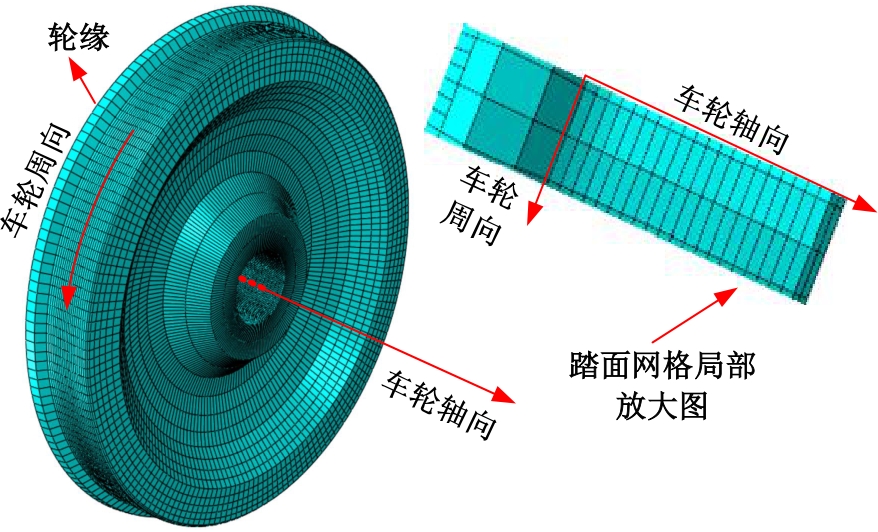
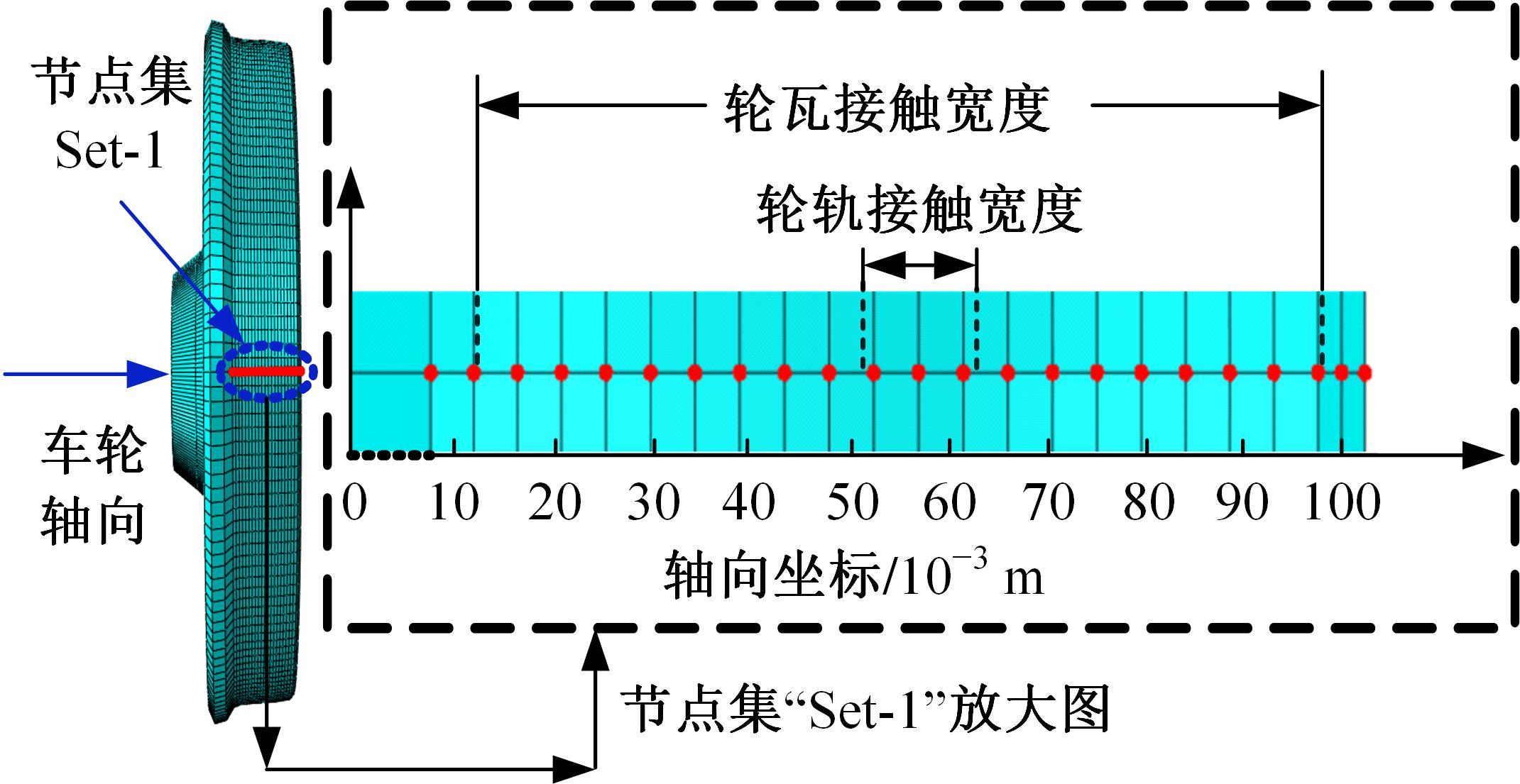
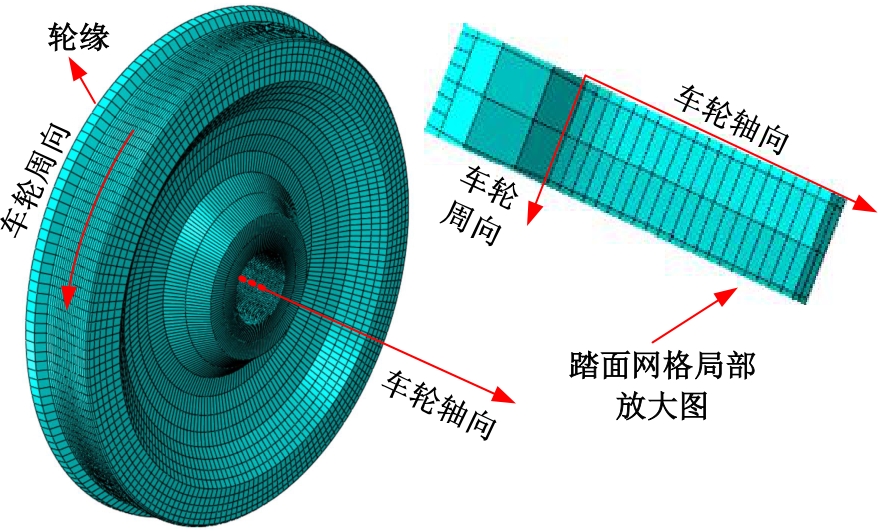
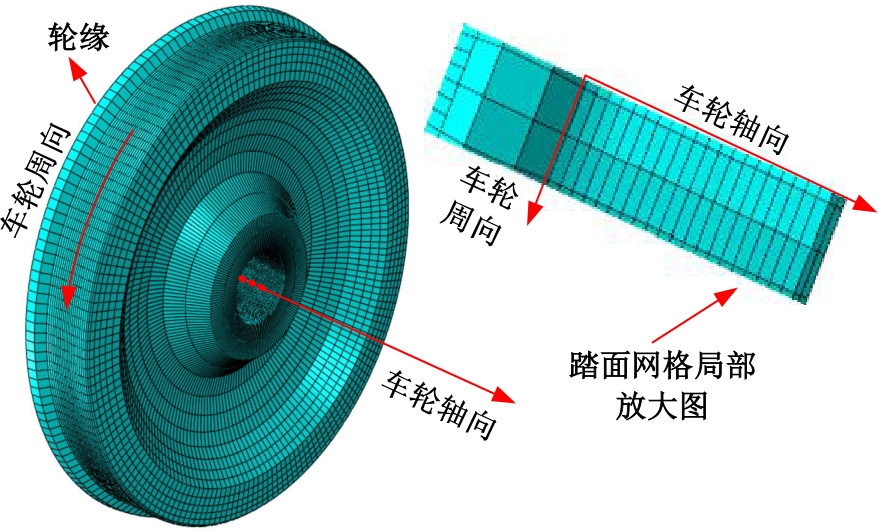
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (3): 866-876.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230550
Previous Articles Next Articles
Fatigue life prediction of brake treads for C80 trains with long downhill cycles
Jian-feng SONG1( ),Xin-lei HUANG2,Si-ran WANG2,Guang-yao XIE2,Yong-gang DONG1(
),Xin-lei HUANG2,Si-ran WANG2,Guang-yao XIE2,Yong-gang DONG1( )
)
- 1.School of Mechanical Engineering,Changshu Institute of Technology,Changshu 215500,China
2.School of Mechanical Engineering,Yanshan University,Qinhuangdao 066004,China
CLC Number:
- U211.5
| 1 | 王延朋, 丁昊昊, 邹强, 等. 列车车轮踏面滚动接触疲劳研究进展[J]. 表面技术, 2020, 49(5): 121-122. |
| Wang Yan-peng, Ding Hao-hao, Zhou Qiang, et al. Research progress on rolling contact fatigue of railway wheel treads[J]. Surface Technology, 2020, 49(5): 121-122. | |
| 2 | 黄龙文, 李正美, 安琦. 轮轨滚动接触疲劳寿命的计算方法[J]. 华东理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 44(6): 918-927. |
| Huang Long-wen, Li Zheng-mei, An Qi. Calculation method of wheel/rail rolling contact fatigue life[J]. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2018, 44(6): 918-927. | |
| 3 | 黄龙文. 轮轨滚动接触力学分析及疲劳寿命预测方法分析[D].上海: 华东理工大学机械学院, 2018. |
| Huang Long-wen. Mechanics analysis and fatigue life prediction method for wheel/rail rolling contact[D].Shanghai: School of Mechanical Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 2018. | |
| 4 | 范新光. 列车车轮滚动接触疲劳裂纹萌生及扩展研究[D].北京: 北京交通大学机械与电子控制工程学院, 2019. |
| Fan Xin-guang. Study of fatigue crack initiation and propagation of railroad wheel under rolling contact[D].Beijing: School of Mechanical and Electronic Control Engineering, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2019. | |
| 5 | 赵吉中,徐祥,丁立,等. 高速列车车轮踏面滚压强化有限元分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2020, 55(6): 1338-1345. |
| Zhao Ji-zhong, Xu Xiang, Ding Li, et al. Finite element analysis of rolling strengthening process for wheel tread of high-speed trains[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(6): 1338-1345. | |
| 6 | 刘颍宾. 列车车轮踏面滚动接触疲劳损伤机制研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学化学与材料科学学院, 2020. |
| Liu Ying-bin. Research on rolling contact fatigue damage mechanism of train wheel tread[D]. Hefei: School of Chemistry and Materials Science, University of Science and Technology of China, 2020. | |
| 7 | 杨柳青,胡明,赵德明,等. CRH5动车组车轮低温概率疲劳寿命研究[J]. 中国机械工程, 2018, 29(9): 1115-1118. |
