on interpretable machine learning framework[J]. Journal of Southeast University(Natural Science Edition),2022, 52(1): 152-161. | |
| [25] | Roger E, Torlay L, Gardette J, et al. A machine learning approach to explore cognitive signatures in patients with temporo-mesial epilepsy[J]. Neuropsychologia, 2020, 142: No.107455. |
| [26] | 陈秀锋, 田家斌, 石英杰, 等. 基于排队消散模型的干线协调控制[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2018, 18(10): 279-283. |
| Chen Xiu-feng, Tian Jia-bin, Shi Ying-jie, et al. Arterial coordination control based on queuing dissipation model[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2018, 18(10): 279-283. | |
| [27] | 赵巍, 徐汉清. 长周期倒计时信号控制对排队消散特性的影响[J]. 城市交通, 2016, 14(6): 67-74. |
| Zhao Wei, Xu Han-qing. Impacts of signal with long cycle and duration countdown on queue discharge at signalized intersections[J]. Urban Transport of China, 2016, 14(6): 67-74. | |
| [28] | 王殿海, 郭佳林, 蔡正义. 基于自动车牌识别数据的混合交通流饱和流率实时估计[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2021, 21(2): 37-43. |
| Wang Dian-hai, Guo Jia-lin, Cai Zheng-yi. Real-time estimation of saturated flow rate of mixed traffic flow based on automatic license plate recognition data[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2021, 21(2): 37-43. |
| [1] | Yi-yong PAN,Jia-cong XU,Yi-wen YOU,Yong-jun QUAN. Multi-scale spatial heterogeneity analysis of influencing factors of ride-hailing travel demand [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1567-1575. |
| [2] | He-shan ZHANG,Meng-wei FAN,Xin TAN,Zhan-ji ZHENG,Li-ming KOU,Jin XU. Dense small object vehicle detection in UAV aerial images using improved YOLOX [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1307-1318. |
| [3] | Jiao-rong WU,Xu-dong LIU. Analysis of influence of built environment of spatial units of different housing types on commuting mode choice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 554-565. |
| [4] | Fa-cheng CHEN,Guang-quan LU,Qing-feng LIN,Hao-dong ZHANG,She-qiang MA,De-zhi LIU,Hui-jun SONG. Review of drivers' takeover behavior in conditional automated driving [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 419-433. |
| [5] | Yong-ming HE,Jia FENG,Kun WEI,Ya-nan WAN. Analysis on influencing factors of vehicle braking sideslip in curved section of superhighway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 591-602. |
| [6] | Sheng CHANG,Hong-fei LIU,Nai-wei ZOU. H∞ loop shaping robust control of vehicle tracking on variable curvature curve [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2141-2148. |
| [7] | Zhao-wei QU,Lin LI,Yong-heng CHEN,Chang-jian WU. Traffic characteristics and safety analysis of long interval U-turn intersections [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2206-2213. |
| [8] | Yong-ming HE,Cong QUAN,Kun WEI,Jia FENG,Ya-nan WAN,Shi-sheng CHEN. Perceptual fusion method of vehicle road cooperation roadside unit in superhighway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1923-1934. |
| [9] | Guo-zhu CHENG,Lin SHENG,Hao-yu WANG,Tian-jun FENG. Safety evaluation method for pedestrians crossing street at signalized intersection considering secondary conflict of right-turn vehicles [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1903-1912. |
| [10] | Ming-ye ZHANG,Min YANG,Yu LI,Shi-yu HUANG,Qing-yun LI. Optimal electric bus scheduling with multiple vehicle types considering coordinated recharging strategy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1293-1301. |
| [11] | Da-yi QU,Ke-kun ZHANG,Yuan GU,Tao WANG,Hui SONG,Shou-chen DAI. Analysis of lane⁃changing decision⁃making behavior and molecular dynamics modeling for autonomous vehicles [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(3): 700-710. |
| [12] | Liang XU,Jing-hou XIAO,Wan-wan SONG,Song ZHOU. Three⁃point bending fatigue properties of carbon fiber composite laminates [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 400-409. |
| [13] | Bin HU,Yi-quan CAI,Xin LUO,Zi-bin MAO,Jun-wei LI,Meng-yu GUO,Jian WANG. Theory and experiment of high⁃speed seed filling in limited gear⁃shaped side space based on seeds group stress [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 574-588. |
| [14] | Xing WEI,Yong-qi ZHANG,Jun-ming ZHAO,Hui-jun WANG,Lin XIAO. Hot spot stress concentration factor for welded skewed-T joints [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3478-3485. |
| [15] | De-lin LI,Jun-xian CHEN,Yong-gang WANG,Lu WANG,Zhao-qing SHEN. Identification of driving behavior on steep sharp curves based on latent class model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3526-3533. |
|