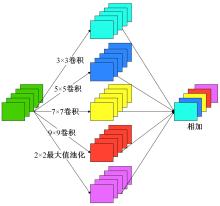
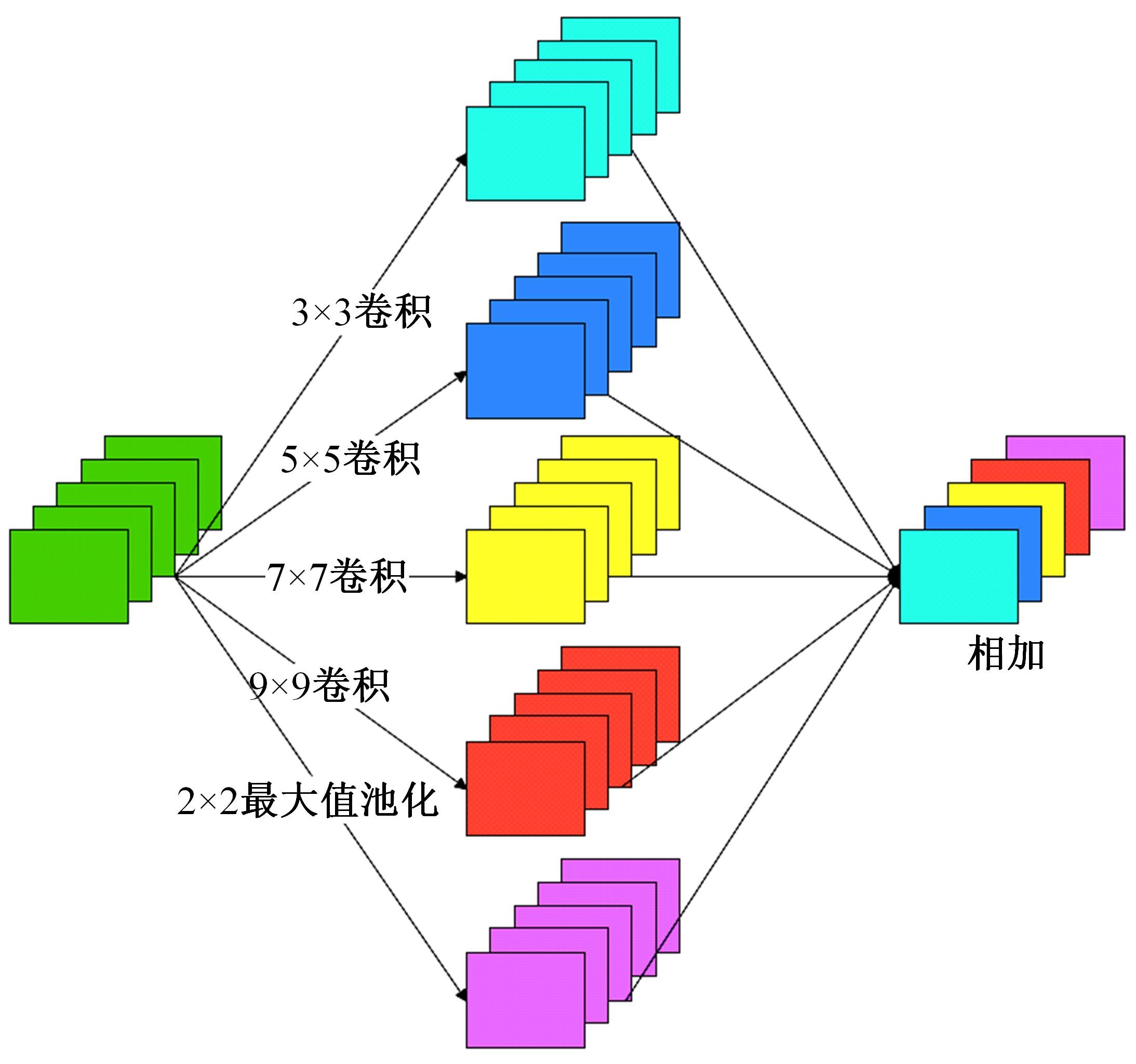
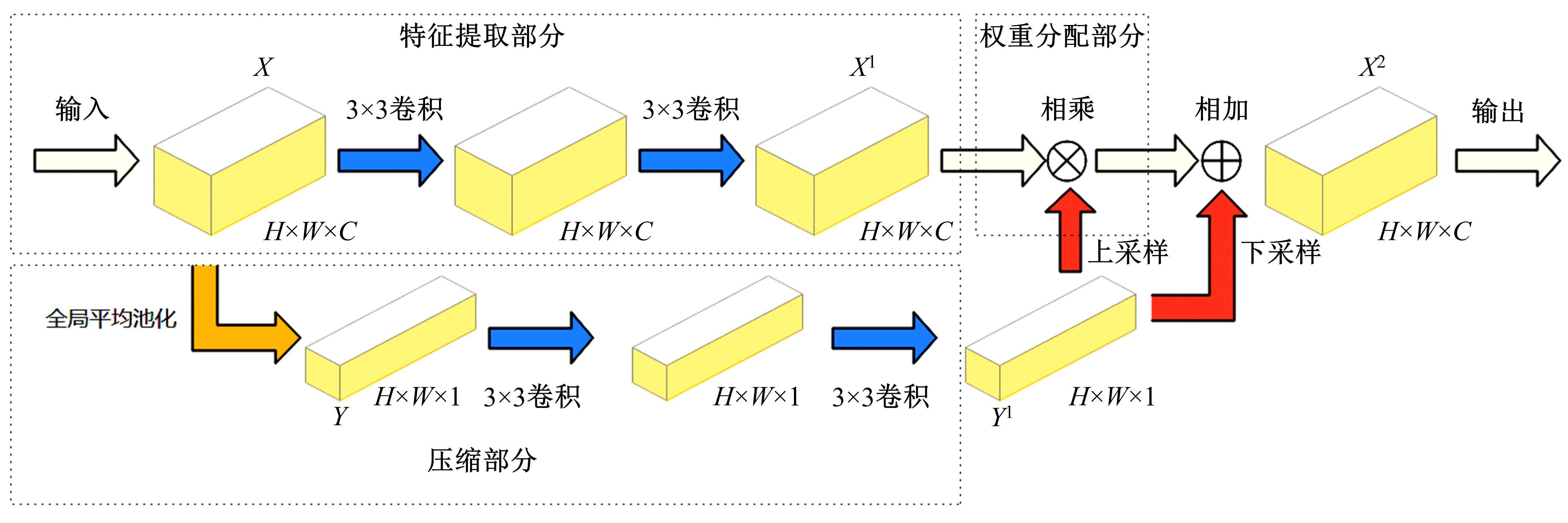
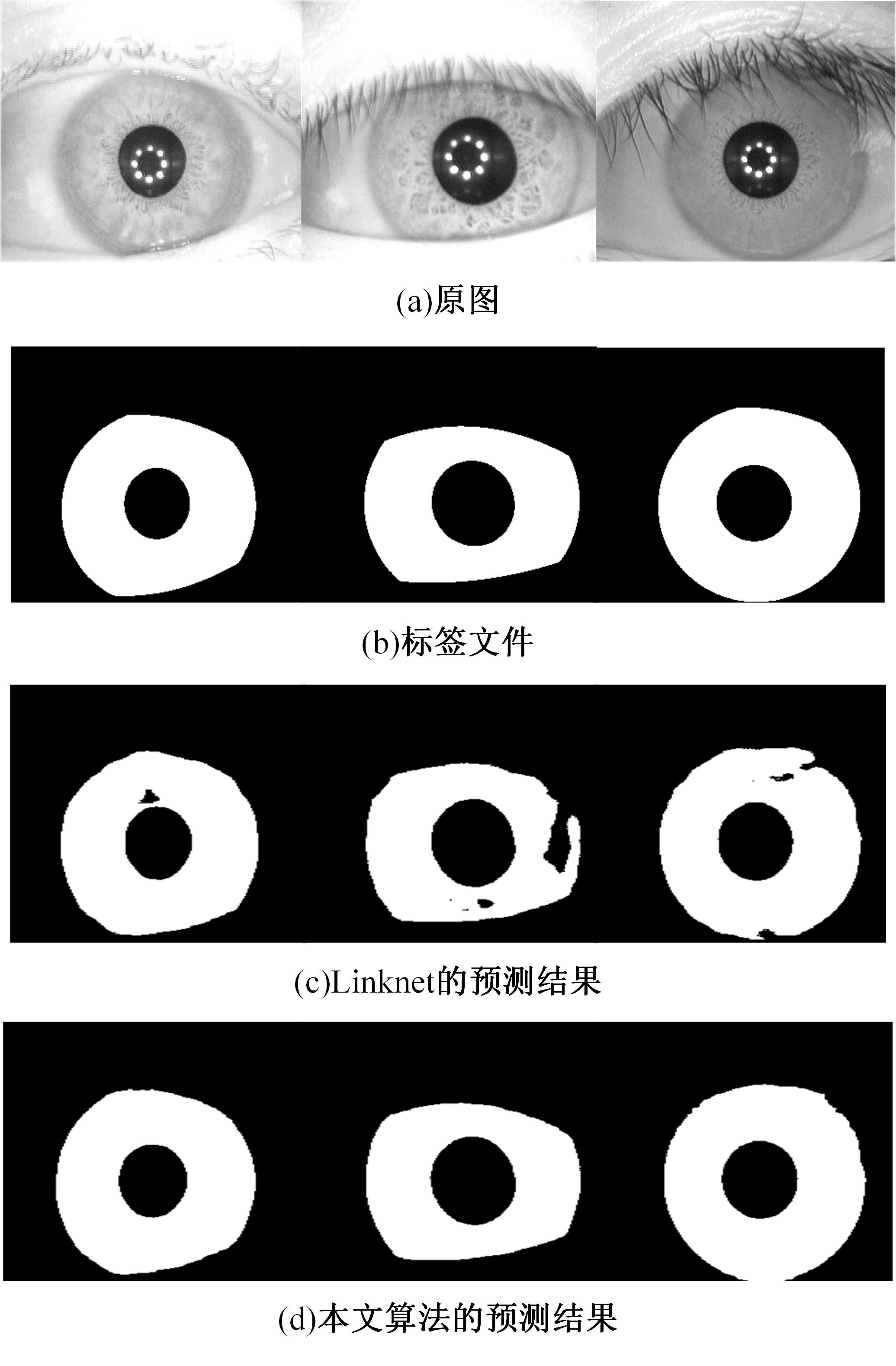
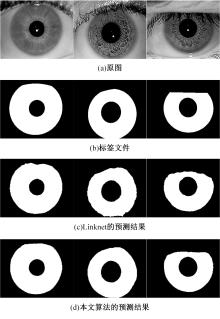
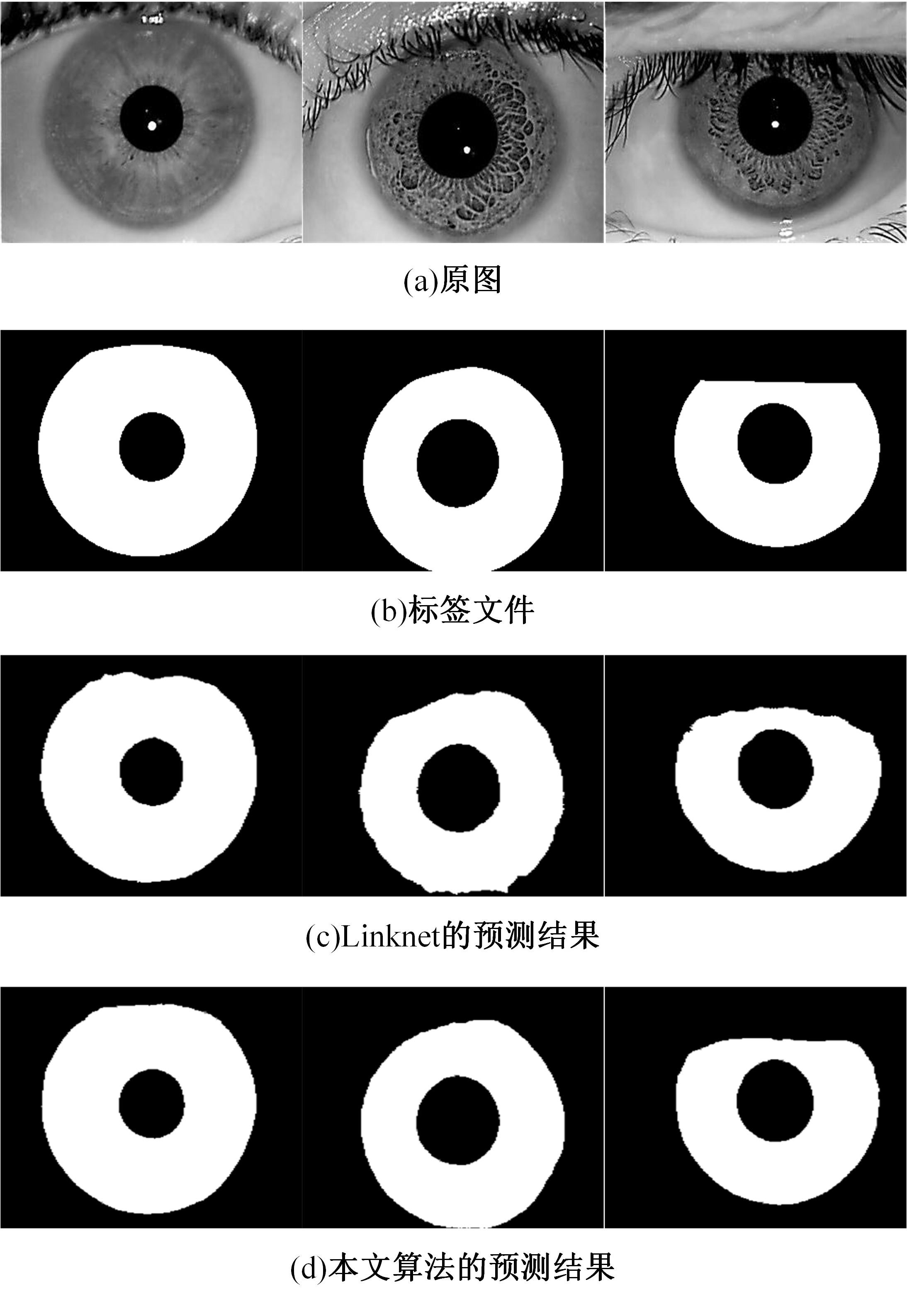
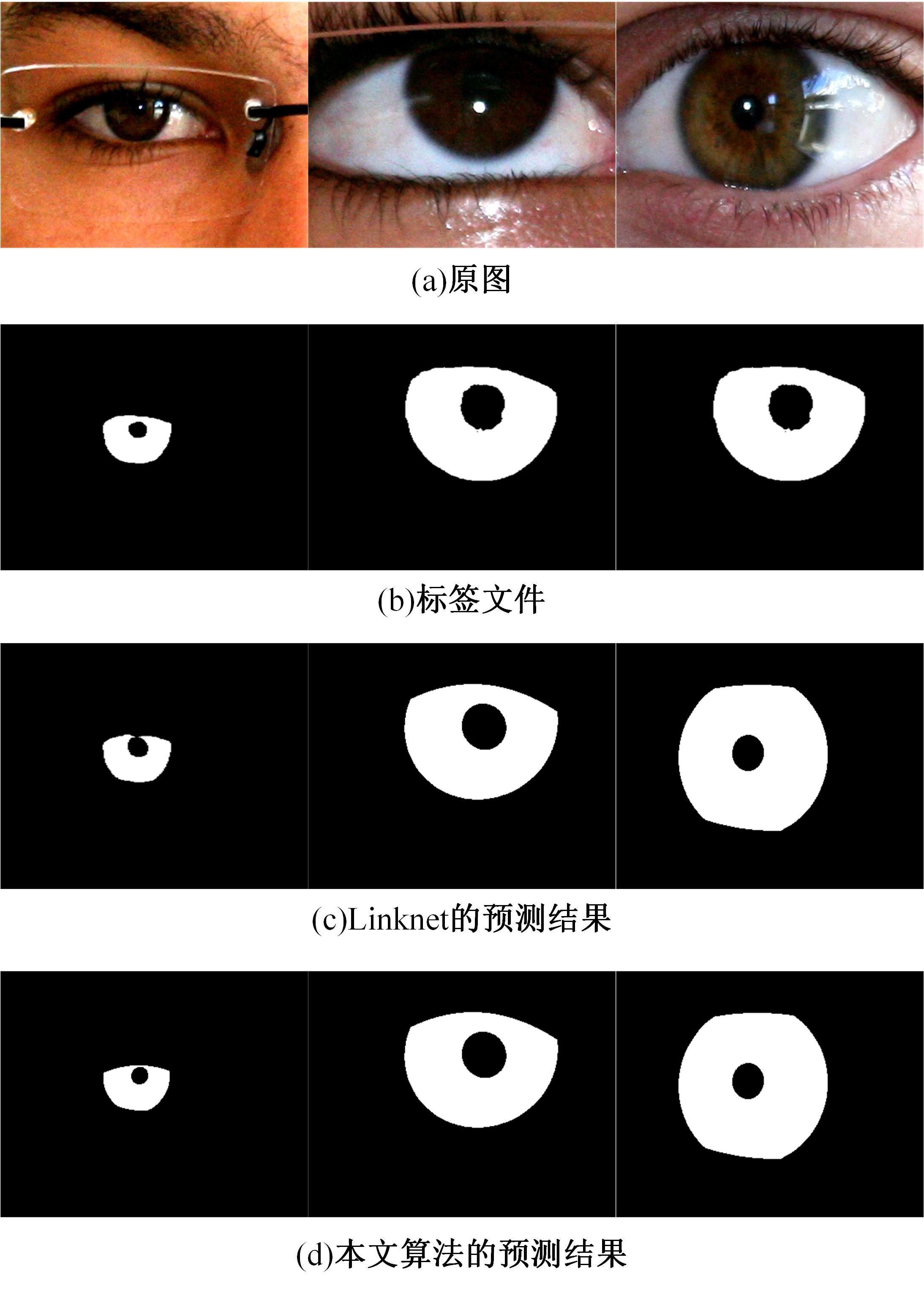
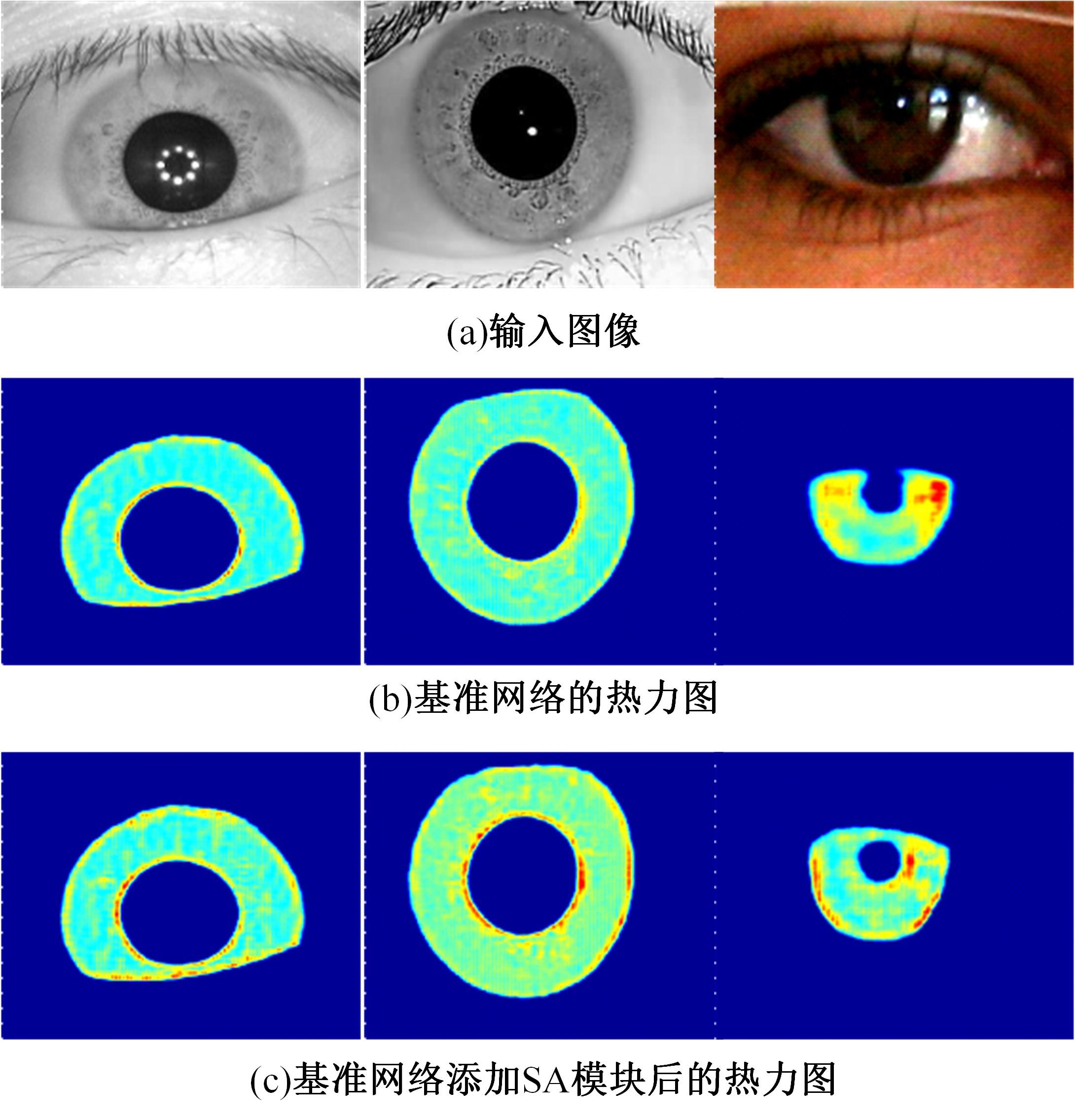
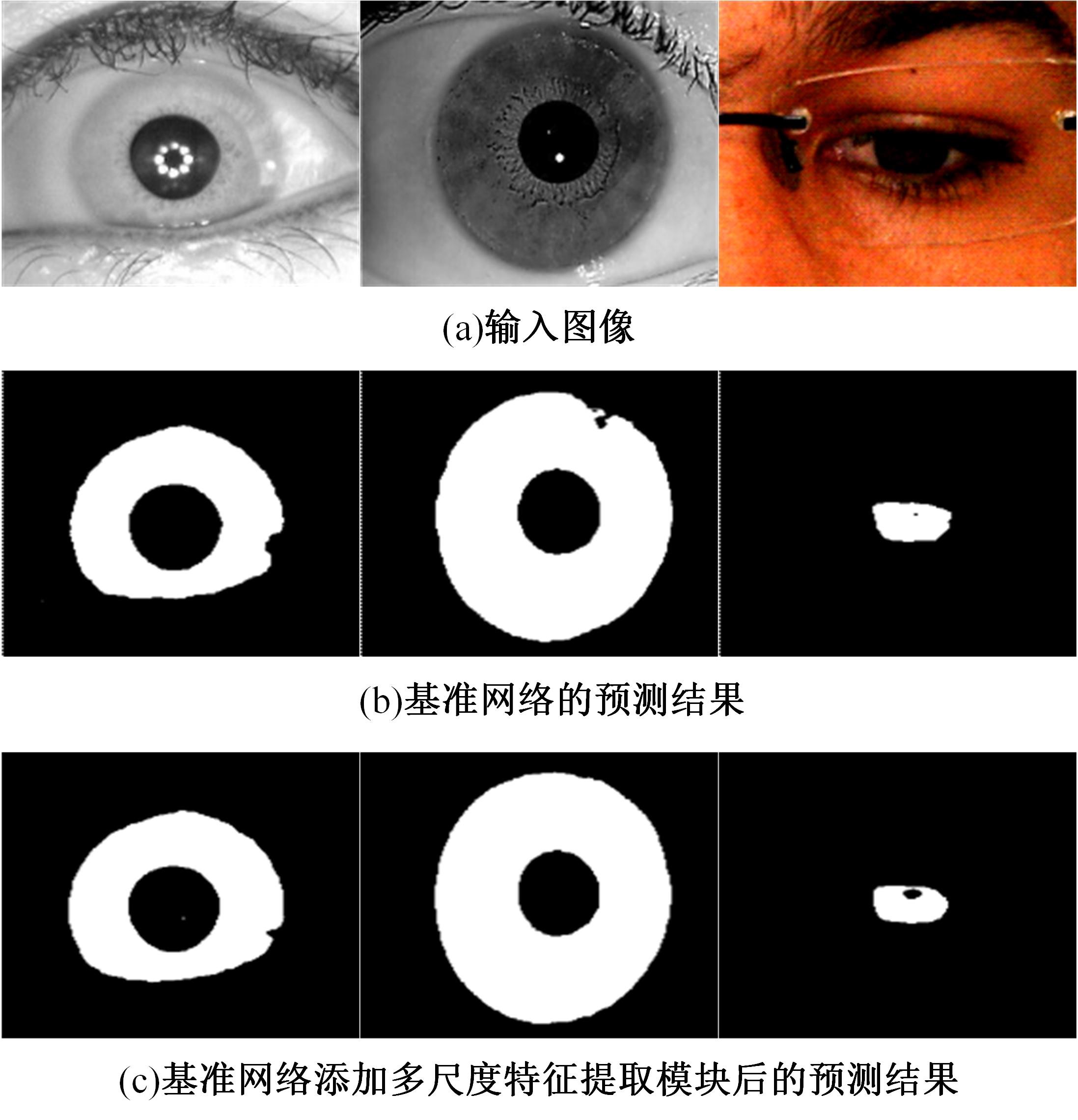
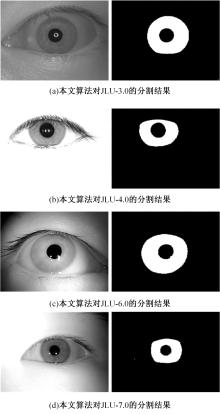
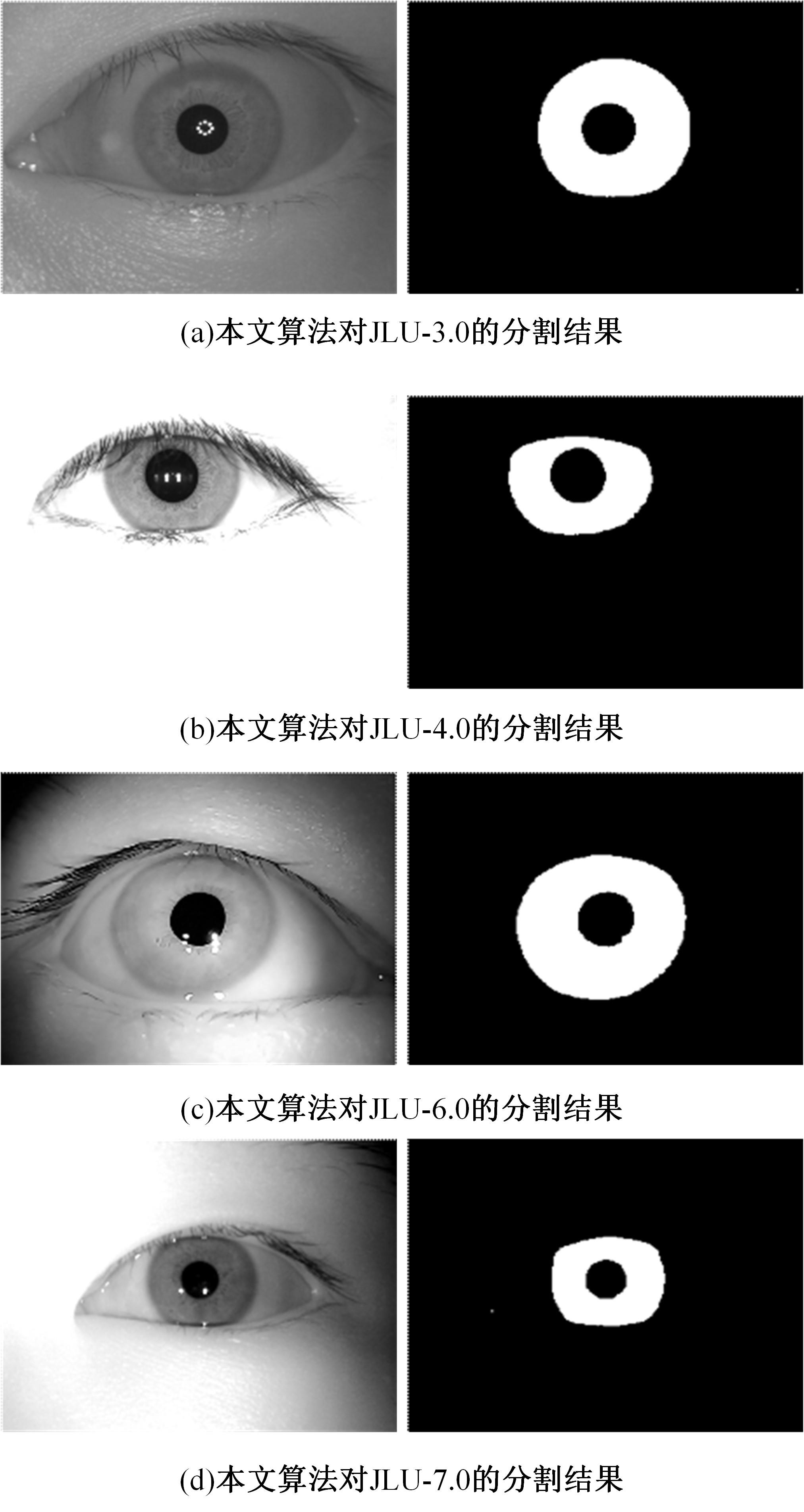
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (9): 2591-2600.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220044
Previous Articles Next Articles
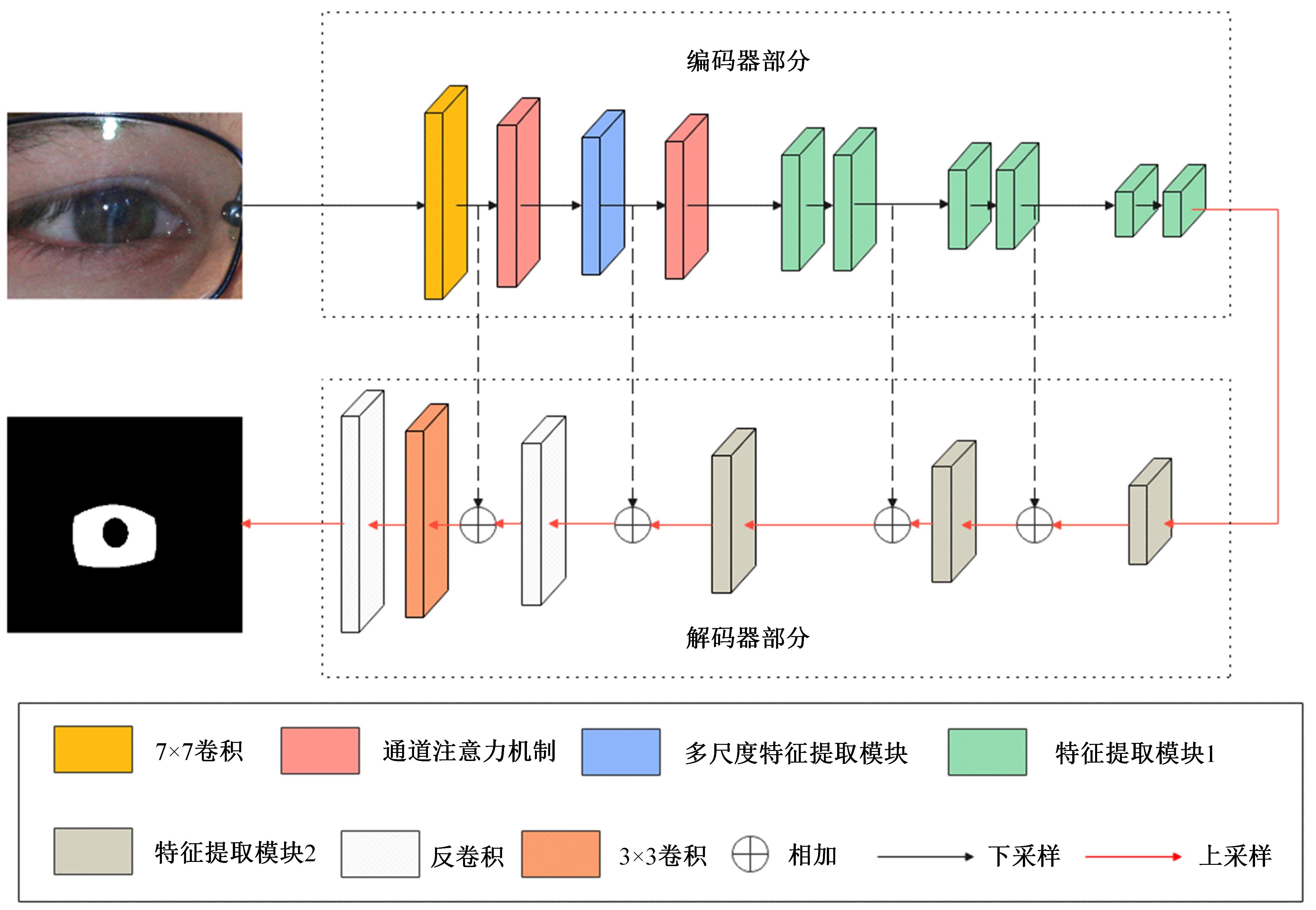
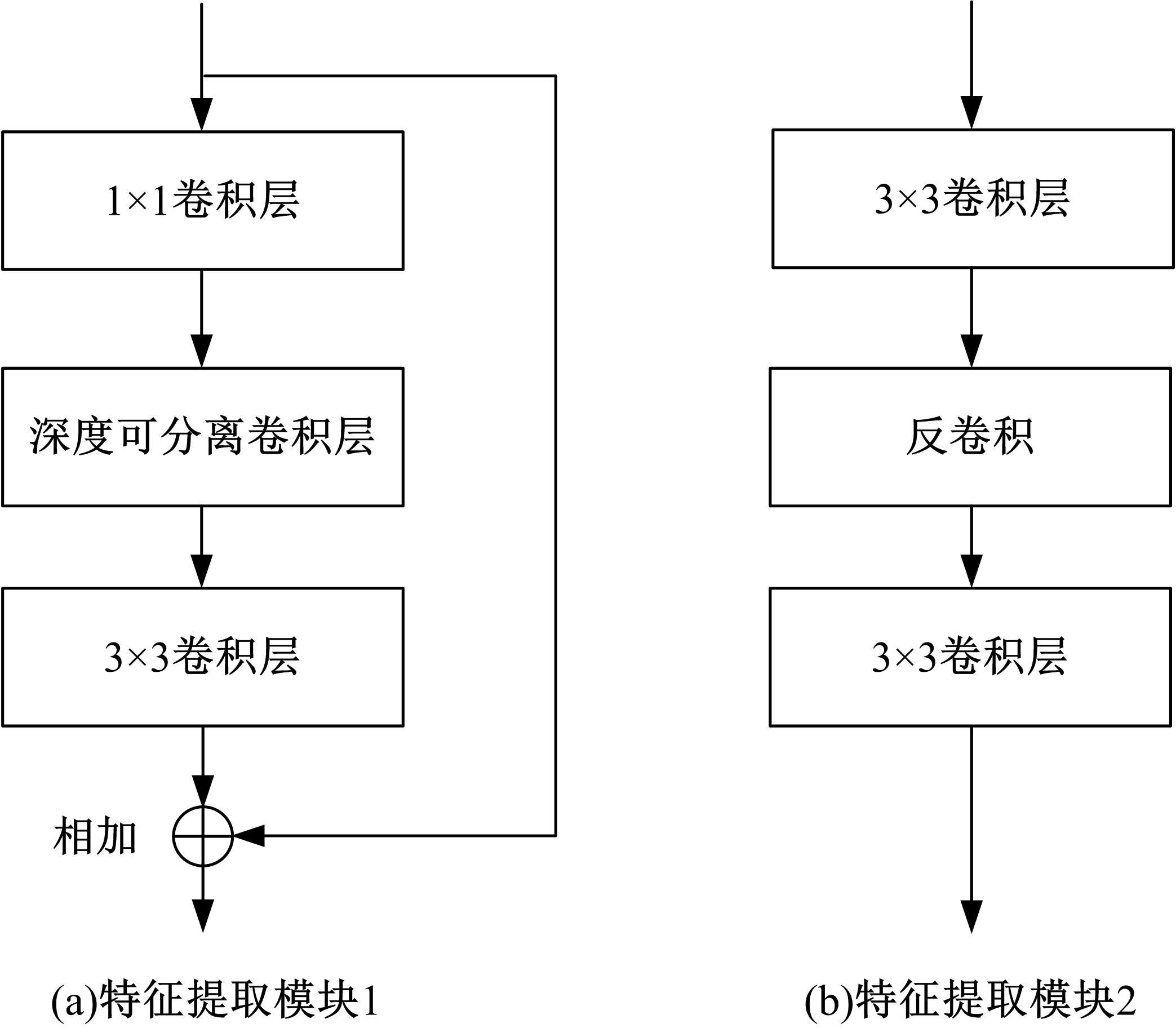
Lightweight iris segmentation model based on multiscale feature and attention mechanism
Guang HUO1( ),Da-wei LIN1,Yuan-ning LIU2,3(
),Da-wei LIN1,Yuan-ning LIU2,3( ),Xiao-dong ZHU2,3,Meng YUAN2,Di GAI4
),Xiao-dong ZHU2,3,Meng YUAN2,Di GAI4
- 1.College of Computer Science,Northeast Electric Power University,Jilin 132012,China
2.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
3.Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
4.School of Software,Nanchang University,Nanchang 330047,China
CLC Number:
- TP391.41
