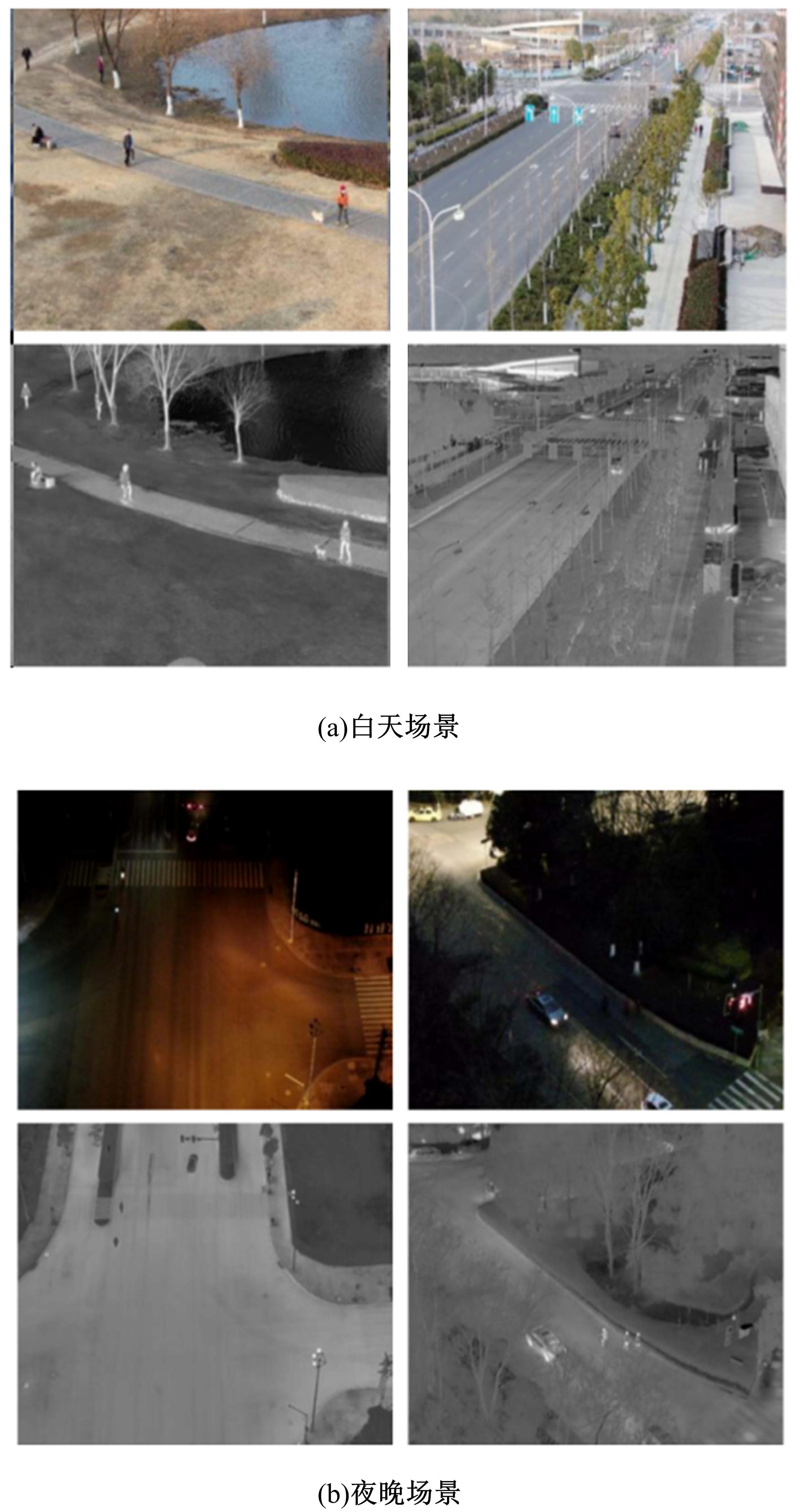
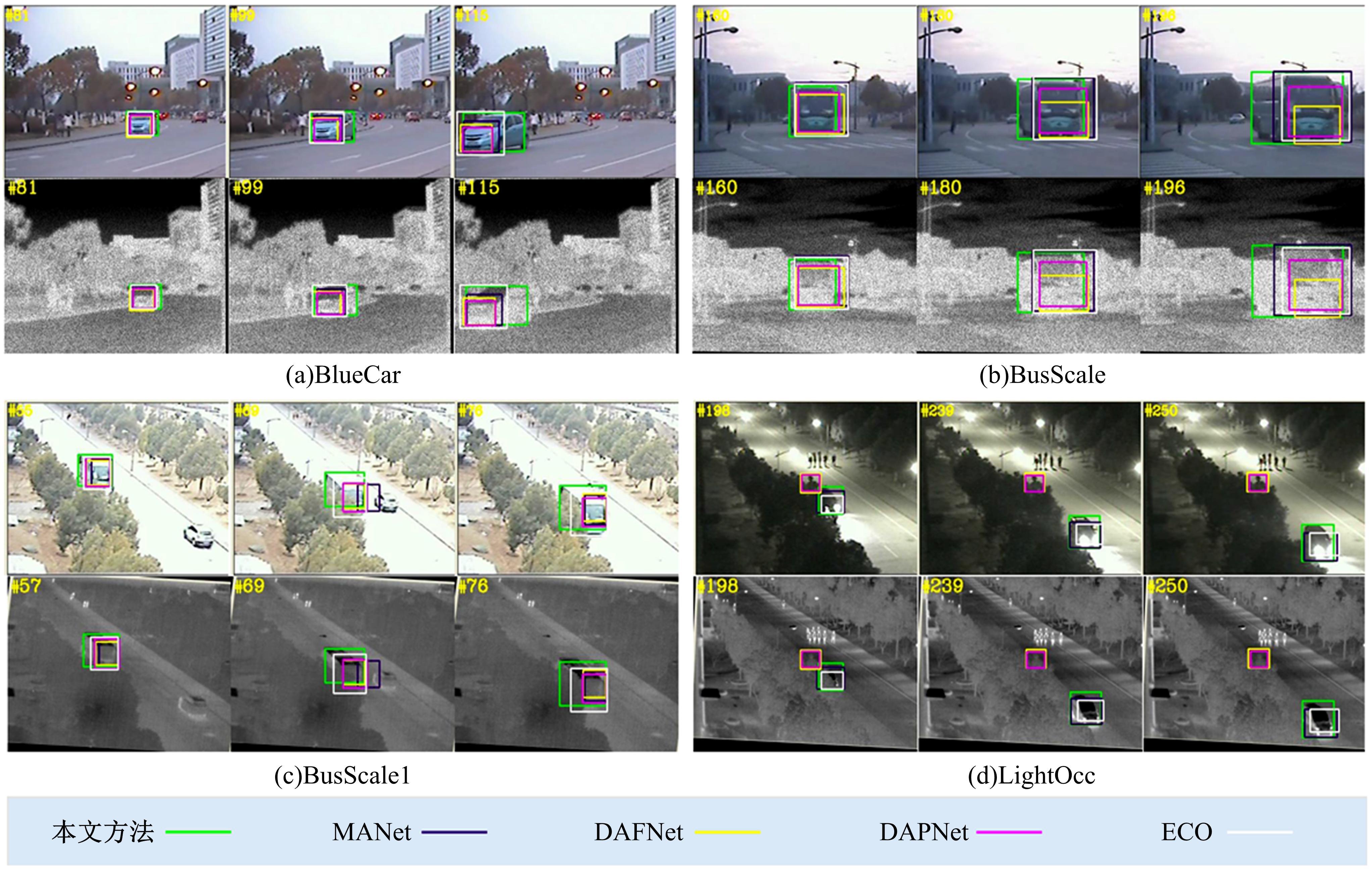
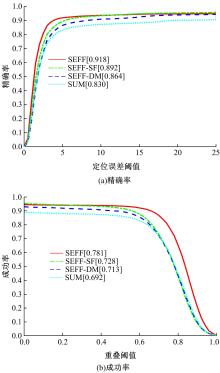
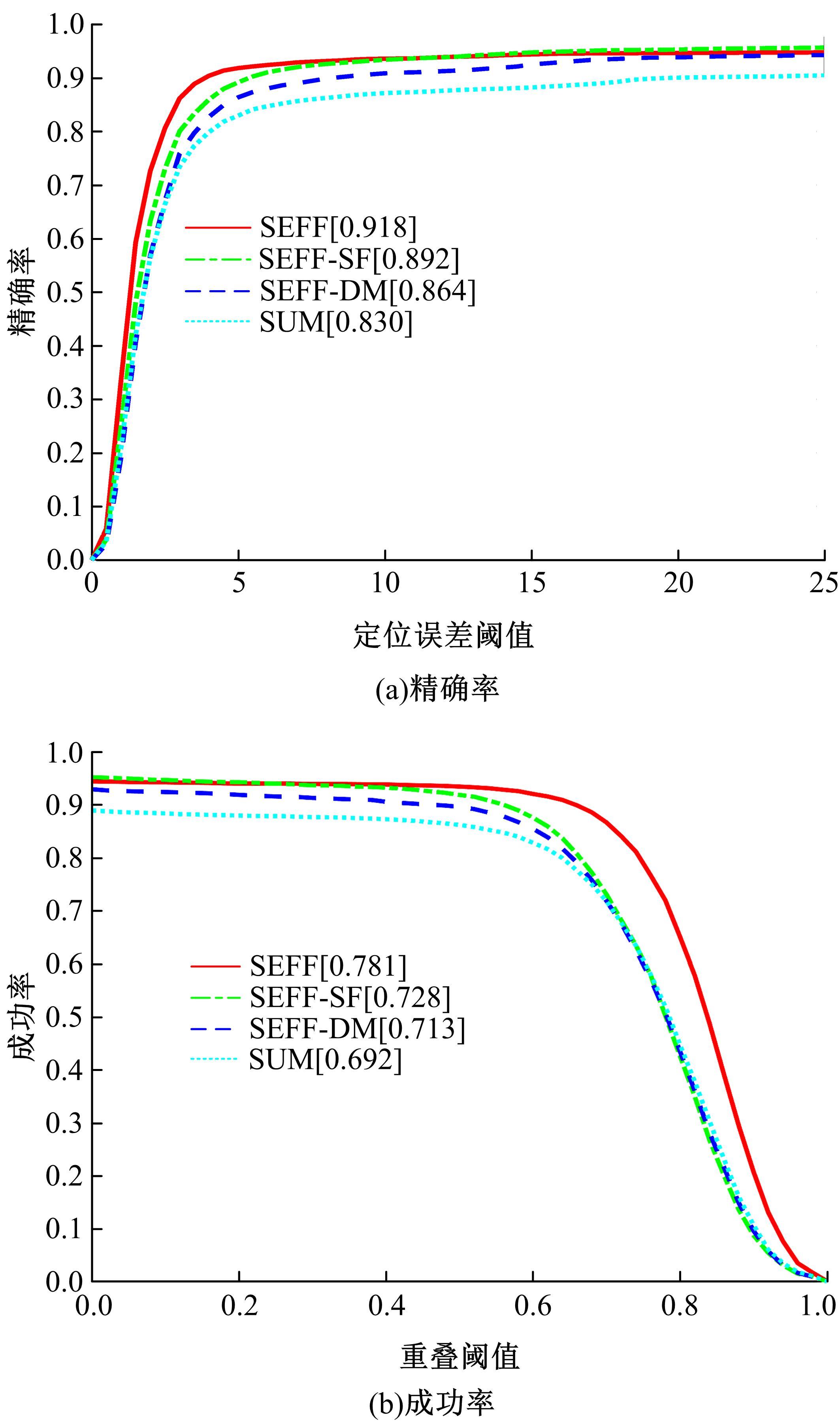
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (12): 2906-2915.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210414
Previous Articles Next Articles
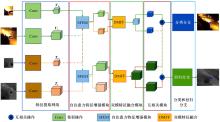
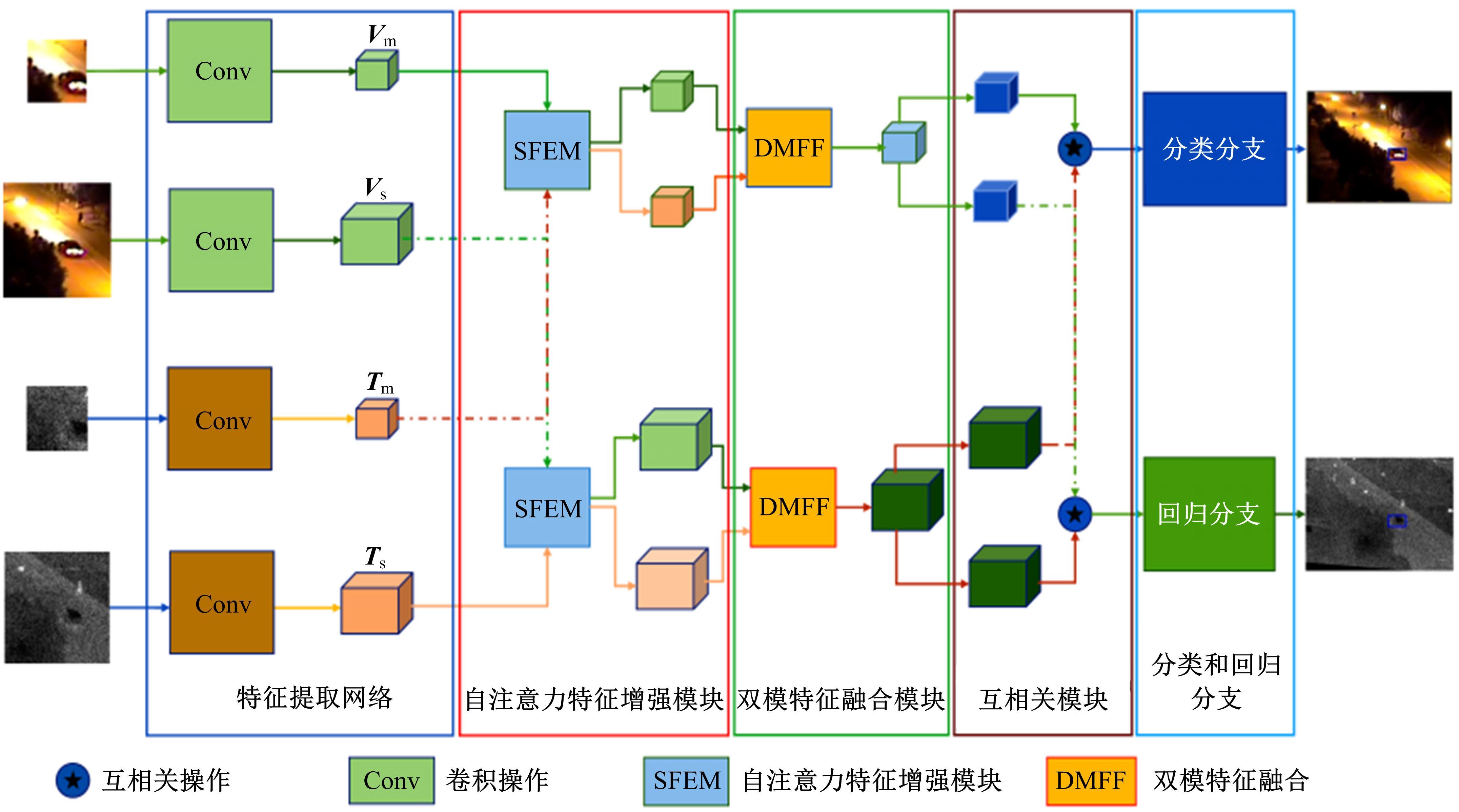
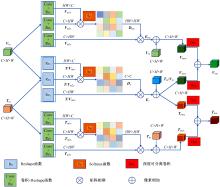
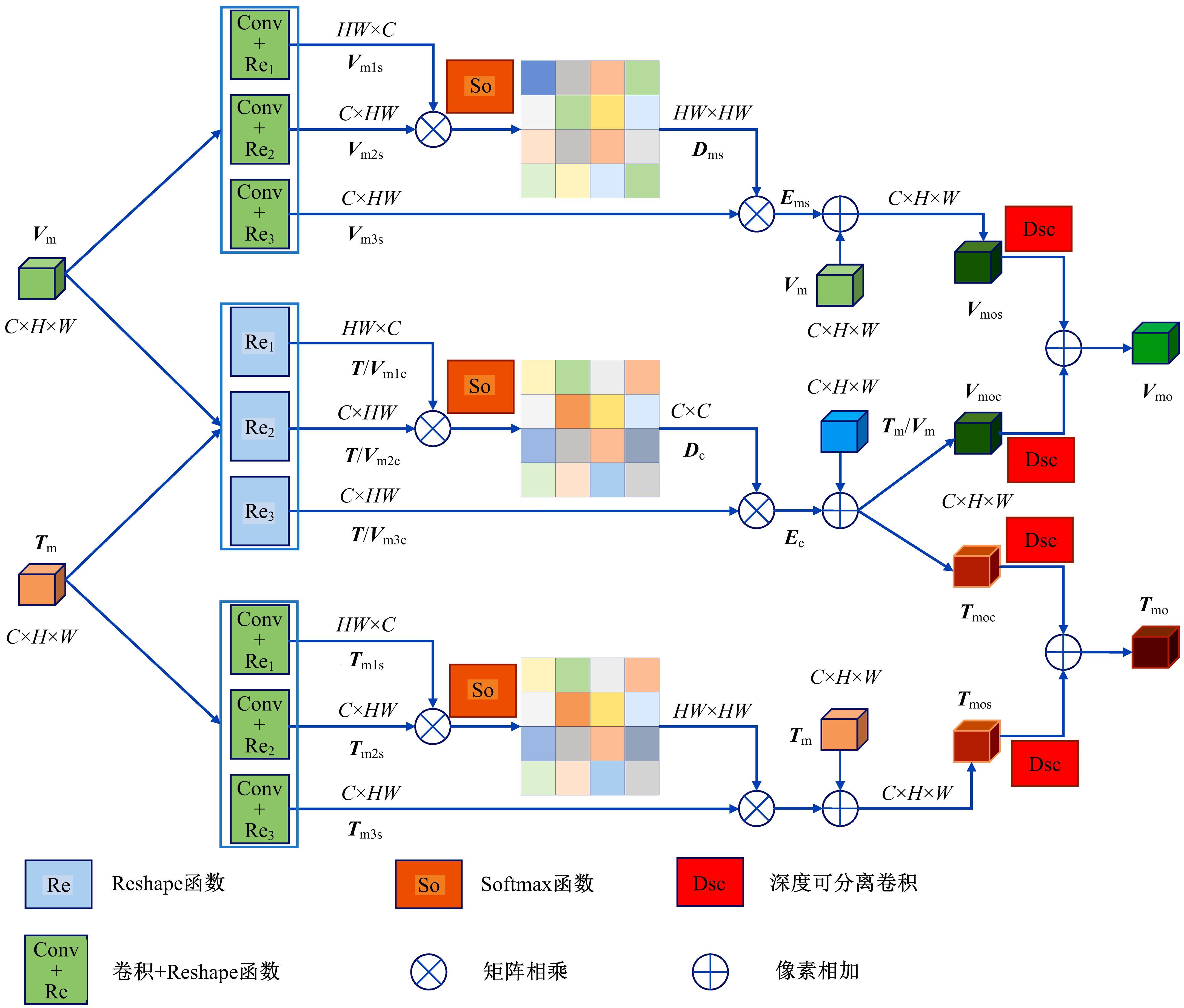
Real⁃time robust RGB⁃T target tracking based on dual Siamese network
Lei FU1( ),Wen-bin GU1(
),Wen-bin GU1( ),Yong-bao AI2,Wei LI3,Nan ZHENG1,Liu-yang WANG1
),Yong-bao AI2,Wei LI3,Nan ZHENG1,Liu-yang WANG1
- 1.College of Field Engineering,Army Engineering University of PLA,Nanjing 210007,China
2.National Academy of Defense Science and Technology Innovation,Academy of Military Sciences,Beijing 100071,China
3.93182 PLA Troops,Shenyang 110000,China
CLC Number:
- TP391.41
| 1 | Lu Z, Rathod V, Votel R, et al. Retinatrack: online single stage joint detection and tracking[C]∥Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 14656-14666. |
