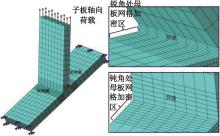
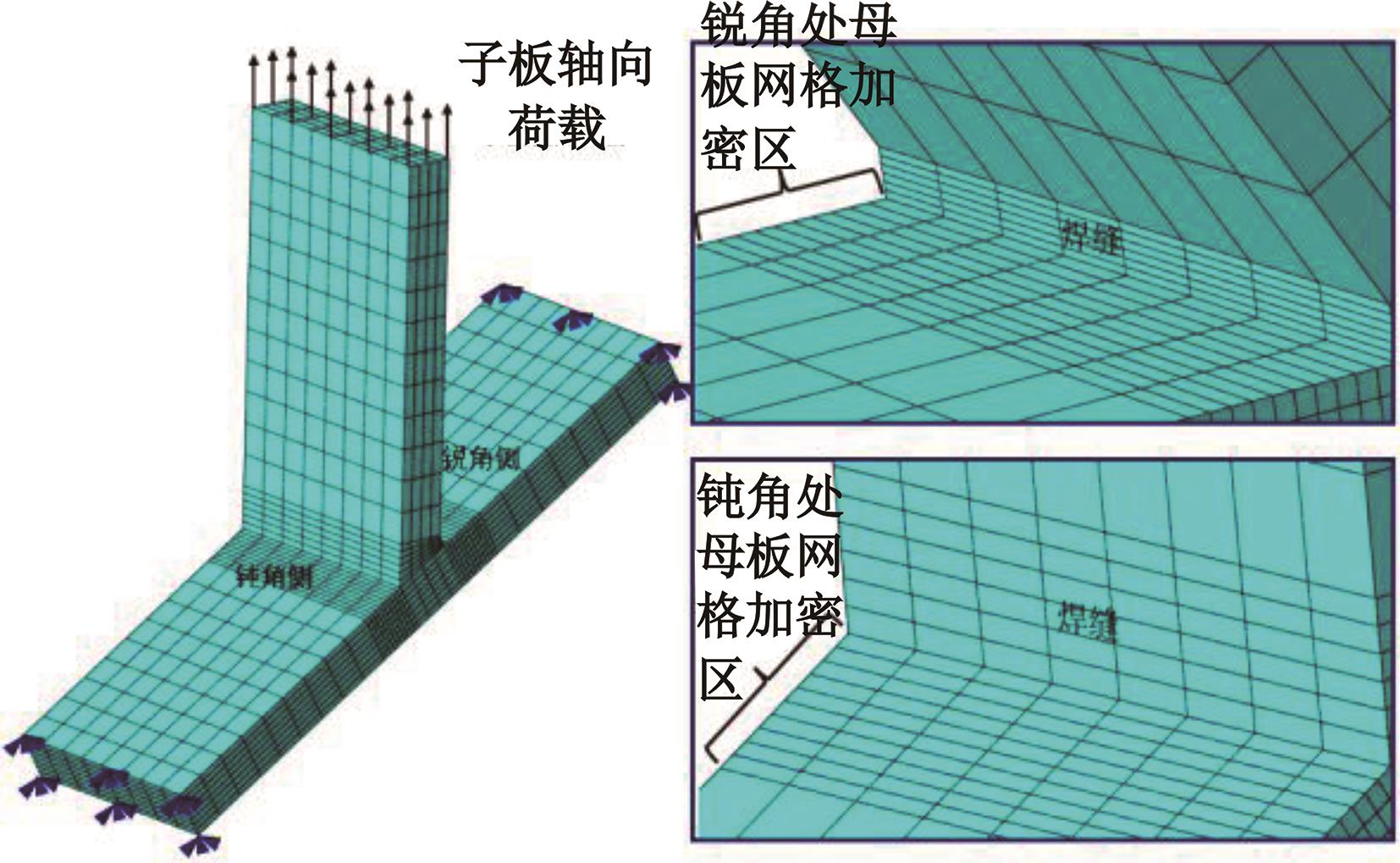
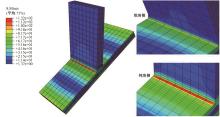
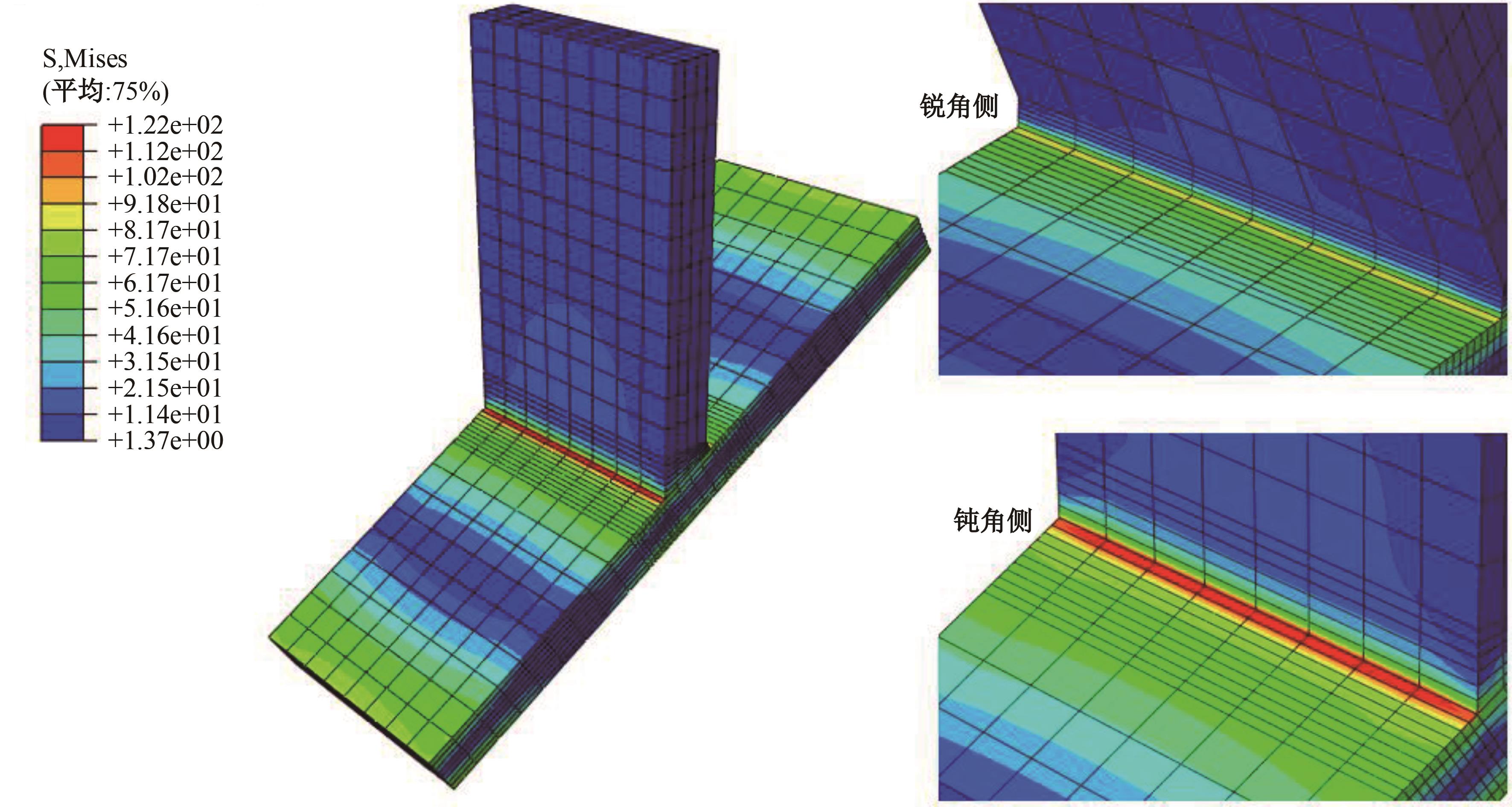
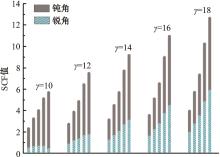
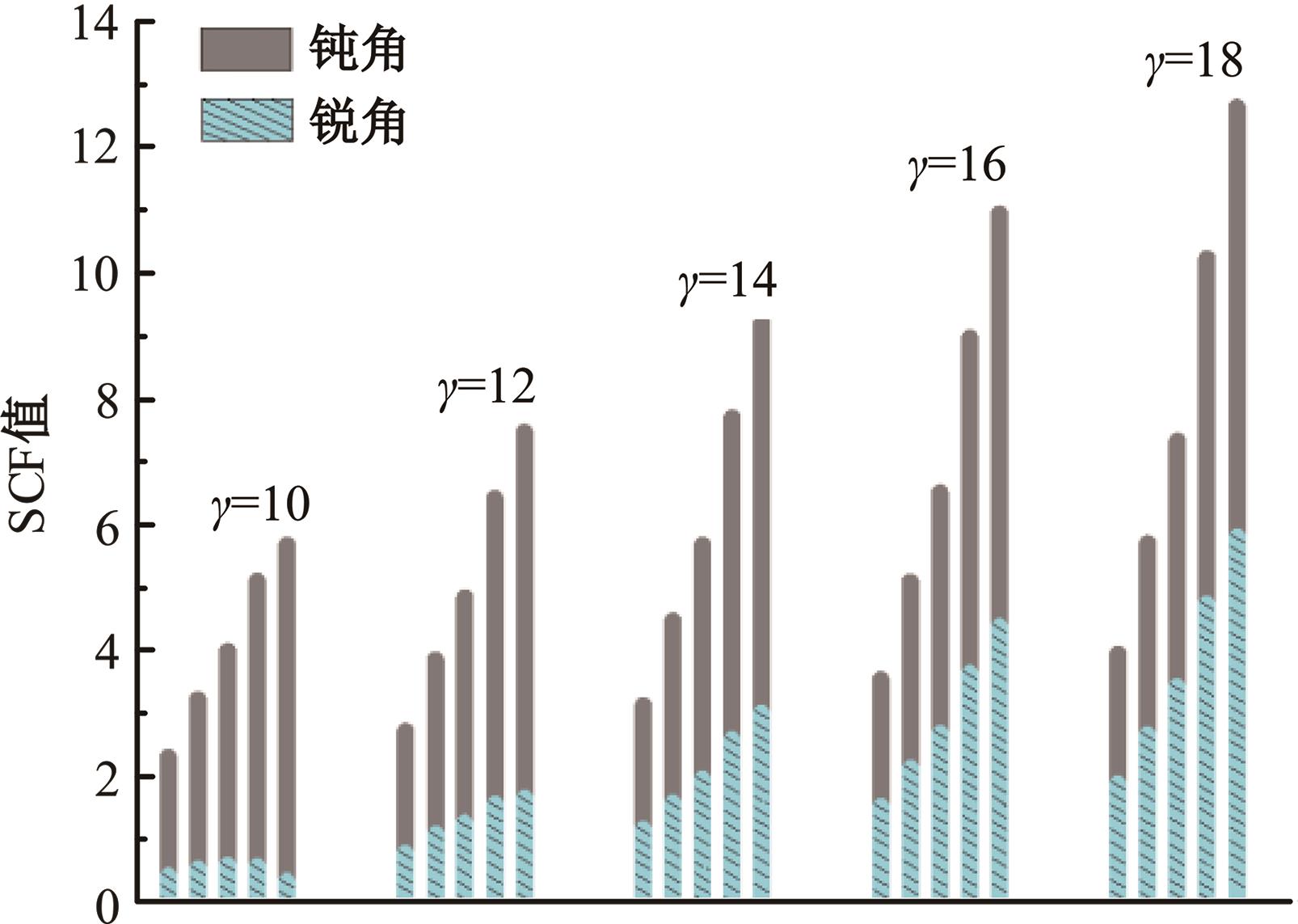
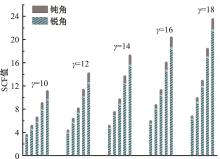
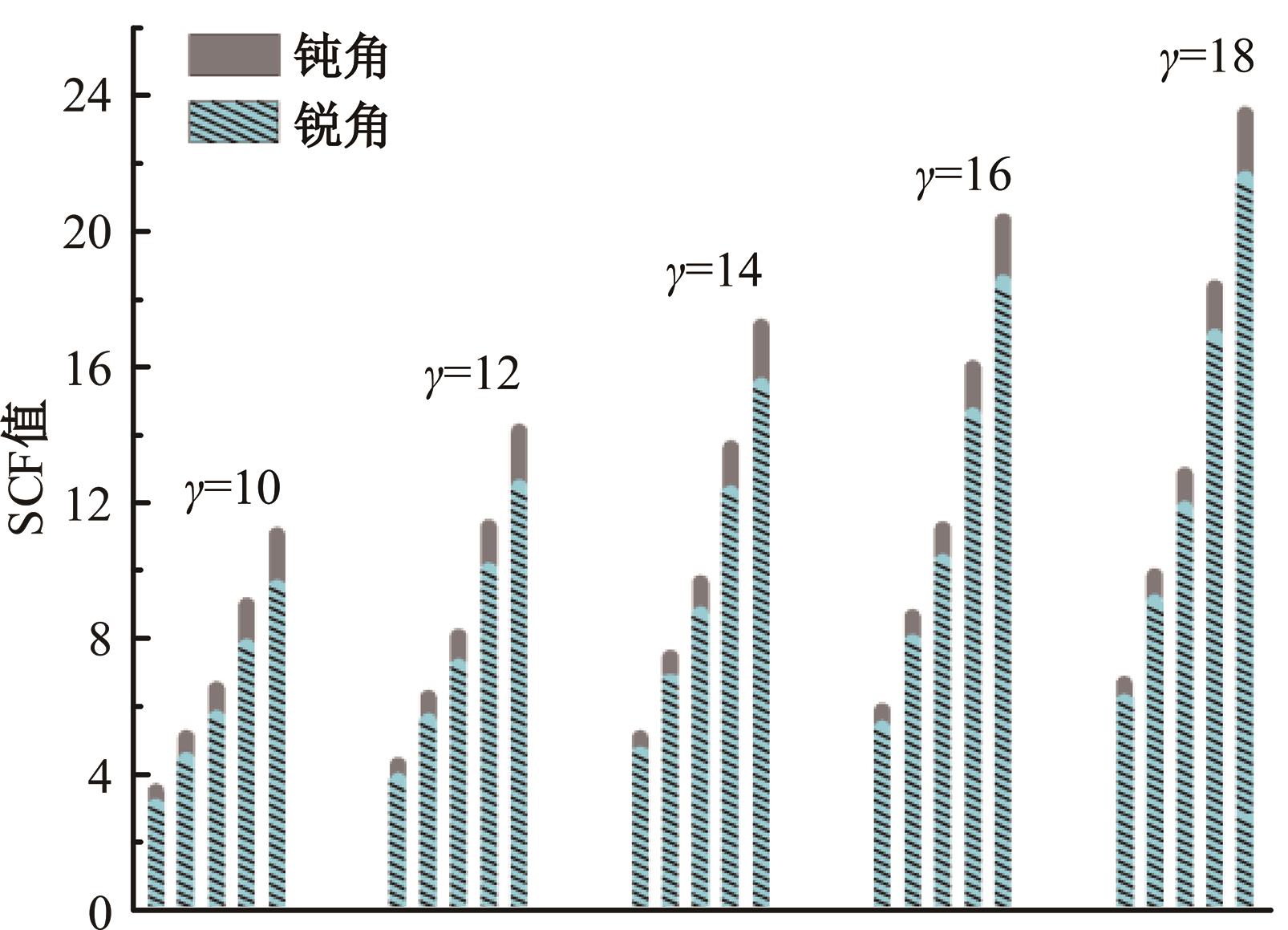
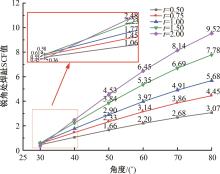
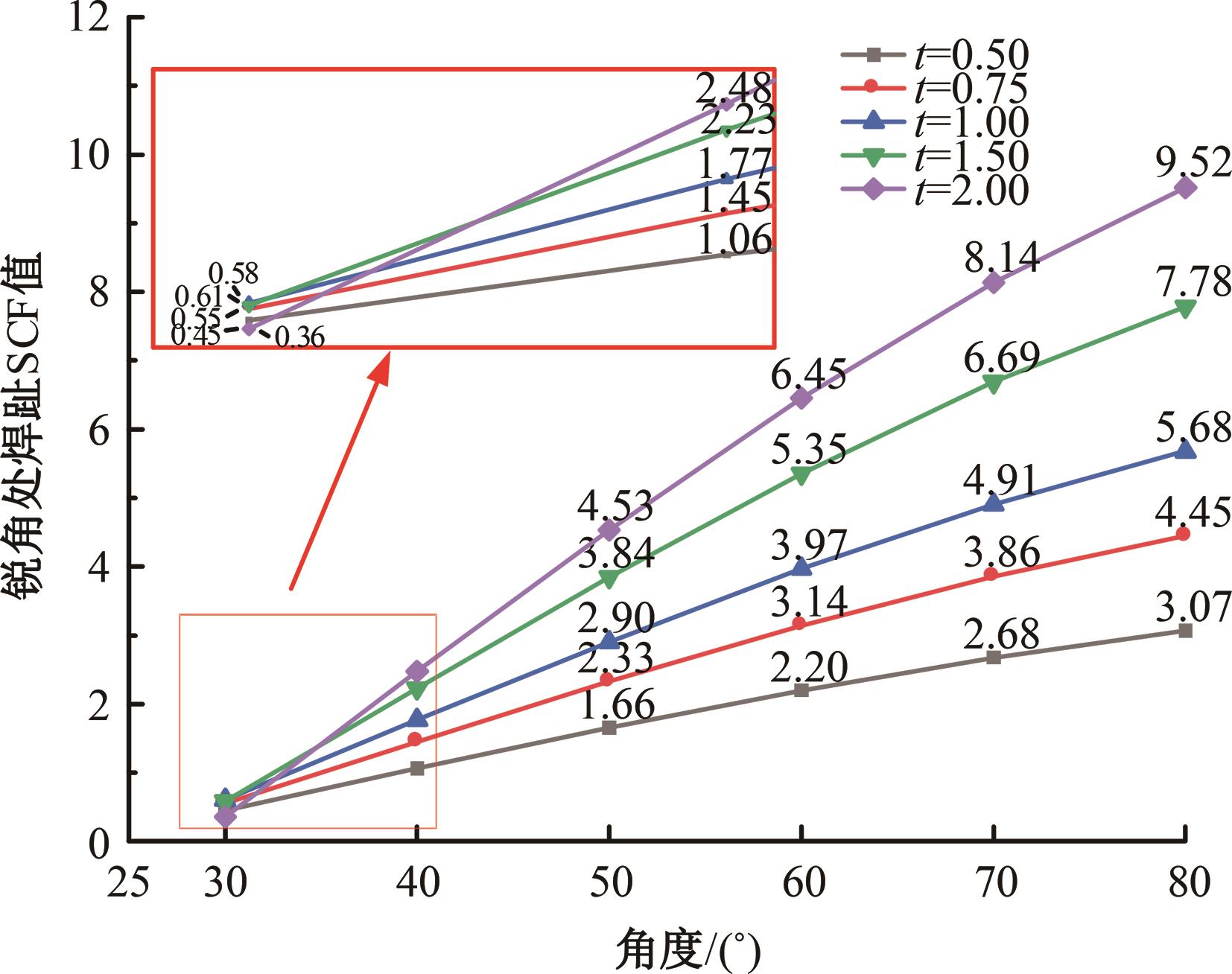
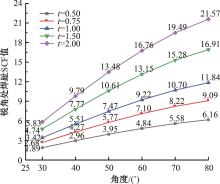
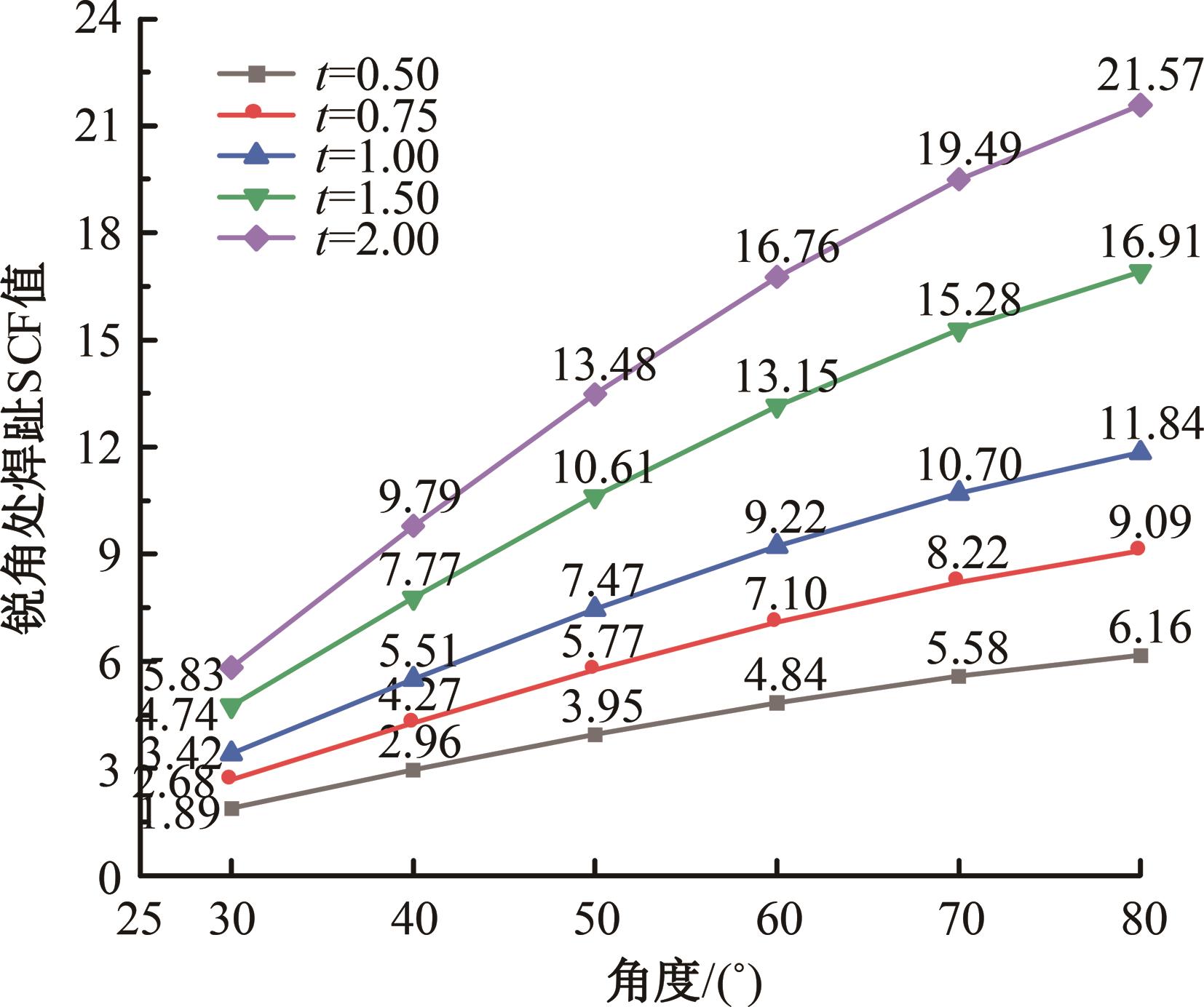
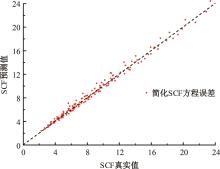
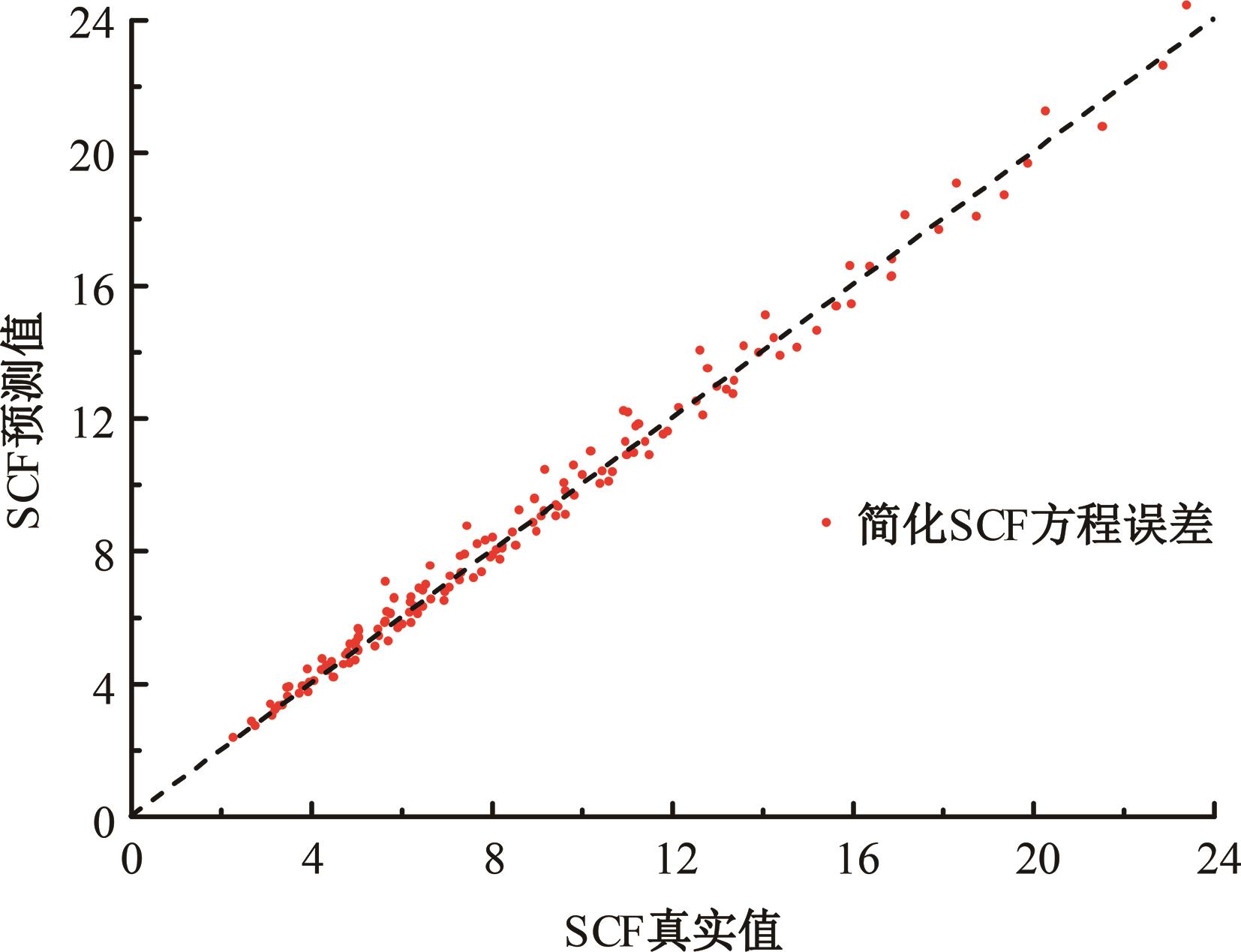
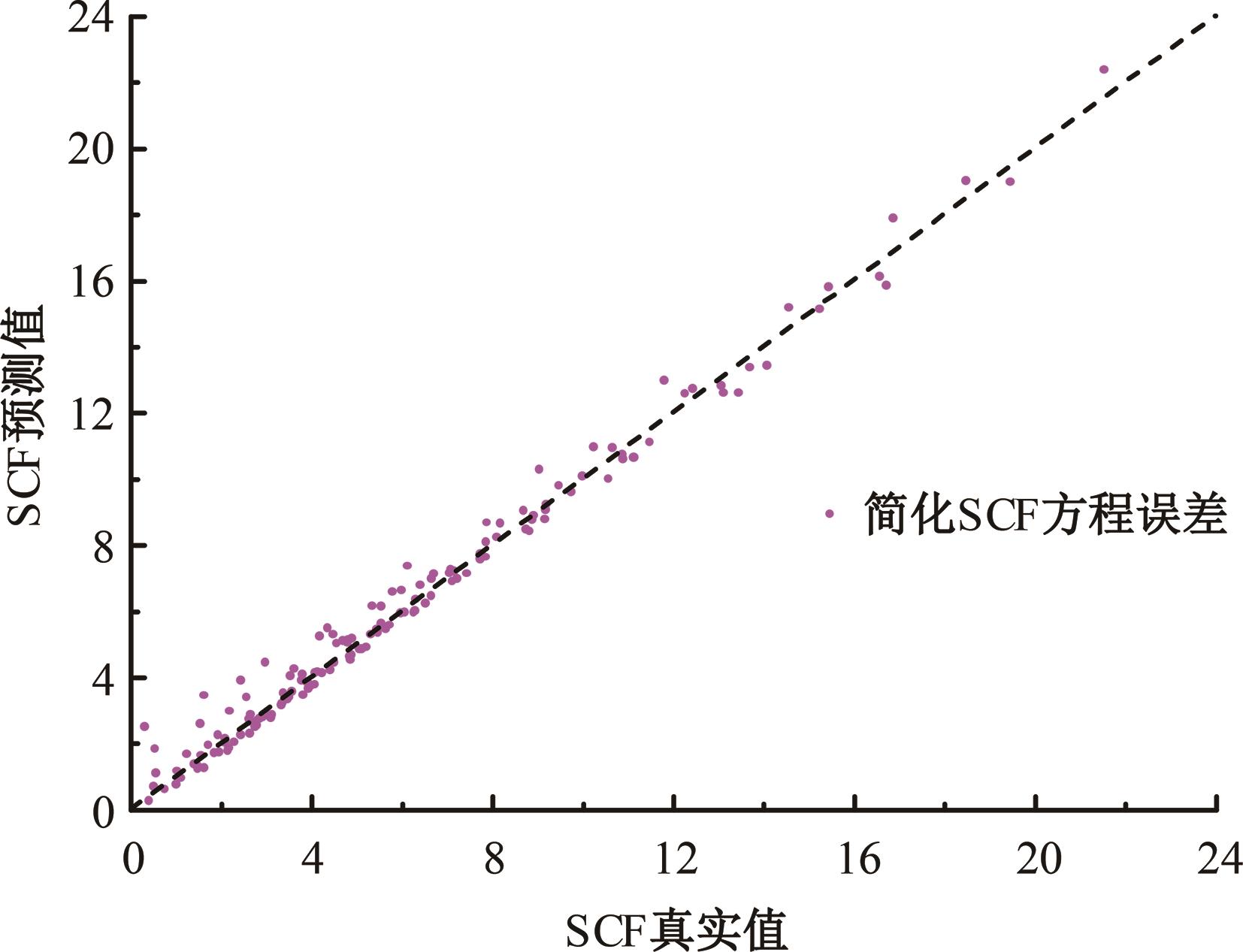
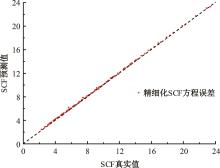
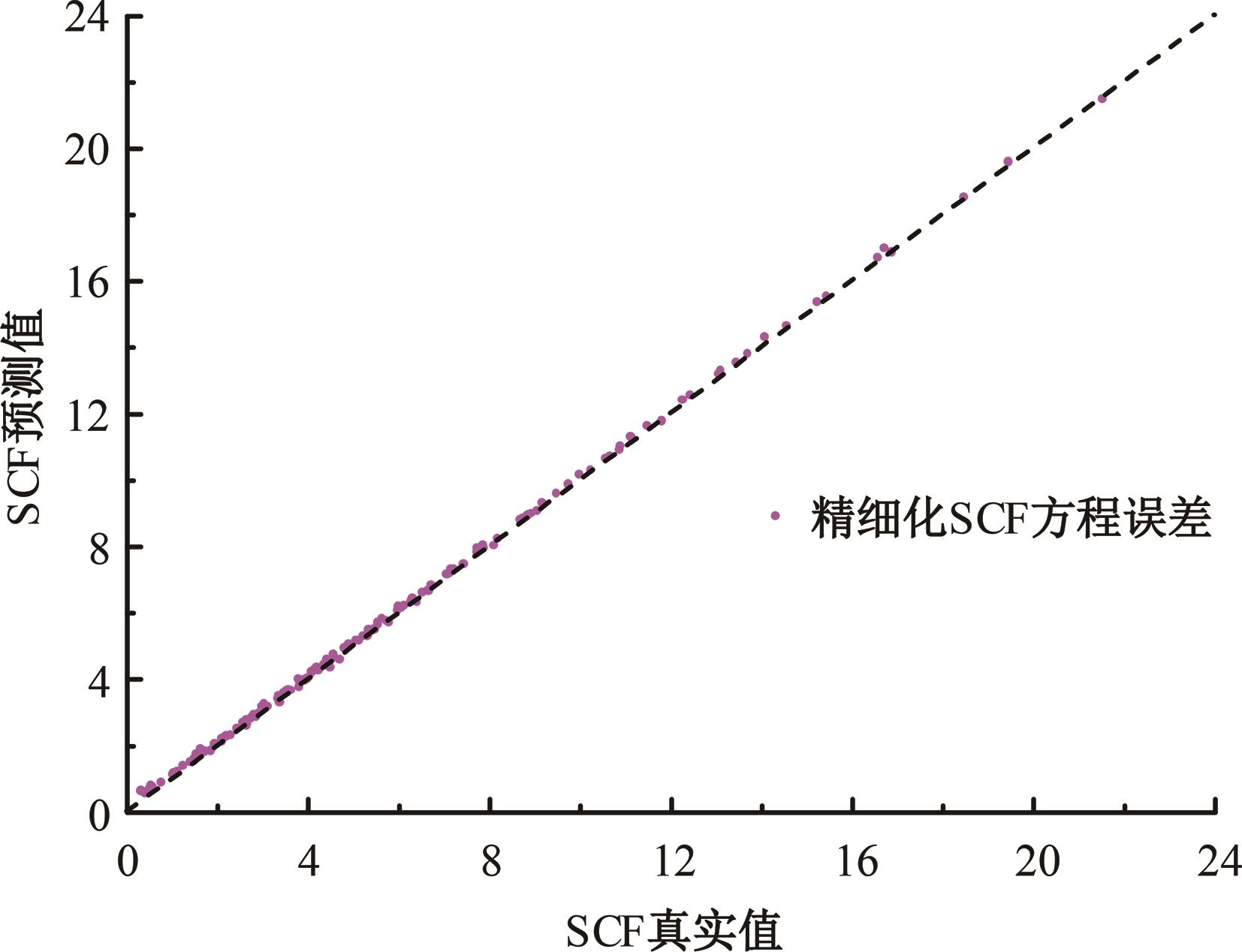
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (12): 3478-3485.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230172
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hot spot stress concentration factor for welded skewed-T joints
Xing WEI1( ),Yong-qi ZHANG2,Jun-ming ZHAO1,Hui-jun WANG1,Lin XIAO1(
),Yong-qi ZHANG2,Jun-ming ZHAO1,Hui-jun WANG1,Lin XIAO1( )
)
- 1.School of Civil Engineering,Southwest Jiaotong University,Chengdu 610031,China