| 1 | Arsalan M, Naqvi R A, Kim D S, et al. IrisDenseNet: robust iris segmentation using densely connected fully convolutional networks in the images by visible light and near-infrared light camera sensors[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(5): No.1501. |
| 2 | Huo Guang, Lin Da-wei, Yuan Meng, et al. Heterogeneous iris segmentation method based on modified U-Net[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2021, 30(6): No.063015. |
| 3 | Umer S, Dhara B C. A fast iris localization using inversion transform and restricted circular hough transform[C]∥Proceedings of the 2015 8th International Conference on Advances in Pattern Recognition, Kolkata, India, 2015: 1-6. |
| 4 | Bendale A, Nigam A, Prakash S, et al. Iris segmentation using improved hough transform[C]∥Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Huangshan, China, 2012: 408-415. |
| 5 | Roy D A, Soni U S. IRIS segmentation using Daughman's method[C]∥Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, and Optimization Techniques, Chennai, India, 2016: 2668-2676. |
| 6 | 周锐烨, 沈文忠. PI-Unet: 异质虹膜精确分割神经网络模型的研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2021, 57(15): 223-229. |
| Zhou Rui-ye, Shen Wen-zhong. PI-Unet: research on precise iris segmentation neural network model for heterogeneous iris[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2021, 57(15): 223-229. | |
| 7 | Shelhamer E, Long J, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(4): 640-651. |
| 8 | Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234-241. |
| 9 | Chaurasia A, Culurciello E. LinkNet: exploiting encoder representations for efficient semantic segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing, Petersburg, USA, 2017: 1-4 |
| 10 | Chen Ying, Wang Wen-yuan, Zeng Zhuang, et al. An adaptive CNNs technology for robust iris segmentation[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 64517-64532. |
| 11 | Wang Cai-yong, Wang Yun-long, Xu Bo-qiang, et al. A lightweight multi-label segmentation network for mobile iris biometrics[C]∥Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Barcelona, Spain, 2020: 1006-1010. |
| 12 | Zhong Z L, Lin Z, Bidart R, et al. Squeeze-and-attention networks for semantic segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 13062-13071. |
| 13 | Biometrics ideal test. CASIA.v4 Database[DB/OL]. [2022-01-06]. |
| 14 | Kumar A, Passi A. Comparison and combination of iris matchers for reliable personal authentication[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2010, 43(3): 1016-1026. |
