吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (4): 1003-1009.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220421
• 临床研究 •
IL-17A在非小细胞肺癌组织中的表达及其通过NF-κB信号通路对VEGF表达的调控作用
- 1.北华大学基础医学院免疫学教研室,吉林 吉林 132013
2.吉林省吉林市化工医院病理科,吉林 吉林 132001
3.北华大学理学院 吉林省中药生物技术创新中心,吉林 吉林 132013
Expression of IL-17A in non-small cell lung cancer tissue and its regulation on VEGF expression via NF-κB signaling pathway
Chengyuan HE1,Hongyu YANG2,Yujing TAN3,Hang SU3,Hongshu LI1,Chun LI1( )
)
- 1.Department of Immunology,College of Basic Medical Sciences,Beihua University,Jilin 132013,China
2.Department of Pathology,Jilin Chemical Technology Hospital,Jilin Province,Jilin 132001,China
3.Jilin Province Chinese Medicine Biotechnology Innovation Center,College of Sciences,Beihua University,Jilin 132013,China
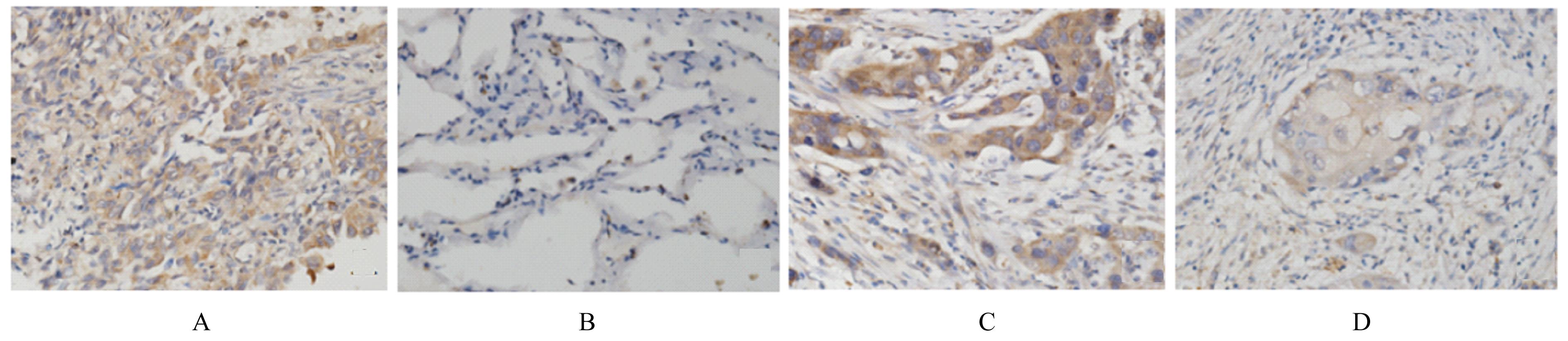
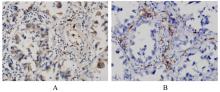
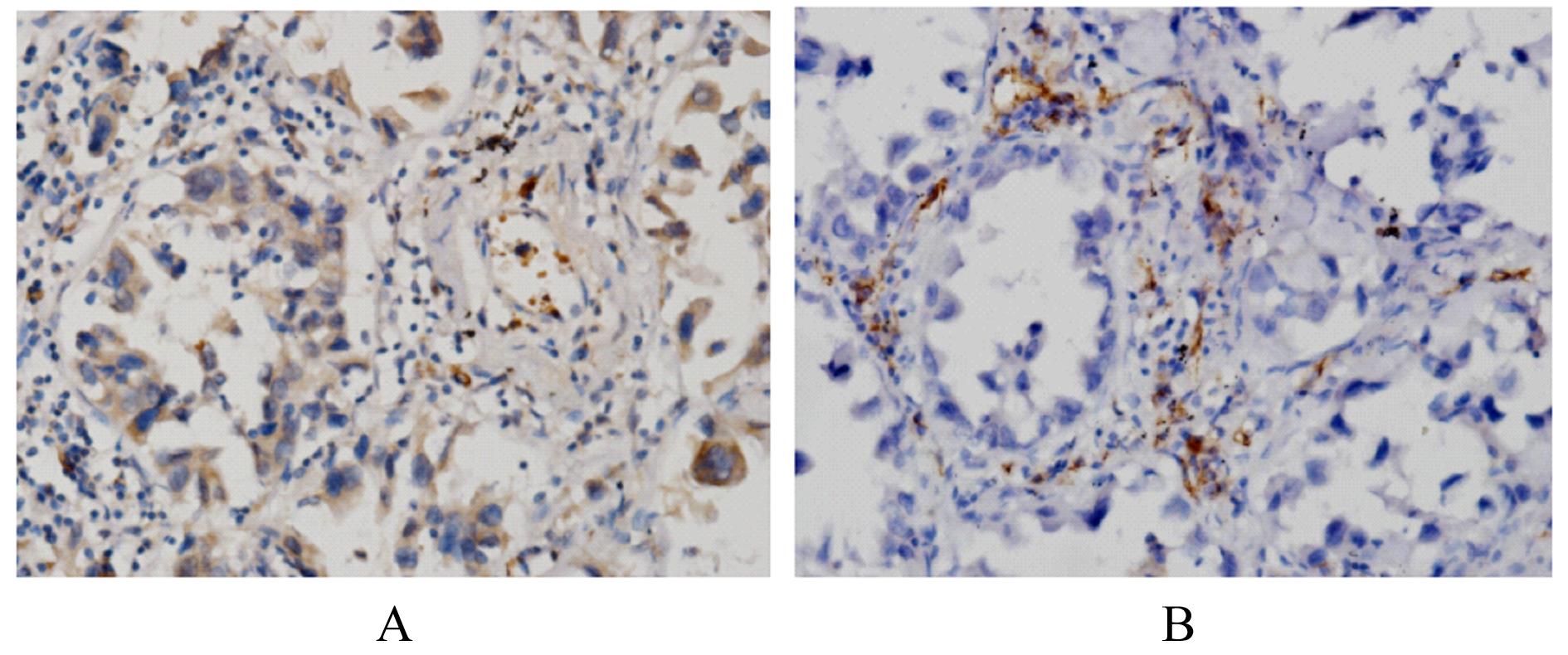
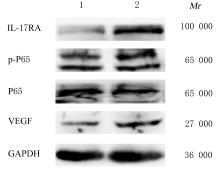
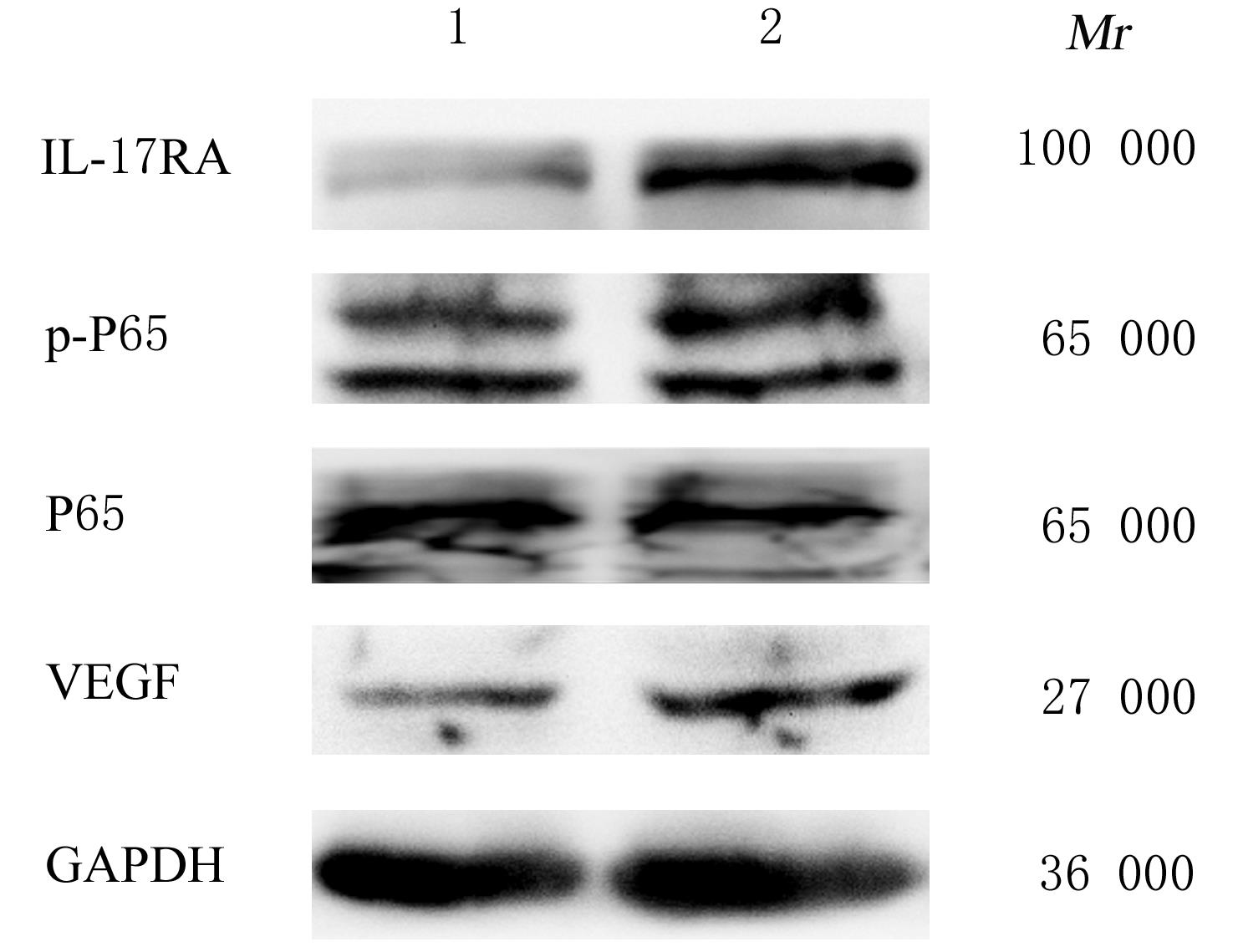
