吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 403-411.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250214
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
高浓度葡萄糖对体外Raw264.7巨噬细胞极化状态的影响
- 1.兰州大学第二临床医学院老年病科,甘肃 兰州 730030
2.兰州大学第二临床医学院检验医学 中心,甘肃 兰州 730030
3.西北民族大学生物医学研究中心 生物工程与技术国家民委重点实验室,甘肃 兰州 730030
Effect of high glucose on polarization of Raw264.7 macrophages in vitro
Xiaoxia HU1,Yalong LI2,Dongliang YANG3,Bazeren LA,Xinyue LIU2( )
)
- 1.Department of Geriatrics,Second Clinical Medical School,Lanzhou University,Lanzhou 730030,China
2.Laboratory Medicine Center,Second Clinical Medical School,Lanzhou University,Lanzhou 730030,China
3.Key Laboratory of Bioengineering and Biotechnology,National Ethnic Affairs Commission,Biomedical Research Center,Northwest Minzu University,Lanzhou 730030,China
摘要:
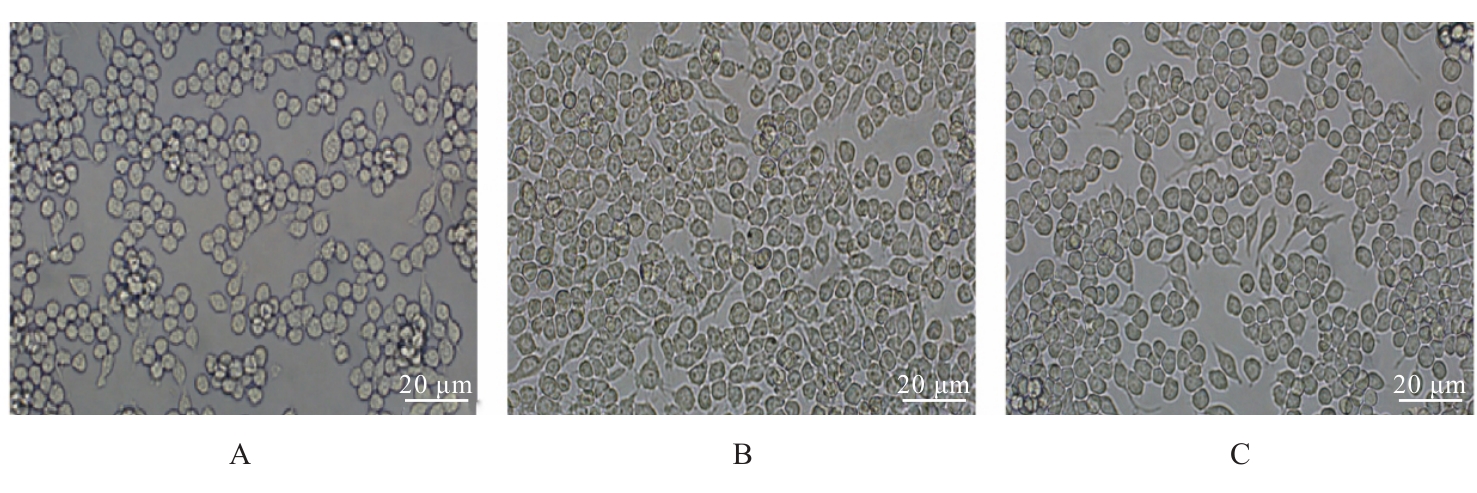
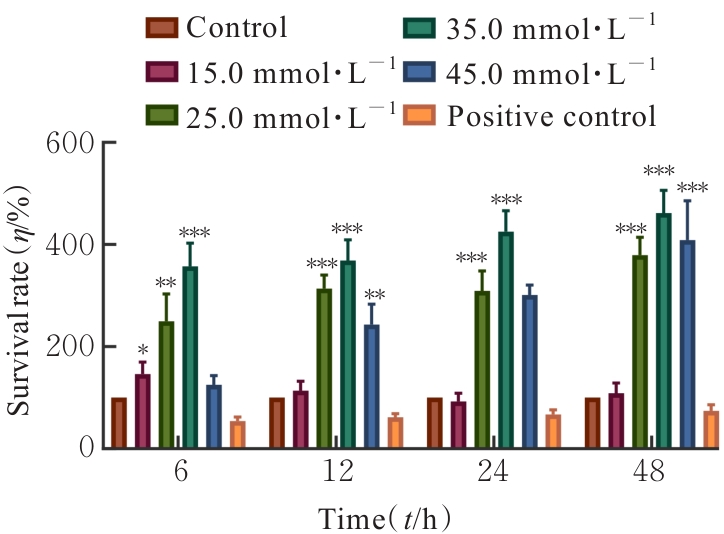
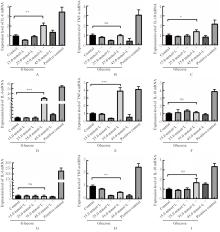
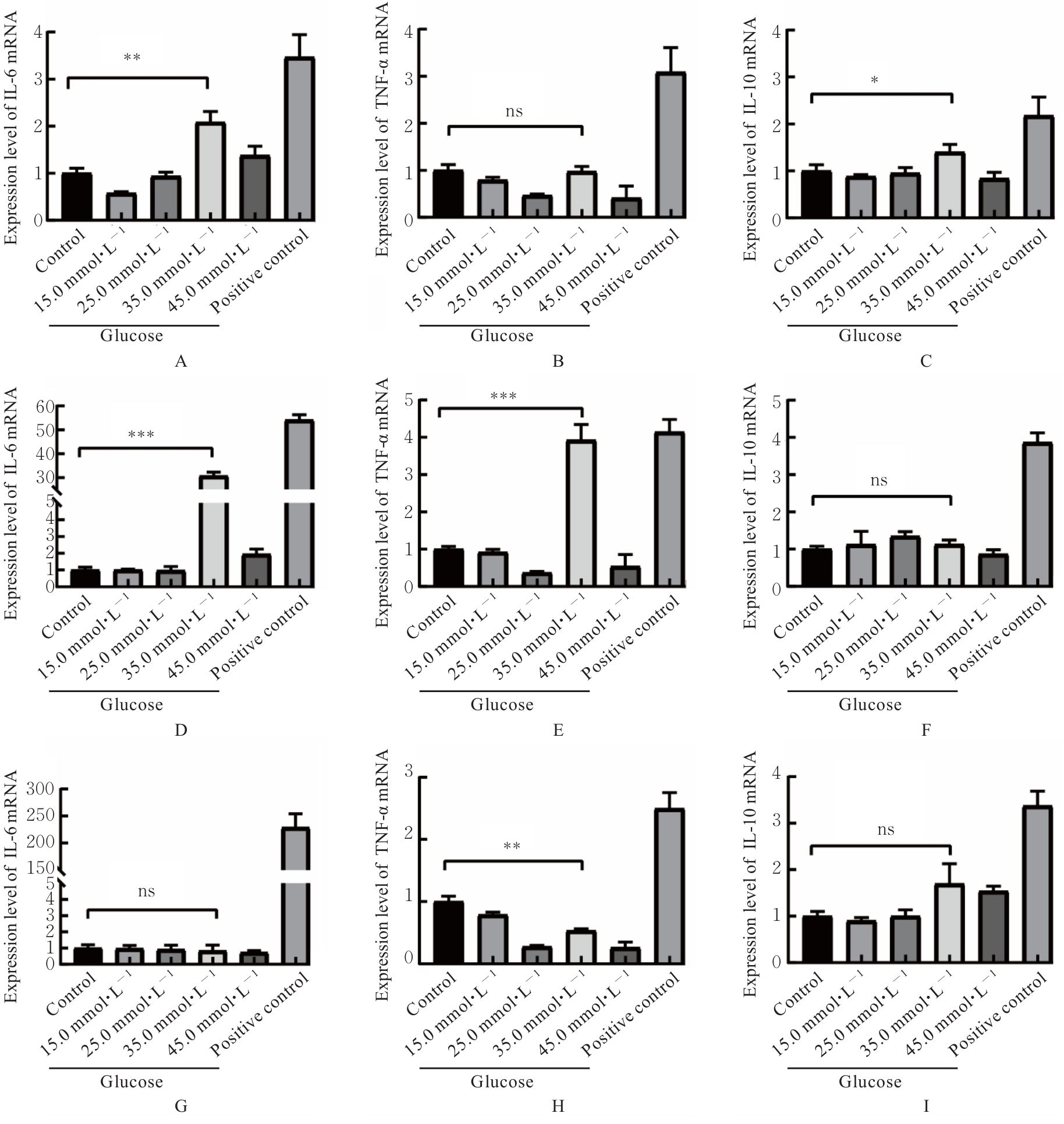
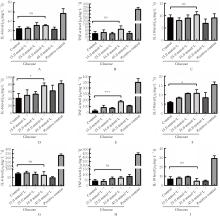
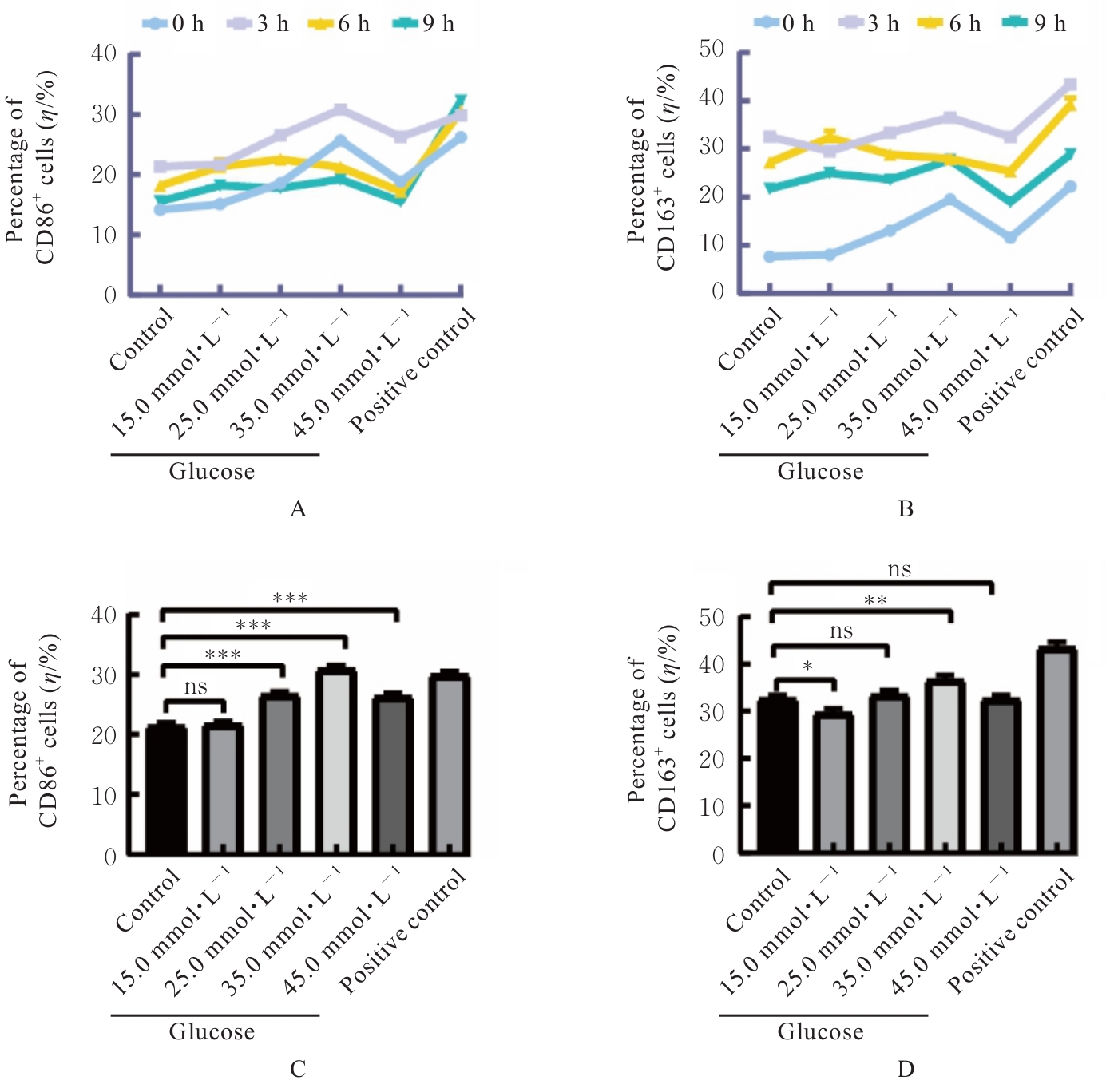
目的 探讨不同浓度葡萄糖对体外Raw264.7巨噬细胞极化的诱导作用。 方法 将DMEM培养基培养的Raw264.7细胞分为对照组(5.5 mmol·L-1葡萄糖)、不同浓度高糖组(15.0、25.0、35.0和45.0 mmol·L-1葡萄糖)和阳性对照组[脂多糖(LPS)],分别培养3、6和9 h,观察各组细胞形态,细胞计数试剂盒8(CCK-8)法检测各组细胞存活率,实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测各组细胞中白细胞介素6(IL-6)、肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