| 15 | Proena H, Filipe S, Santos R, et al. The UBIRIS.v2: a database of visible wavelength iris images captured on-the-move and at-a-distance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(8): 1529-1535. |
| 16 | Milletari F, Navab N, Ahmadi S A. V-Net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the 2016 4th International Conference on 3D Vision, Stanford, USA, 2016: 565-571. |
| 17 | Rathgeb C. Iris Biometrics from Segmentation to Template Security[M]. Iris Biometrics: From Segmentation to Template Security, 2012. |
| 18 | Wild P, Hofbauer H, Ferryman J, et al. Segmentation-level fusion for iris recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference of the Biometrics Special Interest Group, Darmstadt, Germany, 2015: 1-6. |
| 19 | Uhl A, Wild P. Weighted adaptive hough and ellipsopolar transforms for real-time iris segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the 2012 5th IAPR International Conference on Biometrics, New Delhi, India, 2012: 283-290. |
| 20 | A biometric reference system for iris, ersion osiris V 4.1[EB/OL]. [2022-01-06]. |
| 21 | Uhl A, Wild P. Multi-stage visible wavelength and near infrared iris segmentation framework[C]∥Proceedings of the International Conference Image Analysis and Recognition, Aveiro, Portugal, 2012: 1-10. |
| 22 | Ahmad S, Fuller B. Unconstrained iris segmentation using convolutional neural networks[C]∥Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Perth, Australia, 2018: 450-466. |
| 23 | Alonsofern J O. Iris boundaries segmentation using the generalized structure tensor—a study on the effects of image degradation[C]∥Proceedings of the 2012 5th IEEE International Conference on Biometrics: Theory, Applications and Systems, Arlington, USA, 2012: 426-431. |
| 24 | Ehsaneddin J, Andreas U. Iris segmentation using fully convolutional encoder-decoder Networks[C]∥Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New York, USA, 2017: 133-155. |
| 25 | 尤轩昂, 赵鹏, 慕晓冬, 等. 融合注意力机制与密集多尺度特征的异质噪声虹膜分割方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2022, 59(4): 109-120 |
| You Xuan-ang, Zhao Peng, Mu Xiao-dong, et al. Heterogeneous noise iris segmentation based on attention mechanism and dense multi-scale features[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(4): 109-120. | |
