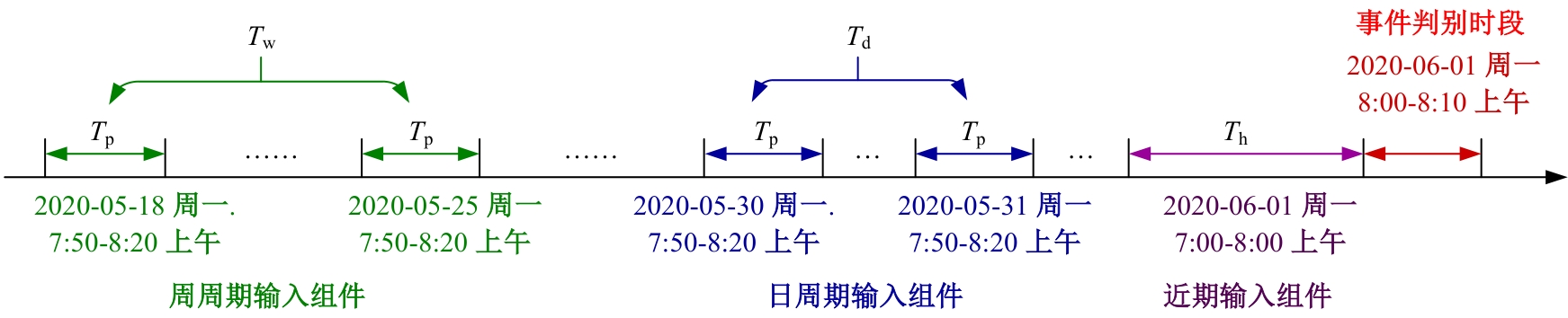
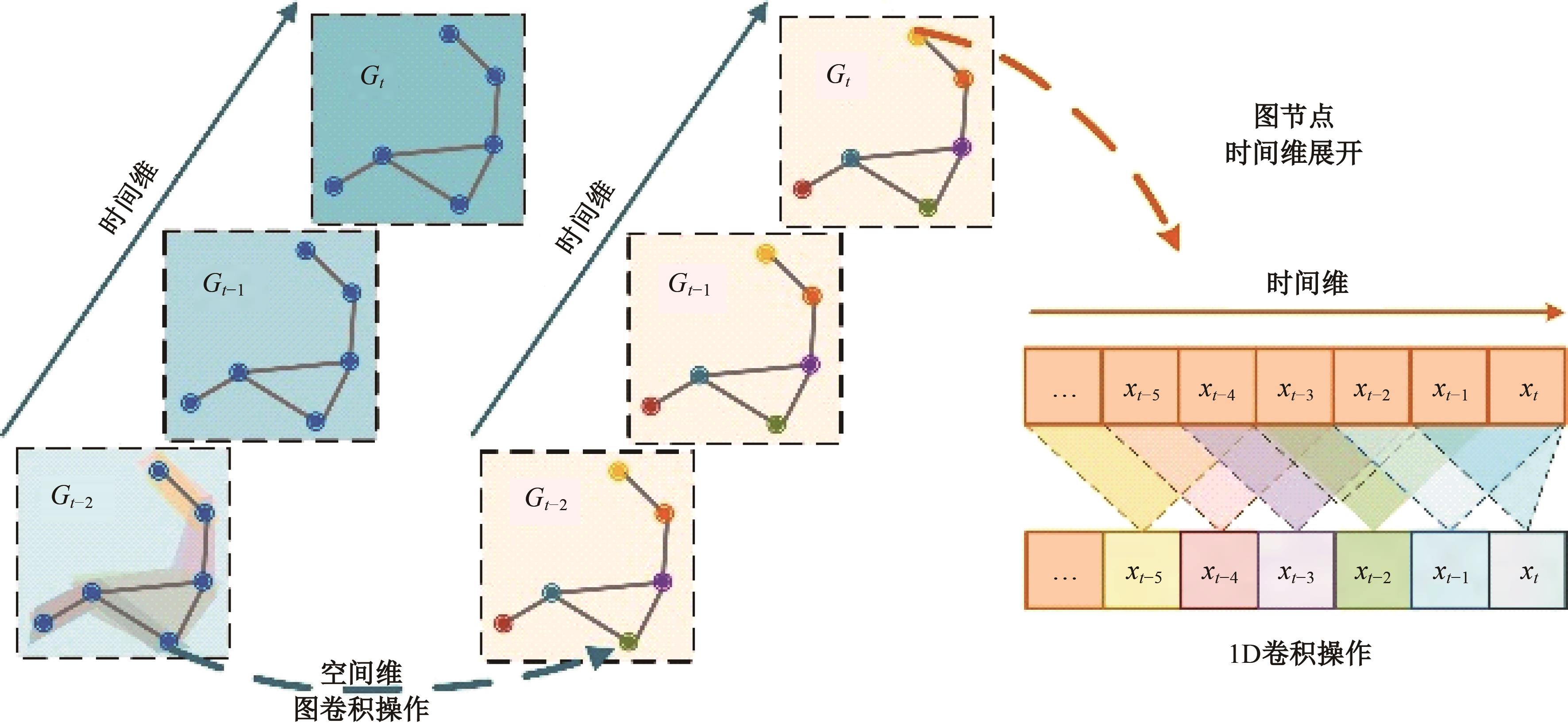
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (7): 2145-2161.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230875
Real-time road network traffic anomaly incident detection based on graph spatial-temporal pattern learning network
Shu-shan CHAI1( ),Zhi-qiang ZHOU1,Hai-tao LI2(
),Zhi-qiang ZHOU1,Hai-tao LI2( ),Jiong-yang XU1
),Jiong-yang XU1
- 1.Research Institute for Road Safety of the Ministry of Public Security,Beijing 100062,China
2.College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
CLC Number:
- U458
| [1] | 刘擎超, 陆建, 陈淑燕. 基于随机森林的交通事件检测方法设计与分析[J]. 东南大学学报: 英文版, 2014, 30(1): 88-95. |
| Liu Qing-chao, Lu Jian, Chen Shu-yan. Design and analysis of traffic detection based on random forest[J]. Journal of Southeast University (English Edition), 2014, 30(1): 88-95. | |
| [2] | Evans J, Waterson B, Hamilton A. Evolution and future of urban road incident detection algorithms[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part A: Systems, 2020, 146(6): No.03120001. |
| [3] | Payne H J, Tignor S C. Freeway incident-detection algorithms based on decision trees with states[J]. Transportation Research Record, 1978, 682: 30-37. |
| [4] | Chakraborty P, Hegde C, Sharma A. Data-driven parallelizable traffic incident detection using spatio-temporally denoised robust thresholds[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2019, 105: 81-99. |
| [5] | 程小洋. 交通事件检测算法的阈值自适应调整与优化[D]. 南京: 东南大学交通学院, 2021. |
| Cheng Xiao-yang. Threshold adaptive adjustment and optimization of traffic incident detection algorithm[D]. Nanjing: School of Transportation, Southeast University, 2021. | |
| [6] | Liu Q C, LU J, Chen S Y, et al. Multiple naive bayes classifiers ensemble for traffic incident detection[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2014, 2014: No.383671. |
| [7] | Srinivasan D, Jin X, Cheu R L. Evaluation of adaptive neural network models for freeway incident detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2004, 5(1): 1-11. |
| [8] | Liu G W, Jin H L, Li J Z, et al. A Bayesian deep learning method for freeway incident detection with uncertainty quantification[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2022, 176: No.106796. |
| [9] | 商强, 林赐云, 杨兆升, 等. 基于变量选择和核极限学习机的交通事件检测[J]. 浙江大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 51(7): 1339-1346. |
| Shang Qiang, Lin Ci-yun, Yang Zhao-sheng, et al. Traffic incident detection based on variable selection and kernel extreme learning machine[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2017, 51(7): 1339-1346. | |
