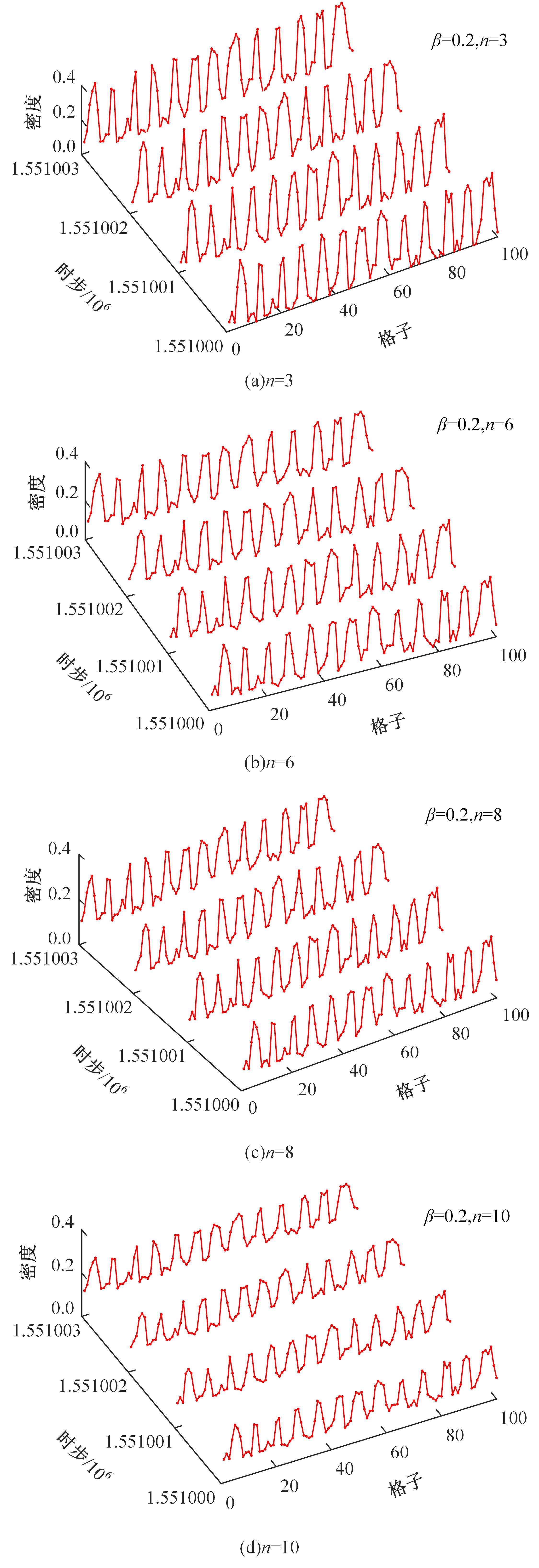
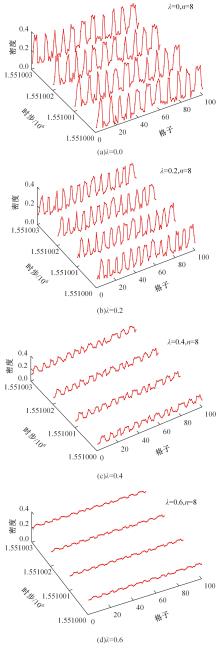
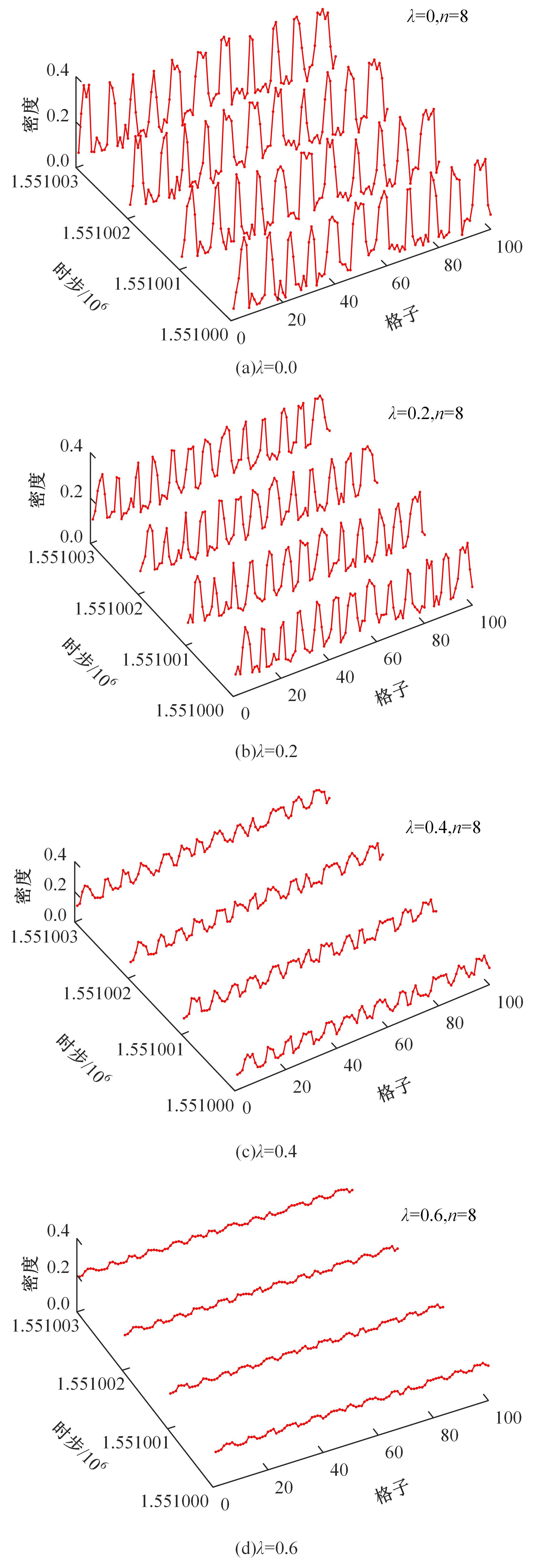
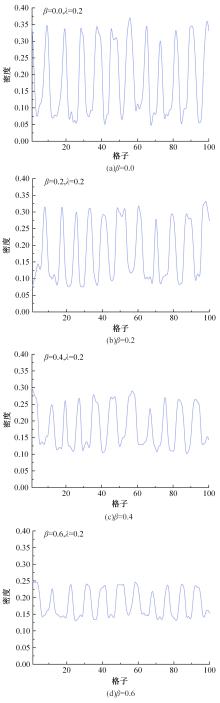
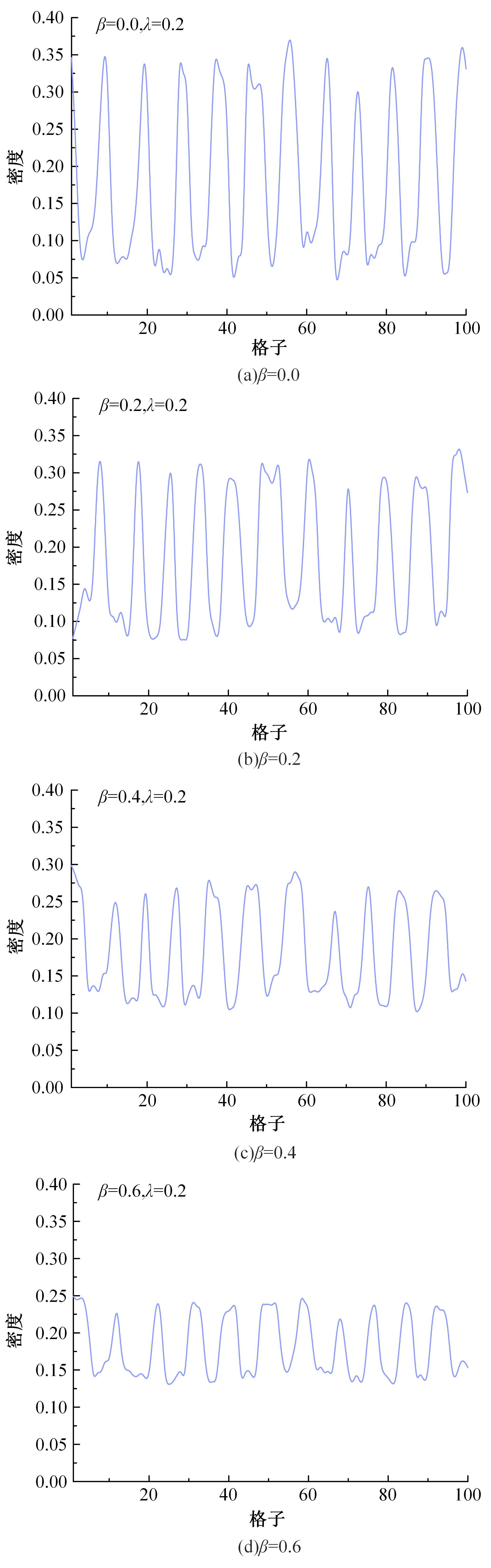
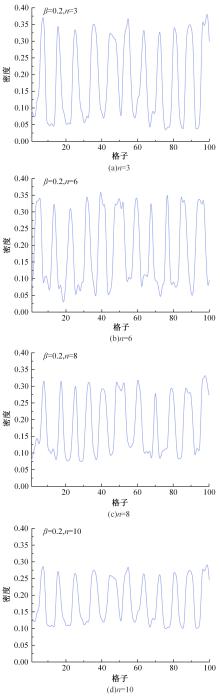
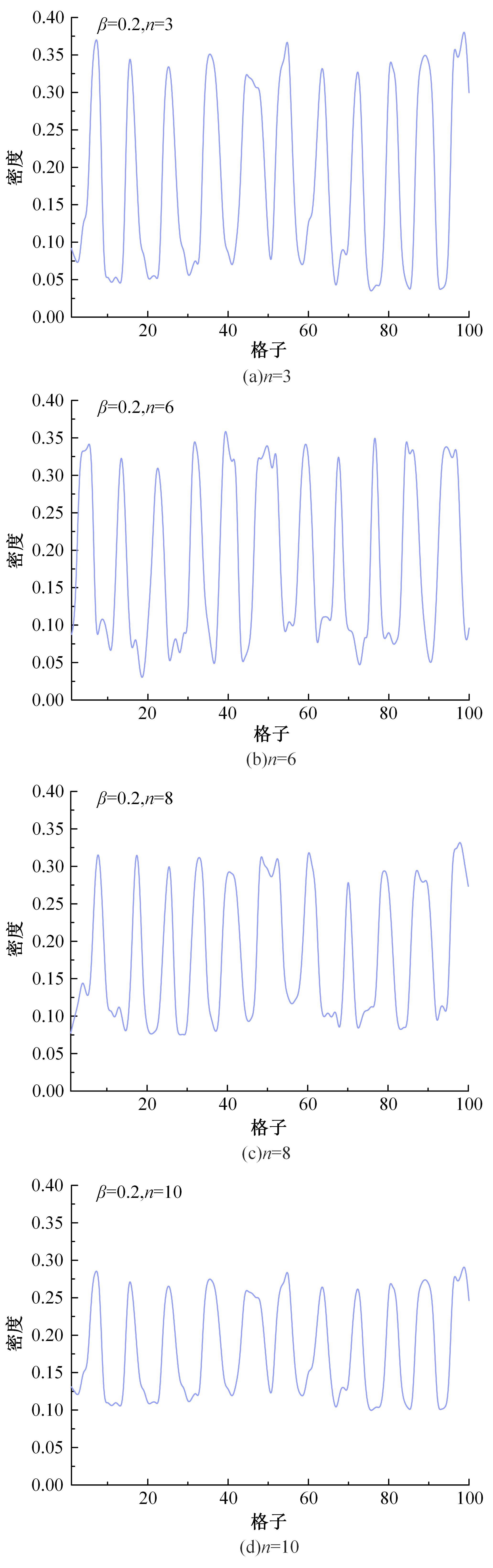
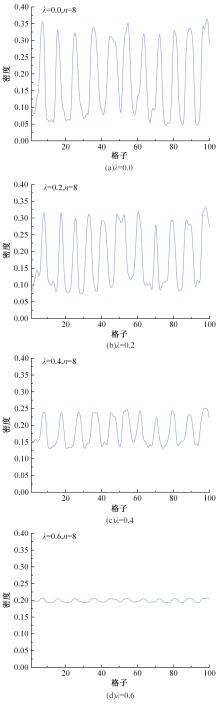
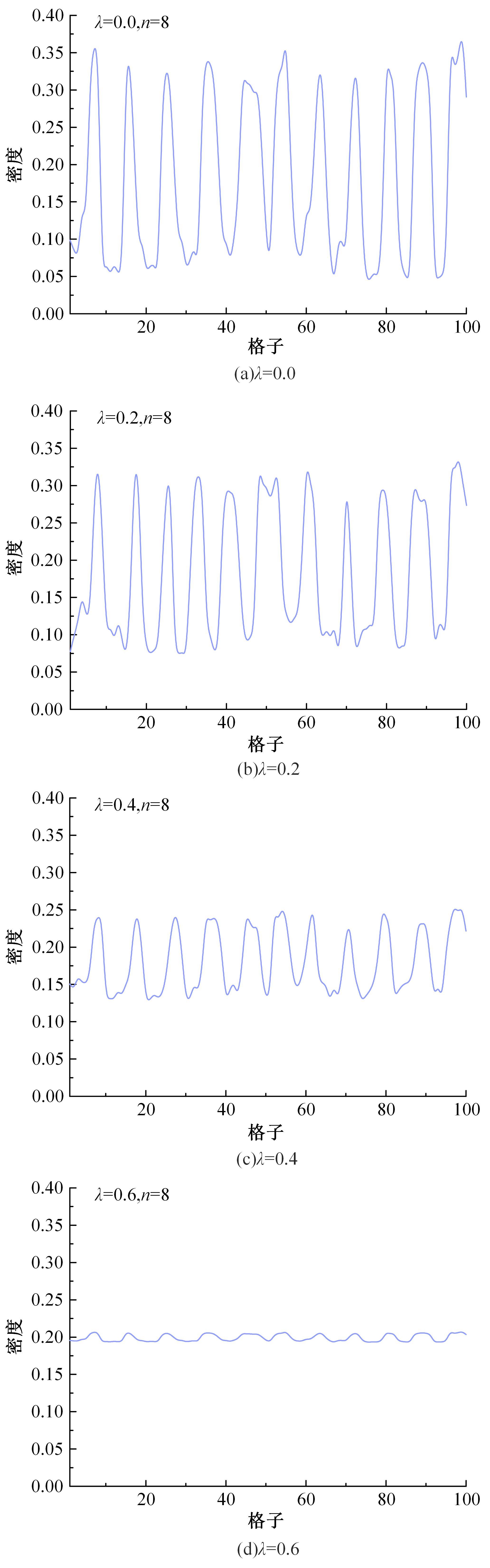
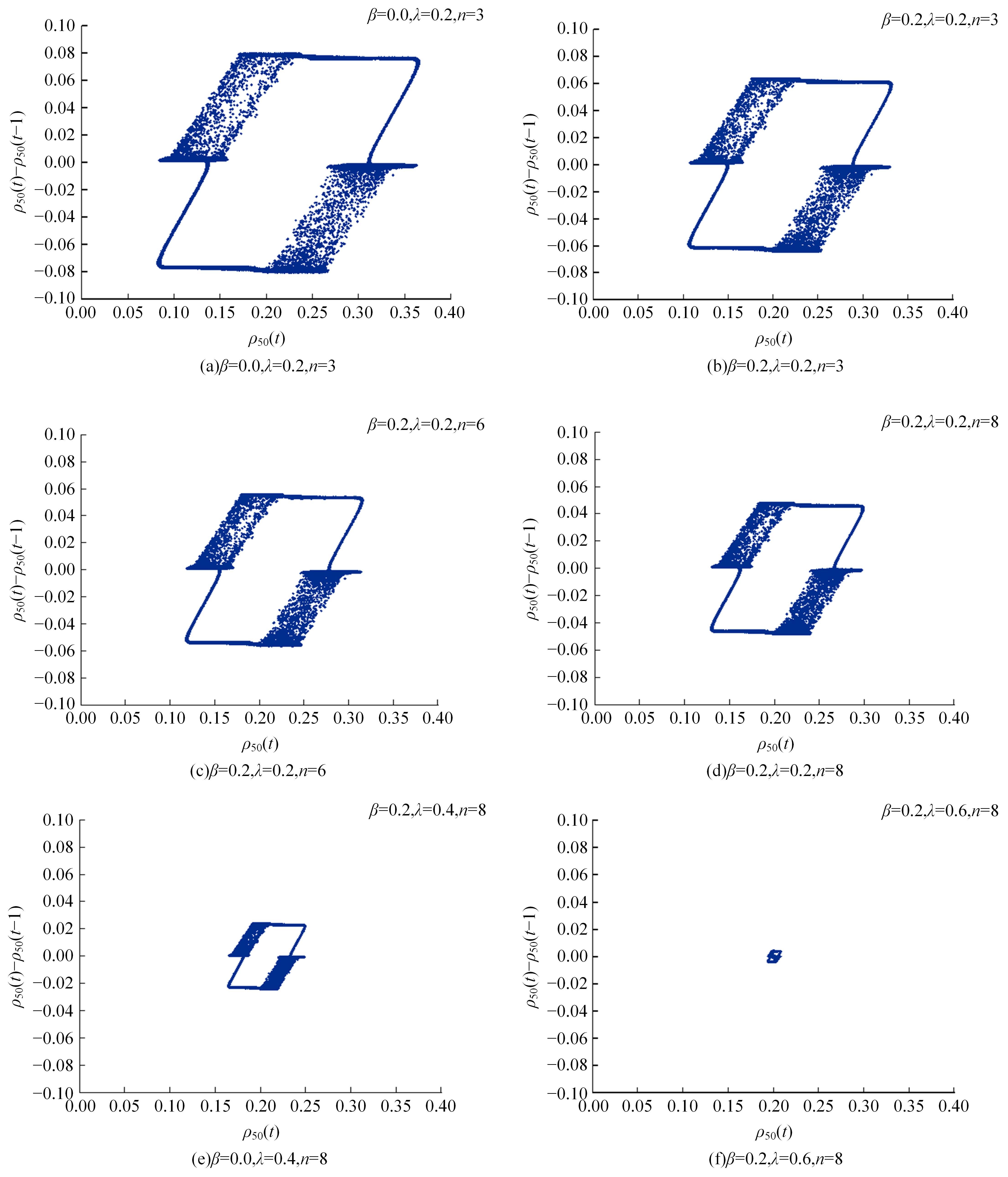
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 2015-2029.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230987
Previous Articles Next Articles
Curve lattice model for connected commercial vehicles based on density dispersion and information transmission delay
Hong-zhuan ZHAO1,2,3,4,5( ),Ze-jian WU1,2,4,5,Xin ZHANG1,2,Sheng-wen SHI4,Wen-yong LI1,Xin ZHAN4,En-yong XU4,Jia-ming WANG4,6
),Ze-jian WU1,2,4,5,Xin ZHANG1,2,Sheng-wen SHI4,Wen-yong LI1,Xin ZHAN4,En-yong XU4,Jia-ming WANG4,6
- 1.Guangxi Key Laboratory of ITS,Guilin University of Electronic Technology,Guilin 541004,China
2.School of Architecture and Transportation Engineering,Guilin University of Electronic Technology,Guilin 541004,China
3.Guangxi Key Laboratory of Precision Navigation Technology and Application,Guilin University of Electronic Technology,Guilin 541004,China
4.Dongfeng Liuzhou Automobile Co. ,Ltd. ,Liuzhou 545005,China
5.GUET-Nanning E-Tech Research Institute Co. ,Ltd,Nanning 530032,China
6.College of Humanities,Art and Design,Guangxi University of Science and Technology,Liuzhou 545006,China
