吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (3): 676-683.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220316
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
木犀草素抑制ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3信号通路激活对小鼠急性呼吸窘迫综合征的改善作用
曲海新1,袁二伟1,郭卫平2,张雅静1,马文霞2,吴丹1
- 1.河北北方学院附属第一医院新生儿科, 河北 张家口 075000
2.河北北方学院附属第一医院儿科, 河北 张家口 075000
Improvement effect of luteolin on acute respiratory distress syndrome by inhibiting ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 signaling pathway activation in mice
Haixin QU1,Erwei YUAN1,Weiping GUO2,Yajing ZHANG1,Wenxia MA2,Dan WU1
- 1.Department of Neonatology,First Affiliated Hospital,Hebei North University,Zhangjiakou 075000,China
2.Department of Pediatrics,First Affiliated Hospital,Hebei North University,Zhangjiakou 075000,China
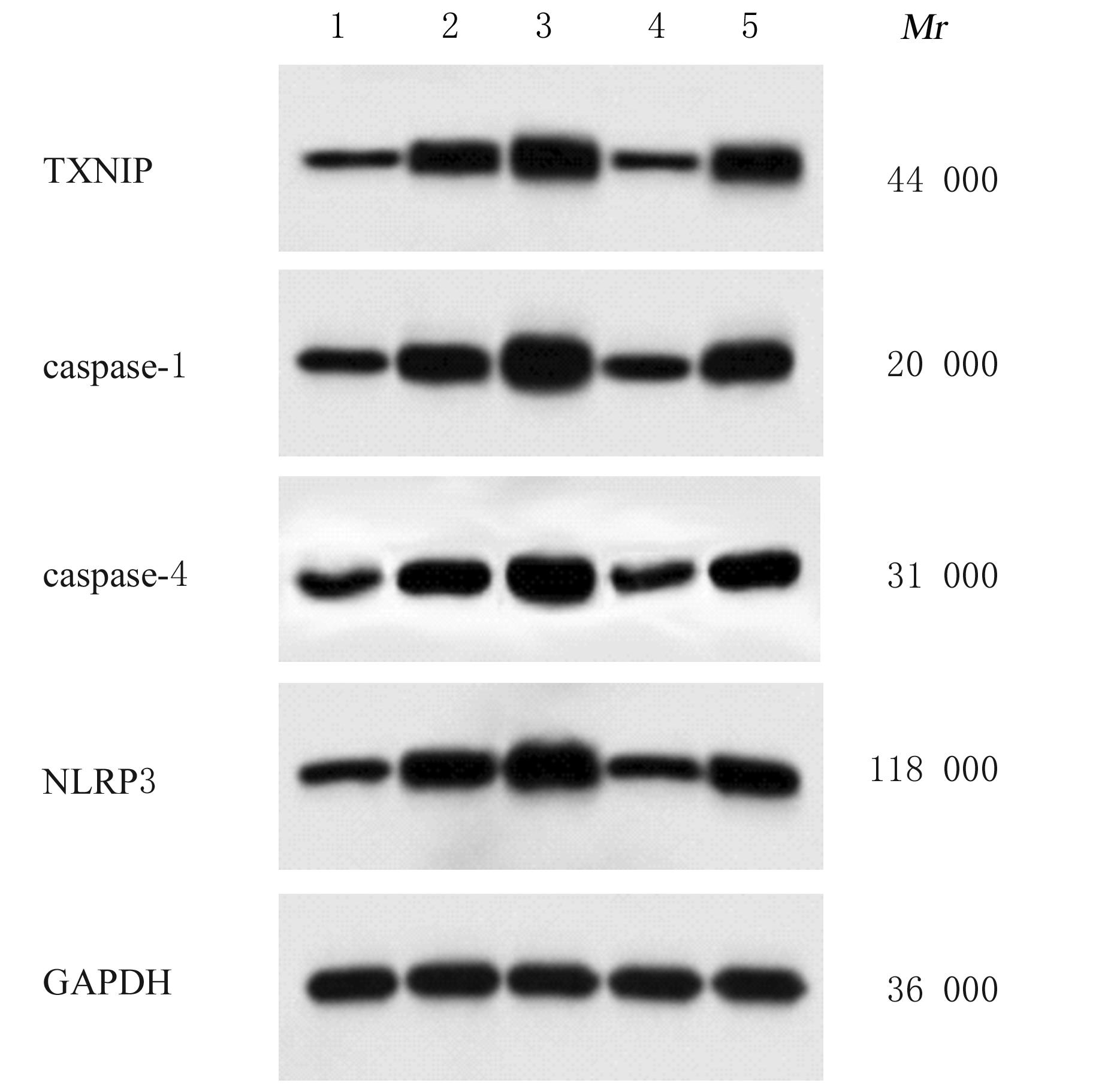
摘要: 探讨木犀草素调控活性氧(ROS)/硫氧还蛋白结合蛋白(TXNIP)/NOD样受体相关蛋白3(NLRP3)信号通路激活对小鼠急性呼吸窘迫综合征(ARDS)的改善作用。 60只SD小鼠随机分为对照组、模型组、木犀草素(20 mg·kg-1)组、邻苯三酚(PG)(75 mg·kg-1)组和木犀草素(20 mg·kg-1)+PG(75 mg·kg-1)组,每组12只。除对照组外,其他组小鼠采用气管滴注脂多糖(LPS)溶液的方法建立ARDS模型,对照组小鼠气管滴注等量生理盐水。称量各组小鼠右肺湿质量和干质量,并计算湿质量/干质量(W/D)比值,检测各组小鼠动脉血氧分压(PaO2),HE染色观察各组小鼠肺组织病理形态表现,检测各组小鼠吸气阻力(Ri)、每分钟通气量(MV)和呼气峰流速(PEF),检测各组小鼠肺组织中ROS、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-Px)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)水平及血清白细胞介素18(IL-18)、白细胞介素1β(IL-1β)和肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)水平,Western blotting法检测各组小鼠肺组织中TXNIP、caspase-1、caspase-4和NLRP3蛋白表达水平。 与对照组比较,模型组小鼠肺泡壁变厚,肺泡塌陷变形,肺间质水肿伴有大量炎性细胞浸润,肺组织有严重病理损伤,W/D比值,Ri,血清IL-18、IL-1β及TNF-α水平,肺组织中ROS水平及TXNIP、caspase-1、caspase-4和NLRP3蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05);MV、PEF、PaO2和肺组织中GSH-Px及CAT水平降低(P<0.05)。与模型组比较,木犀草素组小鼠肺组织病理损伤均有所改善,W/D比值,Ri,血清IL-18、IL-1β及TNF-α水平,肺组织中ROS水平和TXNIP、caspase-1、caspase-4及NLRP3蛋白表达水平均降低(P<0.05),MV、PEF和PaO2及肺组织中GSH-Px和CAT水平均升高(P<0.05);PG组小鼠肺组织病理损伤均加重,W/D比值,Ri,血清IL-18、IL-1β及TNF-α水平,肺组织中ROS水平及TXNIP、caspase-1、caspase-4和NLRP3蛋白表达水平均升高(P<0.05),MV、PEF和PaO2及肺组织中GSH-Px和CAT水平均降低(P<0.05)。 木犀草素可通过抑制ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3信号通路激活,减轻肺部炎症与氧化应激,改善ARDS小鼠肺损伤,修复其肺功能。
中图分类号:
- R563.8