| [10] | Dogru N, Subasi A. Traffic accident detection using random forest classifier[C]∥The 15th Learning and Technology Conference: L&T, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, 2018: 40-45. |
| [11] | Wang L L, Ngan H Y T, Yung N H C. Automatic incident classification for large-scale traffic data by adaptive boosting SVM[J]. Information Sciences, 2018, 467: 59-73. |
| [12] | Xiao J L. SVM and KNN ensemble learning for traffic incident detection[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2019, 517: 29-35. |
| [13] | Wang R, Work D B, Sowers R. Multiple model particle filter for traffic estimation and incident detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2016, 17(12): 3461-3470. |
| [14] | 尹春娥, 陈宽民, 万继志. 基于小波方程的高速公路交通事故自动检测方法[J]. 中国公路学报, 2014, 27(12): 106-112. |
| Yin Chun-er, Chen Kuan-min, Wan Ji-zhi. Automatic detection method for expressway traffic accidents based on wavelet equation[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2014, 27(12): 106-112. | |
| [15] | Adeli H, Samant A. An adaptive conjugate gradient neural network–wavelet model for traffic incident detection[J]. Computer‐Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 2000, 15(4): 251-260. |
| [16] | Lu J, Chen S Y, Wang W, et al. A hybrid model of partial least squares and neural network for traffic incident detection[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2012, 39(5): 4775-4784. |
| [17] | Tang S M, Gao H J. Traffic-incident detection-algorithm based on nonparametric regression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2005, 6(1): 38-42. |
| [18] | Jiang W W, Luo J Y. Graph neural network for traffic forecasting: A survey[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2022, 207: 117921. |
| [19] | 冯宁, 郭晟楠, 宋超, 等. 面向交通流量预测的多组件时空图卷积网络[J]. 软件学报, 2019, 30(3): 759-769. |
| Feng Ning, Guo Sheng-nan, Song Chao, et al. Multi-component spatial-temporal graph convolution networks for traffic flow forecasting[J]. Journal of Software, 2019, 30(3): 759-769. | |
| [20] | Cui Z Y, Henrickson K, Ke R M, et al. Traffic graph convolutional recurrent neural network: A deep learning framework for network-scale traffic learning and forecasting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 21(11): 4883-4894. |
| [21] | 李海涛. 基于深度学习的交通流运行风险评估方法研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学交通学院, 2021. |
| Li Hai-tao. Research on traffic flow operation risk evaluation based on deep learning[D]. Changchun: College of Transportation, Jilin University, 2021. | |
| [22] | Deng L Y, Lian D F, Huang Z Y, et al. Graph convolutional adversarial networks for spatiotemporal anomaly detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning System, 2022, 33(6): 2416-2428. |