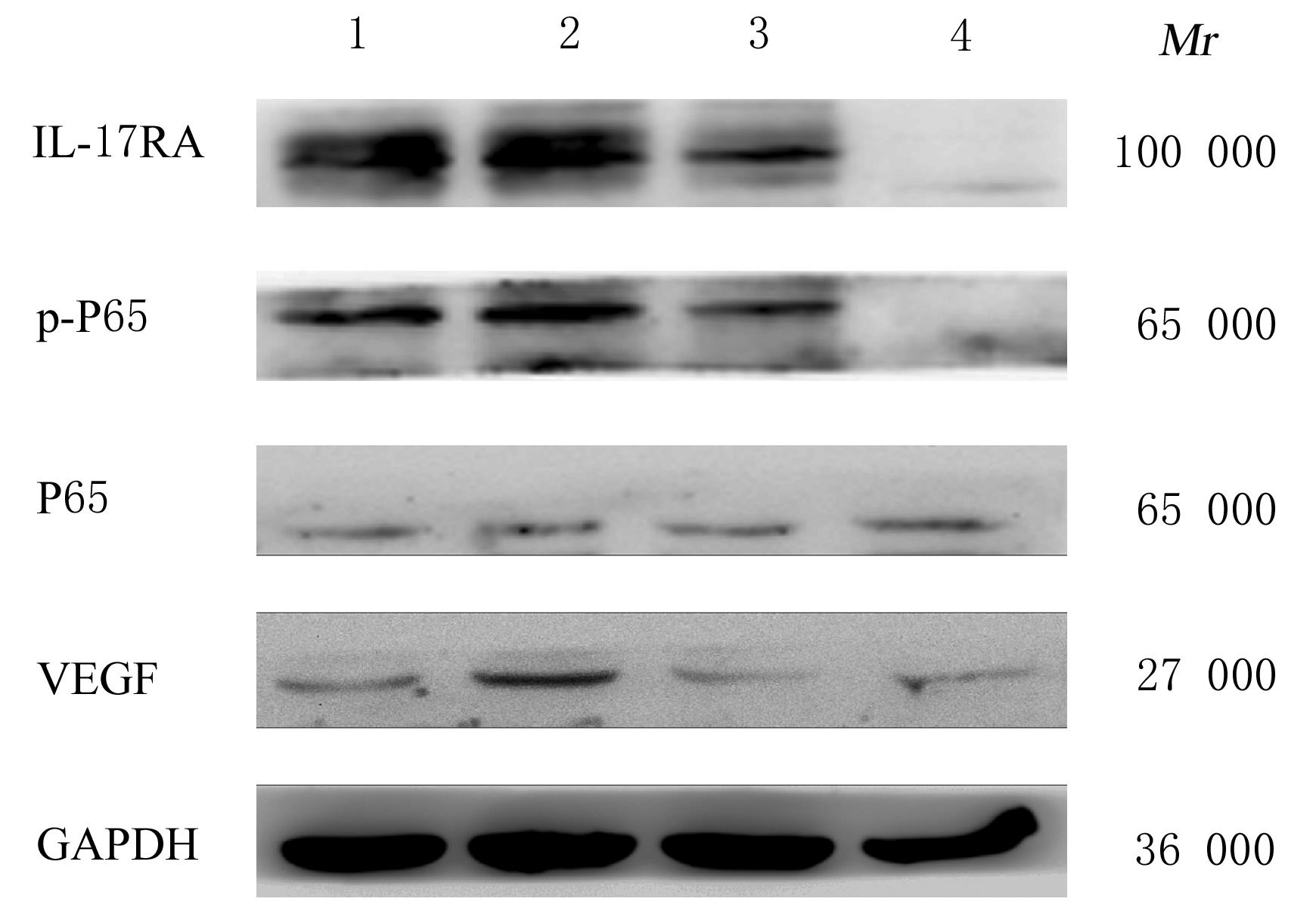
摘要: 探讨白细胞介素17A(IL-17A) 在非小细胞肺癌 (NSCLC)发生发展中的作用及其通过核转录因子κB(NF-κB)信号通路对血管内皮生长因子 (VEGF)的调控作用,阐明其相关机制。 收集NSCLC术后石蜡标本55例,免疫组织化学染色法检测正常肺组织和NSCLC组织中IL-17A和CD31的表达,分析IL-17A阳性表达率与NSCLC患者临床病理参数的关系,Pearson相关分析法分析IL-17A表达与CD31标记的微血管密度(MVD)的相关性。选取对数生长期的人肺腺癌A549细胞,将A549细胞分为对照组(A549细胞)、外源性重组人IL-17A(rhIL-17A)组、BAY11-7082组(NF-κB信号通路抑制剂)和联合组(rhIL-17A+BAY11-7082),Western blotting法检测各组A549细胞中IL-17受体A(IL-17RA)、P65、磷酸化P65(p-P65)和VEGF蛋白表达水平,MTT法检测各组A549细胞培养上清液作用人脐静脉内皮细胞(HUVECs) 48 h后各组细胞增殖活性。 NSCLC组织中IL-17A阳性表达率明显高于正常肺组织(P<0.05),低分化组NSCLC患者IL-17A阳性表达率明显高于高-中分化组(P<0.05),NSCLC组织中IL-17A表达与MVD呈正相关关系(r=0.329,P<0.05)。与对照组比较,rhIL-17A组细胞中IL-17RA、p-P65和VEGF蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05),BAY11-7082组细胞中IL-17RA、p-P65和VEGF表达水平明显降低 (P<0.01);与rhIL-17A组比较,联合组细胞中IL-17RA、p-P65和VEGF表达水平明显降低(P<0.05)。各组培养上清液作用HUVECs后,与对照组比较,rhIL-17A组细胞增殖活性明显升高 (P<0.05),BAY11-7082组细胞增殖活性明显降低(P<0.05);与rhIL-17A组比较,联合组细胞增殖活性明显降低(P<0.05)。 IL-17A在低分化NSCLC细胞中高表达,其可通过NF-κB信号通路调控VEGF的表达进而促进HUVECs的增殖。
中图分类号:
- R734.2