| 2 | 徐涛, 马克, 刘才华. 基于深度学习的行人多目标跟踪方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2021, 51(1): 27-38. |
| Xu Tao, Ma Ke, Liu Cai-hua. Multi object pedestrian tracking based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(1): 27-38. | |
| 3 | 孟琭, 杨旭. 目标跟踪算法综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(7): 1244-1260. |
| Meng Lu, Yang Xu. A survey of object tracking algorithms[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(7): 1244-1260. | |
| 4 | 苑晶, 李阳, 董星亮, 等. 基于运动模式在线分类的移动机器人目标跟踪[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2017, 38(3): 568-577. |
| Yuan Jing, Li Yang, Dong Xing-liang, et al. Target tracking with a mobile robot based on online classification for motion patterns[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2017, 38(3): 568-577. | |
| 5 | Hao J, Zhou Y, Zhang G, et al. A review of target tracking algorithm based on UAV[C]∥Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Cyborg and Bionic Systems, Shenzhen, China, 2018: 328-333. |
| 6 | Zhang X, Ye P, Leung H, et al. Object fusion tracking based on visible and infrared images: a comprehensive review[J]. Information Fusion, 2020, 63: 166-187. |
| 7 | Li C, Wu X, Zhao N, et al. Fusing two-stream convolutional neural networks for RGB-T object tracking[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 281: 78-85. |
| 8 | Zhu Y, Li C, Luo B, et al. Dense feature aggregation and pruning for RGBT tracking[C]∥The 27th ACM International Conference, Nice, France, 2019: 465-472. |
| 9 | Gao Y, Li C, Zhu Y, et al. Deep adaptive fusion network for high performance RGBT tracking[C]∥2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW), Soule, South Korea, 2019: 91-99. |
| 10 | Li C, Lu A, Zheng A, et al. Multi-adapter RGBT tracking[C]∥2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW), Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 2262-2270. |
| 11 | Zhang X C, Ye P, Peng S Y, et al. SiamFT: an RGB-infrared fusion tracking method via fully convolutional Siamese networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7(1): 122122-122133. |
| 12 | 申亚丽. 基于特征融合的RGBT双模态孪生跟踪网络[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2021, 50(3): 20200459. |
| Shen Ya-li. RGBT dual-modal Siamese tracking network with feature fusion[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2021, 50(3): 20200459. | |
