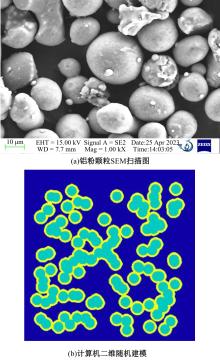
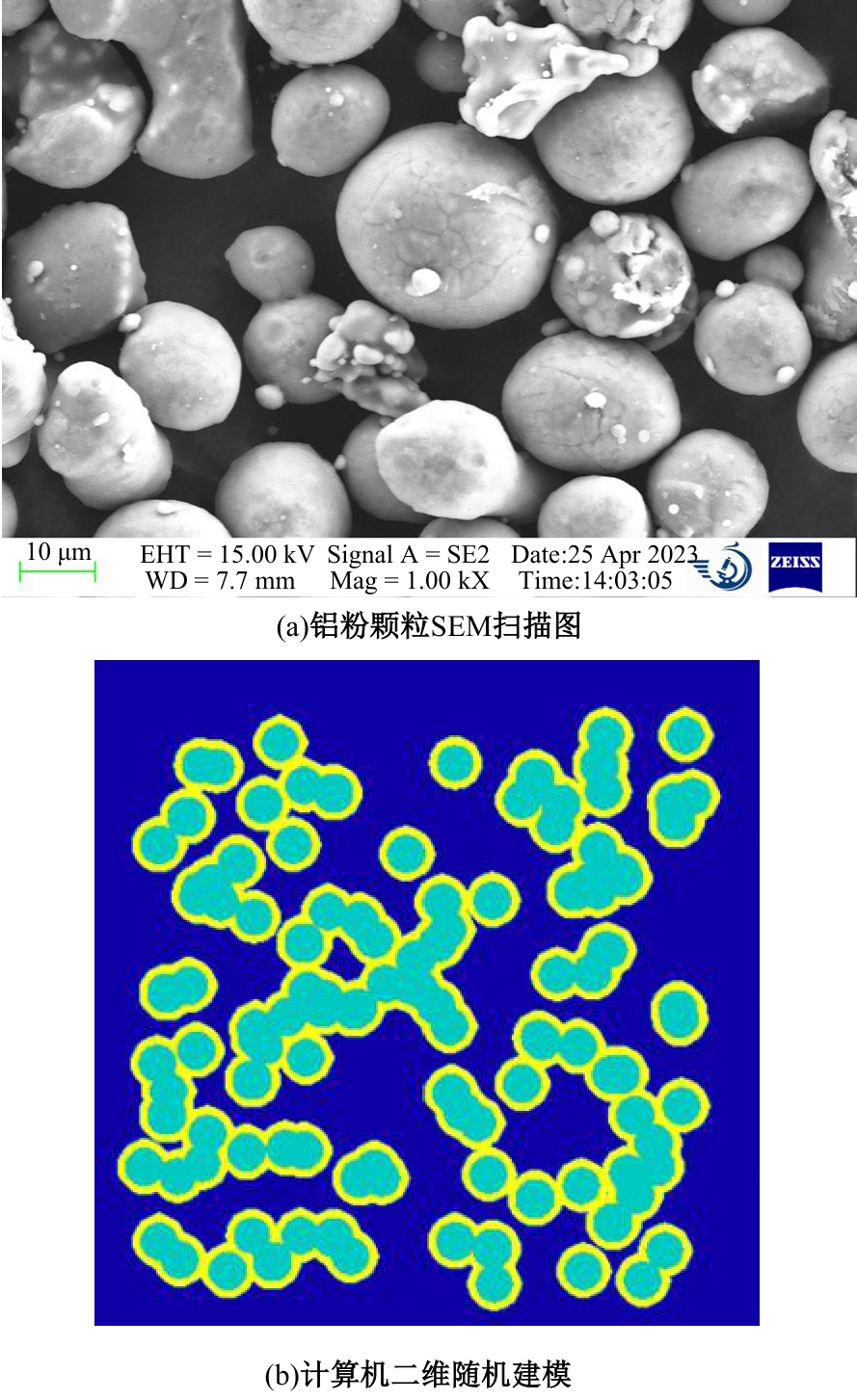
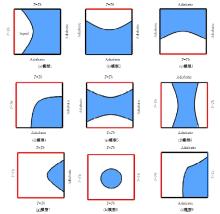
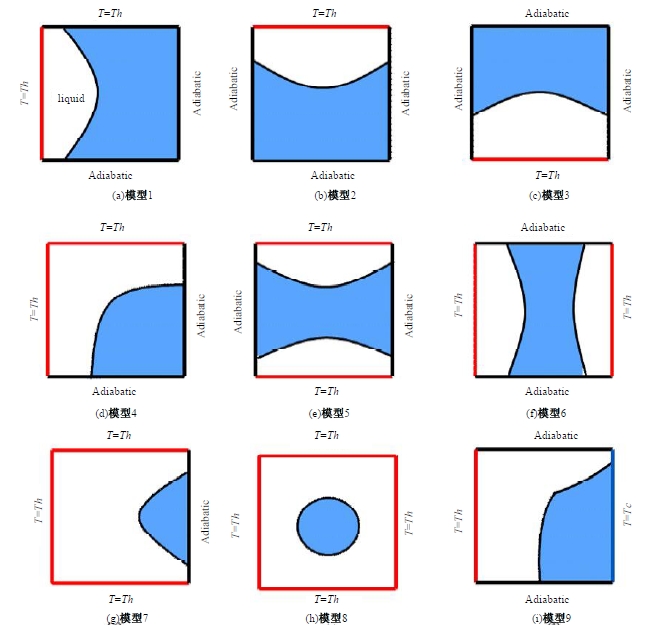
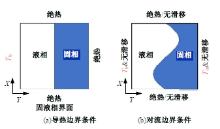
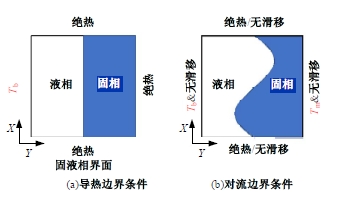
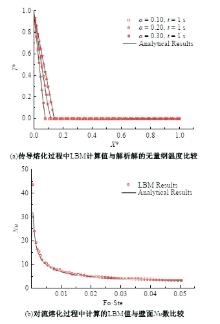
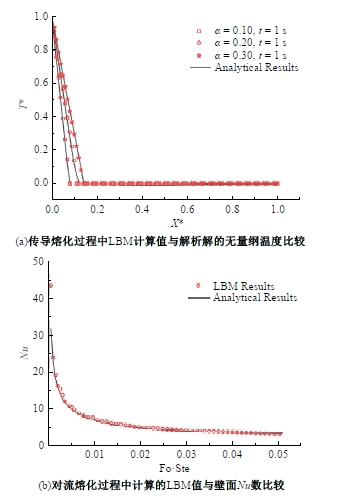
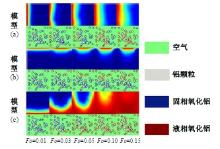
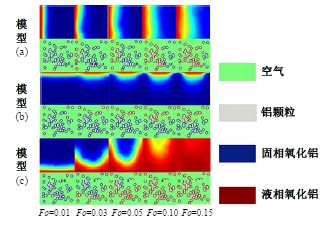
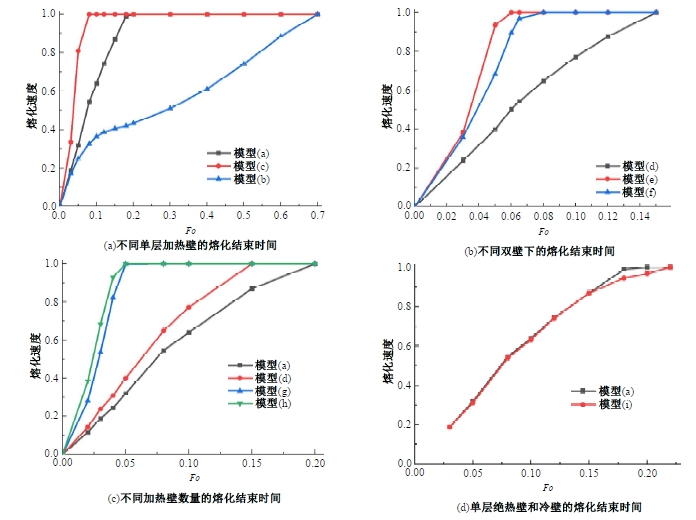
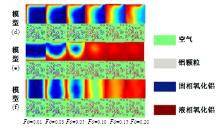
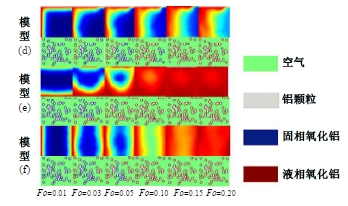
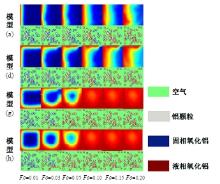
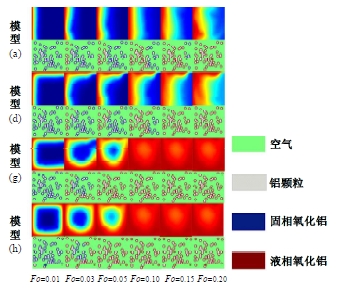
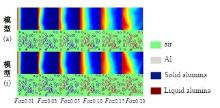
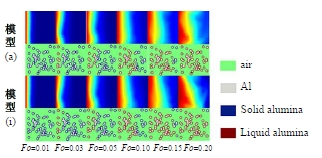
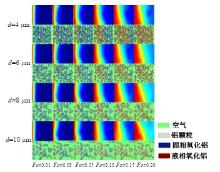
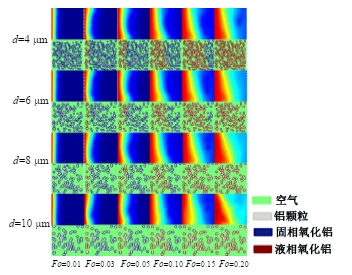
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 1197-1206.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230677
Previous Articles Next Articles
Heat transfer and melting characteristics of micronmeter-sized aluminum particle oxide layers based on lattice Boltzmnn model
Ruo-meng YING1( ),Gao-yi SHANG2,Zhen-chao LIU1(
),Gao-yi SHANG2,Zhen-chao LIU1( ),Deng-wang WANG3,Sheng WANG1
),Deng-wang WANG3,Sheng WANG1
- 1.School of Energy and Power Engineering,Xi'an Jiaotong University,Xi'an 710049,China
2.State Key Laboratory of Electrical Insulation and Power Equipment,School of Energy and Power Engineering,Xi'an Jiaotong University,Xi'an 710049,China
3.Northwest Institute of Nuclear Technology,Xi'an 710024,China
CLC Number:
- TK16
| [1] | 田入园. 复合固体推进剂中Al颗粒燃烧行为数值模拟[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学能源与动力工程学院, 2017. |
| Tian Ru-yuan. Numerical simulation of combustion behavior of aluminum particle in composite solid propellants[D]. Nanjing: School of Energy and Power Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2017. | |
| [2] | 胡松启, 李葆萱. 固体火箭发动机燃烧基础[M]. 西安: 西北工业大学出版社, 2015. |
| [3] | 王克秀. 固体火箭推进剂及燃烧[M]. 北京:国防工业出版社, 1983. |
| [4] | 萨顿·比布拉兹. 火箭发动机基础[M]. 洪鑫, 张宝炯, 等译. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003. |
| [5] | Fang C, Fen L S. Experimental studies on effects of AP content and particle size in NEPE propellant[J]. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 2001, 24(3): 47-53. |
| [6] | 唐伟强, 杨荣杰, 李建民, 等. 高铝固体推进剂中氟化物促进铝燃烧研究进展[J]. 固体火箭技术, 2020,43(6): 679-686. |