)和白细胞介素10(IL-10)mRNA表达水平,酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法检测各组细胞上清中IL-6、TNF-α和IL-10水平,流式细胞仪检测各组细胞M1和M2型巨噬细胞标志物CD86+及CD163+细胞百分比。 结果 对照组Raw264.7细胞贴壁生长,形态以圆形为主;35.0 mmol·L-1高糖组和阳性对照组细胞拉长、伪足形成,呈现炎症性改变。与对照组比较,作用6、12、24和48 h后不同浓度高糖组细胞存活率均升高(P<0.05)。与对照组比较,作用3 h后,35.0 mmol·L-1高糖组细胞中IL-6和IL-10 mRNA表达水平升高(P<0.05或P<0.01),细胞上清中IL-6、TNF-α和IL-10水平无明显变化,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);作用6 h后,35.0 mmol·L-1高糖组细胞中TNF-α mRNA表达水平升高(P<0.001),细胞上清中IL-6、TNF-α和IL-10水平明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.001);作用3 h后,35.0 mmol·L-1高糖组巨噬细胞极化标志物CD86+和CD163+细胞百分比明显升高(P<0.01或P<0.001)。 结论 一定高浓度葡萄糖可诱导体外Raw264.7巨噬细胞向M1亚型极化。
中图分类号:
- R392.11