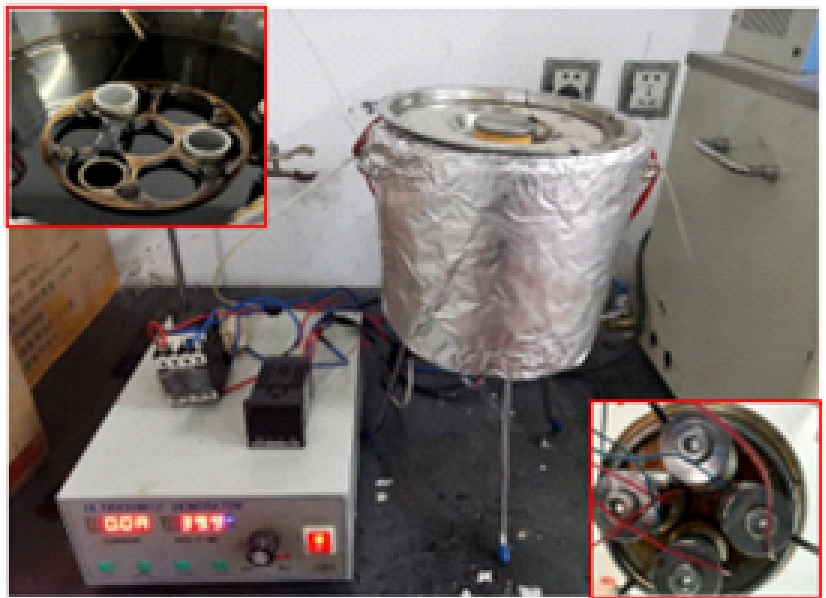
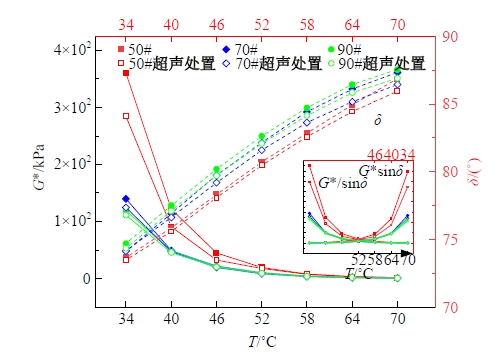
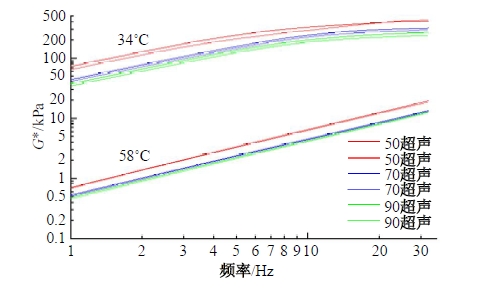
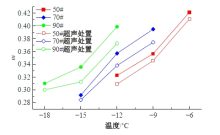
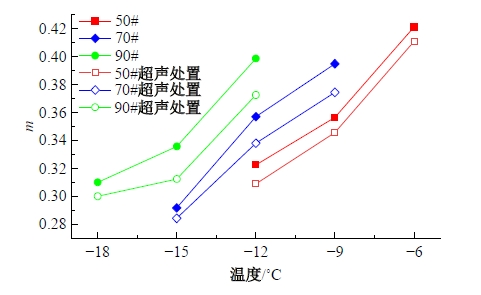
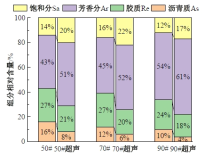
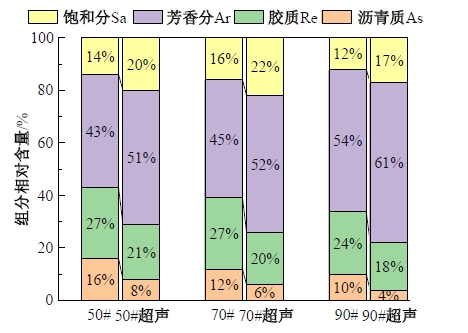
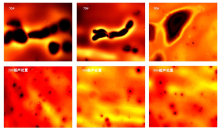
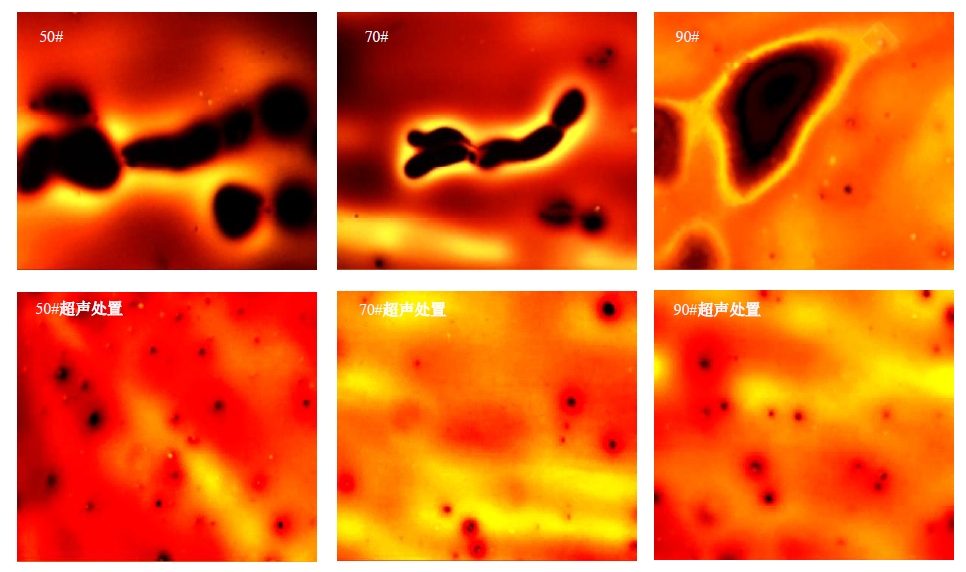
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 1346-1355.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230712
Previous Articles Next Articles
Rheological response and response mechanism of petroleum asphalt treated with ultrasound
Li-ming WANG1( ),Zi-kun SONG1,2,Hui ZHOU3,Wen WEI1,Hao YUAN1
),Zi-kun SONG1,2,Hui ZHOU3,Wen WEI1,Hao YUAN1
- 1.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,Northeast Forestry University,Harbin 150040,China
2.School of Transportation Science and Engineering,Harbin Institute of Technology,Harbin 150010,China
3.Heilongjiang Airport Management Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Harbin 150010,China
CLC Number:
- U414
| [1] | Suslick K S, Price G J. Applications of ultrasound to materials chemistry[J]. Annual Review of Materials Science, 1999, 29(1): 295-326. |
| [2] | 孙仁远, 王连保, 彭秀君, 等. 稠油超声波降黏试验研究[J]. 油气田地面程, 2001, 20(5): 22-23. |
| Sun Ren-yuan, Wang Lian-bao, Peng Xiu-jun, et al. Experimental study on ultrasonic viscosity reduction of thick oil [J]. Oil and Gas Field Surface Procedure, 2001, 20(5): 22-23. | |
| [3] | Mehdi R, Jafar Q. Experimental investigation of the ultrasonic wave effects on the viscosity and thermal behaviour of an asphaltenic crude oil[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing-Process Intensification,2020, 153:1 289-1295. |
| [4] | Abarasi H. A review of technologies for transporting heavy crude oil and bitumen via pipelines[J]. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology, 2014, 4(3): 327-336. |
| [5] | 黄序韬, 梁淑寰. 声波采油的机理与特点研究[J]. 石油学报, 1993(4): 110-116. |
| Huang Xu-Tao, Liang Shu-Huan. Study on the mechanism and characteristics of acoustic wave oil recovery[J]. Journal of Petroleum, 1993(4): 110-116. | |
| [6] | Shedid S A. An ultrasonic irradiation technique for treatment of asphaltene deposition[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science & Engineering, 2004, 42(1): 57-70. |
| [7] | Guo X, Du Z, Li G, et al. High frequency vibration recovery enhancement technology in the heavy oil fields of China[C]∥SPE International Thermal Operations and Heavy Oil Symposium and Western Regional Meeting, Bakersfield, California, USA, 2004. |
| [8] | 黄欣桐, 周翠红, 郭艳彤,等. 超声应用于超重质渣油降黏的实验研究[J]. 北京石油化工学院学报, 2018, 26(1): 9-13. |
