吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 161-167.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240120
• 临床研究 • 上一篇
基于罗汉果治疗糖尿病肾病机制的网络药理学和分子对接分析
- 北华大学附属医院医学影像中心,吉林 吉林 132011
Network pharmacologry and molecular docking analysis based on mechanism of monk fruit in treatment of diabetic nephropathy
Yang YU,Dan TIAN,Donghe NI,Duo ZHANG( )
)
- Medical Imaging Center,Affiliated Hospital,Beihua University,Jilin 132011,China
摘要:
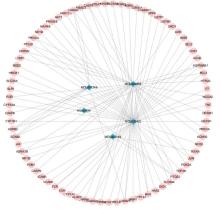
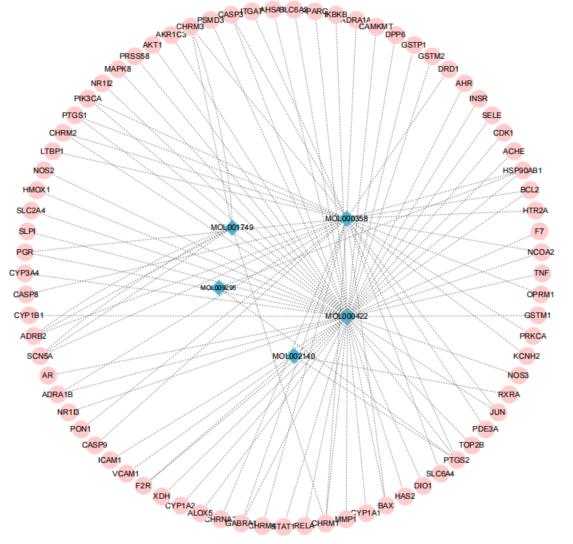
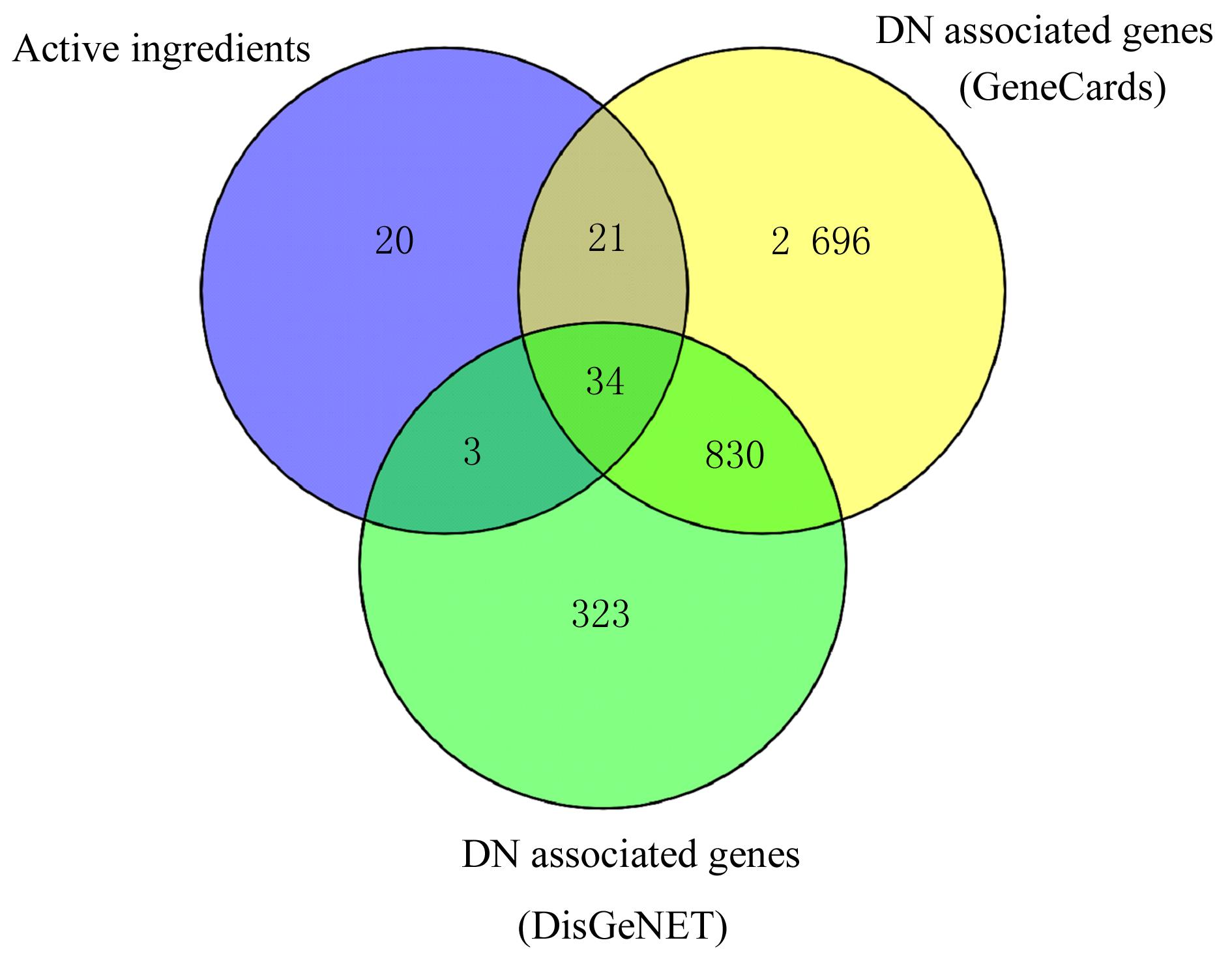
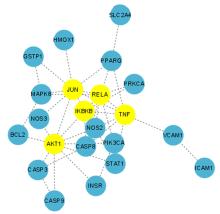
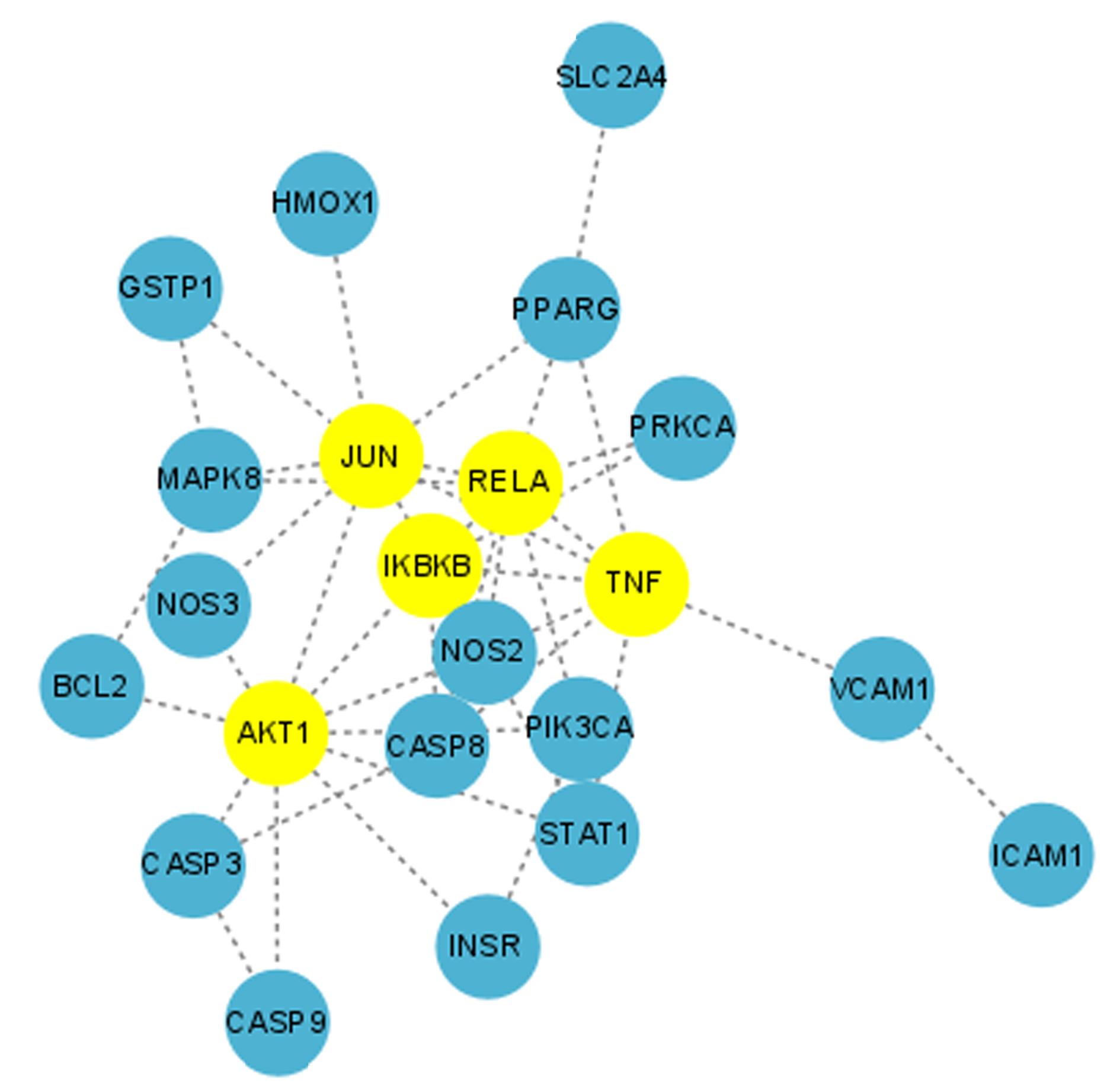
