| [1] |
ALHAMMADI M S, HALBOUB E, FAYED M S, et al. Global distribution of malocclusion traits: a systematic review[J]. Dental Press J Orthod, 2018, 23(6): 40.e1-40.e10.
|
| [2] |
嵇潇雷, 曹 灵. 肌功能训练在安氏Ⅱ类1分类下颌后缩矫正中的临床疗效分析[J]. 口腔生物医学, 2019, 10(4): 205-208.
|
| [3] |
丁 盟, 沈 群, 陈玉成, 等. 下颌后缩型安氏Ⅱ类错牙合功能矫治研究进展[J]. 中国医疗美容, 2024, 14(2): 141-145.
|
| [4] |
TESSE R, MASSAGLI C, LORE M, et al. Association between sleep disordered breathing and oral malocclusion in childhood: Preliminary data[J]. Sleep,2004,27:106-107.
|
| [5] |
MILACIC M, MARKOVIC M. A comparative occlusal and cephalometric study of dental and skeletal anteroposterior relationships[J]. Br J Orthod, 1983, 10(1): 53-54.
|
| [6] |
陈菁菁, 王 密, 刘 芳, 等. Twin-block在骨性Ⅱ类错牙合下颌后缩患儿中的应用[J]. 中国美容医学, 2024, 33(9): 53-57.
|
| [7] |
李亮,郑哲,刘洪. 安氏Ⅱ类下颌后缩儿童Twin-block矫治后气道流体力学[C]//第十四次全国数字化口腔医学学术会议论文集. 太原, 2016: 23.
|
| [8] |
KOUKOU M, DAMANAKIS G, TSOLAKIS A I. Orthodontic management of skeletal class Ⅱ malocclusion with the invisalign mandibular advancement feature appliance: a case report and review of the literature[J]. Case Rep Dent, 2022, 2022: 7095467.
|
| [9] |
汤 雁, 谢 超. 隐形矫治器在青少年安氏Ⅱ类错牙合畸形治疗中的应用[J]. 河南医学研究, 2022, 31(1): 109-112.
|
| [10] |
LOMBARDO E C, LIONE R, FRANCHI L, et al. Dentoskeletal effects of clear aligner vs twin block-a short-term study of functional appliances[J]. J Orofac Orthop, 2024, 85(5): 317-326.
|
| [11] |
KONG L, LIU X Q. Efficacy of invisible advancement correction for mandibular retraction in adolescents based on Pancherz analysis[J]. World J Clin Cases, 2023, 11(6): 1299-1309.
|
| [12] |
阮诗雯, 刘 展, 余 兵, 等. 无托槽隐形矫治治疗青少年安氏Ⅱ类2分类病例[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志, 2022, 36(6): 425-428, 360.
|
| [13] |
赵亚鹏, 高鹏, 郝丽娟. 下颌前导隐形矫治器(MA)治疗高原地区儿童下颌后缩畸形合并OSAHS的临床研究[C]//中国睡眠研究会第七届西部睡眠医学大会论文汇编. 贵阳, 2020: 87.
|
| [14] |
SABOUNI W, HANSA I, AL ALI S M, et al. Invisalign treatment with mandibular advancement: a retrospective cohort cephalometric appraisal[J]. J Clin Imaging Sci, 2022, 12: 42.
|
| [15] |
CARUSO S, NOTA A, CARUSO S, et al. Mandibular advancement with clear aligners in the treatment of skeletal Class Ⅱ. A retrospective controlled study[J]. Eur J Paediatr Dent, 2021, 22(1): 26-30.
|
| [16] |
曹伟清, 林汤毅, 吕 冬. 快速生长期骨性安氏Ⅱ类下颌后缩患者使用无托槽隐形矫治器前导下颌的临床效果分析[J]. 口腔医学, 2023, 43(3): 242-247.