| Huang Xin-tong, Zhou Cui-hong, Guo Yan-tong, et al. Experimental study on ultrasound application to viscosity reduction of super-heavy residue oil[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Petrochemical Technology, 2018, 26(1): 9-13. | |
| [9] | Huang X T, Zhou C H, Suo Q Y, et al. Experimental study on viscosity reduction for residual oil by ultrasonic[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2018, 41:661-669. |
| [10] | Mousavi S M, Ramazani A, Najafi I, et al. Effect of ultrasonic irradiation on rheological properties of asphaltic crude oils[J]. Petroleum Science, 2012, 9(1): 82-88. |
| [11] | 张龙力, 杨国华, 阙国和, 等. 超声波处理对渣油胶体稳定性的改善作用初步研究[J]. 石油学报: 石油加工, 2010, 26(): 203-206. |
| Zhang Long-li, Yang Guo-hua, Que Guo-he, et al. Preliminary study on the improvement effect of ultrasonic treatment on the stability of residue colloid[J].Acta Petrolei Sinica(Petroleum Processing), 2010, 26(Sup.1): 203-206. | |
| [12] | 王瑞和, 万春浩, 周卫东, 等. 空化射流降低稠油黏度机制[J]. 中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 43(5): 101-107. |
| Wang Rui-he, Wan Chun-hao, Zhou Wei-dong, et al. Mechanism of reducing viscosity of heavy oil by cavitation jet[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 43(5): 101-107. | |
| [13] | Hamidi H, Rafati R, Junin R B, et al. A role of ultrasonic frequency and power on oil mobilization in underground petroleum reservoirs[J]. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology, 2012,2(1): 29-36. |
| [14] | 寇杰, 王冰冰, 张益华. 原油超声降黏机制[J].中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 43(5): 185-190. |
| Kou Jie, Wang Bing-bing, Zhang Yi-hua. Ultrasonic viscosity reduction mechanism of crude oil[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 43(5): 185-190. | |
| [15] | 韦胜超, 姚志林, 卞贺, 等. 氢键作用对沥青质超分子聚集的影响[J]. 石油学报: 石油加工, 2021, 37(3):556-565. |
| Wei Sheng-chao, Yao Zhi-lin, Bian He, et al. Effect of hydrogen bonding on asphaltene supramolecular aggregation[J].Acta Petrolei Sinica(Petroleum Processing), 2021, 37(3): 556-565. | |
| [16] | 袁献伟. 超声波强化沥青发育技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学机电工程学院, 2019. |
| Yuan Xian-wei. Research on the development technology of ultrasonic reinforced asphalt [D]. Harbin:School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019. | |
| [17] | Wang L M, Song Z K, Gong C. Power ultrasound on asphalt viscoelastic behavior analysis[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2022, 16: No. e01012 . |
| [18] | 王鹏, 姜海龙, 王健, 等. 碳纳米管/SBS复合改性沥青制备工艺的研究[J]. 山东建筑大学学报, 2019,34(6): 21-26. |
| Wang Peng, Jiang Hai-long, Wang Jian, et al. Study on preparation process of carbon nanotube/SBS composite modified bitumen[J].Journal of Shandong Jianzhu University, 2019, 34(6): 21-26. | |
