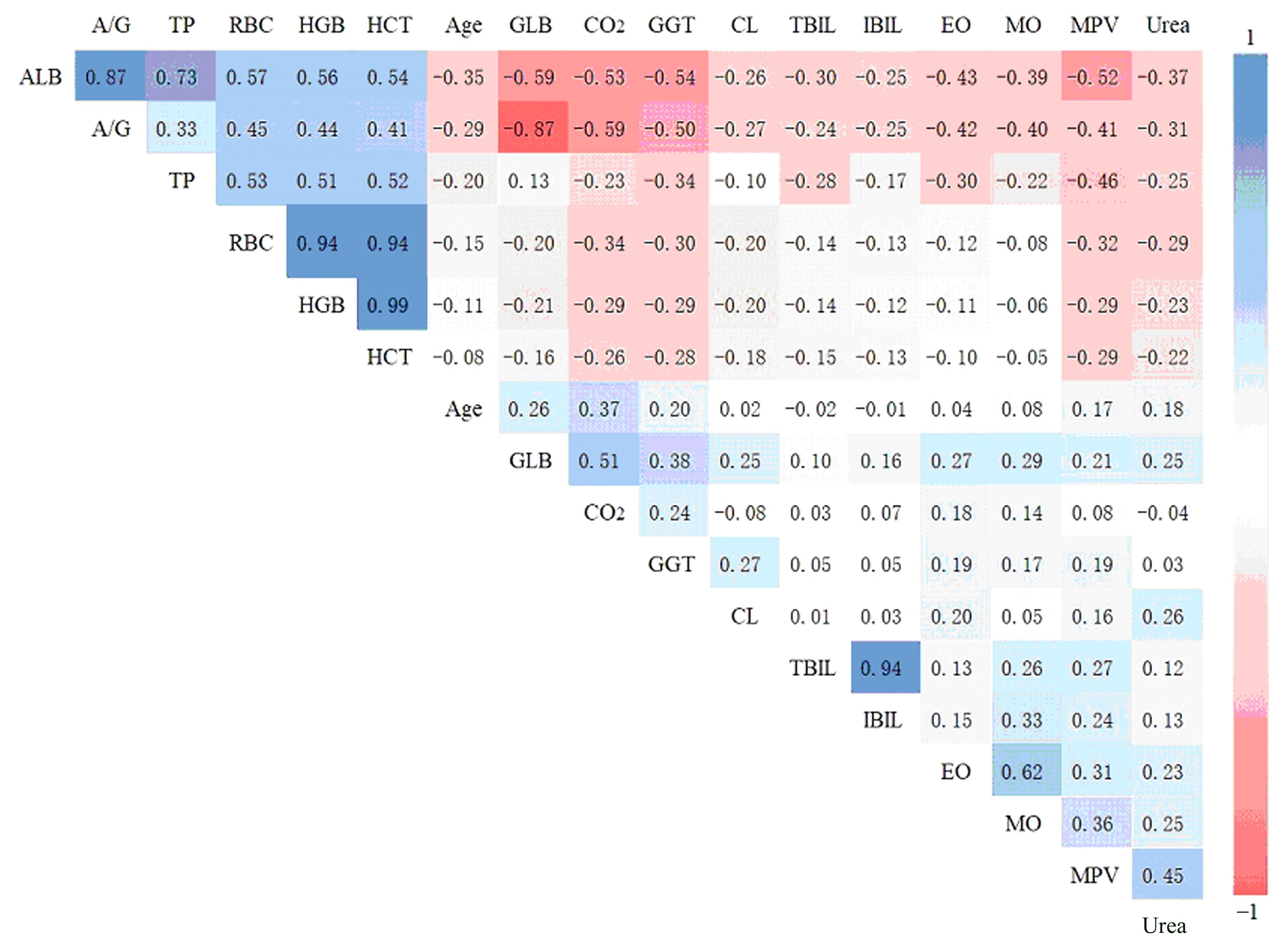
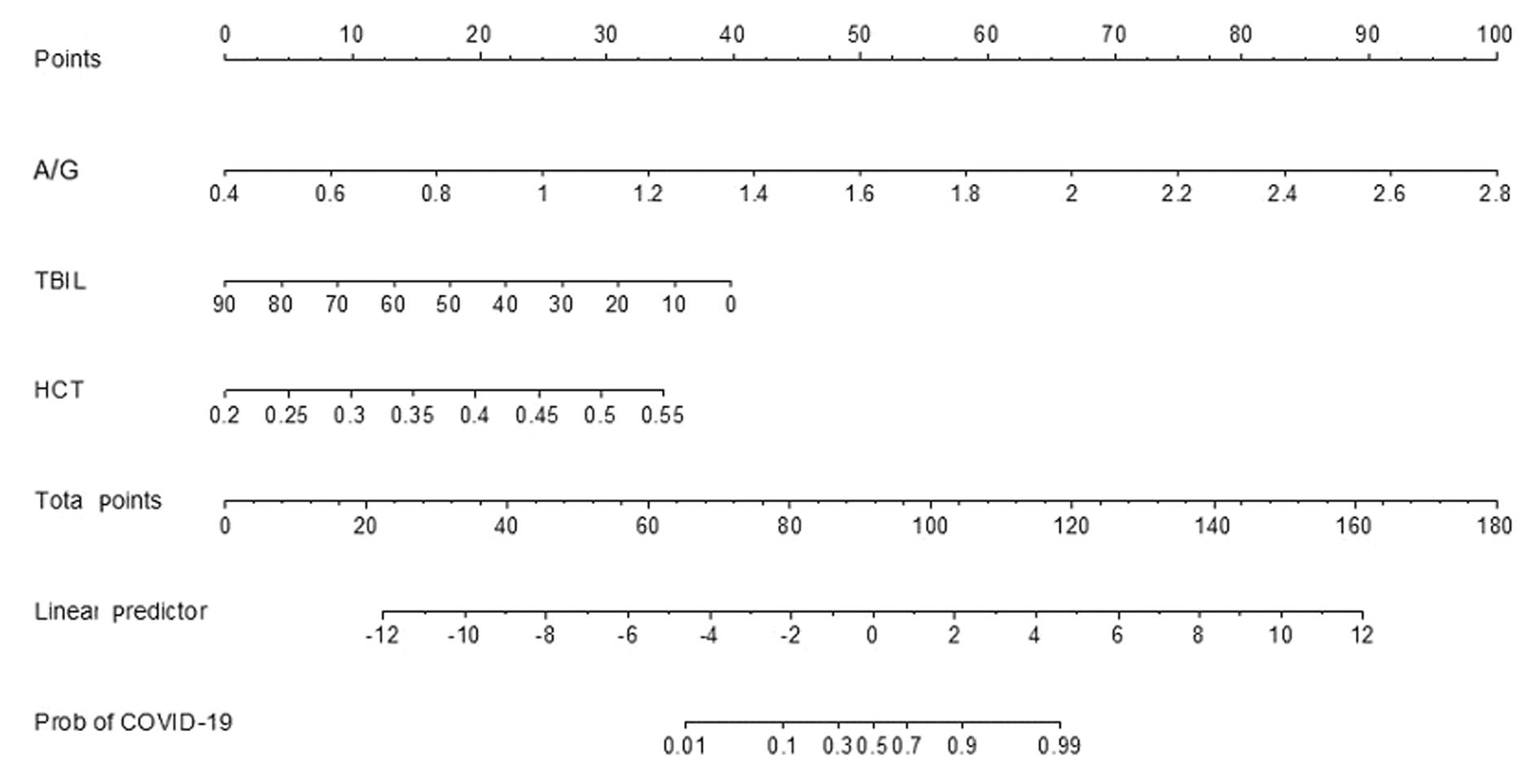
| 1 |
ZHANG Z, NAVARESE E P, ZHENG B, et al.Analytics with artificial intelligence to advance the treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. J Evid Based Med,2020,13(4): 301-312.
|
| 2 |
LEI H, LI Y, XIAO S, et al.Routes of transmission of influenza A H1N1, SARS CoV, and norovirus in air cabin: Comparative analyses[J].Indoor Air,2018,28(3): 394-403.
|
| 3 |
SULLIVAN S J, JACOBSON R M, DOWDLE W R, et al.2009 H1N1 influenza[J]. Mayo Clin Proc,2010, 85(1): 64-76.
|
| 4 |
SCHOEN K, HORVAT N, GUERREIRO N F C, et al.Spectrum of clinical and radiographic findings in patients with diagnosis of H1N1 and correlation with clinical severity[J]. BMC Infect Dis,2019,19(1): 964.
|
| 5 |
GAO H N, LU H Z, CAO B, et al.Clinical findings in 111 cases of influenza A (H7N9) virus infection[J]. N Engl J Med,2013,368(24): 2277-2285.
|
| 6 |
COBB N L, SATHE N A, DUAN K I, et al.Comparison of clinical features and outcomes in critically Ill patients hospitalized with COVID-19 versus influenza[J].Ann Am Thorac Soc,2021,18(4):632-640.
|
| 7 |
SUN Y, KOH V, MARIMUTHU K, et al.Epidemiological and clinical predictors of COVID-19[J]. Clin Infect Dis,2020,71(15): 786-792.
|
| 8 |
TIAN S, ZHU X, SUN X, et al.A Prognostic model to predict recovery of COVID-19 patients based on longitudinal laboratory findings[J].Virol Sin,2020,35(6): 811-819.
|
| 9 |
WANG L, GAO P, ZHANG M, et al.Prevalence and ethnic pattern of diabetes and prediabetes in China in 2013[J]. JAMA,2017,317(24): 2515-2523.