CLC Number:
- U491.1
| [1] | 陈龙, 刘孟协, 蔡英凤, 等.车路协同环境下考虑坡度与前车信息的跟驰模型[J].东南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022, 52(4): 787-795. |
| Chen Long, Liu Meng-xie, Cai Ying-feng, et al. Car-following model considering road gradient and preceding vehicle information in vehicle-infrastructure cooperation environment[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 52(4):787-795. | |
| [2] | 谢济铭, 彭博, 秦雅琴. 基于换道概率分布的多车道交织区元胞自动机模型[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2022, 22(3): 276-285. |
| Xie Ji-ming, Peng Bo, Qin Ya-qin. Cellular automata model of multi-lane weaving area based on lane-changing probability distribution[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2022, 22(3): 276-285. | |
| [3] | Zhang H M. Driver memory, traffic viscosity and a viscous vehicular traffic flow model[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 2003, 37(1): 27-41. |
| [4] | Nagatani T. Jamming transition of high-dimensional traffic dynamics[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 1999, 272(3/4): 592-611. |
| [5] | Wang T, Gao Z, Zhang J, et al. A new lattice hydrodynamic model for two-lane traffic with the consideration of density difference effect[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2014, 75(1): 27-34. |
| [6] | Nagatani T. Modified KdV equation for jamming transition in the continuum models of traffic[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 1998, 261(3/4): 599-607. |