|
| [17] |
高 莹, 于向华, 杨丽娜, 等. 前导式双 垫对生长发育高峰期后骨性Ⅱ类下颌后缩的疗效[J]. 中国临床医学, 2023, 30(3): 502-508. 垫对生长发育高峰期后骨性Ⅱ类下颌后缩的疗效[J]. 中国临床医学, 2023, 30(3): 502-508.
|
| [18] |
余 磊, 李紫薇, 康芙嘉, 等. 隐形功能矫治器对比传统功能矫治器前导下颌治疗骨性Ⅱ类错牙合畸形患者疗效的meta分析[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2023, 41(3): 305-314.
|
| [19] |
谷 玉, 李 沙. 安氏Ⅱ类下颌后缩患者隐形前导矫治器矫治后气道CBCT变化[J]. 医药论坛杂志, 2021, 42(22): 37-42.
|
| [20] |
ELFOULY D, DUMU E J, MADIAN A M, et al. The effect of different functional appliances on the sagittal pharyngeal airway dimension in skeletal class Ⅱ: a retrospective study[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1): 19410.
|
| [21] |
YUE Z, YI Z A, LIU X Y, et al. Comparison of invisalign mandibular advancement and twin-block on upper airway and hyoid bone position improvements for skeletal class Ⅱ children: a retrospective study[J]. BMC Oral Health, 2023, 23(1): 661.
|
| [22] |
邓旭霞, 周美娟, 徐巍巍. 隐形矫治器前导下颌对骨性Ⅱ类错 畸形患者面部美学结构的影响分析[J]. 中国美容医学, 2024, 33(2): 141-145. 畸形患者面部美学结构的影响分析[J]. 中国美容医学, 2024, 33(2): 141-145.
|
| [23] |
LIU C, JIANG S, XIE H, et al. Functional clear aligner technique in the treatment of class Ⅱ malocclusion in juvenile: a case report and literature review[J]. J Radiat Res Appl Sci, 2022, 15(3): 59-64.
|
| [24] |
