吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 1016-1025.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240416
PPC/PBS复合生物膜的屏障功能及其对兔胫骨骨缺损模型的促成骨作用
- 吉林大学口腔医院种植科,吉林 长春 130021
Barrier function of PPC/PBS composite biofilm and its osteogenetic effect on tibial bone defect models of rabbits
Ye TIAN,Xiaolu SHI,Shaobo ZHAI,Yang LIU,Zheng YANG,Yuchuan WU,Shunli CHU( )
)
- Department of Prosthodontics,Stomatology Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
摘要:
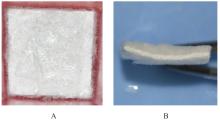
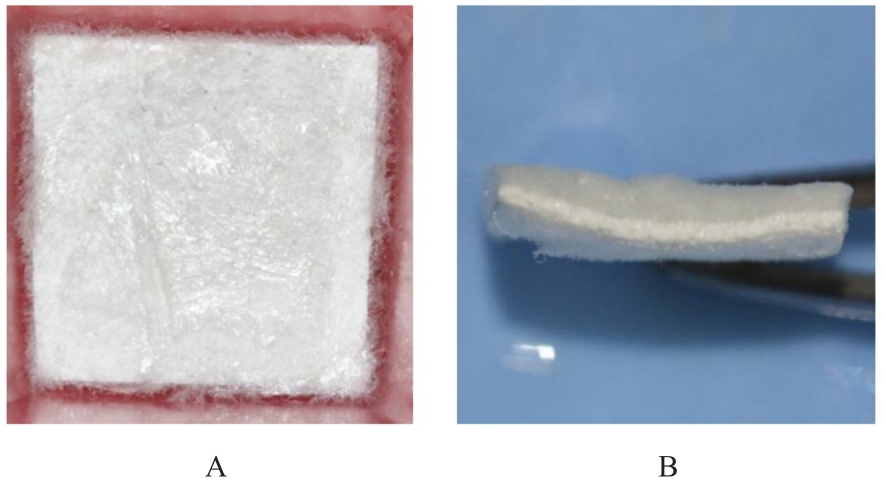
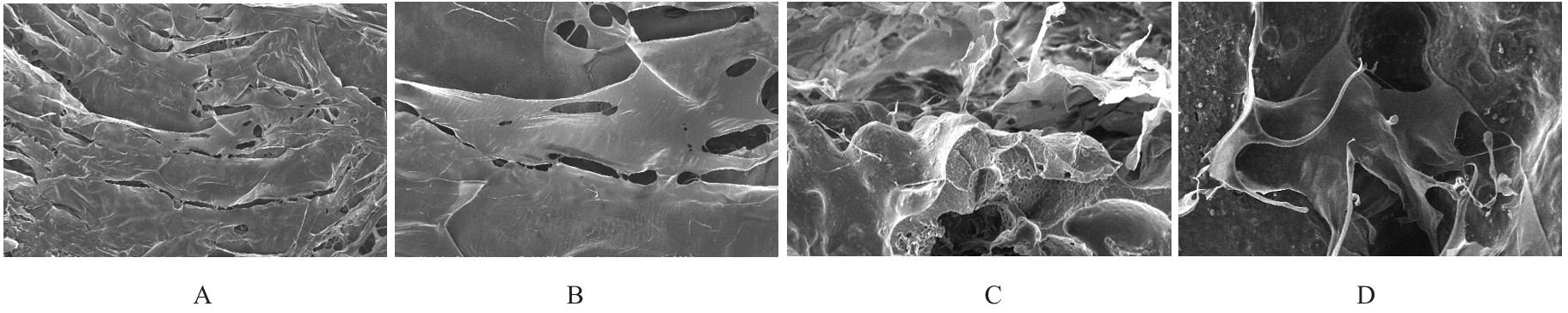
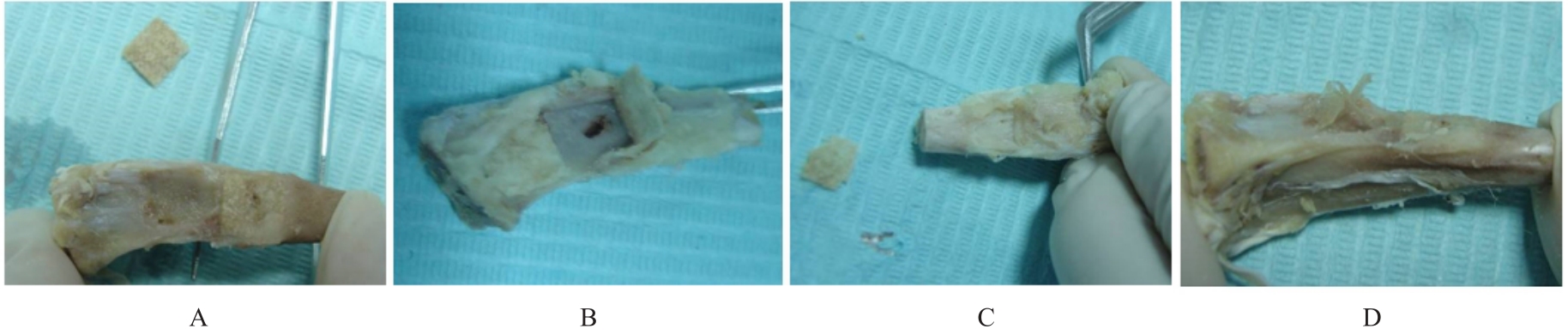
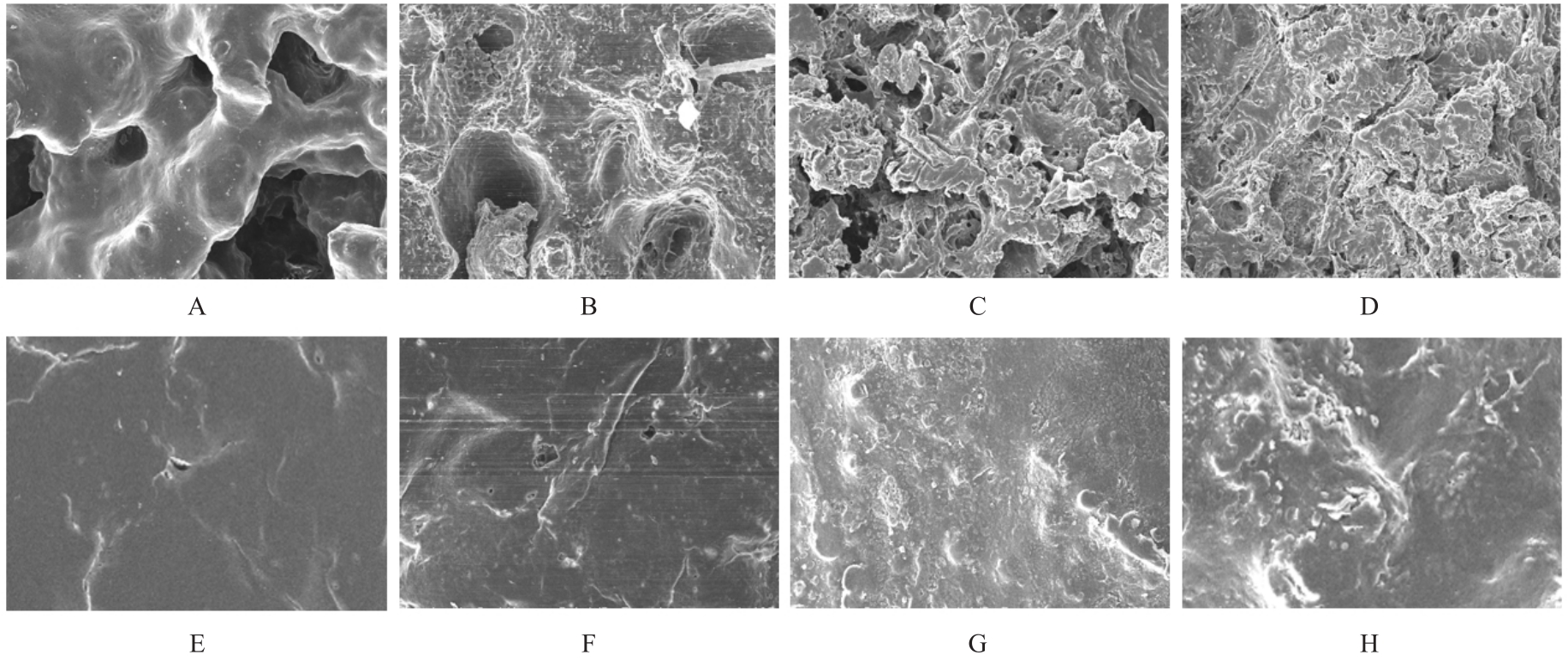
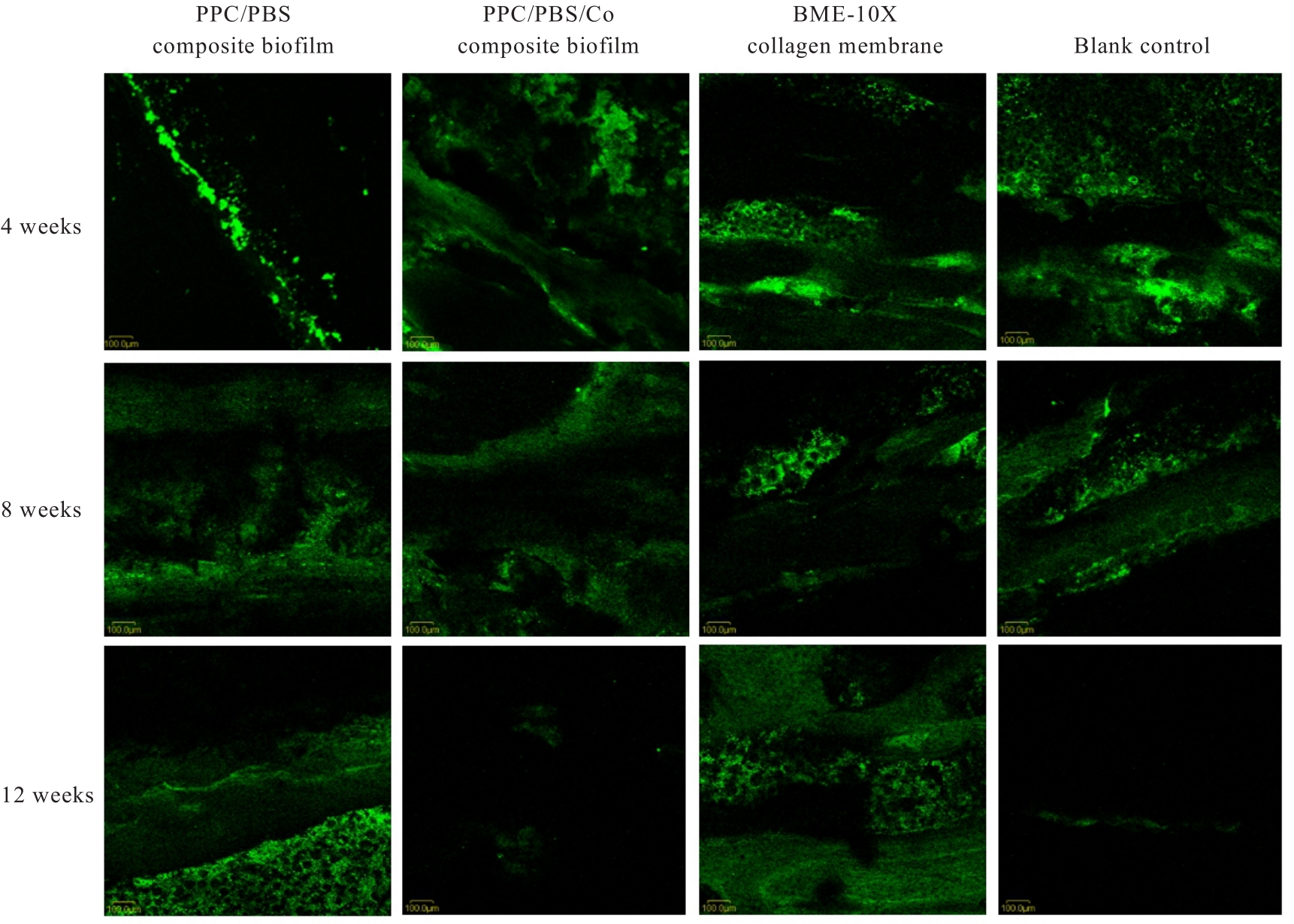
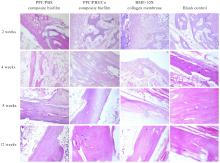