2.China Railway First Survey and Design Institute Group Ltd. ,Xi'an 710043,China
CLC Number:
- U441.4
| 1 | 郑凯锋,冯霄暘,衡俊霖,等. 钢桥2020年度研究进展[J]. 土木与环境工程学报:中英文,2021,43():53-69. |
| Zheng Kai-feng, Feng Xiao-yang, Heng Jun-lin, et al. State-of-the-art review of steel bridges in 2020[J]. Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering, 2021, 43(Sup.1): 53-69. | |
| 2 | A. Structural welding codesheet steel [S]. |
| 3 | 吴琛泰. 钢管混凝土桁架焊接节点热点应力集中系数研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学土木工程学院,2019. |
| Wu Chen-tai. Study on hot spot stress concentration factor of welded concrete-filled stell tubular truss joints[D].Chengdu: School of Civil Engineering,Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019. | |
| 4 | Brennan F P, Peleties P, Hellier A K. Predicting weld toe stress concentration factors for T and skewed T-joint plate connections[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2000, 22(7): 573-584. |
| 5 | Dabiri M, Ghafouri M, Raftar H R R, et al. Neural network-based assessment of the stress concentration factor in a T-welded joint[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2017, 128: 567-578. |
| 6 | Terán G, Albiter A, Cuamatzi-Meléndez R. Parametric evaluation of the stress concentration factors in T-butt welded connections[J]. Engineering Structures, 2013, 56: 1484-1495. |
| 7 | Molski K L, Tarasiuk P. Stress concentration factors for welded plate T-Joints subjected to tensile, bending and shearing loads[J]. Materials, 2021, 14(3): 1-22. |
| 8 | 陈团海,陈国明.T型焊接管节点应力集中系数数值分析[J].焊接学报,2010,31(11):45-48, 115. |
| Chen Tuan-hai, Chen Guo-ming. Numerical analysis on stress concentration factors of joints in welded T-tube[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2010, 31(11): 45-48, 115. | |
| 9 | 陈娟,聂建国,周成野. 钢管混凝土T形相贯节点应力集中系数研究[J].建筑结构学报,2018,39(3): 149-157. |
| Chen Juan, Nie Jian-guo, Zhou Cheng-ye. Study on stress concentration factor of concrete-filled steel tubular T-joints[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2018, 39(3): 149-157. | |
| 10 | 杨德磊,童乐为. 支管受轴向受拉工况下CHS-CFSHS T型节点应力集中系数计算公式[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版,2019,49(6): 1891-1899. |
