吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (2): 348-355.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220211
胡桃醌对宫颈癌细胞增殖的抑制作用及其机制
- 1.吉林医药学院生化教研室,吉林 吉林 132013
2.延边大学基础医学院生化教研室,吉林 延吉 133000
Inhibitory effect of juglone on proliferation of cervical cancer cells and its mechanism
Xingyu ZHAO1,Xin YANG1,Zhihua ZHU1,Han HE2,Zitong SONG1,Wei ZHANG1( )
)
- 1.Department of Biochemistry,Jilin Medical College,Jilin 13201,China
2.Department of Biochemistry,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Yanbian University,Ynabian 133000,China
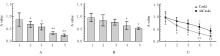
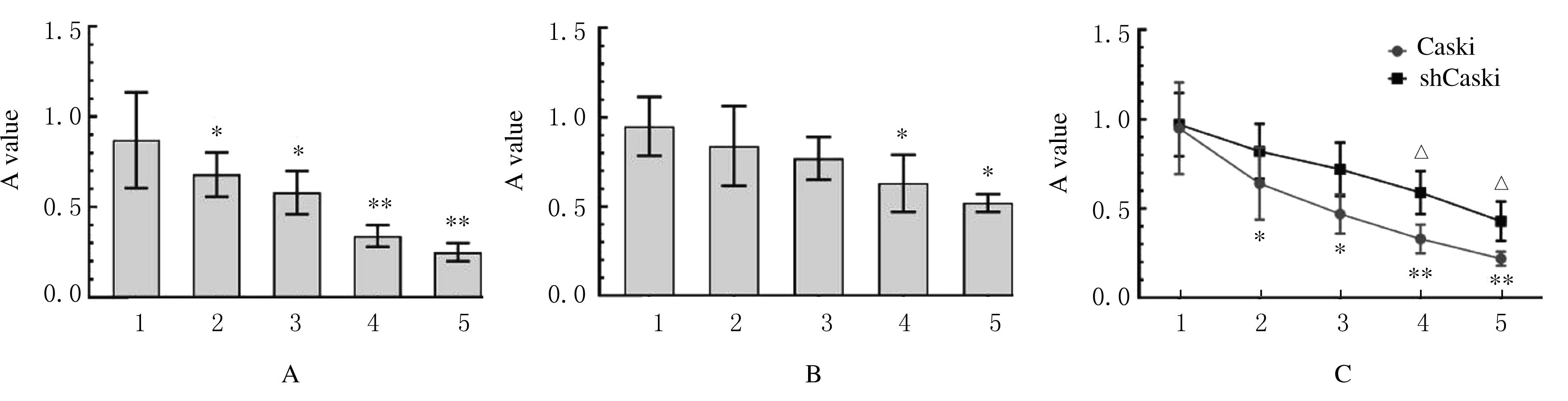
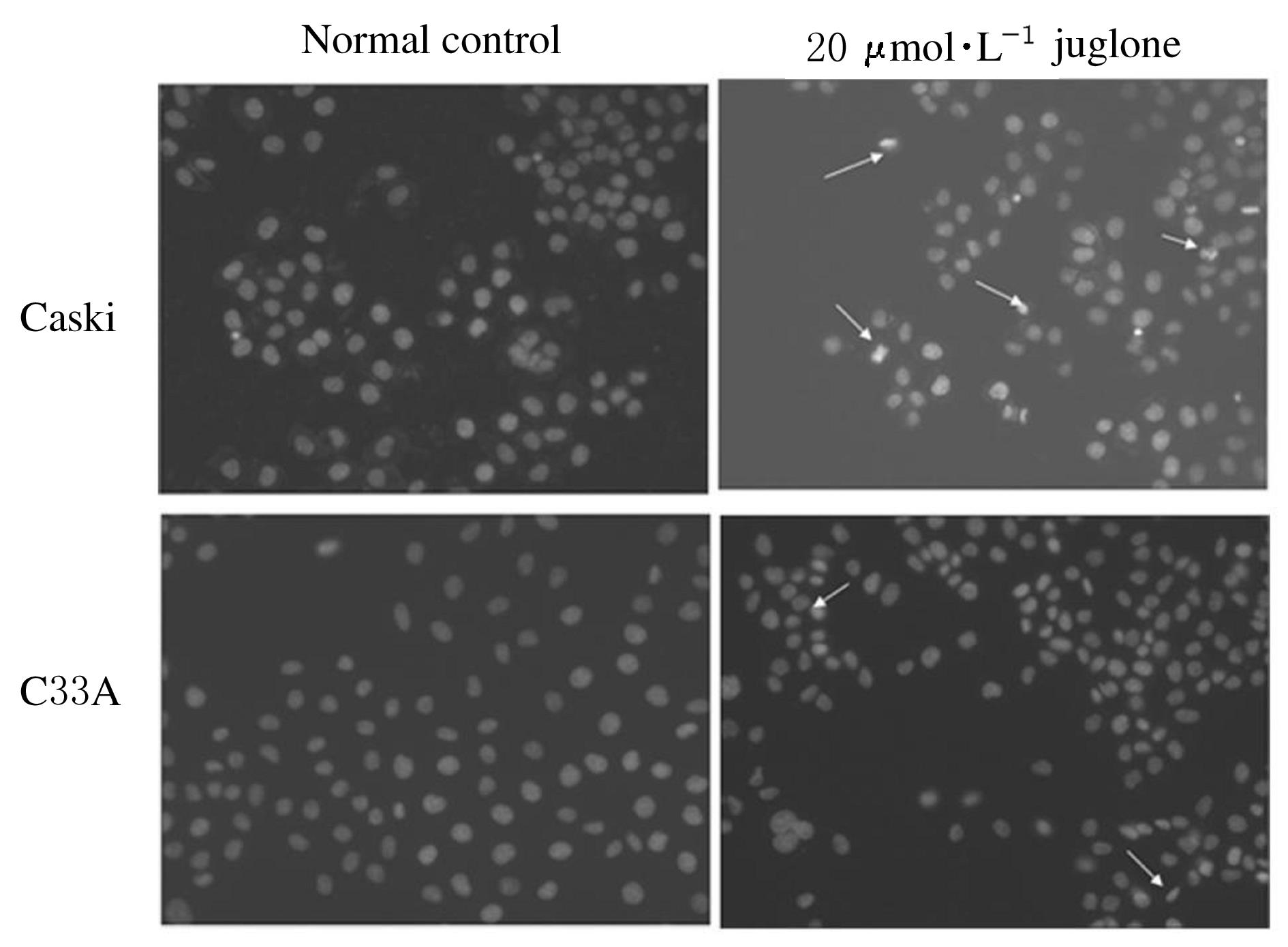
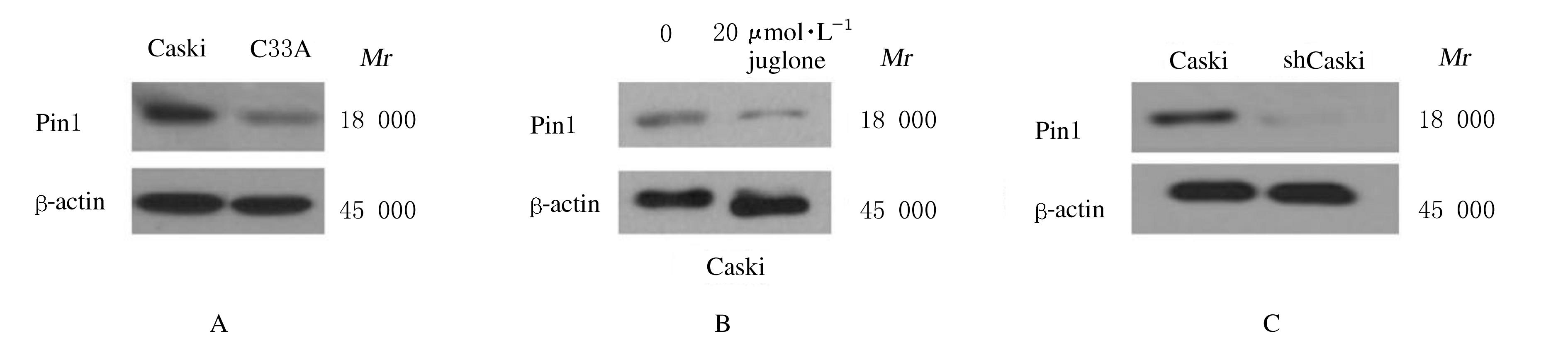