| [7] | Ge H X, Cheng R J. The "backward looking" effect in the lattice hydrodynamic model[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2008, 387(28): 6952-6958. |
| [8] | Peng G H, Cai X H, Cao B F, et al. Non-lane-based lattice hydrodynamic model of traffic flow considering the lateral effects of the lane width[J]. Physics Letters A, 2011, 375(30/31): 2823-2827. |
| [9] | Wang T, Gao Z Y, Zhao X M, et al. Flow difference effect in the two-lane lattice hydrodynamic model[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2012, 21(7): No.070507. |
| [10] | Gupta A K, Redhu P. Analysis of a modified two-lane lattice model by considering the density difference effect[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2014, 19(5): 1600-1610. |
| [11] | Peng G. A new lattice model of two-lane traffic flow with the consideration of optimal current difference[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2013, 18(3): 559-566. |
| [12] | Nagatani T. Jamming transitions and the modified Korteweg-de Vries equation in a two-lane traffic flow[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 1999, 265(1/2): 297-310. |
| [13] | Nagatani T. Jamming transition in a two-dimensional traffic flow model[J]. Physical Review E, 1999, 59(5): No.4857. |
| [14] | Nagatani T. TDGL and MKdV equations for jamming transition in the lattice models of traffic[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 1999, 264(3/4): 581-592. |
