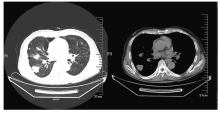
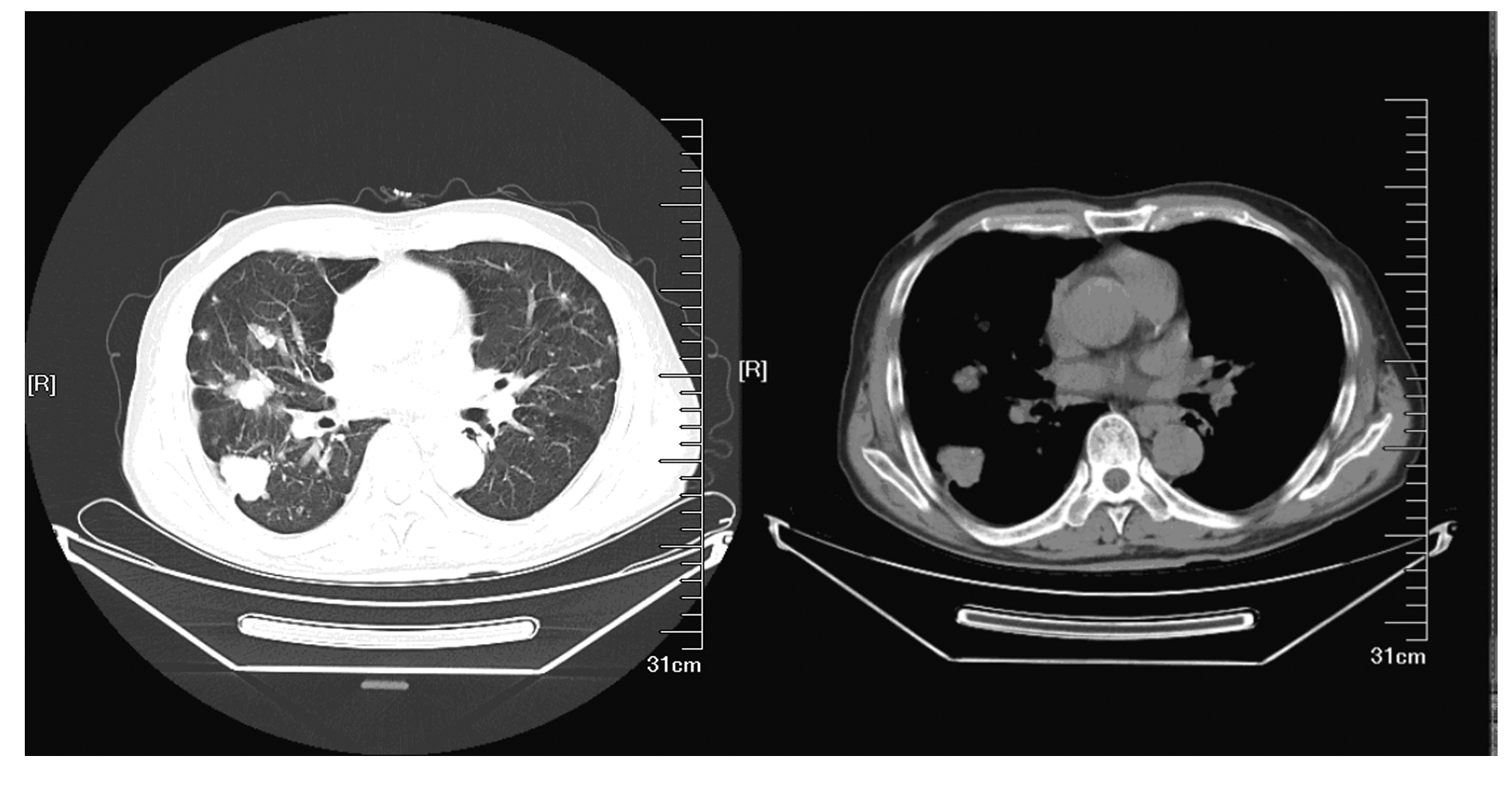
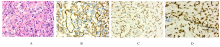
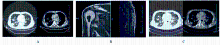
| 1 |
DAIL D, LIEBOW A. Intravascular bronchioloalveolar tumor[J]. Am J Pathol, 1975, 78(1): 6-7.
|
| 2 |
LAU K, MASSAD M, POLLAK C, et al. Clinical patterns and outcome in epithelioid hemangioendothelioma with or without pulmonary involvement: insights from an internet registry in the study of a rare cancer [J]. Chest, 2011, 140(5): 1312-1318.
|
| 3 |
ROSENBERG A, AGULNIK M. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma:update on diagnosis and treatment [J]. Curr Treat Options Oncol, 2018, 19(4): 19.
|
| 4 |
BAGAN P, HASSAN M, LE PIMPEC BARTHES F, et al. Prognostic factors and surgical indications of pulmonary epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A review of the literature [J]. Ann Thorac Surg, 2006, 82(6): 2010-2013.
