吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2): 280-288.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230203
补肺益肾组分方Ⅲ对大鼠实验性肺动脉高压的改善作用
任周新1,2,余海滨1,梅晓峰1,董浩然1,2,沈俊岭3,李建生1,2( )
)
- 1.河南中医药大学呼吸疾病中医药防治省部共建协同创新中心药理平台,河南 郑州 450046
2.河南中医药大学中医药科学院,河南 郑州 450046
3.河南中医药大学第一附属医院 河南省病毒性疾病中医药防治重点实验室,河南 郑州 450000
Improvement effect of Bufei Yishen prescription Ⅲ on experimental pulmonary hepertension of rats
Zhouxin REN1,2,Haibin YU1,Xiaofeng MEI1,Haoran DONG1,2,Junling SHEN3,Jiansheng LI1,2( )
)
- 1.Department of Pharmacology,Collaborative Innovation Center for Chinese Medicine and Respiratory Disease Co-constructed by Henan Province and Education Ministry,Henan University of Chinese Medicine,Zhengzhou 450046,China
2.Academy of Chinese Medicine,Henan University of Chinese Medicine,Zhengzhou 450046,China
3.Key Laboratory of Viral Diseases Prevention and Treatment of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Henan Province,First Affiliated Hospital,Henan University of Chinese Medicine,Zhengzhou 450000,China.
摘要:
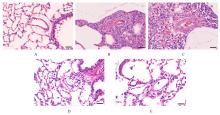
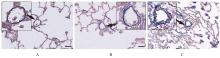
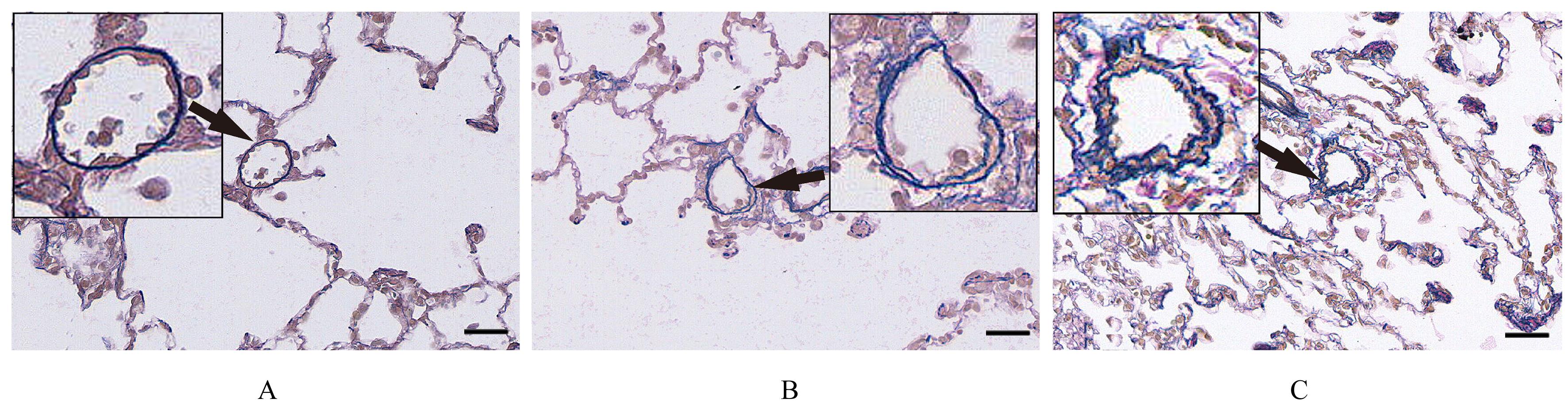
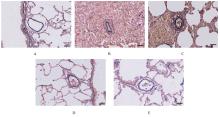
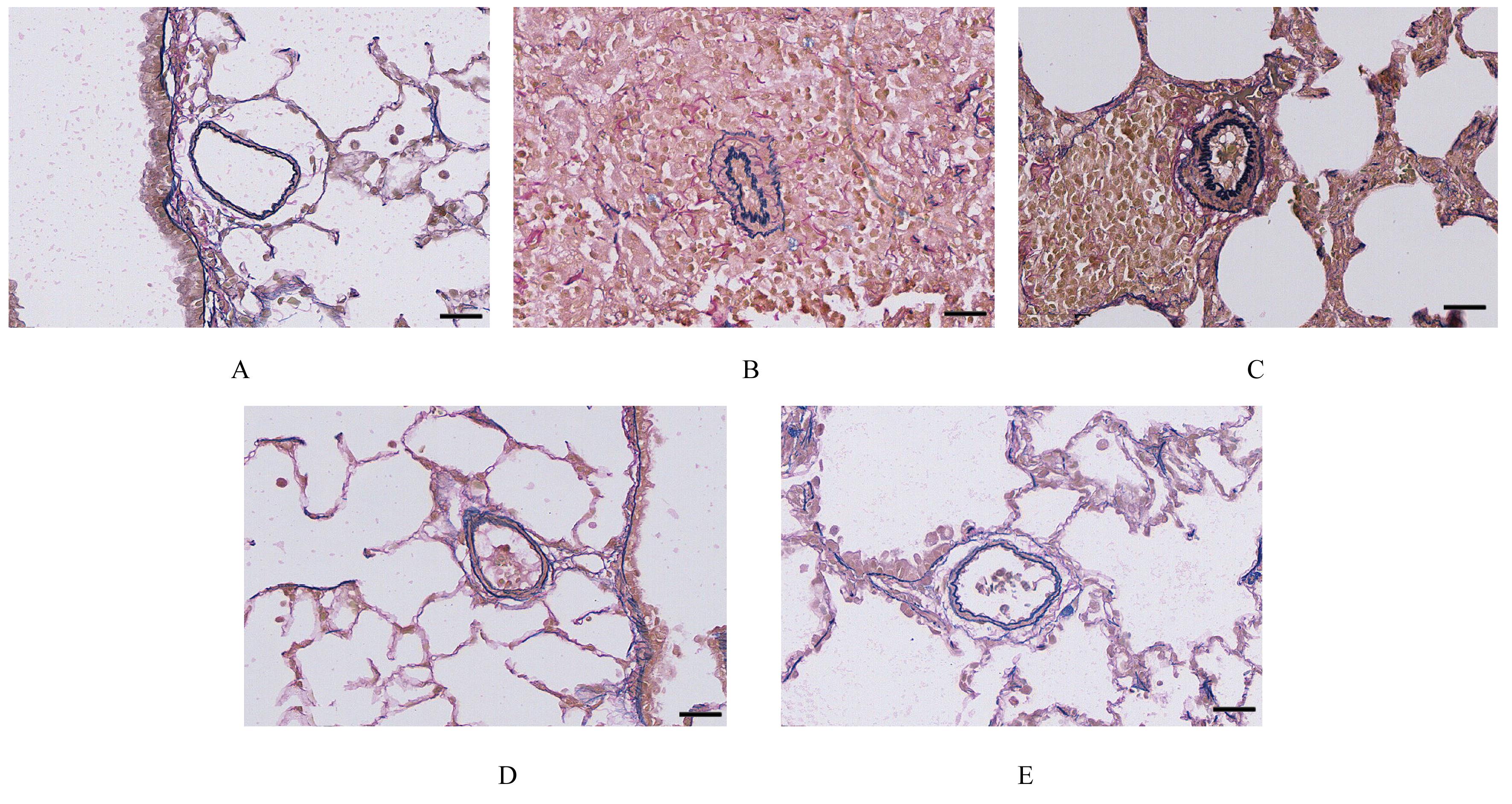