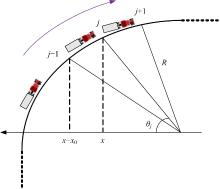
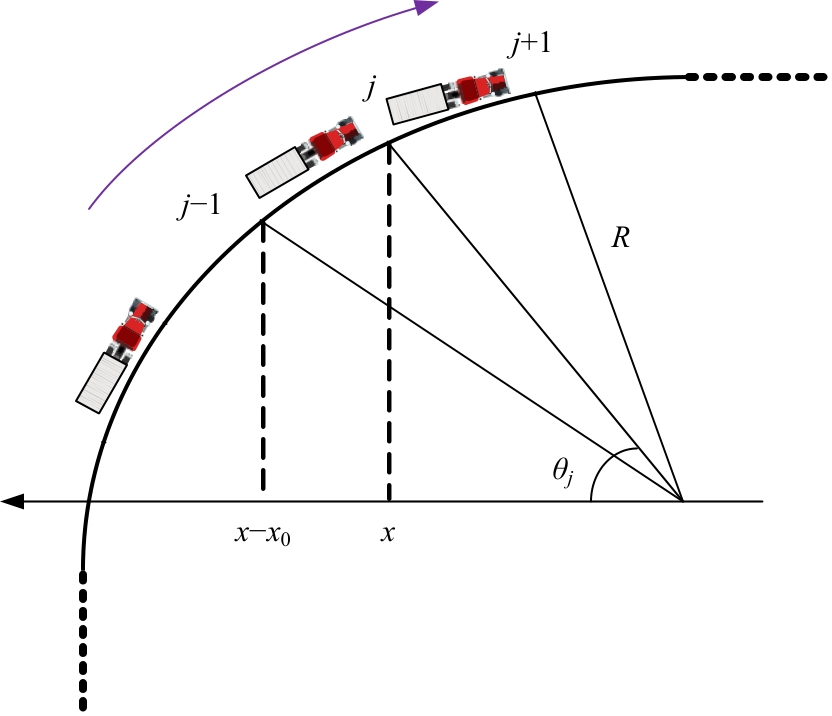
| [15] | Cao J L, Shi Z K. A novel lattice traffic flow model on a curved road[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics C, 2015, 26(11): No.1550121. |
| [16] | Kaur R, Sharma S. Analysis of driver's characteristics on a curved road in a lattice model[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2017, 471: 59-67. |
| [17] | Kaur R, Sharma S. Modeling and simulation of driver's anticipation effect in a two lane system on curved road with slope[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2018, 499: 110-120. |
| [18] | Cheng R, Wang Y. An extended lattice hydrodynamic model considering the delayed feedback control on a curved road[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2019, 513: 510-517. |
| [19] | Wang Z, Zhu W X. Modeling and stability analysis of traffic flow considering electronic throttle dynamics on a curved road with slope[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2022, 597: No.127225. |
| [20] | Redhu P, Gupta A K. Delayed-feedback control in a Lattice hydrodynamic model[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science & Numerical Simulation, 2015, 27(1/3):263-270. |
| [21] | Peng G, Yang S, Zhao H. A delayed-feedback control method for the lattice hydrodynamic model caused by the historic density difference effect[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2018, 509:855-860. |
