吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 216-221.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20210130
领悟社会支持在冠心病患者自尊与焦虑间的中介作用
- 1.吉林大学第一医院心理卫生科,吉林 长春 130021
2.吉林大学第一医院心血管内科,吉林 长春 130021
3.吉林大学公共卫生学院社会医学教研室,吉林 长春 130021
Mediating effect of perceived social support between self-esteem and anxiety in patients with coronary heart disease
Yang YU1,Yang YANG2,Mingtu XU1,Zeying QIN3,Cong FU1,Jingyang LI1( )
)
- 1.Department of Mental Health,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
2.Department of Cardiovascular Medicine,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
3.Department of Social Medicine,School of Public Health,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
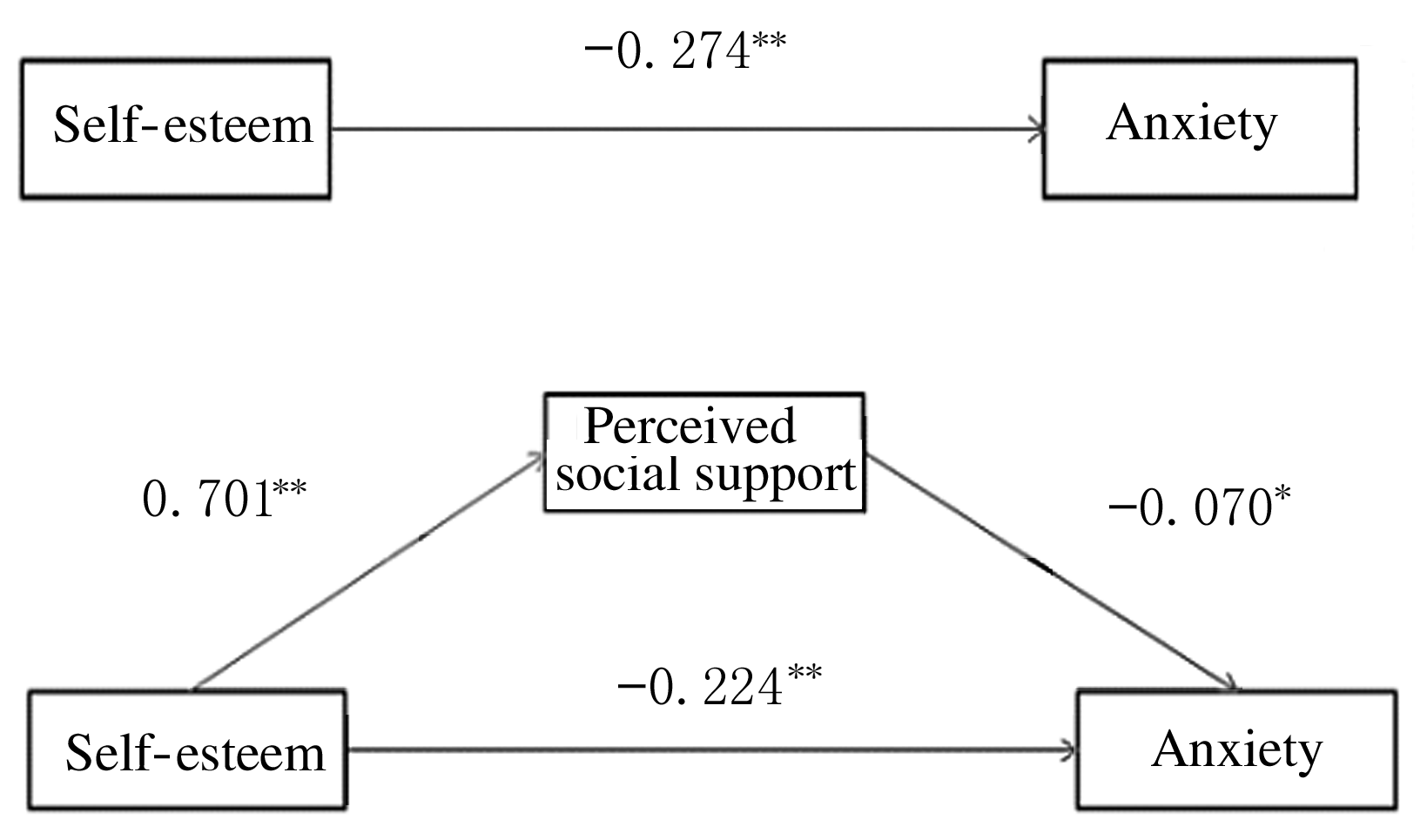
摘要: 探讨冠心病患者的焦虑情绪问题及相关影响因素,考察领悟社会支持在自尊与焦虑间的中介作用。 选择首次确诊入院的冠心病患者315例,采用一般资料调查表、焦虑筛查问卷、自尊量表和领悟社会支持量表进行心理测量及问卷调查,获得有效问卷305份。患者焦虑相关影响因素2组间和多组间比较采用t检验和单因素方差分析,患者自尊、领悟社会支持和焦虑的相关性采用Pearson相关分析, 并采用逐步回归分析法进行中介效应检验。 冠心病患者中,女性的焦虑水平高于男性(t=9.664,P<0.01)。不同文化程度患者焦虑水平比较差异有统计学意义(F=3.146, P<<0.05),文盲患者焦虑水平最高。不同婚姻状况患者焦虑水平比较差异有统计学意义(F=9.113,P<0.01),丧偶患者焦虑水平最高。有睡眠障碍患者焦虑水平高于无睡眠障碍患者(t=19.961, P<0.01)。有嗜酒史患者焦虑水平高于无嗜酒史患者(t=10.462, P<0.01)。自尊与领悟社会支持呈正相关关系(r=0.251,P<0.01),自尊与焦虑呈负相关关系(r=-0.173,P<0.01),领悟社会支持与焦虑呈负相关关系(r=-0.187,P<0.01)。自尊可以直接预测焦虑(β=-0.224,P<0.01),领悟社会支持在自尊与焦虑之间起到部分中介作用(β=-0.224,P<0.01;β=-0.070,P<0.05)。 女性、文盲、丧偶、嗜酒和有睡眠障碍的冠心病患者焦虑情绪问题突出,低自尊和较差的领悟社会支持水平是焦虑情绪的预测因素,领悟社会支持在自尊与焦虑之间具有部分中介作用。
中图分类号:
- R541.4