| 13 | Xu Y, Wang Z, Li Z, et al. Towards robust and accurate visual tracking with target estimation guidelines[C]∥Association for the Advance of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), New York, USA, 2020: 125491-125565. |
| 14 | Li B, Yan J, Wu W, et al. High performance visual tracking with Siamese region proposal network[C]∥Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, USA, 2017: 8971-8980. |
| 15 | Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]∥Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1106-1164. |
| 16 | Fu J, Liu J, Tian H, et al. Dual attention network for scene segmentation[C]∥Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3146-3154. |
| 17 | François C. Xception: deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions[C]∥Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Hawai, USA, 2017: 1800-1807. |
| 18 | Lin T, Goyal P, Girshick R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(2): 318-327. |
| 19 | Yu J, Jiang Y, Wang Z, et al. UnitBox: an advanced object detection network[C]∥ACM international conference on Multimedia, Amsterdam, Netherlands. 2016: 516-520. |
| 20 | Li C, Hui C, Hu S, et al. Learning collaborative sparse representation for grayscale-thermal tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(12): 5743-5756. |
| 21 | Li C, Liang X, Lu Y, et al. RGB-T object tracking: benchmark and baseline[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019: 96: No. 106977. |
| 22 | Jung I, Son J, Beak M, et al. Real-time MDNet[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 89-104. |
| 23 | Zhang Z, Peng H. Deeper and wider Siamese networks for real-time visual tracking[C]∥Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 4591-4600. |
| [1] | Xian-yu QI,Wei WANG,Lin WANG,Yu-fei ZHAO,Yan-peng DONG. Semantic topological map building with object semantic grid map [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 569-575. |
| [2] | Xiao-hu SHI,Jia-qi WU,Chun-guo WU,Shi CHENG,Xiao-hui WENG,Zhi-yong CHANG. Residual network based curve enhanced lane detection method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 584-592. |
| [3] | Peng GUO,Wen-chao ZHAO,Kun LEI. Dual⁃resource constrained flexible job shop optimal scheduling based on an improved Jaya algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 480-487. |