|
| 10 |
WANG L, CHANG L S, LEE I K, et al.Clinical diagnosis of pandemic A(H1N1) 2009 influenza in children with negative rapid influenza diagnostic test by lymphopenia and lower C-reactive protein levels[J]. Influenza Other Respir Viruses,2014, 8(1): 91-98.
|
| 11 |
LI Y, WANG H, WANG F, et al.Comparison of hospitalized patients with pneumonia caused by COVID-19 and influenza A in children under 5 years[J]. Int J Infect Dis,2020,98: 80-83.
|
| 12 |
CHEN Y, LIANG W, YANG S, et al.Human infections with the emerging avian influenza A H7N9 virus from wet market poultry: clinical analysis and characterisation of viral genome[J].Lancet,2013,381(9881): 1916-1925.
|
| 13 |
ONG A K, CHEN M I, LIN L, et al.Improving the clinical diagnosis of influenza--a comparative analysis of new influenza A (H1N1) cases[J]. PLoS One,2009,4(12): e8453.
|
| 14 |
FLICK H, DRESCHER M, PRATTES J, et al.Predictors of H1N1 influenza in the emergency department: proposition for a modified H1N1 case definition[J]. Clin Microbiol Infect,2014,20(2): O105-108.
|
| 15 |
KUMAR A, ZARYCHANSKI R, PINTO R, et al.Critically ill patients with 2009 influenza A(H1N1) infection in Canada[J].JAMA,2009,302(17):1872-1879.
|
| 16 |
RODRIGUEZ-NORIEGA E, GONZALEZ-DIAZ E, MORFIN-OTERO R, et al.Hospital triage system for adult patients using an influenza-like illness scoring system during the 2009 pandemic--Mexico[J].PLoS One,2010,5(5): e10658.
|
| 17 |
PEREZ-PADILLA R, DE LA ROSA-ZAMBONI D, PONCE DE LEON S, et al.Pneumonia and respiratory failure from swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) in Mexico[J]. N Engl J Med,2009,361(7): 680-689.
|
| 18 |
NSEIR S, CAVESTRI B, DI POMPEO C, et al.Factors predicting bacterial involvement in severe acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Respiration,2008,76(3): 253-260.
|
| 19 |
SALVAGNO G L, SANCHIS-GOMAR F, PICANZA A, et al.Red blood cell distribution width: A simple parameter with multiple clinical applications[J]. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci,2015,52(2): 86-105.
|
| 20 |
WEISS G, GOODNOUGH L T.Anemia of chronic disease[J]. N Engl J Med,2005, 352(10): 1011-1023.
|
| 21 |
CHEN N, ZHOU M, DONG X, et al.Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study[J]. Lancet,2020,395(10223): 507-513.
|
| 22 |
SKEVAKI C, FRAGKOU P C, CHENG C, et al.Laboratory characteristics of patients infected with the novel SARS-CoV-2 virus[J]. J Infect,2020,81(2): 205-212.
|
| 23 |
ZHANG J, ZHAO Y, CHEN Y.Laboratory findings in patients with avian-origin influenza A (H7N9) virus infections[J]. J Med Virol,2014,86(5): 895-898.
|
| 24 |
TO K K, SONG W, LAU S Y, et al.Unique reassortant of influenza A(H7N9) virus associated with severe disease emerging in Hong Kong[J]. J Infect, 2014,69(1): 60-68.
|
| 25 |
PAN F, XIAO X, GUO J, et al.No evidence of severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 in semen of males recovering from coronavirus disease 2019[J]. Fertil Steril,2020,113(6): 1135-1139.
|
| 26 |
ABELLEIRA R, RUANO-RAVINA A, LAMA A, et al.Influenza A H1N1 community-acquired pneumonia: characteristics and risk factors-A case-control study[J]. Can Respir J,2019,2019: 4301039.
|
| 27 |
CHENG X, LIU YM, LI H, et al.Metformin is associated with higher incidence of acidosis, but not mortality, in individuals with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes[J].Cell Metablism,2020,32(4): 537-547.e533.
|
| 28 |
TANG X, DU R H, WANG R, et al.Comparison of hospitalized patients with ARDS caused by COVID-19 and H1N1[J]. Chest,2020,158(1): 195-205.
|
| 29 |
ZHANG Y, LIU J, YU L, et al.Prevalence and characteristics of hypoxic hepatitis in the largest single-centre cohort of avian influenza A(H7N9) virus-infected patients with severe liver impairment in the intensive care unit[J]. Emerg Microbes Infect,2016,5: e1.
|
| 30 |
MAKKOCH J, PRACHAYANGPRECHA S, PAYUNGPORN S, et al.Erythrocyte binding preference of human pandemic influenza virus a and its effect on antibody response detection[J]. Ann Lab Med,2012,32(4): 276-282.
|
 )
)
 )
)