吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (4): 978-983.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210422
金银花提取物对LPS诱导的急性前部葡萄膜炎小鼠的抗炎作用及其机制
- 河北医科大学第一医院眼科,河北 石家庄 050031
Anti-inflammatory effect of honeysuckle extract on acute anterior uveitis mice induced by LPS and its mechanism
Kangning LI,Zhiling SONG,Lilong JIA,Miao CHU( ),Chaohui XIONG
),Chaohui XIONG
- Department of Ophthalmology,the First Hospital of Hebei Medical University,Shijiazhuang 050031,China
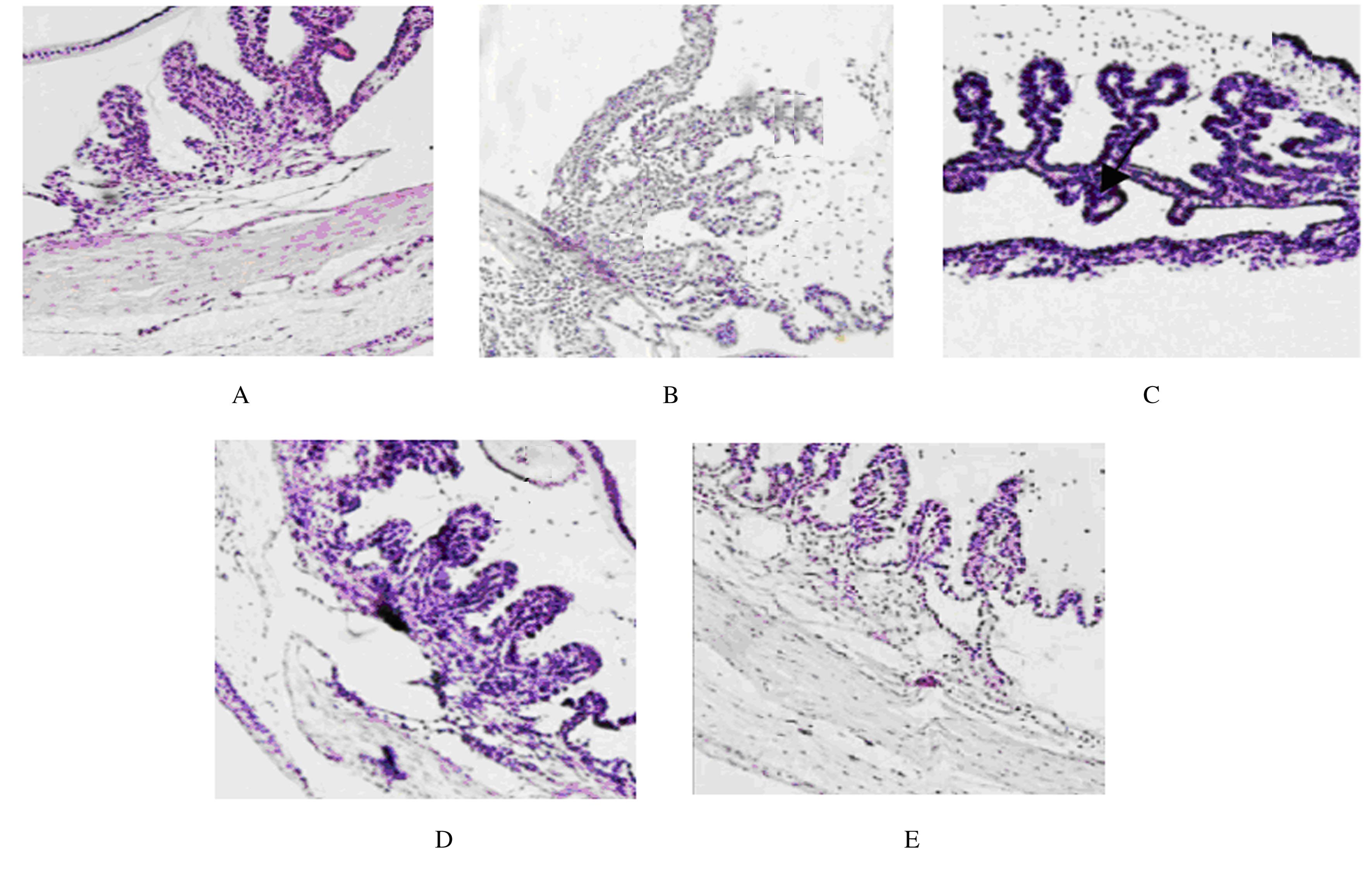
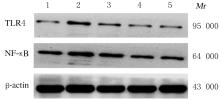
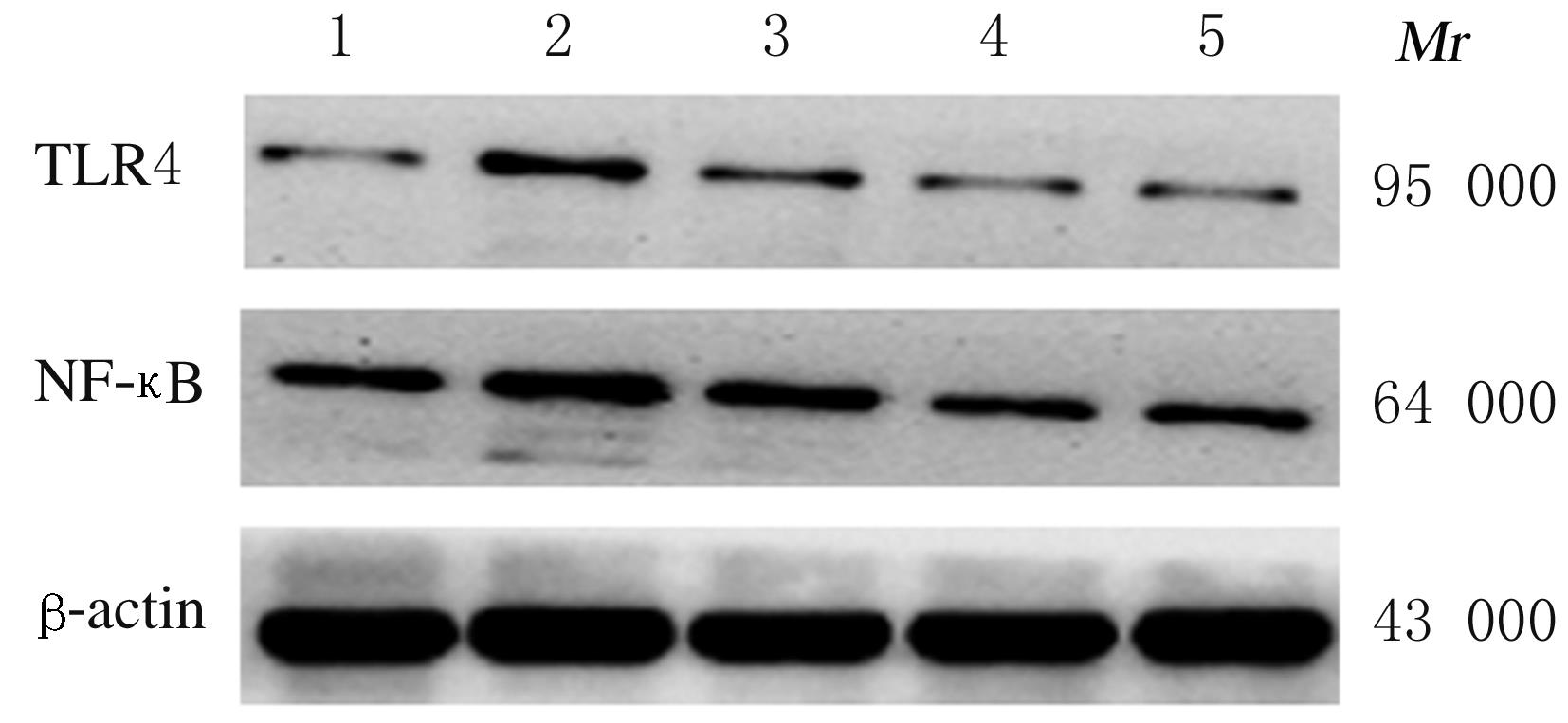
摘要: 探讨金银花提取物对脂多糖(LPS)诱导的急性前部葡萄膜炎(AAU)小鼠的抗炎作用,并阐明其作用机制。 将50只BALB/c小鼠随机分为对照组,模型组,低、中和高剂量金银花提取物组,每组10只。低、中和高剂量金银花提取物组小鼠灌胃给予250、500 和 750 mg·kg-1金银花提取物,对照组和模型组小鼠均给予等体积生理盐水。连续给药15 d后,除对照组外其余各组小鼠于玻璃体腔内注射125 mg·L-1LPS建立小鼠AAU模型。