| [23] | Zhang H Y, Zhao S Y, Liu R H, et al. Automatic traffic anomaly detection on the road network with spatial-temporal graph neural network representation learning[J]. Wireless Communications & Mobile Computing, 2022: No.4222827. |
| [24] | Keogh E, Ratanamaharana C A. Exact indexing of dynamic time warping[J]. Knowledge and Information Systems, 2005, 7(3): 358-386. |
| [25] | Ge L, Li S Y, Wang Y Q, et al. Global spatial-temporal graph convolutional network for urban traffic speed prediction[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(4): 1509. |
| [26] | Qiu J, Dong Y, Ma H, et al. Network embedding as matrix factorization: unifying deepwalk, line, PTE, and node2vec[C]∥The 11th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2018: 459-467. |
| [27] | 李海涛, 李志慧, 王鑫, 等. 基于时间卷积自编码网络的实时交通事件自动检测方法[J]. 中国公路学报, 2022, 35(6): 265-276. |
| Li Hai-tao, Li Zhi-hui, Wang Xin, et al. Real-time automatic method of detecting traffic incidents based on temporal convolutional autoencoder network[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022, 35(6): 265-276. | |
| [28] | Wang J J, Kumbasar T. Parameter optimization of interval Type-2 fuzzy neural networks based on PSO and BBBC methods[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2019, 6(1): 247-257. |
| [29] | Balke K, Conrad L D, Christopher E M. Using probe-measured travel times to detect major freeway incidents in Houston, Texas[J]. Transportation Research Record, 1996, 1554(1): 213-220. |
| [30] | Zhao Z, Chen W H, Wu X M, et al. LSTM network: a deep learning approach for short‐term traffic forecast[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2017, 11(2): 68-75. |
| [31] | Kong X, Zhang J, Wei X, et al. Adaptive spatial-temporal graph attention networks for traffic flow forecasting[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2021, 52: 4300-4316. |
| [32] | Cao Y, Liu D T, Yin Q Z, et al. MSASGCN: Multi-head self-attention spatiotemporal graph convolutional network for traffic flow forecasting[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2022: 1-15. |
| [1] | Hong-zhuan ZHAO,Ze-jian WU,Xin ZHANG,Sheng-wen SHI,Wen-yong LI,Xin ZHAN,En-yong XU,Jia-ming WANG. Curve lattice model for connected commercial vehicles based on density dispersion and information transmission delay [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2015-2029. |
| [2] | Xiang-jiu CHE,Yu-peng SUN. Graph node classification algorithm based on similarity random walk aggregation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2069-2075. |
| [3] | Yi-yong PAN,Jia-cong XU,Yi-wen YOU,Yong-jun QUAN. Multi-scale spatial heterogeneity analysis of influencing factors of ride-hailing travel demand [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1567-1575. |