| [19] | 唐伯明, 丁勇杰, 朱洪洲, 等. 沥青分子聚集状态变化特征研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 2013, 26(3): 50-56, 76. |
| Tang Bo-ming, Ding Yong-jie, Zhu Hong-zhou, et al. Study on the characteristics of asphalt molecular aggregation state change[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2013, 26(3): 50-56, 76. | |
| [20] | 詹小丽, 张肖宁, 卢亮. 沥青低温黏弹性能的预测[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2008,38(3): 530-534. |
| Zhan Xiao-li, Zhang Xiao-ning, Lu Liang. Prediction of low-temperature viscoelastic properties of bitumen[J].Journal of Jilin University(Engineering Science), 2008,38(3): 530-534. | |
| [21] | 孙艳娜, 李立寒, 汪于凯. 沥青疲劳性能评价指标[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2014, 49(6): 1102-1107. |
| Sun Yan-na, Li Li-han, Wang Yu-kai. Evaluation index of fatigue performance of asphalt[J].Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(6): 1102-1107. | |
| [22] | 董雨明, 谭忆秋. 硬质沥青混合料的动态黏弹特性[J]. 公路交通科技, 2015, 32(6): 18-24. |
| Dong Yu-ming, Tan Yi-qiu. Dynamic viscoelastic characteristics of hard asphalt mixture[J].Journal of Highway and Transportation Science and Technology, 2015, 32(6): 18-24. | |
| [23] | 张喜军, 仝配配, 蔺习雄, 等. 基于线性振幅扫描试验评价硬质沥青的疲劳性能[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(18): 18083-18089. |
| Zhang Xi-jun, Tong Pei-pei, Lin Xi-xiong, et al. Evaluation of fatigue properties of hard asphalt based on linear amplitude scanning test[J].Materials Reports, 2021, 35(18): 18083-18089. | |
| [24] | 赵泽鹏, 李源, 李梦园, 等. 沥青老化过程中组分与微观形貌演变研究[J]. 炼油技术与工程, 2022, 52(1): 59-64. |
| Zhao Ze-peng, Li Yuan, Li Meng-yuan, et al. Study on component and micromorphological evolution during asphalt aging[J].Refining Technology and Engineering, 2022, 52(1): 59-64. |
| [1] | An-shun ZHANG,Wei FU,Jun-hui ZHANG,Feng GAO. Shear properties and stress-strain relationships characterization of Changsha compacted clay [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1604-1616. |
| [2] | Jing-yang YU,Dong-zhao LI,Zhi-qing ZHANG,Zhen WANG,Hai-lin SUN,Hai-ling BU,Ming-chun LI. Evolution of damage to performance of environment⁃friendly salt storage asphalt mixture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 888-898. |
| [3] | Jun-peng XU,Chuan-feng ZHENG,Yan-tao DU,Yu-hang WANG,Zheng LU,Wen-jun FAN. Damage effects of water⁃heat⁃force coupling in permeable asphalt mixture in cold region [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 877-887. |
| [4] | Yan-hai YANG,Bai-chuan LI,Ye YANG,Chong-hua WANG,Liang YUE. Aggregate ellipsoidal surface base reconstruction with virtual splitting tests [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 653-663. |