| Yang Liu-qing, Hu Ming, Zhao De-ming, et al. Research on probabilistic fatigue life of CRH5 EMU wheels at low temperature[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 29(9): 1115-1118. | |
| 8 | 扬大巍. CRH5型动车组轮轨滚动接触行为及疲劳寿命研究[D].兰州: 兰州理工大学材料科学与工程学院, 2017. |
| Yang Da-wei. Study on rolling contact behavior and fatigue life of CRH5 type EMU[D].Lanzhou: School of Materials Science and Engineering, Lanzhou University of Technology, 2017. | |
| 9 | Chong T, Liu X L, Wu S, et al. Study on damage tolerance and remain fatigue life of shattered rim of railway wheels[J]. Engineering Fatigue Analysis, 2021, 12(2): 20-28. |
| 10 | Nejad R M, Berto F. Fatigue fracture and fatigue life assessment of railway wheel using non-linear model for fatigue crack growth[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2021, 30(3): 13-15. |
| 11 | Lima E A, Martins T S, Santos A A. Effect of manufacturing residual stress on the fatigue life of railway wheels for heavy-haul transportation[J]. Procedia Structural Integrity, 2019, 33(8): 246-253. |
| 12 | 孔昌昌, 秦凤明, 张晓峰, 等. 含Mo元素CL60钢CCT曲线的测定及分析[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2019, 40(8): 139-141. |
| Kong Chang-chang, Qin Feng-ming, Zhang Xiao-feng, et al. Determination and analysis of CCT curve of CL60 steel containing Mo element[J]. Journal of Materials Heat Treatment, 2019, 40(8): 139-141. | |
| 13 | 马红萍. 重载列车长大下坡制动过程优化控制研究[D]. 南昌: 华东交通大学电气与自动化工程学院, 2019. |
| Ma Hong-ping. Research on optimal braking process control of heavy-haul train on long steep down grade[D]. Nanchang: School of Electrical and Automation Engineering, East China Jiaotong University, 2019. | |
| 14 | 卢立丽. 货车车轮踏面制动热损伤研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学机械与电子控制工程学院, 2007. |
| Lu Li-li. Research on tread brake heat injury of freight wheel[D]. Beijing: School of Mechanical and Electronic Control Engineering, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2007. | |
| 15 | 王铎, 孙毅, 程靳. 理论力学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2016. |
| 16 | 雷国军. 重载列车车轮表面对流传热特性的数值研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州交通大学车辆工程学院, 2020. |
| Lei Guo-jun. Numerical study on convective heat transfer characteristics on the wheel surface of heavy-duty train[D]. Lanzhou: School of Vehicle Engineering, Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2020. | |
| 17 | 包辰铭. 重载列车踏面制动车轮温度场分析及制动故障诊断研究[D].北京: 北京交通大学机械与电子控制工程学院, 2020. |