ZYBUTZ T, DRUMMOND R, LEKIC M, et al. Investigation and comparison of patient experiences with removable functional appliances[J]. Angle Orthod, 2021, 91(4): 490-495.
|
| [25] |
刘 超. 隐形矫治器前导下颌对青少年Ⅱ类错牙合上气道形态结构的影响[D]. 长沙: 湖南中医药大学, 2022.
|
 畸形伴深覆
畸形伴深覆 患者1例报告及文献复习
患者1例报告及文献复习
 )
)
 )
)
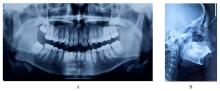
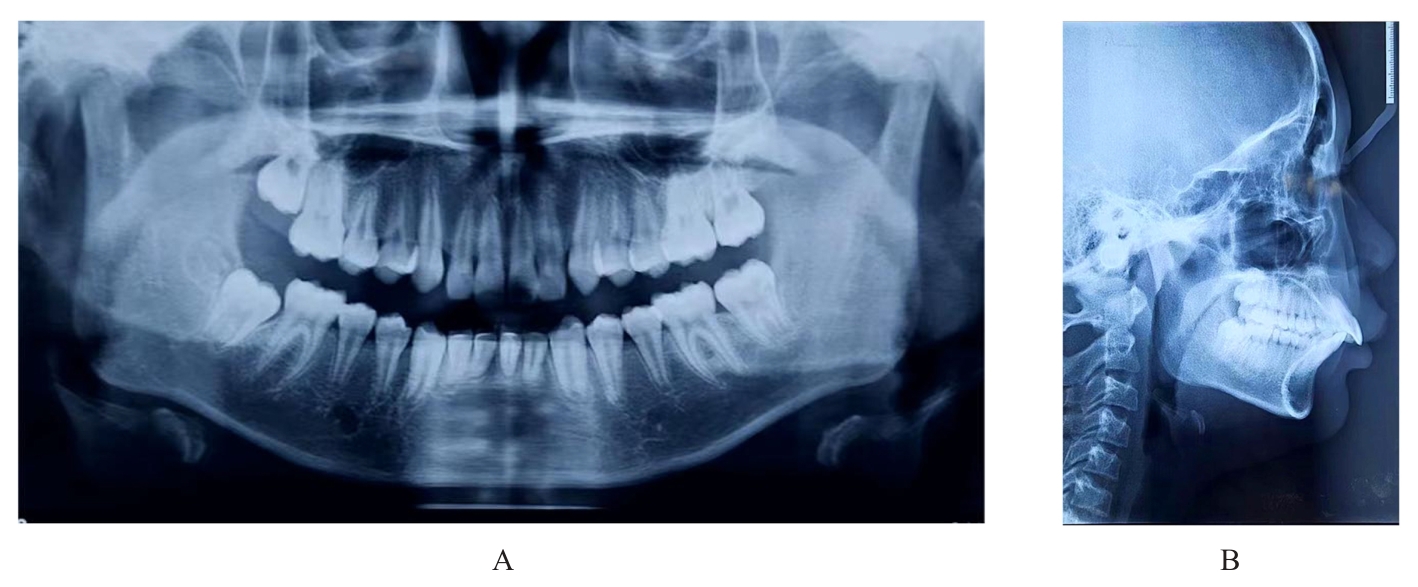
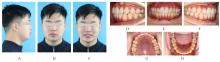
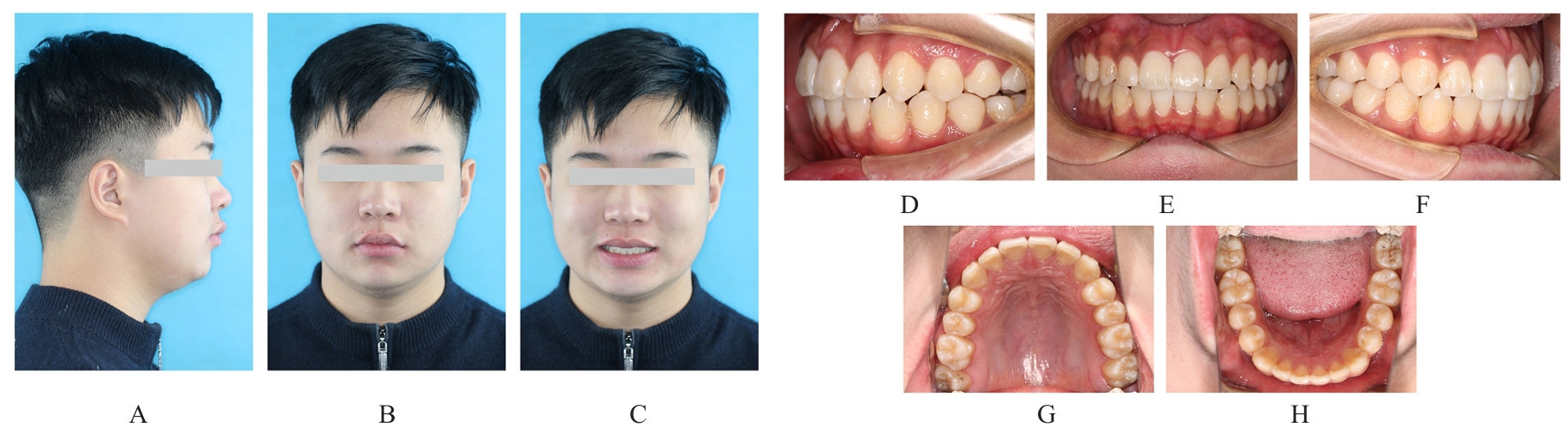
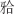 畸形常出现下颌后缩和开唇露齿等,影响患者侧貌,甚至还可能引起上气道狭窄。安氏Ⅱ类错
畸形常出现下颌后缩和开唇露齿等,影响患者侧貌,甚至还可能引起上气道狭窄。安氏Ⅱ类错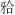 可分为牙性与骨性两类。针对处于生长发育高峰期的伴下颌后缩骨性Ⅱ类患者,临床常采用功能性矫治器进行下颌前导为首选治疗方案。目前国内外关于无托槽隐形矫治器应用于下颌前导治疗的临床应用仍缺乏报道。本文作者报道1例使用无托槽隐形矫治器进行下颌前导配合颌间Ⅱ类牵引以纠正骨性Ⅱ类错