| [5] | Teng-fei NIAN,Zhao HAN,Zhi-qiang WEI,Guo-wei WANG,Jin-guo GE,Ping LI. Mesoscopic numerical modeling method of asphalt mix considering aggregate morphology [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 639-652. |
| [6] | Wan-feng WEI,Ling-yun KONG,Wei-an XUAN,Fan YANG,Peng GUO. Review of characteristics of asphalt foaming and moisture sensitivity of warm mix mixtures [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 20-35. |
| [7] | Feng-chun GUO,Hai-peng BI,Hai-tao WANG,Shu-zheng WU,Hong-yu YANG. Viscoelastic behavior of carbon nano powder modified asphalt based on time-temperature equivalence [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 221-229. |
| [8] | Ya-ning CUI,Chun-di SI,Tao-tao FAN,Fei WANG. Analysis on crack propagation of asphalt bridge deck pavement under water-force coupling action [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1988-1996. |
| [9] | Rong LUO,Yu LIANG,Long-chang NIU,Ting-ting HUANG,Qiang MIAO. Threshold value of water stability evaluation index of asphalt mixture under multi-temperature conditions [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1966-1977. |
| [10] | Ying-li GAO,Xiao-lei GU,Mei-jie LIAO,Xin-lang HU,Yu-tong XIE. Rheological properties and modification mechanism of SiO2 aerogel/reactive elastomer terpolymer/Polyphosphoric acid composite modified asphalt [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1978-1987. |
| [11] | Yong-li XU,Xu-lan YANG,Ji-sen ZHOU,Song-han YANG,Ming-gang SUN. Asphalt fume composition of warm mix asphalt and smoke suppression performance of warm mix agent [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1701-1707. |
| [12] | Zu-zhong LI,Meng-yuan LI,Wei-dong LIU,Xiao-xiao PANG,Hao Tang,Xue-lei ZHANG,Chen-yang MA. Surface modification of bagasse fibers and road performances of asphalt mixture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1738-1745. |
| [13] | Ya-zhen SUN,Bo-xin XUE,Yan SUN,Zhi-chen WANG,Jia-wei PAN. Mesoscale simulation of cracking behavior of asphalt mixture considering heterogeneity [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1708-1718. |
| [14] | Xiao-kang ZHAO,Zhe HU,Zhen-xing NIU,Jiu-peng ZHANG,Jian-zhong PEI,Yong WEN. Meso-cracking behavior of cement-stabilized macadam materials based on heterogeneous model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1258-1266. |
| [15] | Tong-tong WAN,Hai-nian WANG,Wen-hua ZHENG,Po-nan FENG,Yu CHEN,Chen ZHANG. Thermal contraction deformation behavior of asphalt mixture overlay with coordination of unbound aggregate layer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1045-1057. |
|