| Bao Chen-ming. Temperature field analysis of brake wheels on heavy-duty train treads research on brake fault diagnosis[D]. Beijing: School of Mechanical and Electronic Control Engineering, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2020. | |
| 18 | Chen S, Zhao G T, Wang H Y, et al. Study of wheel wear influenced by tread temperature rising during tread braking[J]. Wear, 2019, 32(3): 1-10. |
| 19 | 李辉平, 贺连芳, 赵国群,等. 硼钢B1500HS界面传热系数与压力关系的研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2013, 49(16): 78-82. |
| Li Hui-ping, He Lian-fang, Zhao Guo-qun, et al. Research on the surface heat transfer coefficient depending on surface pressure of boron steel B1500HS[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 49(16): 78-82. | |
| 20 | 孙晓冉,宋月,谷秀锐,等. 汽车用SPHC热轧薄钢板的低周疲劳特性[J]. 机械工程材料, 2021, 45(4): 58-60. |
| Sun Xiao-ran, Song Yue, Gu Xiu-rui, et al. Low cycle fatigue characteristics of SPHC hot-rolled steel sheet for automobile[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 45(4): 58-60. | |
| 21 | 张然治. 疲劳试验测试分析理论与实践[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2011. |
| 22 | 秦大同. 现代机械设计手册[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2011. |
| 23 | 黄协思. 疲劳约束下航空发动机涡轮盘结构优化设计[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学机械与电气工程学院, 2020. |
| Huang Xie-si. Structural optimization design of aero engine turbine disc under fatigue constraint[D]. Chengdu: School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020. | |
| 24 | 卢碧红, 徐超, 郭宏远. C80型铁路货车制动装置运用性能预测[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2021, 21(6): 289-297. |
| Lu Bi-hong, Xu Chao, Guo Hong-yuan. Operation performance prediction of C80 railway freight car braking device[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2021, 21(6): 289-297. |
| [1] | Shu-kun WANG,Yu-ze FENG,Jing-ran ZHANG,Xin-ming ZHANG,Long ZHENG. Analysis on decontamination performance of lower lip structure of imitation scavenger [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 392-400. |
| [2] | Xian-zhen HUANG,Rui YU,Hui-zhen LIU,Ji-wu TANG. Spindle vibration reliability analysis considering bearing nonlinear restoring force [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 116-124. |
| [3] | Chen WANG,Te LUO,Qian-qian HUI,Zhong-hao WANG,Fang-fang WANG. Design and verification of electromechanical system for docking and locking of modular flying vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2130-2140. |
| [4] | Yang LIU. Simulation and experiment of elastic roughing for rubber shoe [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2167-2173. |