| Tang Wei-qiang, Yang Rong-jie, Li Jian-min et al. Research progress of fluorides in high aluminum solid propellant to promote aluminum combustion[J]. Solid Rocket Technology, 2020, 43(6): 679-686. | |
| [7] | Jeurgens L P H, Sloof W G, Tichelaar F D, et al. Thermodynamic stability of amorphous oxide films on metals: application to aluminum oxide films on aluminum substrates[J]. Physical Review B, 2000, 62(7): 4707-4719. |
| [8] | Jeurgens L P H, Sloof W G, Tichelaar F D, et al. Structure and morphology of aluminiumoxide films formed by thermal oxidation of aluminium[J]. Thin solid Films, 2002, 418(2): 89-101. |
| [9] | Merzhanov A G, Grigorjev Y M, Galchenko Y A. Aluminum ignition[J]. Combustion and Flame, 1977, 29: 1-14. |
| [10] | Breiter A L, Mal´Tsev V M, Popov E I. Models of metal ignition[J]. Combustion, Explosion and Shock Waves, 1977, 13(4): 475-484. |
| [11] | Ermakov V A, Razdobreev A A, Skorik A I, et a1. Temperature of aluminum particles at the time of ignition and combustion[J]. Combustion, Explosion and Shock Waves, 1982, 18(2): 256-257. |
| [12] | Desjardin P E, Felske J D, Carrara M D. Mechanistic model for aluminum particle ignition and combustion in air[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2005, 21(3): 478-485. |
| [13] | Yang H, Lee J, Kim K, et a1. Simplified model for single aluminum particle combustion[C]∥The 47th AIAA Aerospace Science Meeting Including, The New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, Orlando,USA, 2009: 1-9. |
| [14] | Volkov K N. Combustion of Single Aluminum Droplet in Two-phase Flow[M]. Hauppauge: Nova Science, 2011. |
| [15] | Mohammadian S K, Zhang Y. Convection heat transfer with internal heat generation in porous media: implementation of thermal lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Numerical Heat Transfer Part A: Applications, 2019, 76(3): 101-114. |
| [16] | Jourabian M, Darzi A, Akbari O A, et al. The enthalpy-based lattice Boltzmann method(LBM) for simulation of NePCM melting in inclined elliptical annulus[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2019, 548: No.123887. |
| [17] | Ghasemi K, Tasnim S, Mahmud S. Shape-stabilized phase change material convective melting by considering porous configuration effects[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2022, 355: No.118956. |
