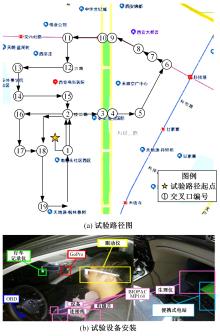
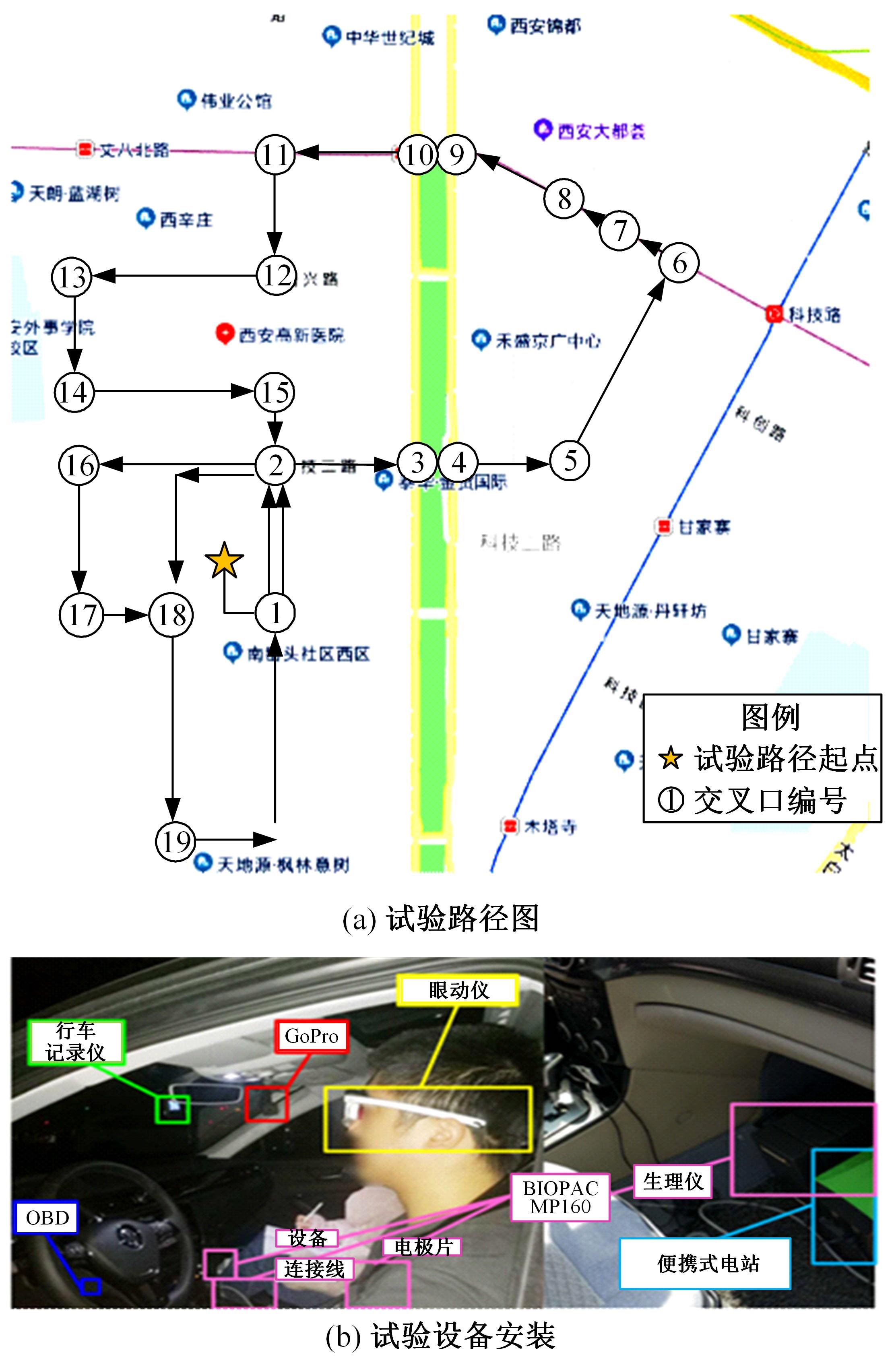
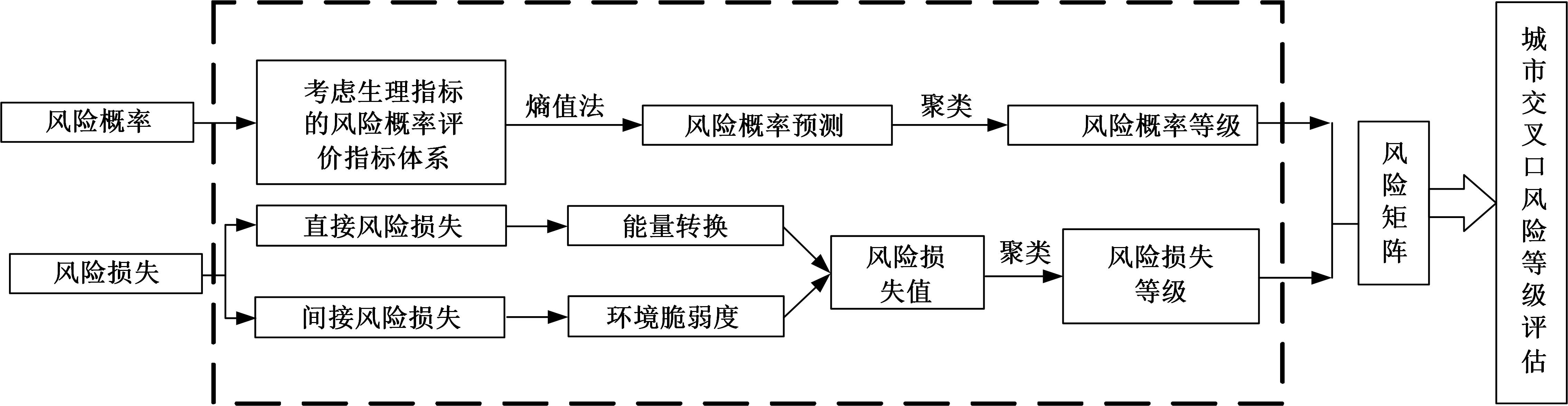
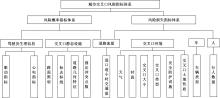
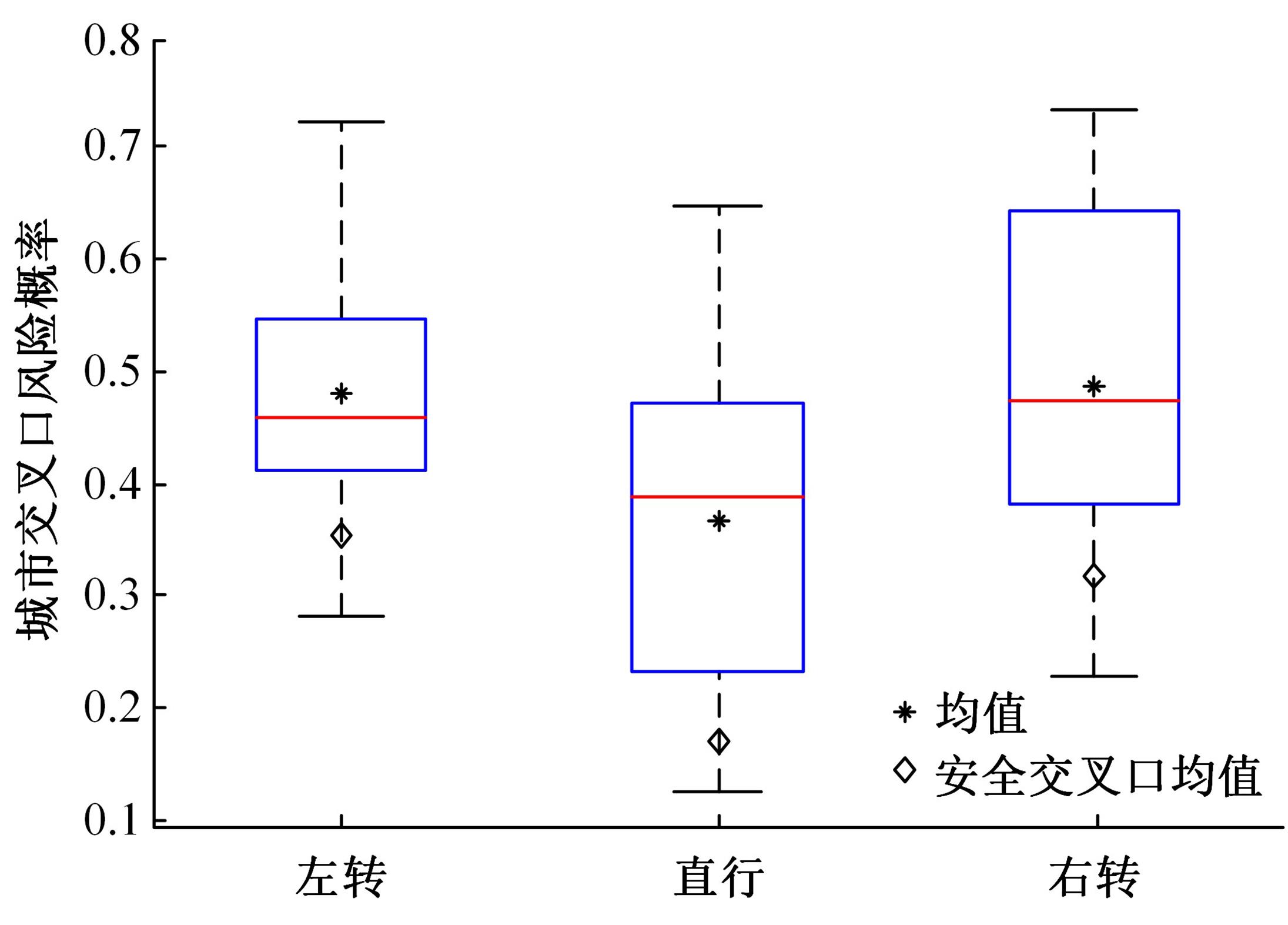
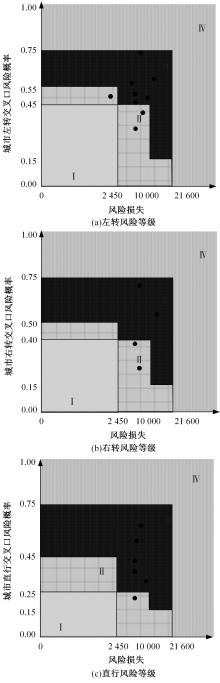
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (5): 1277-1284.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220755
A risk evaluation method for urban intersections considering drivers' physiological information
Gui-zhen CHEN1( ),Hui-ting CHENG2,Cai-hua ZHU1,Yu-ran LI1,Yan LI1(
),Hui-ting CHENG2,Cai-hua ZHU1,Yu-ran LI1,Yan LI1( )
)
- 1.College of Transportation Engineering,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
2.School of Rail Transportation,Chongqing Vocational College of Transportation,Chongqing 402247,China
CLC Number:
- U491
| 1 | Laureshyn A, Ceunynck T D, Karlsson C, et al. In search of the severity dimension of traffic events: extended Delta-V as a traffic conflict indicator[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2017, 98(1):46-56. |
| 2 | 朱彤,秦丹,董傲然,等.公交车驾驶人历史违规数据与事故责任的随机参数模型研究[J].安全与环境学报,2021,21(4):1566-1572. |
| Zhu Tong, Qin Dan, Dong Ao-ran, et al. Investigation on the random parameter model of bus drivers' history violation data and accident liability[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2021,21(4):1566-1572. | |
| 3 | Khattak A J, Khattak A J, Council F M. Effects of work zone presence on injury and non-injury crashes [J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2002, 34(1): 19-29. |
| 4 | 潘恒彦,王永岗,李德林,等.基于交通冲突的长纵坡路段追尾风险评估及预测 [J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2023, 53(5): 1355-1363. |
| Pan Heng-yan, Wang Yong-gang, Li De-lin, et al. Evaluating and forecasting rear-end collision risk of long longitudinal gradient roadway via traffic conflict[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5):1355-1363. | |
