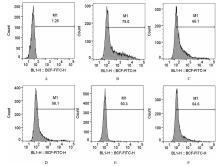
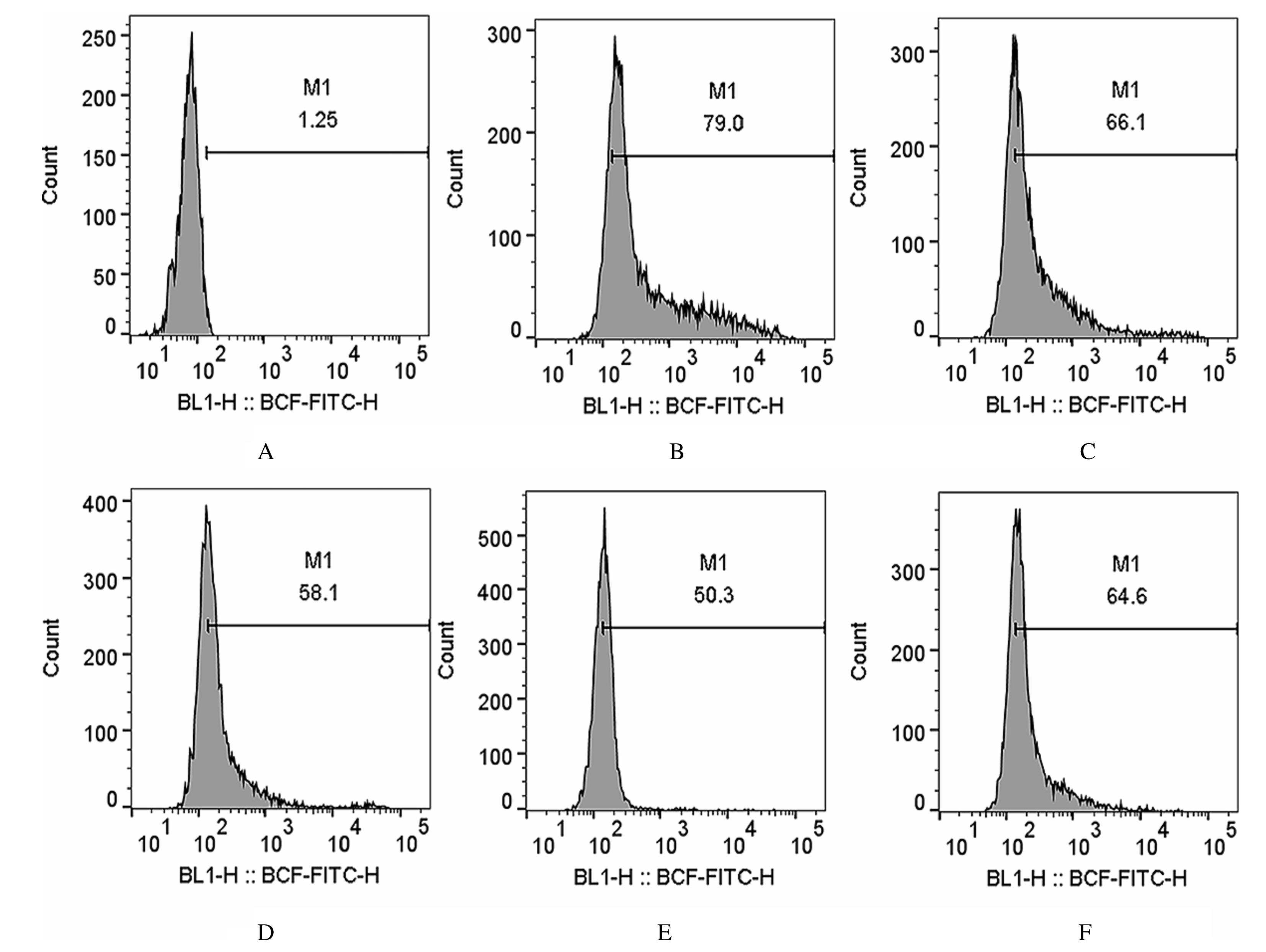
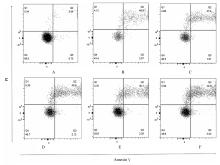
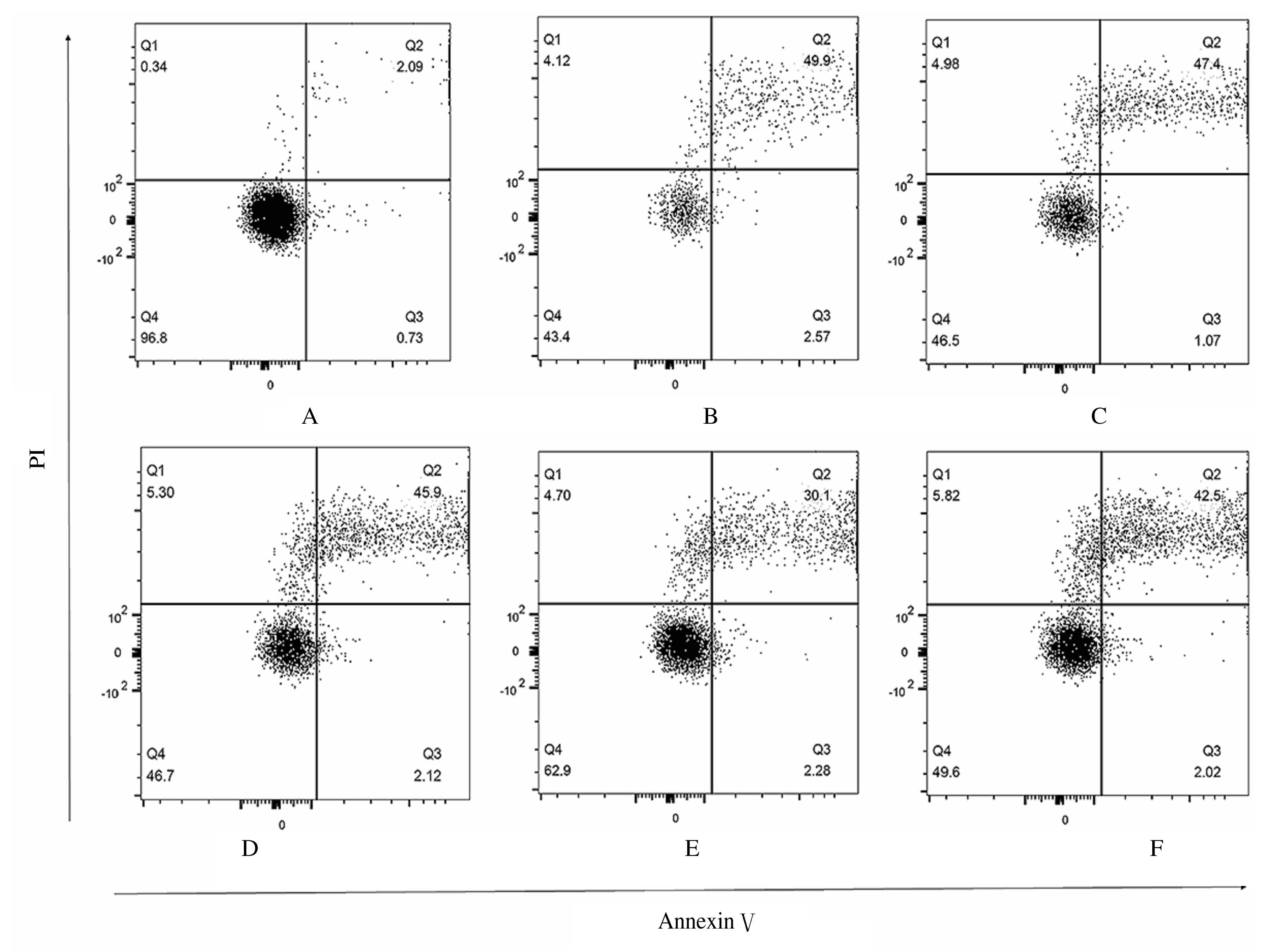
| 1 |
SALIM S. Oxidative stress and the central nervous system[J]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2017, 360(1): 201-205.
|
| 2 |
KHATRI N, THAKUR M, PAREEK V, et al. Oxidative stress: major threat in traumatic brain injury[J].CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets,2018,17(9): 689-695.
|
| 3 |
陈 洁, 赵明峰. 活性氧在免疫应答中的作用[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2015, 31(6): 855-858.
|
| 4 |
FERLAZZO N, ANDOLINA G, CANNATA A,et al. Is melatonin the cornucopia of the 21st century? [J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2020, 9(11): 1088.
|
| 5 |
ZHANG H M, ZHANG Y Q.Melatonin: a well-documented antioxidant with conditional pro-oxidant actions[J]. J Pineal Res, 2014, 57(2): 131-146.