采用HE染色观察小鼠眼组织病理形态表现,采用实时荧光定量PCR法(RT-qPCR)和Western blotting法检测小鼠眼组织中Toll样受体4(TLR4)及核因子κB(NF-κB)mRNA和蛋白表达水平,采用酶联免疫吸附测定法(ELISA)检测小鼠眼组织中肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)、白细胞介素6(IL-6)和白细胞介素10(IL-10)水平。 对照组小鼠眼组织结构完整,无炎症细胞浸润;模型组小鼠视网膜水肿,葡萄膜组织中出现大量炎症细胞浸润;与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量金银花提取物组小鼠葡萄膜组织中炎症细胞浸润不同程度减轻。与对照组比较,模型组小鼠眼组织中TLR4及NF-κB mRNA和蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05),TNF-α、IL-6和IL-10水平明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量金银花提取物组小鼠眼组织中TLR4及NF-κB mRNA和蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05),TNF-α、IL-6和IL-10水平明显降低(P<0.05);与低剂量金银花提取物组比较,中和高剂量金银花提取物组小鼠眼组织中TLR4及NF-κB mRNA和蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05),TNF-α、IL-6和IL-10水平明显降低(P<0.05);与中剂量金银花提取物组比较,高剂量金银花提取物组小鼠眼组织中TLR4及NF-κB mRNA和蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05),TNF-α、IL-6和IL-10水平明显降低(P<0.05)。 金银花提取物可通过TLR4/NF-κB信号通路下调炎症细胞表达,减轻AAU小鼠的眼部组织炎症反应,且呈剂量依赖性。
中图分类号:
- R773.9