| Yang De-lei, Tong Le-wei. Calculation formula of SCF for CHS-CFSHS welded T-joints with brace under axial tension[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1891-1899. | |
| 11 | 卫星,赵骏铭,肖林,等. 钢管混凝土桁架焊接型管节点热点应力集中系数研究[J].中国铁道科学,2022,43(2): 1-9. |
| Wei Xing, Zhao Jun-ming, Xiao Lin, et al. Hot spot stress concentration factor of welded tubular T-ointsin concrete-filled steel tube truss[J]. China Railway Science, 2022, 43(2): 1-9. | |
| 12 | 揭志羽,李亚东,卫星,等. 复杂应力场下焊接接头疲劳寿命评估的热点应力法[J].中国公路学报,2017,30(5): 97-103. |
| Zhi-yu Jie, Li Ya-dong, Wei Xing, et al. Hot spot stress method for fatigue life assessment of welded joints under complex stress fields[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2017, 30(5): 97-103. | |
| 13 | IIW Document IIW-1823-07 ex XIII-2151r4-07/ XV-1254r4-07 recommended fatigue design procedure for welded hollow section joints [S]. |
| 14 | Marquardt D W. An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters[J]. Journal of the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 1963, 11(2): 431-441. |
| 15 | 李松柏, Stefan Kirchberg,谢磊,等. PP+FeSi复合材料流变性能测试及数值模拟[J].高分子材料科学与工程,2010,26(3): 164-167, 171. |