| 5 | Hirose T, Takada T, Oikawa S, et al. Validation of driver support system based on real-world bicycle and motor vehicle flows[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2021, 156(9): 106131. |
| 6 | 马艳丽, 祁首铭, 吴昊天, 等. 基于PET算法的匝道合流区交通冲突识别模型 [J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2018, 18(2): 142-148. |
| Ma Yan-li, Qi Shou-ming, Wu Hao-tian, et al. Traffic conflict identification model based on post encroachment time algorithm in ramp merging area[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2018, 18(2): 142-148. | |
| 7 | 郭延永, 刘攀, 吴瑶, 等. 基于贝叶斯多元泊松-对数正态分布的交通冲突模型 [J]. 中国公路学报, 2018, 31(1): 101-109. |
| Guo Yan-yong, Liu Pan, Wu Yao,et al. Traffic conflict model based on bayesian multivariate poisson-lognormal normal distribution[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2018, 31(1): 101-109. | |
| 8 | 郭伟伟, 曲昭伟, 王殿海. 交通冲突判别模型[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2011, 41(1): 35-40. |
| Guo Wei-wei, Qu Zhao-wei, Wang Dian-hai. Traffic conflict discrimination model[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2011, 41(1): 35-40. | |
| 9 | Kaye S A, Lewis I, Freeman J. Comparison of self-report and objective measures of driving behavior and road safety: a systematic review[J]. Journal of Safety Research, 2018, 65:141-151. |
| 10 | Minea M, Dumitrescu C M, Costea I M. Advanced e-call support based on non-intrusive driver condition monitoring for connected and autonomous vehicles [J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(24): 82723701. |
| 11 | Quddus A, Zandi A S, Prest L, et al. Using long short term memory and convolutional neural networks for driver drowsiness detection[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2021, 156(1): 106107. |