| [22] | Peng G, Yang S, Xia D, et al. Delayed-feedback control in a car-following model with the combination of V2V communication[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2019, 526: No.120912. |
| [23] | Zhang Y, Wang S, Pan D, et al. Stability analysis for a new lattice hydrodynamic model with time-varying delay in sensing traffic flux[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2021, 561: No.125269. |
| [24] | 罗春莉. V2X环境下基于交通信息协同传输的优化建模与能耗控制[D]. 桂林:广西师范大学物理科学与技术学院, 2023. |
| Luo Chun-li. Optimization modeling and energy consumption control based on traffic information collaborative transmission under V2X environment[D]. Guilin:College of Physical Science and Technology, Guangxi Normal University, 2023. | |
| [25] | 贾特提. V2X环境下基于协同信息传输延迟的交通系统优化建模与能耗控制[D]. 桂林:广西师范大学物理科学与技术学院, 2023. |
| Jia Te-ti. Optimal modeling and energy consumption control of traffic system based on cooperative information transmission delay under V2X environment[D]. Guilin:College of Physical Science and Technology, Guangxi Normal University, 2023. | |
| [26] | 贾洪飞, 隽志才, 魏丽英. 饱和流率的部分影响因素修正系数的标定[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2000, 30(2): 99-102. |
| Jia Hong-fei, Zhi-cai Juan, Wei Li-ying. Calibration to the revision coefficients of some factors affecting saturation flow rate[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2000,30(2): 99-102. | |
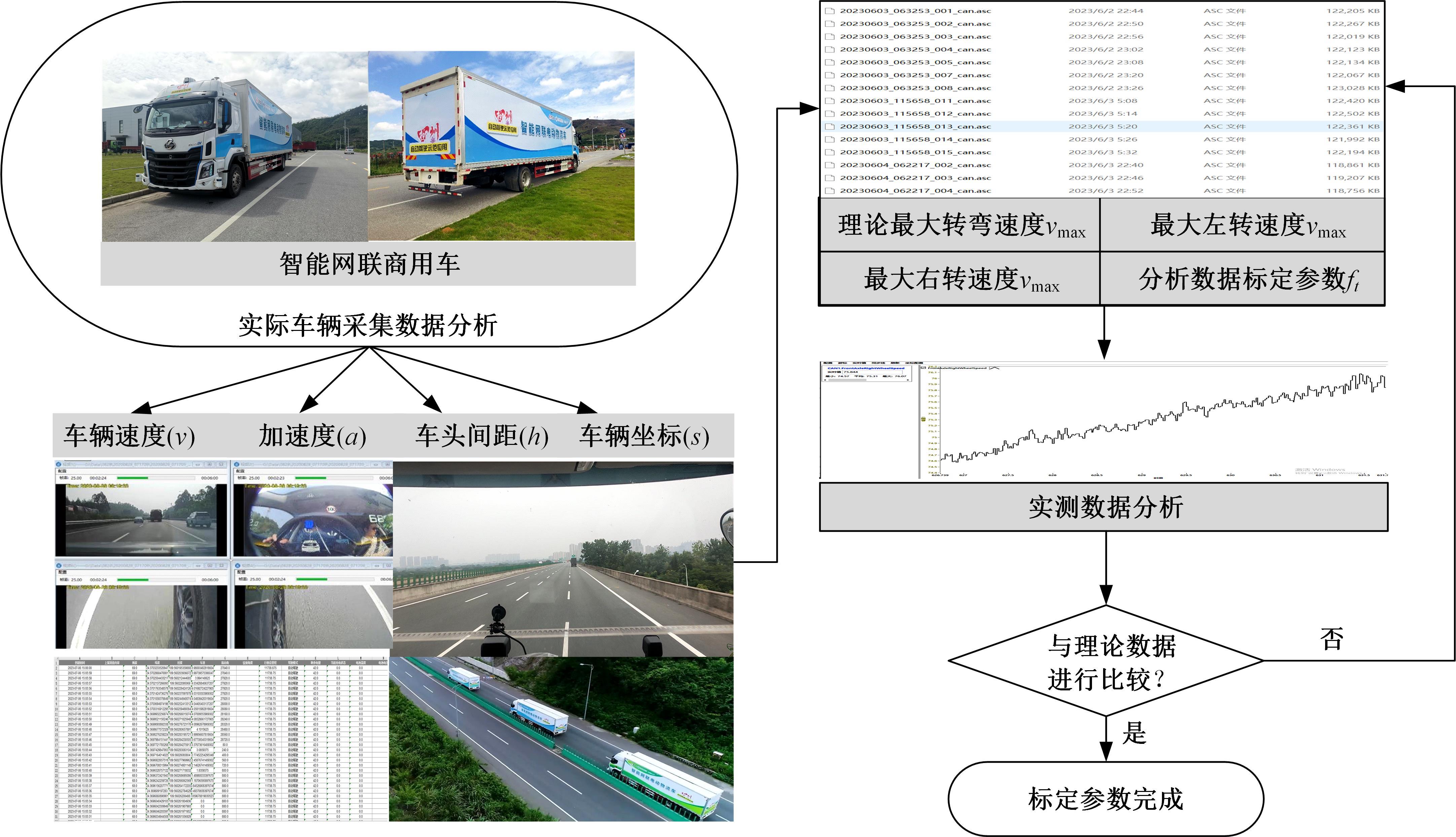
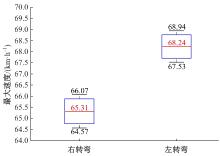