| [18] | Chen D, Riaz A, Aute V C, et al. A solid–liquid model based on lattice Boltzmann method For phase change material melting with porous media in cylindrical heat exchangers[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2022, 207: No.118080. |
| [19] | He P, Chen L, Mu Y, et al. Lattice Boltzmann method simulation of ice melting process in the gas diffusion layer of fuel cell[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 149(2): No.119121. |
| [20] | Eshraghi M, Felicelli S D. An implicit lattice Boltzmann model for heat conduction with phase change[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2012, 55(9, 10): 2420-2428. |
| [21] | Zhao C Y, Dai L N, Tang G H, et al. Numerical study of natural convection in porous media (metals) using lattice Boltzmann method(LBM)[J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 2010, 31(5): 925-934. |
| [22] | Jiang Z H, Yang G G, Li S A, et al. Investigation of the ice melting process in a simplified gas diffusion layer of fuel cell by the lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Energy and Fuel, 2022, 36(10): 5403-5414. |
| [23] | Jany P, Bejan A. Scaling theory of melting with natural convection in an enclosure[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1988, 31(6): 1221-1235. |
| [1] | Zhen-jun XU,Rui-feng ZHANG,Jia-xiang CHEN,Xiao-hui ZHANG,Xiao-guang MI,Jie CHEN,Lin CHEN. Influence for backheating on low temperature high mass experimental system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1133-1138. |
| [2] | Zi-rong YANG,Yan LI,Xue-feng JI,Fang LIU,Dong HAO. Sensitivity analysis of operating parameters for proton exchange membrane fuel cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 1971-1981. |
| [3] | Zhen-jun XU,Hao WANG,Yin-cheng WANG,Nuo ZHANG,Meng CHEN,Qing-qing LI. Flow heat transfer performance of microchannel low temperature heat exchanger [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(10): 2294-2299. |
| [4] | Wei LAN,Jiang LIU,Li XIN,Jing-xi LI,Xing-jun HU,Jing-yu WANG,Tao SANG. Influence of rearview mirror styling on water phase distribution on side windows [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1590-1599. |
| [5] | MENG Yu-bo, LI Pi-mao, ZHANG You-tong, WANG Zhi-ming. Inhibition of pressure fluctuation and multi-injection fuel mass deviation in high pressure common rail system [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 760-766. |