| 12 | Li Y, Wang F, Ke H, et al. A driver's physiology sensor-based driving risk prediction method for lane-changing process using hidden markov model [J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(12): 26701105. |
| 13 | Patel M, Lal S K L, Kavanagh D, et al. Applying neural network analysis on heart rate variability data to assess driver fatigue[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2011, 38(6): 7235-7242. |
| 14 | Wang J Q, Zheng Y, Li X F, et al. Driving risk assessment using near-crash database through data mining of tree-based model[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2015, 84(11): 54-64. |
| 15 | 刘建蓓, 马小龙, 张志伟,等. 基于心电分析的青藏高原驾驶员疲劳特性[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2016, 16(4): 151-158. |
| Liu Jian-bei, Ma Xiao-long, Zhang Zhi-wei, et al. Fatigue characteristics of driver in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau based on electrocardiogram analysis[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2016, 16(4): 151-158. | |
| 16 | 徐文会, 刘开华, 王丽婷. 使用改进Welch法估计心率变异功率谱分析人体疲劳程度 [J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2016, 33(1): 67-71. |
| Xu Wen-hui, Liu Kai-hua, Wang Li-ting. Estimation of the power spectrum of heart rate variability using improved welch method to analyze the degree of fatigue[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2016, 33(1): 67-71. | |
| 17 | 袁伟, 付锐, 郭应时, 等. 基于视觉特性的驾驶员换道意图识别[J]. 中国公路学报, 2013, 26(4): 132-138. |
| Yuan Wei, Fu Rui, Guo Ying-shi, et al. Drivers lane changing intention identification based on visual characteristics[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2013, 26(4): 132-138. | |
| 18 | 朱才华, 孙晓黎, 李岩. 站点分类下的城市公共自行车交通需求预测 [J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版,2021, 51(2): 531-540. |
| Zhu Cai-hua, Sun Xiao-li, Li Yan. Forecast of urban public bicycle traffic demand by station classification[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2021, 51(2): 531-540. | |