| Li Song-bai, Stefan Kirchberg, Xie Lei, et al. Rheological Experiment and numerical simulation of PP+FeSi composite materials[J]. Polymeric Materials Science and Engineering, 2010, 26(3): 164-167, 171. | |
| 16 | 范金龙,宋国良,宋维健,等. 内嵌逆流柱型风帽阻力特性冷态试验研究[J].动力工程学报,2015,35(7): 531-536. |
| Fan Jin-long, Song Guo-liang, Song Wei-jian, et al.Experimental study on resistance characteristics ofInternal counterflow wind caps with inner tubes[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering, 2015, 35(7): 531-536. | |
| 17 | 舒志乐,刘保县,黄山,等. 软岩非线性黏弹塑性蠕变模型及参数识别[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2017,34(4): 803-809. |
| Shu Zhi-le, Liu Bao-xian, Huang Shan, et al. Nonlinear viscoelasto-plastic creep model of soft rock and its parameters identification[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2017, 34(4): 803-809. | |
| 18 | 李萍,念腾飞,魏定邦,等. FTIR定量分析方法与老化沥青流变参数新探[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 46(2): 34-39. |
| Li Ping, Teng-fei Nian, Wei Ding-bang, et al. Quantitative analysis method for FTIR and exploration on rheological parameters of aging asphalt binders[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(2): 34-39. |