| [6] | SUN Zheng, HUANG Yu-qi, YU Xiao-li. Numerical simulation of flow and heat transfer in journal bearing lubrication [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 744-751. |
| [7] | MENG Yu-bo, ZHANG You-tong, WANG Zhi-ming, ZHANG Xiao-chen, FAN Li-kang, LI Tao. Couple hysteretic thermo-electro-mechanical performance of piezoelectric actuators for fuel injector [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 480-485. |
| [8] | LI Ming-da, KUI Hai-lin, MEN Yu-zhuo, BAO Cui-zhu. Aerodynamic drag of heavy duty vehicle with complex underbody structure [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 731-736. |
| [9] | LI Shen-long, LIU Shu-cheng, XING Qing-kun, ZHANG Jing, LAI Yu-yang. Clutch friction pair motion effect caused by oil flow based on LBM-LES [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 490-497. |
| [10] | CUI Jin-sheng, HOU Xu-yan, DENG Zong-quan, PAN Wan-jing, JIANG Sheng-yuan. Measurement system and experiment study of the effective thermal conductivity of granular system in a vacuum [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 457-464. |
| [11] | QI Zi Shu, GAO Qing, LIU Yan, BAI Li. Model calculation and analysis of operation condition of heat pump using earth energy system for years [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 1811-1816. |
| [12] | QI Zi-shu, GAO Qing, LIU Yan, YU Ming. Analysis of temperature of underground heat exchanger and efficiency of heat pump with combined cooling and heating [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(02): 339-343. |
| [13] | SONG Min,JIANG Ping,YAN Guang-wu. Lattice Boltzmann model for multi-seismic resources pressure wave in isotropic medium [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(增刊2): 341-0343. |
| [14] | Gao Yin-han,Chen Wang-feng,Cheng Peng,Li Zhen-lei,Chi Juncheng,Li Qiang3 . Twophase three dimension flow field simulation in a cyclone separator [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(增刊): 85-0089. |
| [15] |
Li Zhong-jian,Zheng Mao-yu,Wang Fang .
Optimization of irreversible fourheatsource absorption refrigerator with finite heat capacity [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(02): 283-0286. |
|