| [27] | 王宪彬, 施树明, 裴玉龙. 面向网联商用车行驶工况优化设计的高速公路工况识别[J]. 中国公路学报, 2022, 35(6): 355-362. |
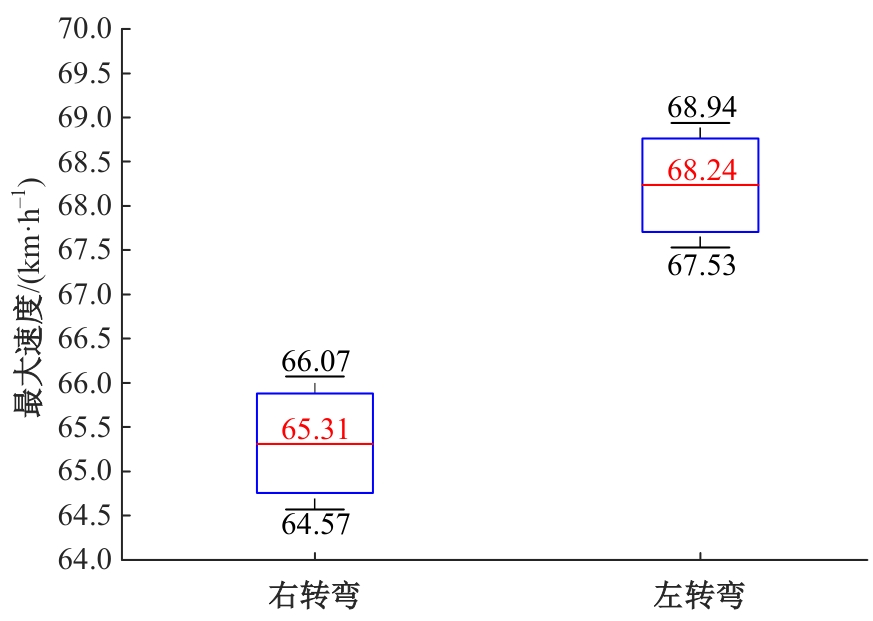
| Wang Xian-bin, Shi Shu-ming, Pei Yu-long. Identification of expressway driving cycles for optimization of commercial vehicle driving cycles[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022, 35(6): 355-362. | |
| [28] | 唐易, 刘诗昆, 刘恒. 基于多源数据的高速公路交通运行特征与治堵策略研究:以深圳市机荷高速为例[J]. 交通与运输, 2022, 35(S1): 132-138. |
| Tang Yi, Liu Shi-kun, Liu Heng. Research on traffic operation characteristics of expressway and control strategy of traffic congestion based on multi-source data:Taking Shenzhen Jihe Expressway as an example[J]. Traffic & Transportation, 2022, 35(Sup.1): 132-138. | |
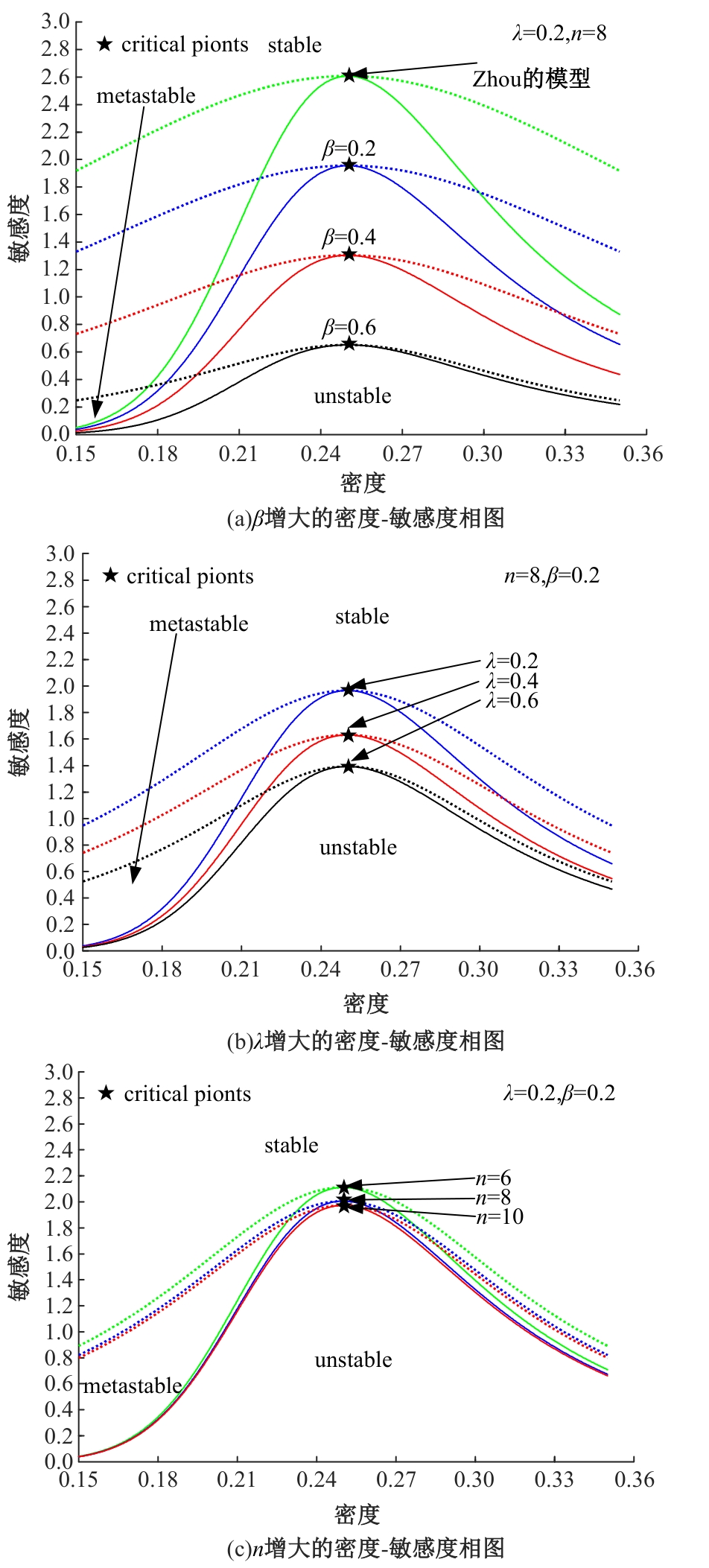
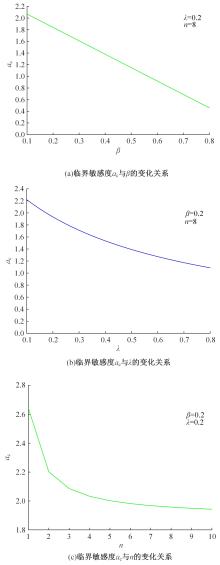
| [29] | Zhou J, Shi Z K. Lattice hydrodynamic model for traffic flow on curved road[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2016, 83: 1217-1236. |
| [1] | Yi-yong PAN,Jia-cong XU,Yi-wen YOU,Yong-jun QUAN. Multi-scale spatial heterogeneity analysis of influencing factors of ride-hailing travel demand [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1567-1575. |
| [2] | Kai-ming LU,Yan-yan CHEN,Yao TONG,Jian ZHANG,Yong-xing LI,Ying LUO. Data-driven prediction of departure state for tail vehicles in queues at signalized intersections [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1275-1286. |