| [5] | Lei WANG,Dong-xia LI,Song ZHOU,Li HUI,Zhen-xin SHEN. Fatigue crack propagation behavior and life prediction of 2024-O aluminum alloy FSW joints [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1563-1569. |
| [6] | Yang LIU,Tao JIANG. Interference calculation model of Hooke joint of 6-DOF platform considering installation angle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1519-1527. |
| [7] | Xiao-dan TAN,Yong-peng WANG,Robert Hall,Tian-shuang XU,Qing-xue HUANG. Haul truck dump body optimization for autonomous shovel loading [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1227-1236. |
| [8] | Shi-jun WANG,Guan-wei LUO. Periodic motion transition characteristics of a vibro-impact system with multiple impact constraints [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 902-916. |
| [9] | Wei SUN,Jun YANG. Finite element modeling and vibration reduction analysis of cylindrical shell structures with equal⁃angle attachment of piezoelectric shunt patches [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 365-374. |
| [10] | Bin HU,Yi-quan CAI,Xin LUO,Zi-bin MAO,Jun-wei LI,Meng-yu GUO,Jian WANG. Theory and experiment of high⁃speed seed filling in limited gear⁃shaped side space based on seeds group stress [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 574-588. |
| [11] | Jian-xing YU,Ming-xiu WEI,Yang YU,Yu-peng CUI,Yu PAN. Reliability-based topology optimization and engineering design of stiffened plates [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(10): 2781-2791. |
| [12] | Ya-bing CHENG,Ze-yu YANG,Yan LI,Li-chi AN,Ze-hui XU,Peng-yu CAO,Lu-xiang CHEN. Vibration and noise characteristics base on timing silent chain system of hybrid electric vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2465-2473. |
| [13] | Jia-yi WANG,Xin-hui LIU,Zhan WANG,Jin-shi CHEN,Ya-fang HAN,Yu-qi WANG. Flow characteristics analysis of constant flow control valve based on AMESim [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2499-2507. |
| [14] | Yan YANG,Yu-qing SHI,Xiao-rong ZHANG,Guan-wei LUO. Dynamic stability analysis of a amplitude⁃limited vibration system with multiple rigid constraints [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 364-375. |
| [15] | Jian-feng SONG,Xin-lei HUANG,Shuai YI,Zhen-xi YANG,Yong-gang DONG,Shu-lin LI. Temperature field and stress-strain distribution of tread during train braking [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(10): 2773-2784. |
|
||