| 26 | Lozej J, Meden B, Struc V, et al. End-to-end iris segmentation using U-Net[C]∥Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Work Conference on Bioinspired Intelligence,San Carlos, Costa Rica, 2018: 1-6. |
| 27 | Zhang Wei, Lu Xiao-qi, Gu Yu, et al. A robust iris segmentation scheme based on improved U-Net[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 85082-85089. |
| 28 | Wang Qi, Meng Xiang-yue, Sun Ting, et al. A light iris segmentation network[J]. The Visual Computer, 2021, 38: 2591-2601. |
| 29 | He Kai-ming, Zhang Xiang-yu, Ren Shao-qiang, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| [1] | Ying HE,Zhuo-ran WANG,Xu ZHOU,Yan-heng LIU. Point of interest recommendation algorithm integrating social geographical information based on weighted matrix factorization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2632-2639. |
| [2] | Yun-zuo ZHANG,Xu DONG,Zhao-quan CAI. Multi view gait cycle detection by fitting geometric features of lower limbs [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2611-2619. |
| [3] | Ming-yao XIAO,Xiong-fei LI,Rui ZHU. Medical image fusion based on pixel correlation analysis in NSST domain [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2640-2648. |
| [4] | Ya-hui ZHAO,Fei-yu LI,Rong-yi CUI,Guo-zhe JIN,Zhen-guo ZHANG,De LI,Xiao-feng JIN. Korean⁃Chinese translation quality estimation based on cross⁃lingual pretraining model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2371-2379. |
| [5] | Xiao-xin GUO,Jia-hui LI,Bao-liang ZHANG. Joint segmentation of optic cup and disc based on high resolution network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2350-2357. |
| [6] | Xiao-jun JIN,Yan-xia SUN,Jia-lin YU,Yong CHEN. Weed recognition in vegetable at seedling stage based on deep learning and image processing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2421-2429. |
| [7] | Xiang-jiu CHE,Huan XU,Ming-yang PAN,Quan-le LIU. Two-stage learning algorithm for biomedical named entity recognition [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2380-2387. |
| [8] | Qing-tian GENG,Zhi LIU,Qing-liang LI,Fan-hua YU,Xiao-ning LI. Prediction of soil moisture based on a deep learning model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2430-2436. |
| [9] | Lian-ming WANG,Xin WU. Method for 3D motion parameter measurement based on pose estimation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 2099-2108. |