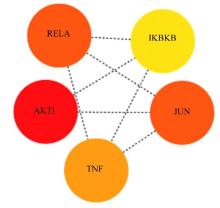
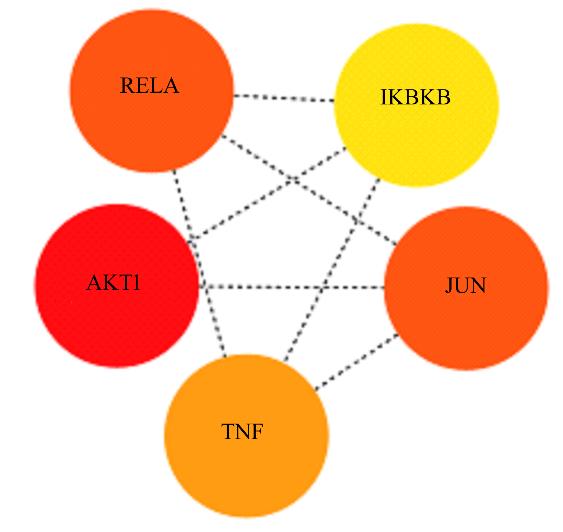
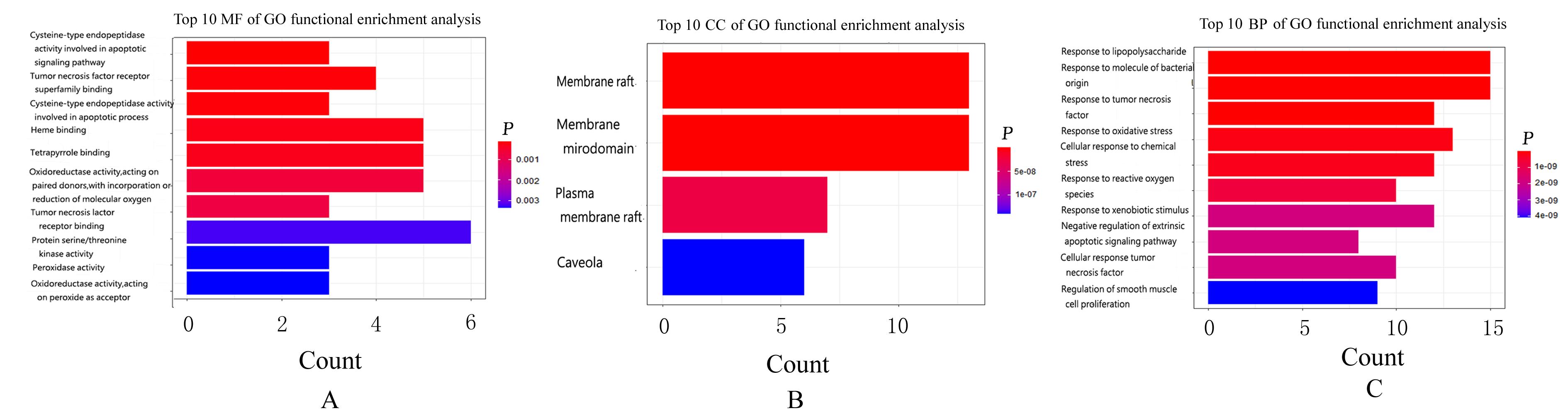
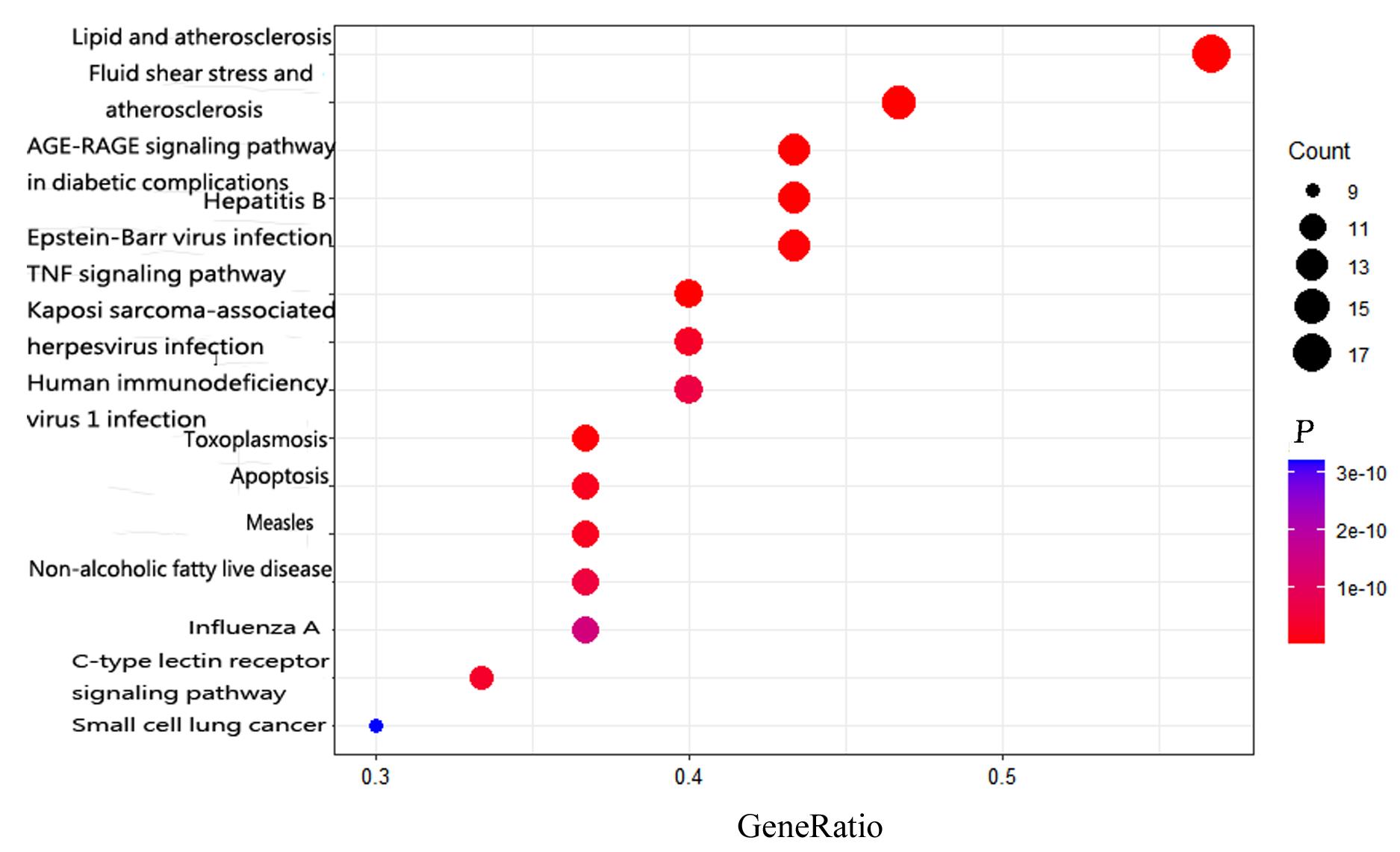
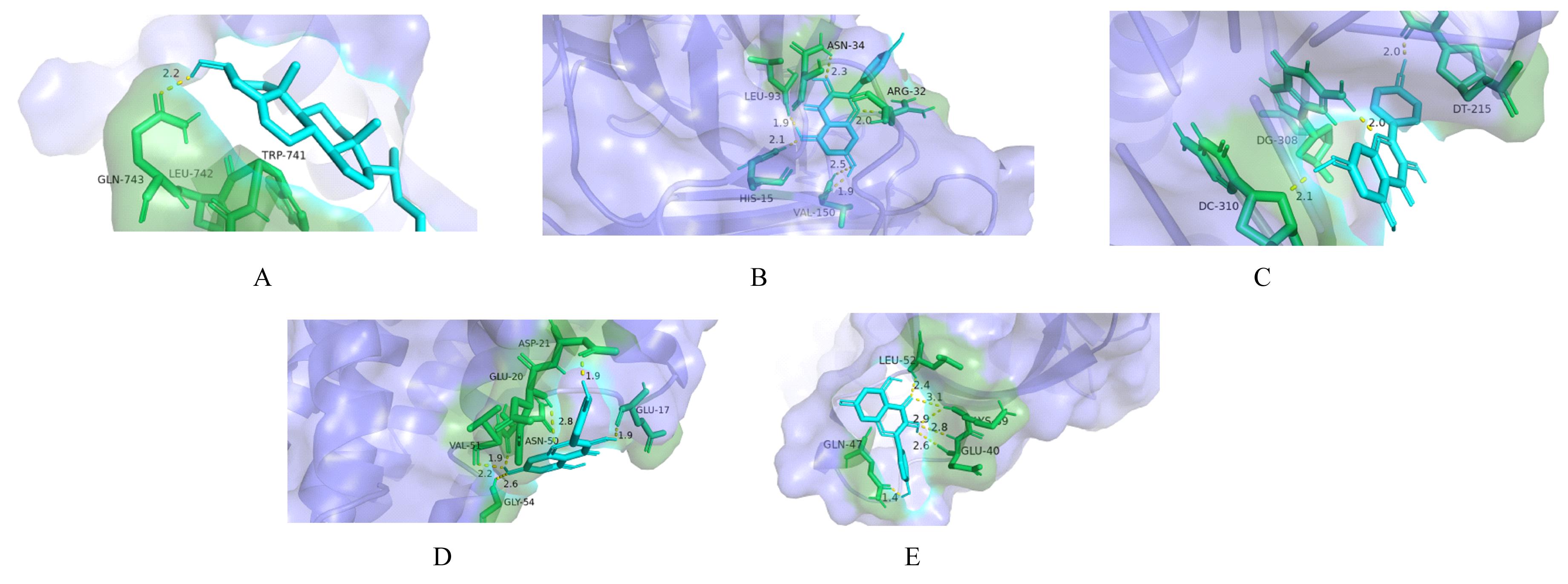
目的 利用网络药理学分析罗汉果对糖尿病肾病(DN)的改善作用,阐明其可能的相关机制。 方法 采用中药系统药理学数据库和分析平台(TCMSP)确定罗汉果中的有效成分及其作用靶点。通过DisGeNET数据库和GeneCards数据库筛选DN靶基因。将罗汉果与DN靶点进行对比,获取罗汉果对DN的关键靶点。