| [3] | He-shan ZHANG,Meng-wei FAN,Xin TAN,Zhan-ji ZHENG,Li-ming KOU,Jin XU. Dense small object vehicle detection in UAV aerial images using improved YOLOX [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1307-1318. |
| [4] | Shu-xu ZHAO,Zhi-chao SUN,Xiao-long WANG. Dynamic authentication protocol for mobile edge computing scenarios [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 1050-1060. |
| [5] | Jiao-rong WU,Xu-dong LIU. Analysis of influence of built environment of spatial units of different housing types on commuting mode choice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 554-565. |
| [6] | Fa-cheng CHEN,Guang-quan LU,Qing-feng LIN,Hao-dong ZHANG,She-qiang MA,De-zhi LIU,Hui-jun SONG. Review of drivers' takeover behavior in conditional automated driving [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 419-433. |
| [7] | Yong-ming HE,Jia FENG,Kun WEI,Ya-nan WAN. Analysis on influencing factors of vehicle braking sideslip in curved section of superhighway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 591-602. |
| [8] | Gao-cheng AN,Zhen-hua HU,Hong-quan DONG,Bao-yu LIU,Kai GAO,Wen-kang WANG. Design and analysis of guide curve of radial piston motor with low argument distribution coefficient [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 485-493. |
| [9] | Zhao-wei QU,Lin LI,Yong-heng CHEN,Chang-jian WU. Traffic characteristics and safety analysis of long interval U-turn intersections [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2206-2213. |