目的 探讨补肺益肾组分方Ⅲ(ECC-BYP Ⅲ)对烟雾和细菌诱导的大鼠肺动脉高压(PH)的改善作用,初步阐明其作用机制。 方法 SPF级SD大鼠随机分为对照组(n=9)和造模组(n=140)。对照组大鼠常规饲养,造模组大鼠给予香烟烟雾和克雷伯杆菌(Kp),制备PH模型。停止造模后,造模大鼠按照肺功能均匀的原则分为模型组(n=10)和低剂量(3.24 mg·kg-1·d-1,n=9)、中剂量(6.48 mg·kg-1·d-1,n=10)及高剂量(12.96 mg·kg-1·d-1,n=10)ECC-BYP Ⅲ组。给药大鼠按照组别每天分别给予相应剂量的ECC-BYP Ⅲ灌胃,对照组和模型组大鼠给予等量生理盐水灌胃。连续给药4周。第29天检测各组大鼠肺动脉平均压(mPAP)、收缩压(PASP)、舒张压(PADP)和右心肥大指数(RVHI)。取大鼠肺组织,部分采用苏木精-伊红(HE)染色,观察各组大鼠肺组织中肺小动脉周围炎症等病变;部分采用维多利亚蓝染色,测定各组大鼠肺小动脉血管中非肌性血管、部分肌性血管和肌性血管的百分比,肺小动脉管壁厚度占管径的百分比(WT%)及血管腔面积占血管总面积百分比(LA%)。另取大鼠肺组织,采用酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法检测各组大鼠肺组织中白细胞介素6(IL-6)、肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)、内皮素1(ET-1)和前列环素(PGI2)水平。 结果 与对照组比较,模型组大鼠mPAP、PASP和PADP明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.01),RVHI明显增加(P<0.01),肺小动脉周围炎症细胞浸润明显,肺组织中TNF-α和IL-6水平明显升高(P<0.01),肌性血管百分比和肺小动脉WT%明显升高(P<0.01),非肌性血管百分比和LA%明显降低(P<0.01),肺组织中ET-1水平和ET-1/PGI2比值明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.01)。与模型组比较,高剂量ECC-BYP Ⅲ组大鼠mPAP和PADP明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,中和高剂量ECC-BYP Ⅲ组大鼠肺小动脉周围炎症细胞浸润明显改善,中和高剂量ECC-BYP Ⅲ组大鼠肺组织中TNF-α及IL-6水平、WT%及肌性血管百分比明显降低(P<0.01),LA%明显升高(P<0.01);与模型组比较,中和高剂量ECC-BYP Ⅲ组大鼠肺组织中ET-1水平明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01),高剂量ECC-BYP Ⅲ组大鼠ET-1/PGI2比值明显降低(P<0.05)。与低剂量ECC-BYP Ⅲ组比较,中和高剂量ECC-BYP Ⅲ组大鼠WT%和肺组织中ET-1水平明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01),LA%明显升高(P<0.01);中剂量ECC-BYP Ⅲ组大鼠肺组织中TNF-α水平,高剂量ECC-BYP Ⅲ组大鼠肺组织中IL-6水平和ET-1/PGI2比值明显降低(P<0.05)。 结论 ECC-BYP Ⅲ可降低PH,减小肺血管壁厚度,改善管腔狭窄和肺小动脉肌化,改善肺血管重构,其机制可能与减轻肺血管周围炎症反应、改善血管周围收缩血管因子水平/舒张血管因子水平失衡有关。
中图分类号:
- R544.1