可分为牙性与骨性两类。针对处于生长发育高峰期的伴下颌后缩骨性Ⅱ类患者,临床常采用功能性矫治器进行下颌前导为首选治疗方案。目前国内外关于无托槽隐形矫治器应用于下颌前导治疗的临床应用仍缺乏报道。本文作者报道1例使用无托槽隐形矫治器进行下颌前导配合颌间Ⅱ类牵引以纠正骨性Ⅱ类错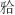 畸形伴深覆
畸形伴深覆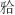 的青少年患者。治疗采用垂直向对前牙进行压低以改善深覆
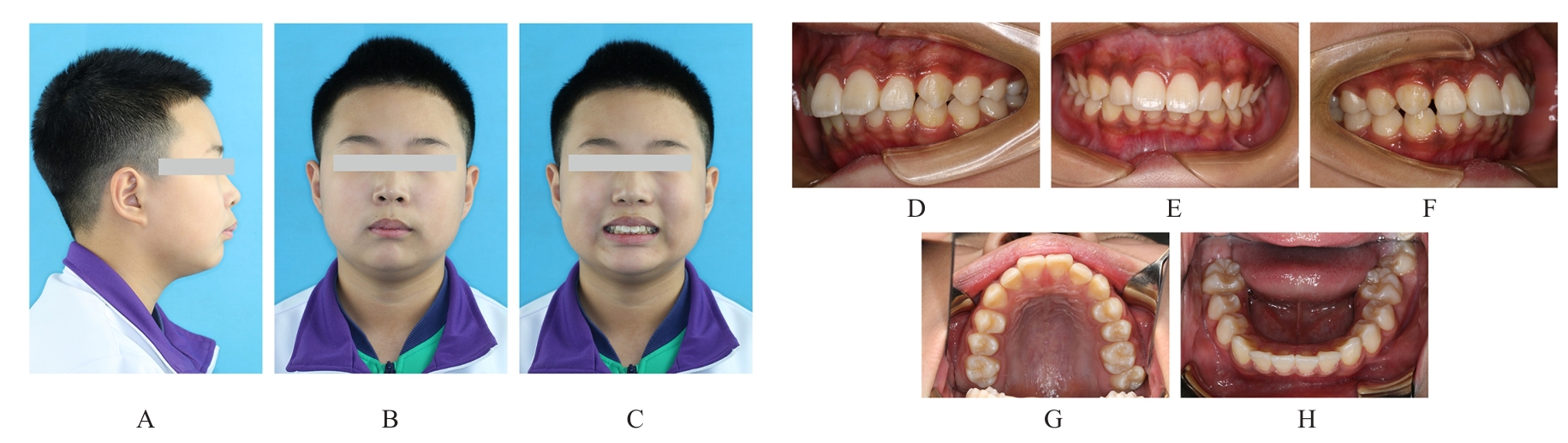
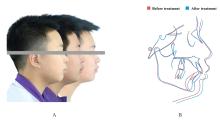
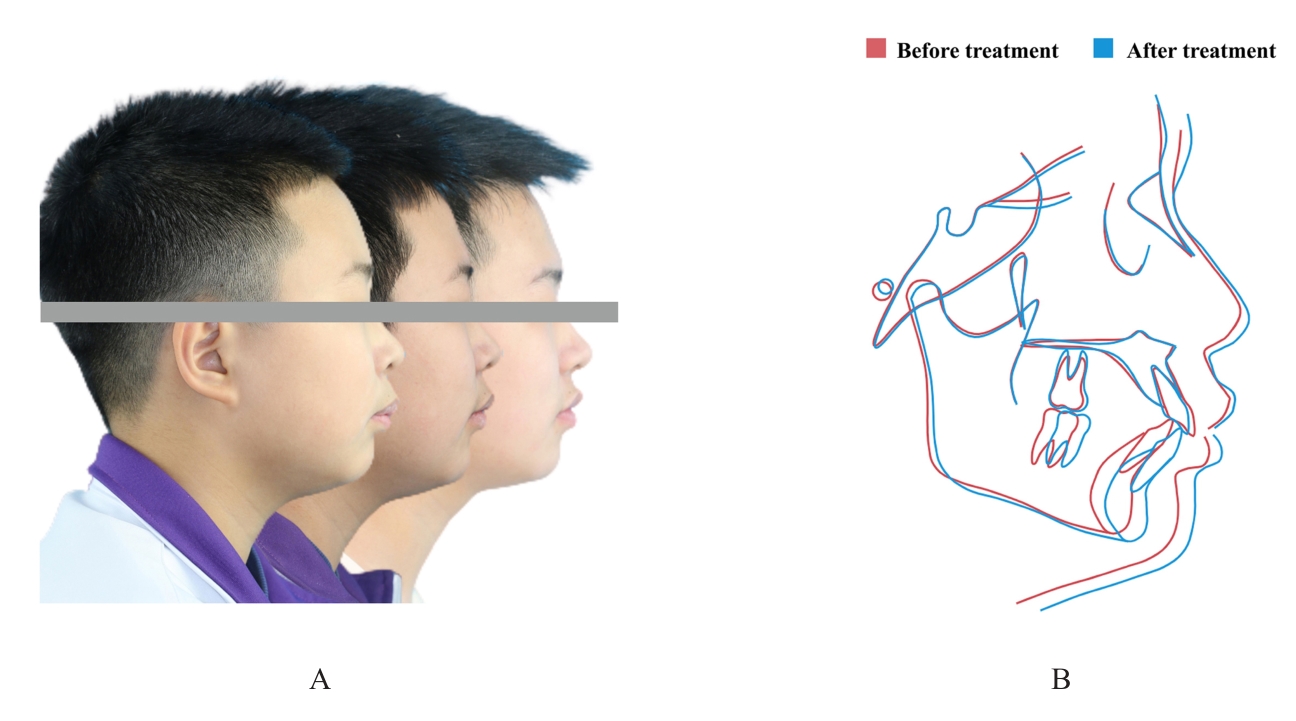
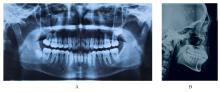
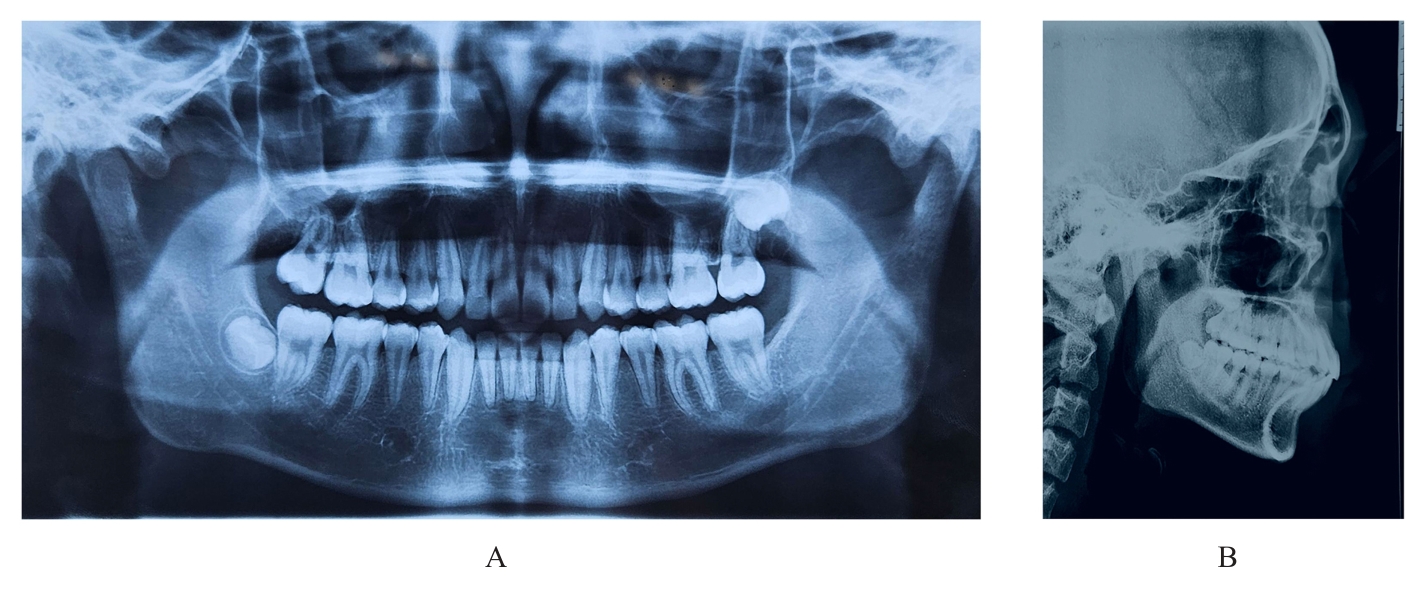
的青少年患者。治疗采用垂直向对前牙进行压低以改善深覆 ,水平向对上下颌进行扩弓以协调牙弓宽度,应用不对称前导技术改善中线。经过35个月矫治,患者凸面型和下颌后缩得到明显改善,上牙槽座点-鼻根点-下牙槽座点角(ANB)由6.8°减小至3.9°;覆