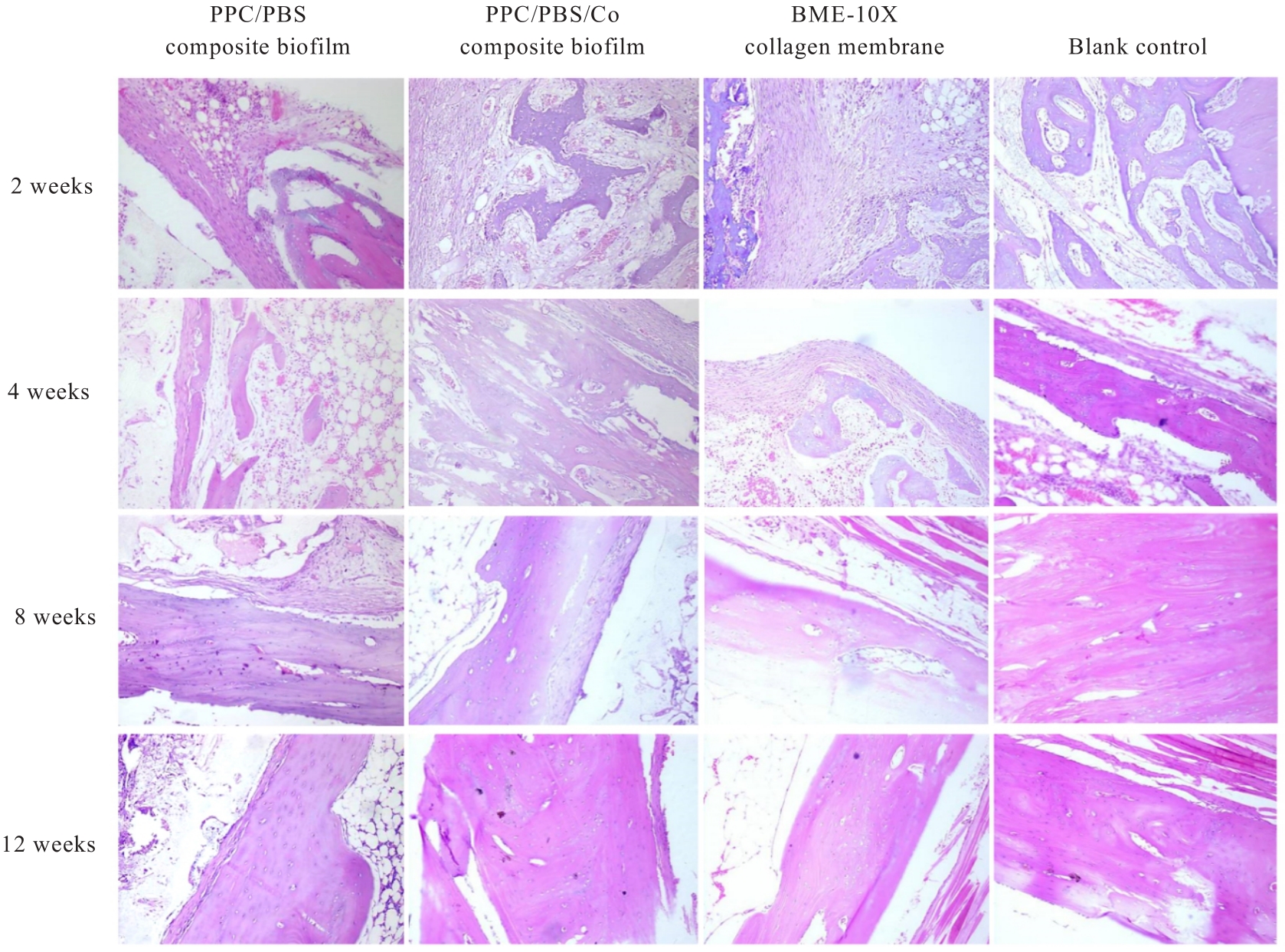
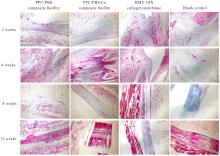
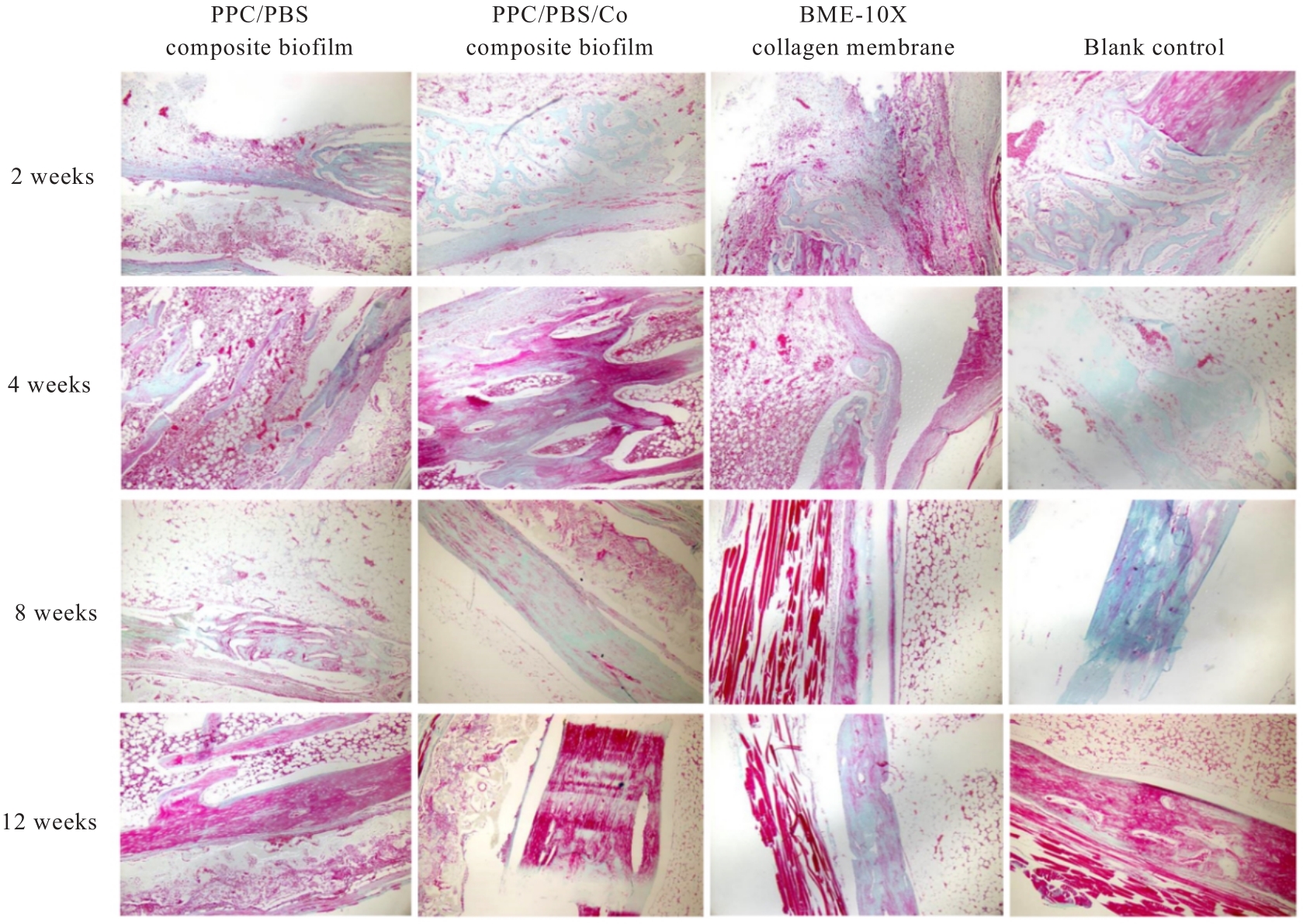
目的 探讨聚碳酸1,2-丙二酯(PPC)/聚丁二酸丁二醇酯(PBS)复合生物膜在兔胫骨骨缺损模型中的空间支撑能力及其对成骨效果的影响,阐明其屏障功能的可靠性和体内促成骨作用。 方法 制备PPC/PBS和PPC/PBS/Ⅰ型胶原(Col-Ⅰ)(PPC/PBS/Co)复合生物膜。选用18只日本大耳白兔,于兔每侧胫骨制备2处骨缺损,随机选择6只兔于骨缺损处放置PPC/PBS复合生物膜,术后4、8和12周各处死2只兔,扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察兔骨缺损区PPC/PBS复合生物膜表面微观结构。 