| [1] | Yong-xin SUN,Peng-zhen LIN,Zi-jiang YANG,Wei JI. Calculation method for crack width of UHPC beams considering bond slip effect [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2600-2608. |
| [2] | Bao-dong LIU,Fang LI,Xiao-xi WANG,Meng GAO. Flexural stiffness and bearing capacity of corrugated steel plate composite structures reinforced by concrete [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2502-2510. |
| [3] | Yu-xin XUE,Yong-jun ZHOU,Ye-lu WANG,Kai-xiang FAN,Yu ZHAO. Application of dynamic load allowance test method of simply supported girder bridge based on suspension hammer system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2557-2567. |
| [4] | Xue-lian GUO,Wan-shui HAN,Tao WANG,Kai ZHOU,Xiu-shi ZHANG,Shu-ying ZHANG. Assessment method of resistant overturning stability safety factors of curved bridge under customized transport vehicles [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2229-2237. |
| [5] | Lin XIAO,Huan-bo WEI,Xing WEI,Zhi-rui KANG. Numerical analysis on cracking behavior of concrete slab due to corrosion expansion of stud connector in steel-concrete composite beam [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1958-1965. |
| [6] | Chun-lei ZHANG,Chang-yu SHAO,Qing-tian SU,Chang-yuan DAI. Experimental on positive bending behaviour of composite bridge decks with steel-fiber-reinforced concrete and longitudinal bulb-flat ribs [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1634-1642. |
| [7] | Han-hui HUANG,Kang-ming CHEN,Qing-xiong WU. Flexural behavior of composite continuous girders with concrete-filled steel tubular truss chords [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1665-1676. |
| [8] | Chang-jiang SHAO,Hao-meng CUI,Qi-ming QI,Wei-lin ZHUANG. Longitudinal seismic mitigation of near⁃fault long⁃span RC soft⁃lighten arch bridge based on viscous damper [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1355-1367. |
| [9] | Qiu ZHAO,Peng CHEN,Yu-wei ZHAO,Ao YU. Overall mechanical performance of jointless bridges with arch structure behind abutment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1016-1027. |
| [10] | Hong ZHANG,Zhi-wei ZHU,Tian-yu HU,Yan-feng GONG,Jian-ting ZHOU. Bridge bolt defect identification method based on improved YOLOv5s [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(3): 749-760. |
| [11] | Liang XU,Jing-hou XIAO,Wan-wan SONG,Song ZHOU. Three⁃point bending fatigue properties of carbon fiber composite laminates [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 400-409. |
| [12] | Zhi-qiang HAN,Gang XIE,Ya-juan ZHUO,Zuo-long LUO,Hua-teng LI. Vibration response of continuous girder bridge based on wheel⁃deck coherent excitation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 436-444. |
| [13] | Guo-jun YANG,Ya-hui QI,Xiu-ming SHI. Review of bridge crack detection based on digital image technology [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 313-332. |
| [14] | Xie-li ZHANG,Chong WU,Qing-tian SU. Experiment on load capacity of profiled steel sheeting-concrete composite bridge decks [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(10): 2870-2883. |
| [15] | Qing-wei HUANG,Qing-xiong WU,Bao-chun CHEN,Kang-ming CHEN,Zhi-wei YE. Calculation method of out-of-plane elastic stability bearing capacity for concrete-filled steel tubular arch bridges with circular tube ribs [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(10): 2930-2940. |
|