| [4] | Kai-ming LU,Yan-yan CHEN,Yao TONG,Jian ZHANG,Yong-xing LI,Ying LUO. Data-driven prediction of departure state for tail vehicles in queues at signalized intersections [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1275-1286. |
| [5] | He-shan ZHANG,Meng-wei FAN,Xin TAN,Zhan-ji ZHENG,Li-ming KOU,Jin XU. Dense small object vehicle detection in UAV aerial images using improved YOLOX [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1307-1318. |
| [6] | Xiao-dong CAI,Qing-song ZHOU,Yan-yan ZHANG,Yun XUE. Social recommendation based on global capture of dynamic, static and relational features [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 700-708. |
| [7] | Jiao-rong WU,Xu-dong LIU. Analysis of influence of built environment of spatial units of different housing types on commuting mode choice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 554-565. |
| [8] | Xiang-jiu CHE,Yu-ning WU,Quan-le LIU. A weighted isomorphic graph classification algorithm based on causal feature learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 681-686. |
| [9] | Fa-cheng CHEN,Guang-quan LU,Qing-feng LIN,Hao-dong ZHANG,She-qiang MA,De-zhi LIU,Hui-jun SONG. Review of drivers' takeover behavior in conditional automated driving [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 419-433. |
| [10] | Yong-ming HE,Jia FENG,Kun WEI,Ya-nan WAN. Analysis on influencing factors of vehicle braking sideslip in curved section of superhighway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 591-602. |
| [11] | Zhao-wei QU,Lin LI,Yong-heng CHEN,Chang-jian WU. Traffic characteristics and safety analysis of long interval U-turn intersections [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2206-2213. |
| [12] | Yong-ming HE,Cong QUAN,Kun WEI,Jia FENG,Ya-nan WAN,Shi-sheng CHEN. Perceptual fusion method of vehicle road cooperation roadside unit in superhighway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1923-1934. |
| [13] | Guo-zhu CHENG,Lin SHENG,Hao-yu WANG,Tian-jun FENG. Safety evaluation method for pedestrians crossing street at signalized intersection considering secondary conflict of right-turn vehicles [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1903-1912. |
| [14] | Xi-jun ZHANG,Guang-jie YU,Yong CUI,Ji-yang SHANG. Short-term traffic flow prediction based on clustering algorithm and graph neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1593-1600. |
| [15] | Ming-ye ZHANG,Min YANG,Yu LI,Shi-yu HUANG,Qing-yun LI. Optimal electric bus scheduling with multiple vehicle types considering coordinated recharging strategy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1293-1301. |
|
||