,水平向对上下颌进行扩弓以协调牙弓宽度,应用不对称前导技术改善中线。经过35个月矫治,患者凸面型和下颌后缩得到明显改善,上牙槽座点-鼻根点-下牙槽座点角(ANB)由6.8°减小至3.9°;覆 、覆盖恢复正常;双侧尖牙及磨牙达到中性关系;颏唇沟深度(Si-LiPg')和颏唇沟厚度(Pm-Pm')较矫治前减小,颏唇沟变浅,面部软组织侧貌更为协调。下中切牙-下颌平面角(IMPA)由116.6°减小至110.7°,表明下颌前导过程中下前牙得到内收。综上,骨性Ⅱ类患者采用隐形矫治器进行下颌前导的矫治策略可以避免上下前牙过度代偿,并缩短正畸治疗周期。
、覆盖恢复正常;双侧尖牙及磨牙达到中性关系;颏唇沟深度(Si-LiPg')和颏唇沟厚度(Pm-Pm')较矫治前减小,颏唇沟变浅,面部软组织侧貌更为协调。下中切牙-下颌平面角(IMPA)由116.6°减小至110.7°,表明下颌前导过程中下前牙得到内收。综上,骨性Ⅱ类患者采用隐形矫治器进行下颌前导的矫治策略可以避免上下前牙过度代偿,并缩短正畸治疗周期。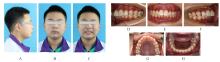
 垫对生长发育高峰期后骨性Ⅱ类下颌后缩的疗效[J]. 中国临床医学, 2023, 30(3): 502-508.
垫对生长发育高峰期后骨性Ⅱ类下颌后缩的疗效[J]. 中国临床医学, 2023, 30(3): 502-508. 畸形患者面部美学结构的影响分析[J]. 中国美容医学, 2024, 33(2): 141-145.
畸形患者面部美学结构的影响分析[J]. 中国美容医学, 2024, 33(2): 141-145.