实验分为空白对照组、 PPC/PBS 复合生物膜组、 BME-10X 胶原膜组和PPC/PBS/Co复合生物膜组,分别行手术将上述生物膜放置于兔相应骨缺损处,空白对照组兔不放置复合生物膜,于术后2、4、8和12周时分别处死3只兔,采用软X线检测各组兔骨缺损区再生骨组织灰度值,荧光标记后采用激光共聚焦显微镜观察各组兔骨缺损区再生骨组织荧光强度,采用HE染色和改良Gomori三色染色法观察各组兔骨缺损区再生骨组织病理形态表现,免疫组织化学染色法检测各组兔骨缺损区再生骨组织中骨形态发生蛋白2(BMP-2)和骨桥蛋白(OPN)蛋白表达水平。 结果 大体观察, PPC/PBS 复合生物膜紧密覆盖于骨缺损区, 未见移位及塌陷。 SEM观察,PPC/PBS复合生物膜多孔面随时间延长表面出现微孔结构并数量增多,而光滑面基本未形成微孔样结构。软X线检测,各组兔骨缺损区再生骨组织灰度值均随时间延长而升高,12周时PPC/PBS/Co复合生物膜组兔骨缺损区再生骨组织灰度值明显高于其他各组(P<0.05)。共聚焦显微镜观察,4、8 和 12 周时 PPC/PBS/Co 复合生物膜组兔骨缺损区再生骨组织荧光强度与空白对照组相近;与PPC/PBS复合生物膜组和BME-10X胶原膜组比较,4周时PPC/PBS/Co复合生物膜组兔骨缺损区再生骨组织荧光强度升高(P<0.05),8和12 周时PPC/PBS/Co复合生物膜组兔骨缺损区再生骨组织荧光强度降低(P<0.05)。HE染色和改良Gomori染色,与PPC/PBS复合生物膜组和BME-10X胶原膜组比较,2和4周时PPC/PBS/Co复合生物膜组和空白对照组兔骨缺损区形成新骨的速度较快,在12周时骨缺损区形成的层板状骨矿化程度较高。免疫组织化学染色,2和4周时,与空白对照组、PPC/PBS复合生物膜组和BME-10X胶原膜组比较,PPC/PBS/Co复合生物膜组兔骨缺损区再生骨组织中BMP-2 和 OPN 蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05 或 P<0.01); 与空白对照组和PPC/PBS复合生物膜组比较, BME-10X 胶原膜组兔骨缺损区再生骨组织中 BMP-2 和 OPN 蛋白表达水平均降低(P<0.05 或 P<0.01)。 结论 PPC/PBS 复合生物膜具有较好的空间支撑能力,物理屏障功能可靠,且PPC/PBS/Co复合生物膜具有良好的体内促成骨作用。
中图分类号:
- R783.1