|
| 6 |
NOPPARAT C, SINJANAKHOM P, GOVITRAPONG P. Melatonin reverses H2O2 -induced senescence in SH-SY5Y cells by enhancing autophagy via sirtuin 1 deacetylation of the RelA/p65 subunit of NF-κB[J]. J Pineal Res, 2017, 63(1): e12407.
|
| 7 |
REDDY P H, OLIVER D M. Amyloid beta and phosphorylated tau-induced defective autophagy and mitophagy in Alzheimer’s disease[J].Cells,2019,8(5): 488.
|
| 8 |
CHANG C C, HUANG T Y, CHEN H Y, et al. Protective effect of melatonin against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis and enhanced autophagy in human retinal pigment epithelium cells[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2018, 2018: 9015765.
|
| 9 |
NIU X L, ZHENG S M, LIU H T, et al. Protective effects of taurine against inflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress in brain injury[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2018, 18(5): 4516-4522.
|
| 10 |
LUO P, CHEN T, ZHAO Y B, et al. Protective effect of Homer 1a against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in PC12 cells[J]. Free Radic Res, 2012, 46(6): 766-776.
|
| 11 |
HU X L, NIU Y X, ZHANG Q, et al. Neuroprotective effects of kukoamine B against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis and potential mechanisms in SH-SY5Y cells[J]. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol, 2015, 40(1): 230-240.
|
| 12 |
TAN D X, REITER R J, MANCHESTER L C, et al. Chemical and physical properties and potential mechanisms: melatonin as a broad spectrum antioxidant and free radical scavenger[J]. Curr Top Med Chem, 2002, 2(2): 181-197.
|
| 13 |
TORII K, UNEYAMA H, NISHINO H, et al. Melatonin suppresses cerebral edema caused by middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion in rats assessed by magnetic resonance imaging[J]. J Pineal Res, 2004, 36(1): 18-24.
|
| 14 |
CHETSAWANG B, CHETSAWANG J, GOVITRAPONG P. Protection against cell death and sustained tyrosine hydroxylase phosphorylation in hydrogen peroxide- and MPP-treated human neuroblastoma cells with melatonin[J]. J Pineal Res, 2009, 46(1): 36-42.
|
| 15 |
FILOMENI G, DE ZIO D, CECCONI F. Oxidative stress and autophagy: the clash between damage and metabolic needs[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2015, 22(3): 377-388.
|
| 16 |
SCHERZ-SHOUVAL R, ELAZAR Z. Regulation of autophagy by ROS: physiology and pathology[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2011, 36(1): 30-38.
|
| 17 |
YANG S S, LIAN G J. Ros and diseases: role in metabolism and energy supply[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2020, 467(1/2): 1-12.
|
| 18 |
HAMASAKI M, FURUTA N, MATSUDA A, et al. Autophagosomes form at ER-mitochondria contact sites[J]. Nature, 2013, 495(7441): 389-393.
|
| 19 |
FERNÁNDEZ A, ORDÓÑEZ R, REITER R J, et al. Melatonin and endoplasmic reticulum stress: relation to autophagy and apoptosis[J]. J Pineal Res, 2015, 59(3): 292-307.
|
| 20 |
NAKATOGAWA H. Mechanisms governing autophagosome biogenesis[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2020, 21(8): 439-458.
|
| 21 |
LIN Y N, JIANG M, CHEN W J, et al. Cancer and ER stress: mutual crosstalk between autophagy, oxidative stress and inflammatory response[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 118: 109249.
|
| 22 |
SAN-MIGUEL B, CRESPO I, VALLEJO D, et al. Melatonin modulates the autophagic response in acute liver failure induced by the rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus[J]. J Pineal Res, 2014, 56(3): 313-321.
|
| 23 |
DING K, XU J G, WANG H D, et al. Melatonin protects the brain from apoptosis by enhancement of autophagy after traumatic brain injury in mice[J]. Neurochem Int, 2015, 91: 46-54.
|
| 24 |
YANG F, YANG L, LI Y,et al.Melatonin protects bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells against iron overload-induced aberrant differentiation and senescence[J].J Pineal Res,2017.DOI:10.1111/jpi.12422 .
doi: 10.1111/jpi.12422
|
| 25 |
YU L M, DONG X, XUE X D, et al. Melatonin attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy and reduces myocardial vulnerability to ischemia-reperfusion injury by improving mitochondrial quality control: role of SIRT6[J]. J Pineal Res, 2021, 70(1): e12698.
|
 )
)