吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (6): 1407-1414.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230601
• 基础研究 • 下一篇
局部脉冲振动刺激对兔前交叉韧带重建后本体感觉恢复的影响
- 1.解放军总医院第八医学中心骨科,北京 100091
2.河北北方学院研究生学院外科,河北 张家口 075051
Effect of local impulse vibration stimulation on proprioception recovery after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in rabbits
Xinqiang ZHANG1,2,Bo WANG2,Huicheng FENG1( )
)
- 1.Department of Orthopedics, Eighth Medical Center, PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100091, China
2.Department of Surgery, Graduate School, Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou 075000, China
摘要:
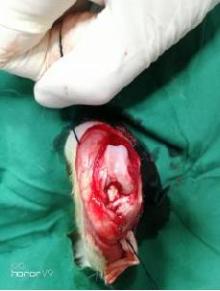
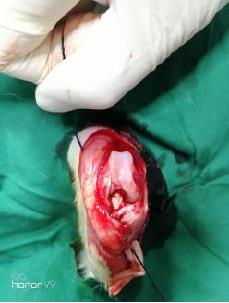
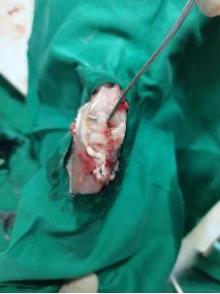
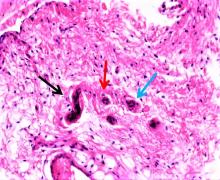
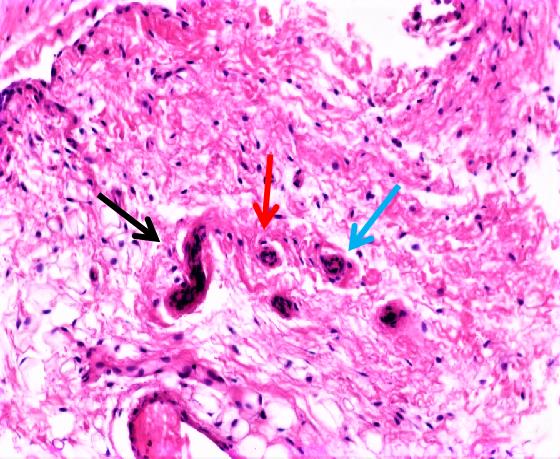
目的 探讨不同局部脉冲振动刺激治疗条件对兔前交叉韧带重建(ACLR)术后本体感觉恢复的影响,为临床实践提供参考。 方法 选取45只健康新西兰大白兔,15只兔制备同种异体移植肌腱,30只兔制备前交叉韧带(ACL)模型,造模后将兔随机分为对照组和9个振动刺激治疗组(振动刺激治疗1~9组),每组3只。正交实验设计振动刺激治疗参数,采集各组兔ACL样本。HE染色观察各组兔ACL本体感受器形态表现,S100免疫组织化学染色观察各组兔ACL本体感受器分型,计数各组兔ACL本体感受器细胞数,实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测各组兔ACL组织中生长相关蛋白43(GAP-43) mRNA表达水平,正交分析法筛选ACLR术后康复振动刺激治疗的最优参数。 结果 兔移植物张力尚可,无松弛状态,前抽屉实验和Lachman实验阴性;ACL组织移植物连续性存在,与胫骨和股骨腱骨愈合。ACL本体感受器中Ruffini小体为卵圆形或树突状形态,直径25~330 μm;Pacinian小体为圆形或椭圆形感受器,直径40~220 μm;Golgi腱器官感受器呈梭形,直径140~900 μm;游离神经末梢为无髓鞘神经末梢,长度0.5~1.5 μm。移植ACL中本体感受器主要分布于ACL的胫骨和股骨附着点,主要为类Ruffini小体和类Pacinian小体,无典型的类Golgi腱器官。与对照组比较,振动刺激治疗3、振动刺激治疗5和振动刺激治疗7组兔ACL本体感受器细胞数明显增加(F=28.49,P<0.01)。各组兔ACL组织中GAP-43 mRNA表达水平比较差异无统计学意义(F=0.83,P>0.05)。振幅强度、振动频率和作用时间对局部脉冲振动刺激治疗ACLR术后本体感受器数均存在较大影响,影响程度为振幅强度>作用时间>振动频率。其中最优振幅强度为3 mm,最优振动频率为25 Hz,最佳作用时间为10 min。 结论 局部脉冲振动刺激治疗可促进兔ACLR术后ACL本体感受器恢复,采用低振幅、低振动频率和短时间的局部脉冲振动刺激治疗可加快ACLR术后本体感觉的恢复。
中图分类号:
- R684