| [4] | Jin-Zhen Liu,Guo-Hui Gao,Hui Xiong. Multi⁃scale attention network for brain tissue segmentation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 576-583. |
| [5] | Gui-he QIN,Jun-feng HUANG,Ming-hui SUN. Text input based on two⁃handed keyboard in virtual environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1881-1888. |
| [6] | Fu-heng QU,Tian-yu DING,Yang LU,Yong YANG,Ya-ting HU. Fast image codeword search algorithm based on neighborhood similarity [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1865-1871. |
| [7] | Tian BAI,Ming-wei XU,Si-ming LIU,Ji-an ZHANG,Zhe WANG. Dispute focus identification of pleading text based on deep neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [8] | Feng-feng ZHOU,Hai-yang ZHU. SEE: sense EEG⁃based emotion algorithm via three⁃step feature selection strategy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1834-1841. |
| [9] | Feng-feng ZHOU,Yi-chi ZHANG. Unsupervised feature engineering algorithm BioSAE based on sparse autoencoder [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1645-1656. |
| [10] | Jun WANG,Yan-hui XU,Li LI. Data fusion privacy protection method with low energy consumption and integrity verification [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1657-1665. |
| [11] | Yao-long KANG,Li-lu FENG,Jing-an ZHANG,Fu CHEN. Outlier mining algorithm for high dimensional categorical data streams based on spectral clustering [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1422-1427. |
| [12] | Wen-jun WANG,Yin-feng YU. Automatic completion algorithm for missing links in nowledge graph considering data sparsity [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1428-1433. |
| [13] | Xue-yun CHEN,Xue-yu BEI,Qu YAO,Xin JIN. Pedestrian segmentation and detection in multi-scene based on G-UNet [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(4): 925-933. |
| [14] | Shi-min FANG. Multiple source data selective integration algorithm based on frequent pattern tree [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(4): 885-890. |
| [15] | Da-xiang LI,Meng-si CHEN,Ying LIU. Spontaneous micro-expression recognition based on STA-LSTM [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(4): 897-909. |
|