通过STRING 数据库和 Cytoscape 软件构建蛋白-蛋白互作(PPI)网络图,通过Cytoscape 软件进行基因本体论(GO) 功能富集分析和京都基因与基因组百科全书 (KEGG) 信号通路富集分析。采用分子对接技术预测DN核心靶点与罗汉果主要活性成分的结合能力。 结果 采用TCMSP 数据库结合选入标准共筛选出罗汉果5种活性成分(ZINC03860434、Perlolyrine、beta-sitosterol、Kaempferol和Flazin)及丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶1(AKT1)、转录因子RELA、c-Jun氨基末端激酶(JUN)和肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)为代表的85个靶点,其中kaempferol所含靶点最多。筛选出的85个靶点中与DN相关的靶点有34个。GO功能富集分析主要涉及氧化应激、炎症及凋亡调控和细胞信号传导等生物学过程(BP)。KEGG信号通路富集分析涉及晚期糖基化终产物(AGE)-AGE受体(AGE-RAGE)信号通路、TNF信号通路和C型凝集素受体信号通路等。罗汉果主要活性成分与DN靶点蛋白分子对接分析,5种活性成分分子对接结合能均在-8.00~ -5.00 kJ·mol-1之间。 结论 Kaempferol是罗汉果中对DN治疗最有效的活性成分,其作用机制主要与抑制炎症有关。
中图分类号:
- R285.5