| 19 | 潘福全, 陆键, 项乔君, 等. 公路信号平面交叉口安全服务水平研究 [J]. 东南大学学报:自然科学版, 2008, 38(2): 298-303. |
| Pan Fu-quan, Lu Jian, Xiang Qiao-jun, et al. Level of safety service for highway signalized intersections [J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 38(2): 298-303. | |
| 20 | 张志刚. 道路因素、交通环境与交通事故分析 [J]. 公路交通科技, 2000, 17(6): 56-59. |
| Zhang Zhi-gang. Road conditions, traffic environment and traffic accident analysis[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2000, 17(6): 56-59. |
| [1] | Xiao-hua ZHAO,Chang LIU,Hang QI,Ju-shang OU,Ying YAO,Miao GUO,Hai-yi YANG. Influencing factors and heterogeneity analysis of highway traffic accidents [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 987-995. |
| [2] | Xiu-jian YANG,Xiao-han JIA,Sheng-bin ZHANG. Characteristics of mixed traffic flow taking account effect of dynamics of vehicular platoon [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 947-958. |
| [3] | Bo-song FAN,Chun-fu SHAO. Urban rail transit emergency risk level identification method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 427-435. |
| [4] | Chang-jiang ZHENG,Huan HU,Mu-qing DU. Design of multimodal express delivery network structure considering hub failure [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2304-2311. |
| [5] | Dian-hai WANG,You-wei HU,Zheng-yi CAI,Jia-qi ZENG,Wen-bin YAO. Dynamic road resistance model of intermittent flow on urban roads based on BPR function [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 1951-1961. |
| [6] | Yan-bo LI,Bai-song LIU,Bo-bin YAO,Jun-shuo CHEN,Kai-fa QU,Qi-sheng WU,Jie-ning CAO. Location of electrical changing station of expressway considering stochastic characteristics of road network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1364-1371. |