| [10] | Wei-tiao WU,Kun ZENG,Wei ZHOU,Peng LI,Wen-zhou JIN. Deep learning method for bus passenger flow prediction based on multi-source data and surrogate-based optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 2001-2015. |
| [11] | Fei-fei TANG,Hai-lian ZHOU,Tian-jun TANG,Hong-zhou ZHU,Yong WEN. Multi⁃step prediction method of landslide displacement based on fusion dynamic and static variables [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1833-1841. |
| [12] | Pei-yong LIU,Jie DONG,Luo-feng XIE,Yang-yang ZHU,Guo-fu YIN. Surface defect detection algorithm of magnetic tiles based on multi⁃branch convolutional neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1449-1457. |
| [13] | Zhen-hai ZHANG,Kun JI,Jian-wu DANG. Crack identification method for bridge based on BCEM model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1418-1426. |
| [14] | Ze-qiang ZHANG,Wei LIANG,Meng-ke XIE,Hong-bin ZHENG. Elite differential evolution algorithm for mixed⁃model two⁃side disassembly line balancing problem [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1297-1304. |
| [15] | Yan-tao TIAN,Xing HUANG,Hui-qiu LU,Kai-ge WANG,Fu-qiang XU. Multi⁃mode behavior trajectory prediction of surrounding vehicle based on attention and depth interaction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1474-1480. |
|