吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 1055-1061.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240420
拔牙矫治对成年骨性Ⅱ类高角错𬌗患者上气道及周围组织的影响
- 1.吉林大学口腔医院正畸科,吉林 长春 130021
2.海军军医大学附属第一医院口腔科,上海 200433
Effect of extraction orthodontic treatment on upper airway and surrounding tissue in adult patients with skeletal class Ⅱhigh angle malocclusion
Yu CHEN1,2,Huan JIANG1,Min HU1( )
)
- 1.Department of Orthodontics,Stomatology Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
2.Department of Stomatology,First Affiliated Hospital,Naval Medical University,Shanghai 200433,China
摘要:
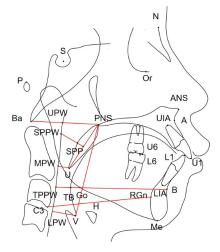
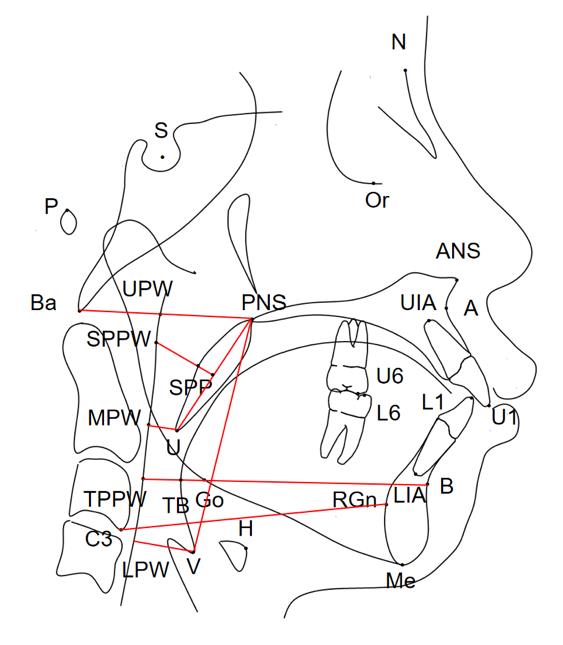
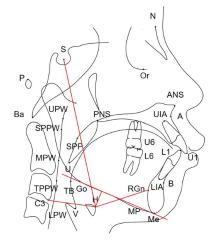
目的 通过对比骨性Ⅱ类高角错𬌗成年患者拔牙和不拔牙矫治前后上气道形态、舌骨位置和颅颌面结构的变化,分析拔牙矫治对该类患者上气道形态结构的影响,为其临床治疗方案的选择提供理论依据。 方法 收集就诊于吉林大学口腔医院正畸科已完成正畸治疗的骨性Ⅱ类高角错𬌗成年患者 60例,根据是否进行减数矫治分为拔牙组和非拔牙组,每组30例,对2组患者的临床资料进行回顾性分析。获取患者治疗前后的头颅定位侧位片,应用Dolphin软件对患者上气道形态、舌骨位置和颅颌面组织结构进行定点描绘和测量,采用SPSS 23.0统计软件对相关测量数据进行统计学分析。 结果 与矫治前比较,矫治后拔牙组患者悬雍垂尖与中咽壁点的距离(U-MPW)、会厌谷点与下咽壁点的距离(V-LPW)、上中切牙长轴与前颅底平面的下内交角(U1-SN)和下中切牙长轴与下颌平面的上内交角(L1-MP)明显减小(P<0.05),𬌗平面与前颅底平面的夹角(OP-SN)和上下中切牙长轴之间的夹角(U1-L1)明显增大,(P<0.05),其余测量指标差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);与矫治前比较,矫治后非拔牙组患者矫治后上牙槽座点-鼻根点-下牙槽座点角(ANB)明显减小(P<0.05),OP-SN和L1-MP明显增大(P<0.05),其余测量指标差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 结论 成年骨性Ⅱ类高角错𬌗患者在拔牙矫治后上气道矢状径变窄,主要发生在上气道口咽段和喉咽段,而舌骨位置未发生明显改变。
中图分类号:
- R783.5

 颅-舌骨的平面投影关系[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志, 2021, 39(3): 282-285.
颅-舌骨的平面投影关系[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志, 2021, 39(3): 282-285. 畸形患者正畸掩饰性治疗后上气道形态和舌骨位置的变化[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2022,57(6): 816-821.
畸形患者正畸掩饰性治疗后上气道形态和舌骨位置的变化[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2022,57(6): 816-821. 畸形儿童上气道矢状径主要影响因素分析
畸形儿童上气道矢状径主要影响因素分析