| [7] | Ying HU,Chun-fu SHAO,Shu-ling WANG,Xi JIANG,Hai-rui SUN. Identification of road riding quality based on shared bike trajectory data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1040-1046. |
| [8] | Rong-han YAO,Wen-tao XU,Wei-wei GUO. Drivers' takeover behavior and intention recognition based on factor and long short⁃term memory [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 758-771. |
| [9] | Zhan-zhong WANG,Ting JIANG,Jing-hai ZHANG. Evaluation of road transportation efficiency based on fuzzy double frontiers network model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 385-395. |
| [10] | Min YANG,Cong-wei ZHANG,Da-wei LI,Chen-xiang MA. Travel satisfaction model for air-rail integration passengers based on Bayesian network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(10): 2839-2846. |
| [11] | Qian CAO,Zhi-hui LI,Peng-fei TAO,Yong-jian MA,Chen-xi YANG. Traffic accident risk assessment method for road network considering risk heterogeneity [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(10): 2817-2825. |
| [12] | Yan-yan QIN,Xiao-qing YANG,Hao WANG. Impacts of CO2 emissions and improving method for connected and automated mixed traffic flow [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(1): 150-158. |
| [13] | Jie-yu ZHU,Yan-li MA. Real-time risk assessment method of multi-vehicle interaction at merging area [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1574-1581. |
| [14] | Hao-nan PENG,Ming-huan TANG,Qi-wen ZHA,Wei-zhong WANG,Wei-da WANG,Chang-le XIANG,Yu-long LIU. Optimization⁃based lane changing trajectory planning approach for autonomous vehicles on two⁃lane road [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(12): 2852-2863. |
| [15] | Yun-juan YAN,Wei-xiong ZHA,Jun-gang SHI,Jian LI. Mixed network equilibrium model with stochastic charging demand [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(1): 136-143. |
|
||