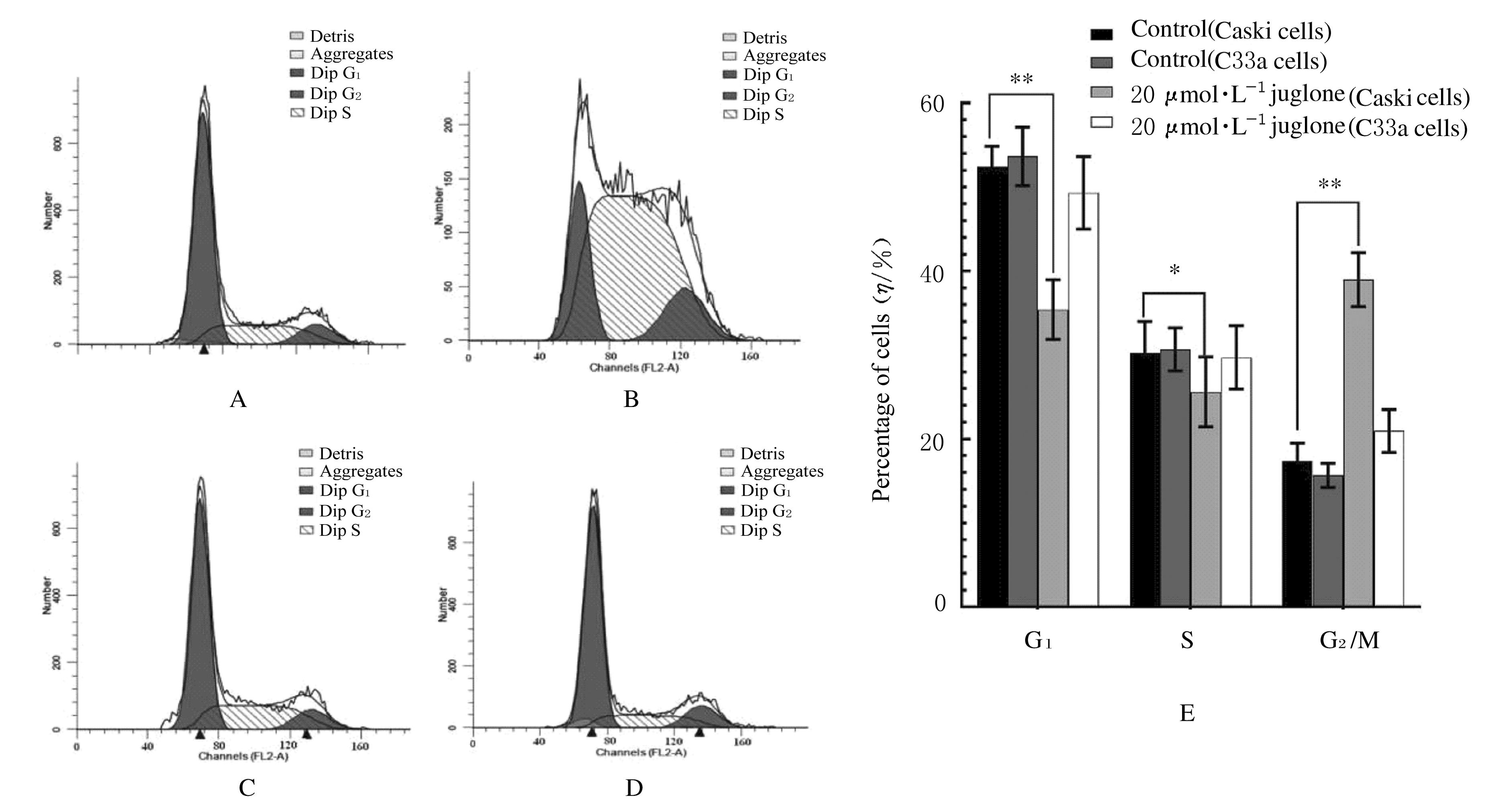
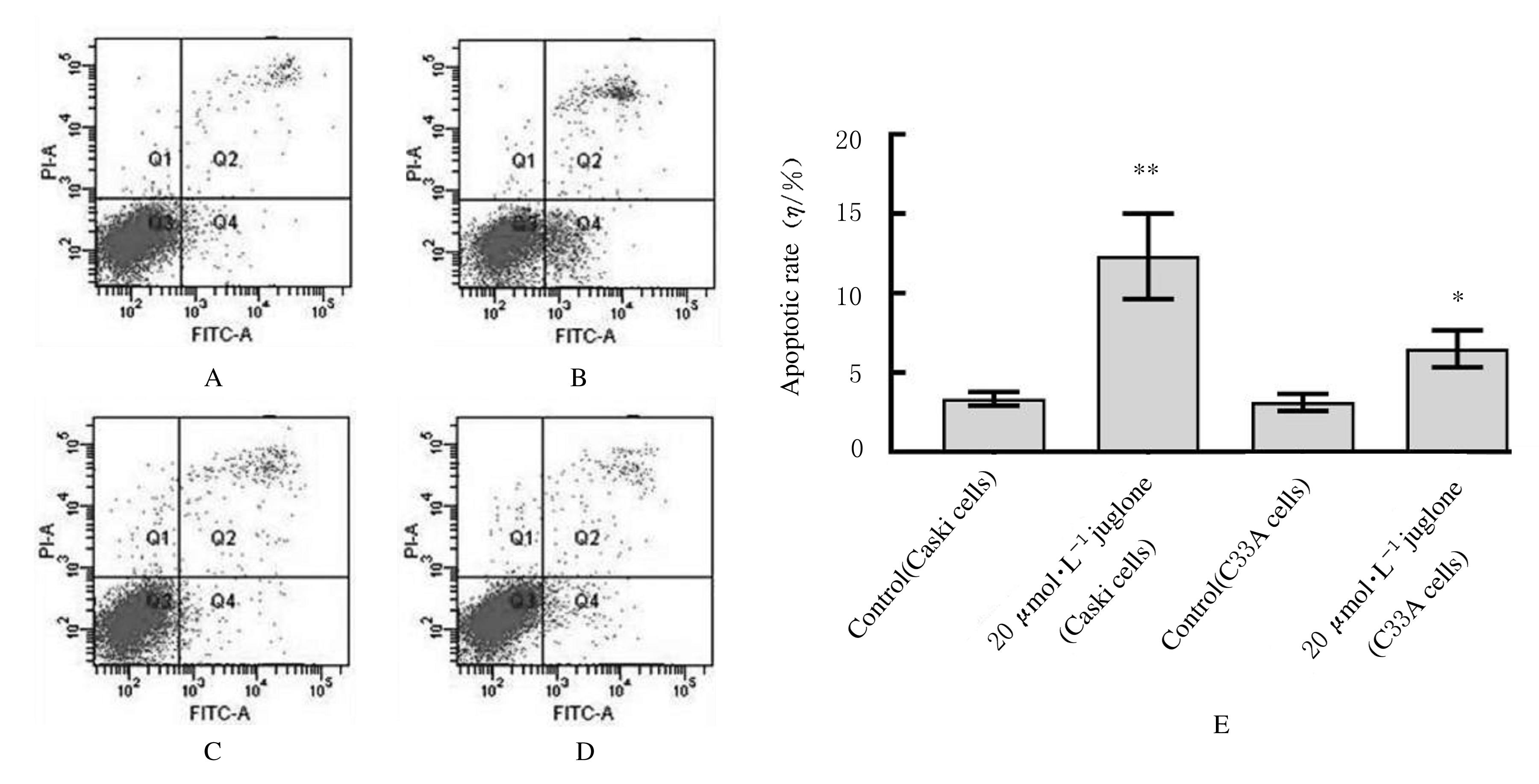
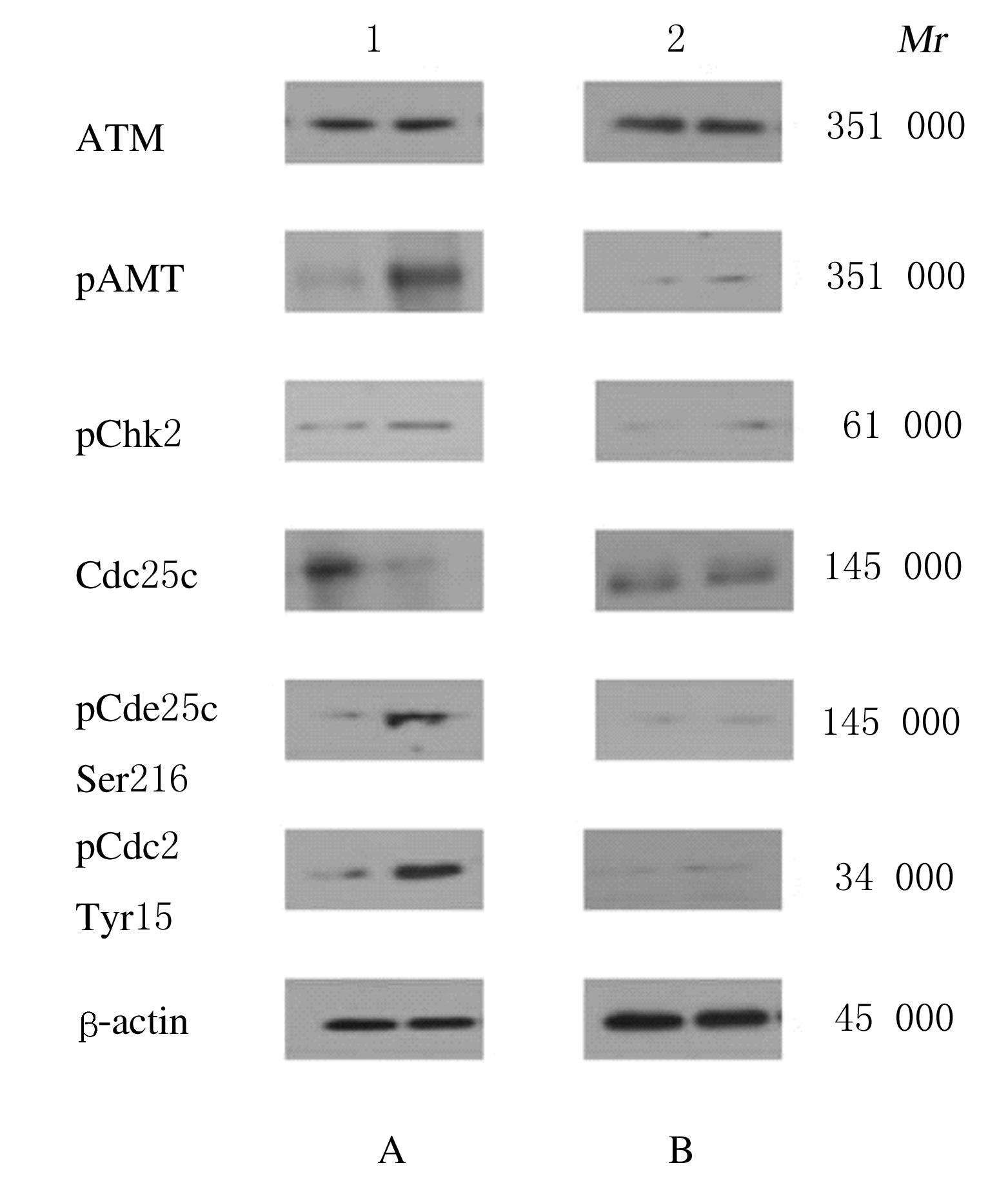
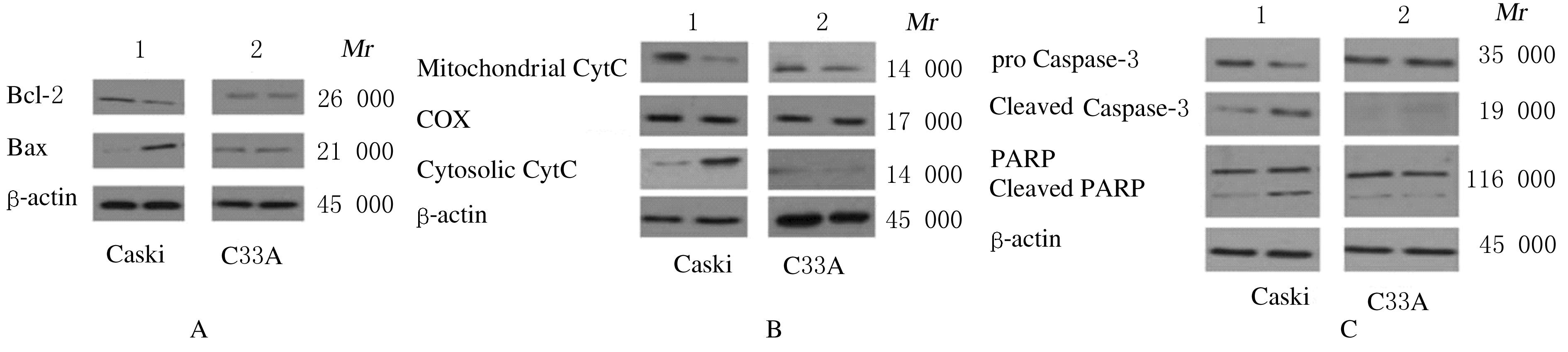
摘要: 比较胡桃醌对人乳头瘤病毒(HPV)阳性宫颈癌Caski细胞、HPV阴性C33A细胞和敲减脯氨酰顺反异构酶1(Pin1)基因的Caski细胞(shCaski细胞)增殖的抑制作用,探讨其可能的作用机制。 构建表达Pin1 shRNA慢病毒载体用于感染细胞,筛选得到稳定的shCaski细胞。取对数生长期的Caski、shCaski和C33A细胞,分为正常对照组、10、20、50和100 μmol·L-1胡桃醌组,胡桃醌处理24 h后,采用MTT法检测各组的细胞增殖活性。