吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (5): 1124-1130.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210507
莪术醇对小鼠肝窦内皮细胞结构的影响及其对肝内血管新生的抑制作用
- 1.广西中医药大学赛恩斯新医药学院医学系,广西 南宁 530222
2.广西中医药大学基础医学院 生理教研室,广西 南宁 530222
Influence of curcumol in structure of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells of mice and its inhibitiory effect on intrahepatic angiogenesis
Yang ZHENG1,Jiahui WANG1,Yue PENG2,Xianling YUAN2,Lei WANG1,Tiejian ZHAO2( )
)
- 1.Department of Medicine,Faculty of Chinese Medicine Science,Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine,Nanning 530021,China
2.Department of Physiology,College of Basic Medical Sciences,Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine,Nanning 530021,China
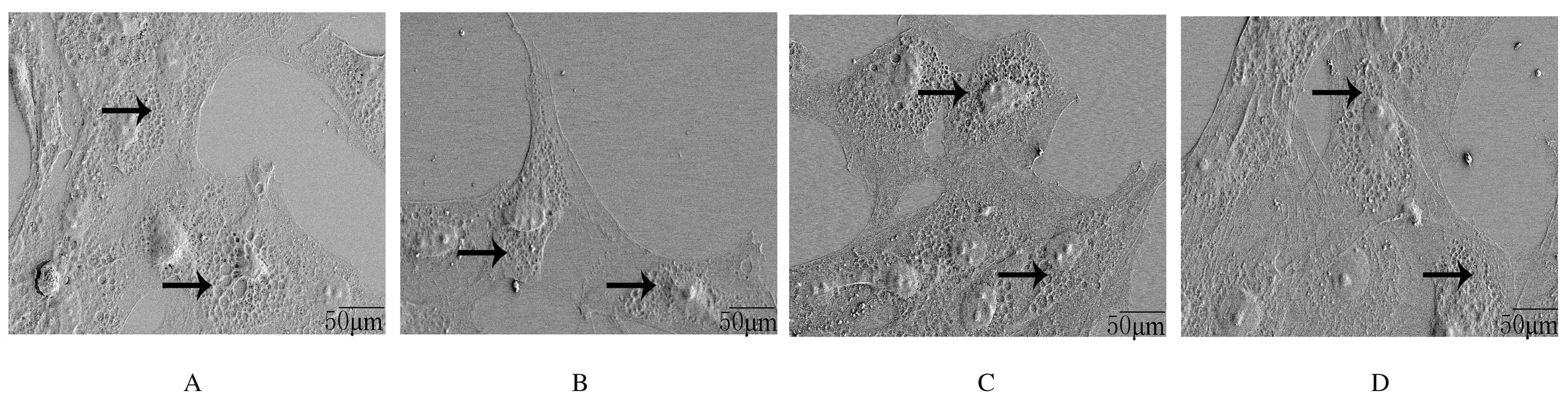
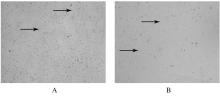
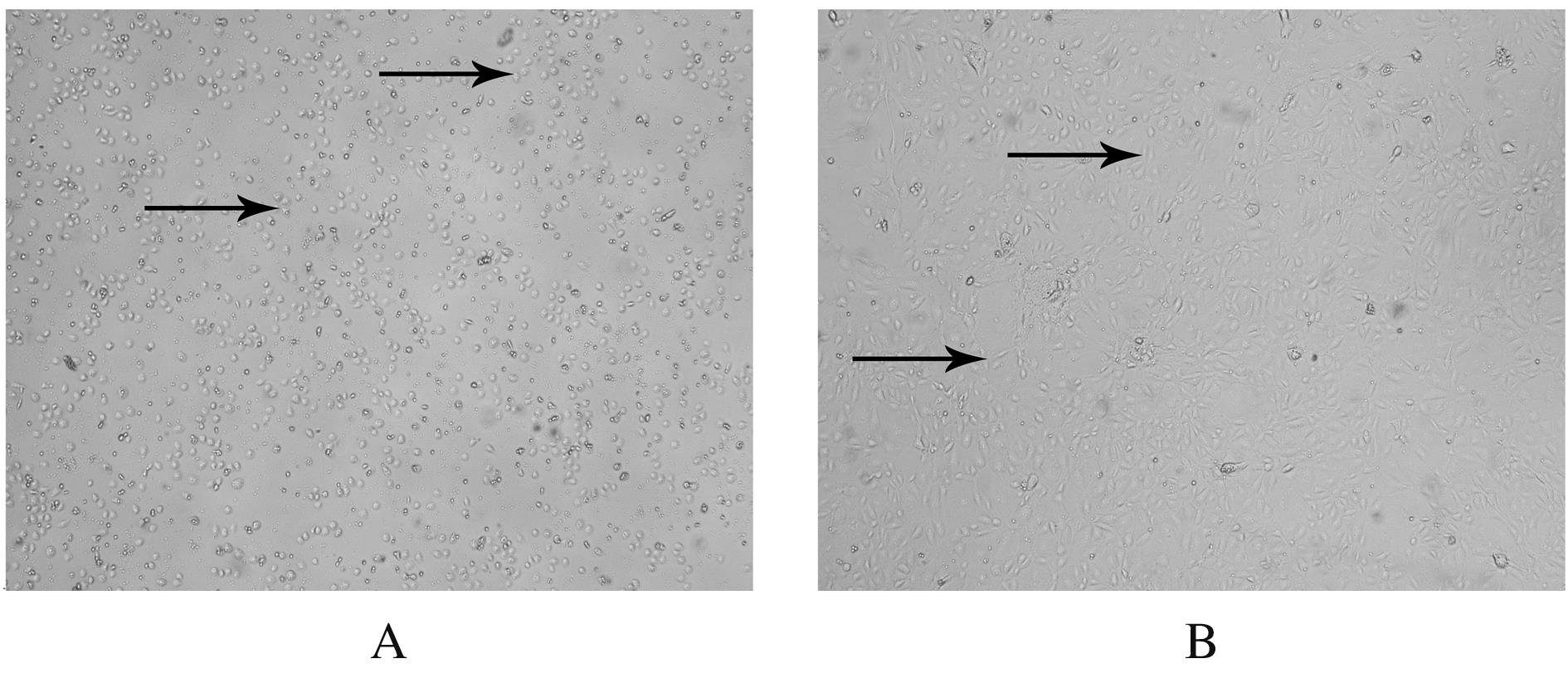
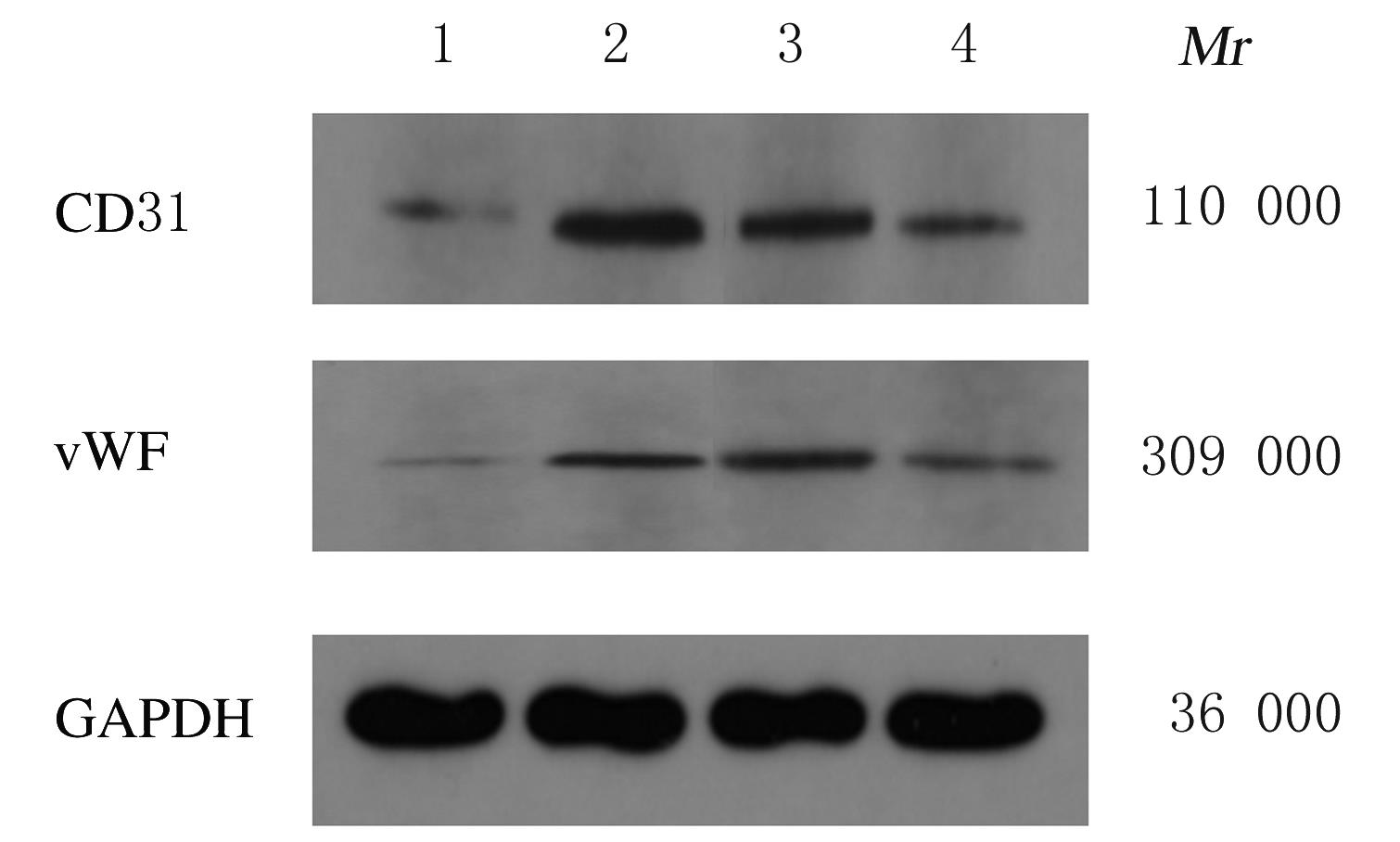
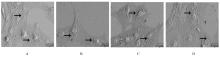
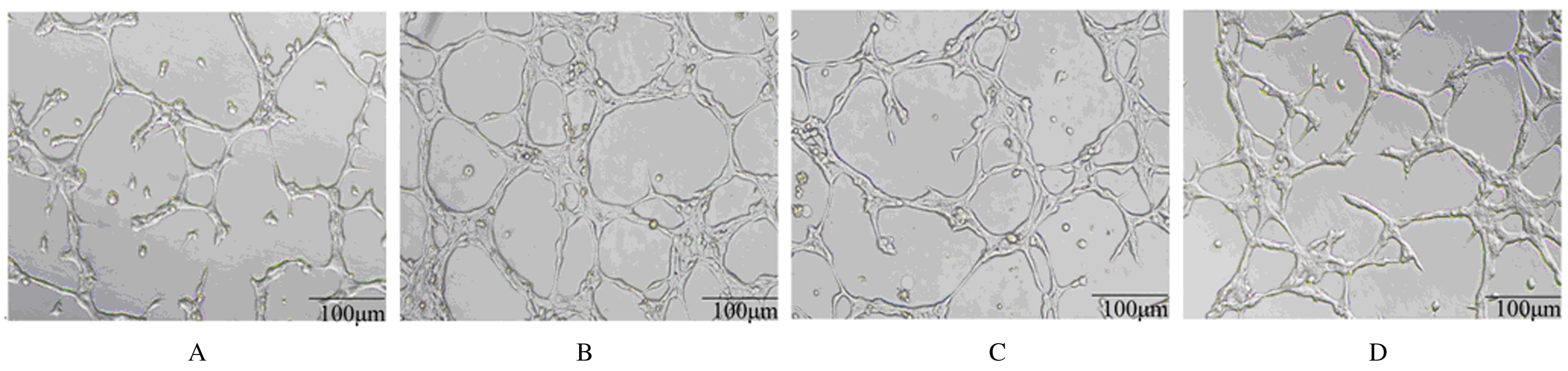
摘要: 探讨莪术醇对小鼠肝窦内皮细胞(LSEC)结构的影响,阐明其对LSEC介导的肝内血管新生的作用。 30只SPF级KM小鼠使用灌注及消化法分离原代LSEC,将其分为空白对照组、模型组、莪术醇组和丹参酚酸B组,空白对照组仅用普通培养基处理;模型组用100 μg·L-1廋素进行活化,培养细胞48 h;莪术醇组先用45 mg·L-1莪术醇处理30 min再用廋素培养细胞48 h;丹参酚酸B组先用1×10-6 mmol·L-1丹参酚酸B处理30 min再用廋素培养细胞48 h。采用MTT法检测各组细胞增殖率,实时荧光定量聚合酶链式反应(RT-qPCR)法检测各组细胞中分化抗原簇31(CD31)和血管性血友病因子(vWF) mRNA表达水平,免疫印迹法检测CD31和vWF蛋白表达水平,扫描电镜观察LSEC窗孔的结构,血管形成实验观察肝内血管新生情况。 