|
| 5 |
LAMAR J M, MOTILAL NEHRU V, WEINBERG G. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma as a model of YAP/TAZ-driven cancer: Insights from a rare fusion sarcoma [J]. Cancers (Basel), 2018, 10(7):E229.
|
| 6 |
KIM E Y, KIM T S, HAN J, et al. Thoracic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: imaging and pathologic features [J]. Acta Radiol, 2011, 52(2): 161-166.
|
| 7 |
HAN Y J, KIM H J, KONG K A, et al. Diagnosis of small pulmonary lesions by transbronchial lung biopsy with radial endobronchial ultrasound and virtual bronchoscopic navigation versus CT-guided transthoracic needle biopsy:a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(1): e0191590.
|
| 8 |
FLUCKE U, VOGELS R J, DE SAINT AUBAIN SOMERHAUSEN N, et al. Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma: clinicopathologic, immunhisto-chemical, and molecular genetic analysis of 39 cases [J]. Diagn Pathol, 2014, 9:131.
|
| 9 |
ANDERSON T, ZHANG L, HAMEED M, et al. Thoracic epithelioid malignant vascular tumors: a clinicopathologic study of 52 cases with emphasis on pathologic grading and molecular studies of WWTR1-CAMTA1 fusions [J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2015, 39(1): 132-139.
|
| 10 |
SHON W, BILLINGS S D. Epithelioid vascular tumors: A review [J]. Adv Anat Pathol, 2019, 26(3): 186-197.
|
| 11 |
GILL R, O’DONNELL R J, HORVAI A. Utility of immunohistochemistry for endothelial markers in distinguishing epithelioid hemangioendothelioma from carcinoma metastatic to bone [J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2009, 133(6): 967-972.
|
| 12 |
PAPKE D J JR,HORNICK J L. What is new in endothelial neoplasia? [J]. Virchows Arch, 2020, 476(1): 17-28.
|
| 13 |
ERRANI C, ZHANG L, SUNG Y S, et al. A novel WWTR1-CAMTA1 genes fusion is a consistent abnormality in epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of different anatomic sites [J]. Genes Chromosome Cancer, 2011, 50(8): 644-653.
|
| 14 |
MEHRABI A, KASHFI A, FONOUNI H, et al. Primary malignant hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a comprehensive review of the literature with emphasis on the surgical therapy [J]. Cancer, 2006, 107(9): 2108-2121.
|
| 15 |
KITAICHI M, NAGAI S, NISHIMURA K, et al. Pulmonary epithelioid haemangioendothelioma in 21 patients, including three with partial spontaneous regression [J]. Eur Respir J, 1998, 12(1): 89-96.
|
| 16 |
KANEMURA S, KURIBAYASHI K, MORIYA Y, et al. Pemetrexed for epithelioid haemangioendothelioma of the pleura [J]. Respirol Case Rep, 2016, 4(6): e00191.
|
| 17 |
WOO J H, KIM T J, LEE K S, et al. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma in the thorax: Clinicopathologic, CT, PET, and prognostic features [J]. Medicine (Madr), 2016, 95(30): e4348.
|
| 18 |
YE B, LI W, FENG J, et al. Treatment of pulmonary epithelioid hemangioendothelioma with combination chemotherapy: Report of three cases and review of the literature [J]. Oncol Lett, 2013, 5(5): 1491-1496.
|
| 19 |
PINET C, MAGNAN A, GARBE L, et al. Aggressive form of pleural epithelioid haemangioendothelioma: complete response after chemotherapy [J]. Eur Respir J, 1999, 14(1): 237-238.
|
| 20 |
MERIKAS E, GRAPSA D, DIKOUDI E, et al. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma treated with bevacizumab: A case series [J]. Cancer Treat Commun, 2015, 4(1):59-64.
|
| 21 |
ZHENG Z P, WANG H Y, JIANG H L, et al. Apatinib for the treatment of pulmonary epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A case report and literature review [J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2017, 96(45): e8507.
|
| 22 |
SEMENISTY V, NARODITSKY I, KEIDAR Z, et al. Pazopanib for metastatic pulmonary epithelioid hemangioendothelioma-a suitable treatment option: case report and review of anti-angiogenic treatment options [J]. BMC Cancer, 2015, 15:402.
|
| 23 |
HANSEN C G, NG Y L, LAM W L, et al. The Hippo pathway effectors YAP and TAZ promote cell growth by modulating amino acid signaling to mTORC1 [J]. Cell Res, 2015, 25(12): 1299-1313.
|
| 24 |
STACCHIOTTI S, PROVENZANO S, DAGRADA G, et al. Sirolimus in Advanced epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A retrospective case-series analysis from the Italian rare cancer network database [J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2016, 23(9): 2735-2744.
|
| 25 |
DEYRUP A T, TIGHIOUART M, MONTAG A G, et al. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of soft tissue: a proposal for risk stratification based on 49 cases [J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2008, 32(6): 924-927.
|
| 26 |
AMIN R M, HIROSHIMA K, KOKUBO T, et al. Risk factors and independent predictors of survival in patients with pulmonary epithelioid haemangioendothelioma. Review of the literature and a case report [J]. Respirology, 2006, 11(6): 818-825.
|
 )
)