取对数生长期的Caski细胞和C33A细胞,分为对照组和20 μmol·L-1胡桃醌组,各组细胞处理24 h后,流式细胞术检测各组不同周期细胞百分率和早期凋亡率,Hoechst33258荧光染色观察各组细胞形态表现,Western blotting法检测各组细胞周期和凋亡相关蛋白表达水平。 MTT实验,与正常对照组比较,不同浓度胡桃醌组Caski细胞增殖活性明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01); 50和100 μmol·L-1胡桃醌组C33A和shCaski细胞增殖活性明显降低(P<0.05)。Hoechst 33258染色,与对照组比较,20 μmol·L-1胡桃醌组Caski细胞和C33A细胞中均可观察到核碎解增加,Caski细胞核碎解数量较C33A细胞多。流式细胞术检测,与对照组比较,20 μmol·L-1胡桃醌组Caski细胞G2期细胞百分率明显升高(P<0.01),20 μmol·L-1胡桃醌组C33A细胞G2期细胞百分率差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);与对照组比较,20 μmol·L-1胡桃醌组Caski细胞早期凋亡率明显升高(P<0.01),20 μmol·L-1胡桃醌组C33A细胞早期凋亡率差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);Western blotting法检测,与C33A细胞比较,Caski细胞中Pin1蛋白表达量明显升高;胡桃醌组Caski细胞和shCaski细胞中Pin1蛋白表达量明显低于对照组;与对照组比较,胡桃醌组C33A细胞中细胞周期相关蛋白表达水平明显改变;Caski细胞中磷酸化ATM(Patm)、磷酸化细胞周期检查点激酶2(pChk2)、216位丝氨酸磷酸化细胞分裂周期蛋白25c(pCdc25c Ser216)和pCdc25c Tyr216蛋白表达量升高,磷酸化细胞分裂周期蛋白25c(pCdc25c)蛋白表达量降低,Cdk1蛋白表达量变化不明显;与对照组比较,胡桃醌处理组Caski细胞中Bcl-2蛋白和线粒体CytC蛋白表达量降低,胞质CytC、Bax、Cleaved Caspase-3和Cleaved PARP蛋白表达量升高。 胡桃醌对HPV阳性宫颈癌细胞增殖抑制及促凋亡作用效果均强于HPV阴性细胞,其机制可能与胡桃醌特异性抑制Pin1基因有关。
中图分类号:
- R737.33