MTT法检测,模型组细胞增殖率较空白对照组明显降低(P<0.05),莪术醇组和丹参酚酸B组细胞增殖率较模型组明显下降(P<0.05),丹参酚酸B组与莪术醇组细胞增殖率比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。RT-qPCR法检测,模型组细胞中CD31和vWF mRNA表达水平较空白对照组明显升高(P<0.05),莪术醇组和丹参酚酸B组细胞中CD31和vWF mRNA表达水平较模型组明显降低(P<0.05),丹参酚酸B组与莪术醇组细胞中CD31和vWF mRNA表达水平比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。免疫印迹法检测,模型组细胞中CD31和vWF蛋白表达水平较空白对照组明显升高(P<0.05),莪术醇组和丹参酚酸B组细胞中CD31和vWF蛋白表达水平较模型组明显降低(P<0.05),莪术醇组与丹参酚酸B组细胞中CD31和vWF蛋白表达水平比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。扫描电镜观察,空白对照组LSEC窗孔数量较多,与空白对照组比较,模型组窗孔数量减少;与模型组比较,莪术醇组和丹参酚酸B组LSEC窗孔数量有所增加。血管形成实验检测,模型组血管形成数量较空白对照组明显增加(P<0.05),莪术醇组和丹参酚酸B组血管形成数量较模型组明显减少(P<0.05),莪术醇组与丹参酚酸B组血管形成数量比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 莪术醇通过调控小鼠LSEC的窗孔结构,从而抑制肝内血管新生。
中图分类号:
- R657.3