| [10] | Xue-lian GUO,Wan-shui HAN,Tao WANG,Kai ZHOU,Xiu-shi ZHANG,Shu-ying ZHANG. Assessment method of resistant overturning stability safety factors of curved bridge under customized transport vehicles [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2229-2237. |
| [11] | Sheng CHANG,Hong-fei LIU,Nai-wei ZOU. H∞ loop shaping robust control of vehicle tracking on variable curvature curve [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2141-2148. |
| [12] | Guo-zhu CHENG,Lin SHENG,Hao-yu WANG,Tian-jun FENG. Safety evaluation method for pedestrians crossing street at signalized intersection considering secondary conflict of right-turn vehicles [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1903-1912. |
| [13] | Yong-ming HE,Cong QUAN,Kun WEI,Jia FENG,Ya-nan WAN,Shi-sheng CHEN. Perceptual fusion method of vehicle road cooperation roadside unit in superhighway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1923-1934. |
| [14] | Guo-lin YANG,Yi-fan YANG,Hao-dong XU,Gui-jun LUO,Hong-bo XIAO. Calculation method and influencing factors of surface displacement during construction of curved shield tunnel [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1997-2008. |
| [15] | Yan-ling ZHANG, JIAYun-fei,Xiao-yuan JIA,Wang ZHENG,Yun-sheng LI. Proposed formulae for transverse distribution factor of internal forces of prefabricated small box-girder bridge [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1688-1700. |
|