吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 749-756.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250319
• 临床研究 • 上一篇
子宫颈癌患者MSX1基因甲基化与临床病理特征及预后的关联性分析
- 武汉科技大学附属普仁医院妇产科,湖北 武汉 430080
Analysis on relationship between methylation of MSX1 gene and clinical pathological features and prognosis of patients with cervical cancer
Xialing HUANG,Dandan ZHANG,Xuemei ZHANG( )
)
- Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,Affiliated Puren Hospital,Wuhan University of Science and Technology,Wuhan 430080,China
摘要:
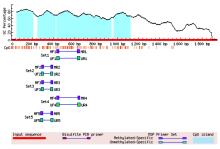
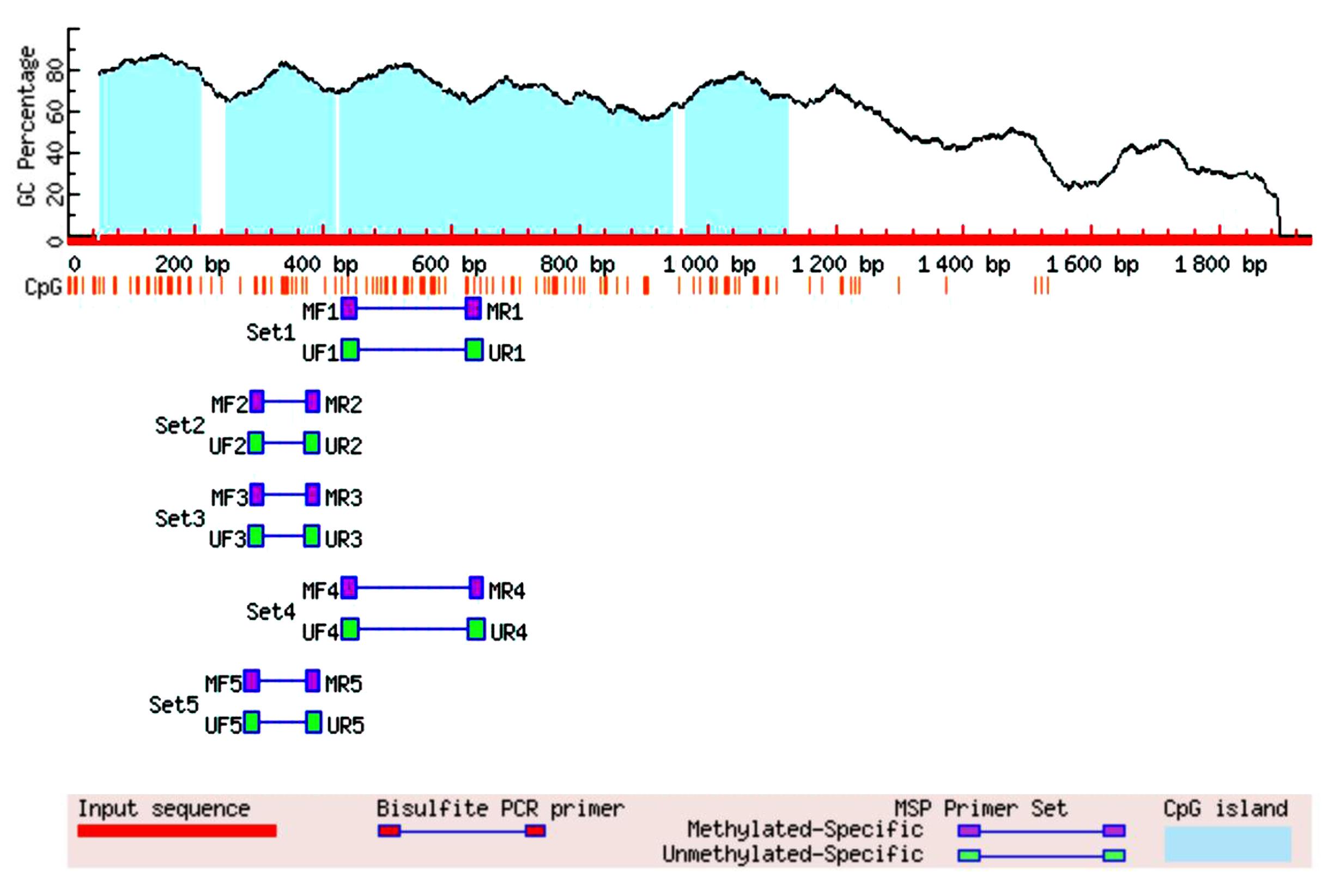
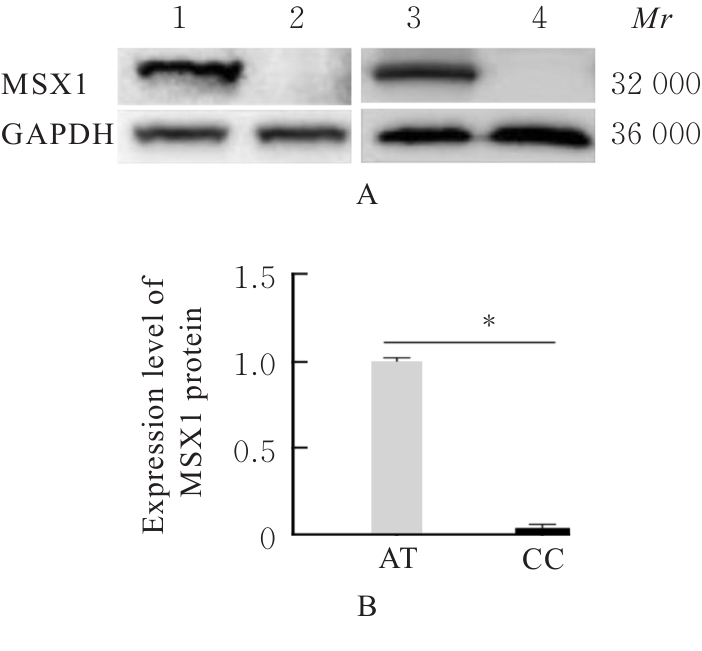
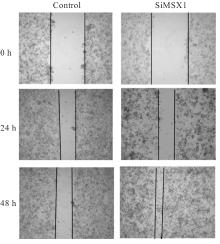
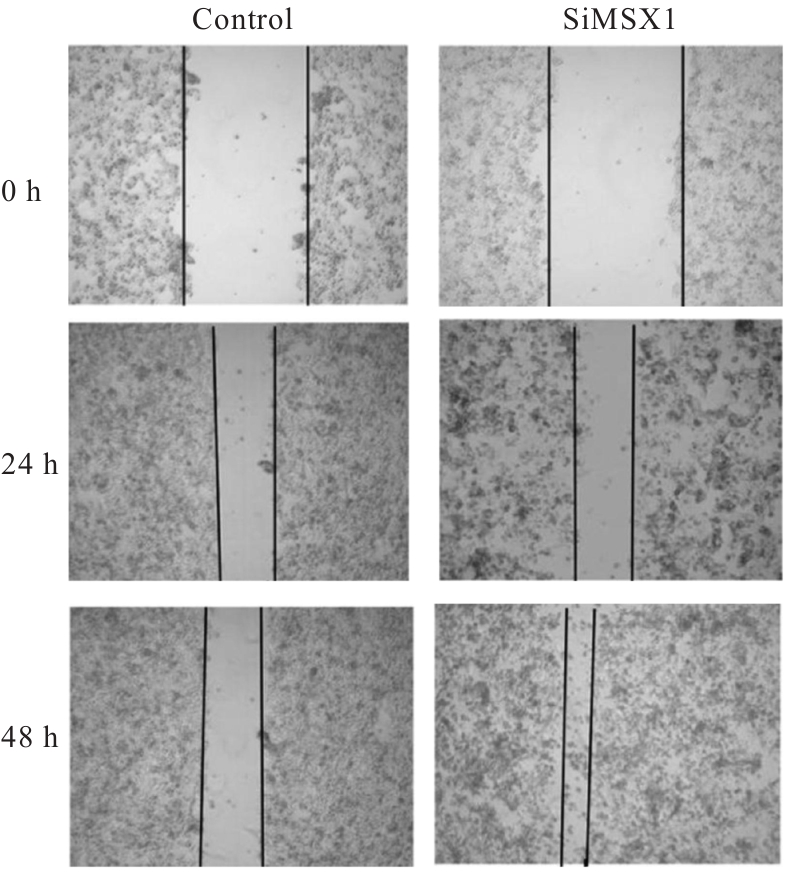
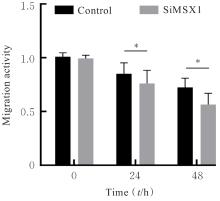
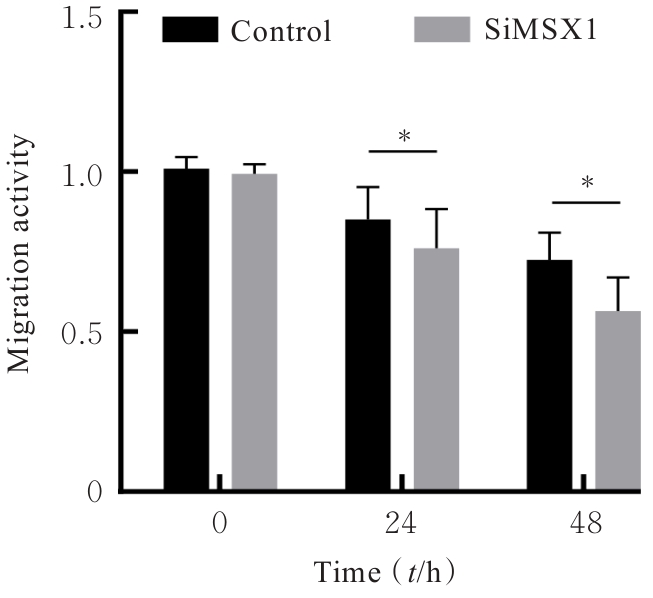
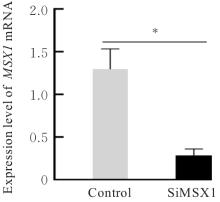
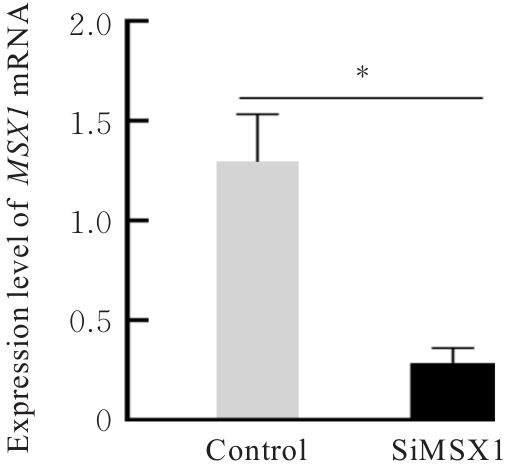
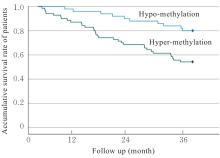
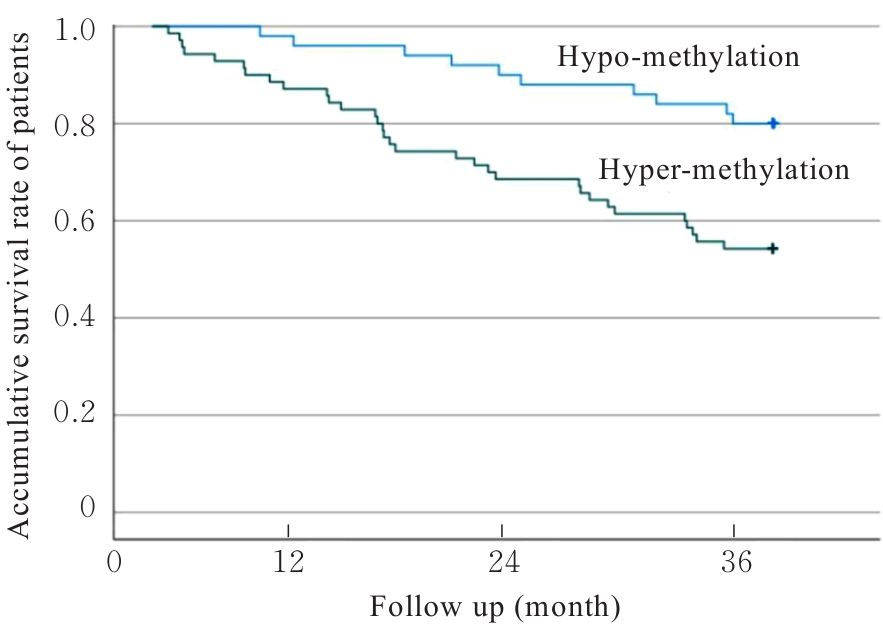
目的 探讨Msh同源框1(MSX1)基因甲基化与子宫颈癌(CC)患者临床病理特征及预后的关系,分析MSX1基因甲基化在CC诊治过程的应用前景。 方法 收集2019年1月—2020年6月期间行CC手术120例患者的临床资料和癌组织及癌旁正常组织,并对全部CC患者进行为期3年的随访。采用甲基化特异性PCR(MSP)法检测CC患者癌组织中MSX1基因甲基化状态,分为MSX1基因低甲基化组(n=50)和MSX1基因高甲基化组(n=70),MSP法检测CC患者癌组织中MSX1基因甲基化水平,分析MSX1基因甲基化状态与CC患者临床病理特征和预后的关系,Western blotting法检测CC患者癌组织和癌旁正常组织中MSX1蛋白表达水平。设计靶向MSX1 mRNA的小干扰RNA(siRNA),将CC细胞分为对照组(转染空白载体)和siMSX1组(转染MSX1 siRNA),采用实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法验证细胞转染效率,细胞划痕实验检测2组CC细胞迁移活性,Logistic回归分析CC患者预后的影响因素。 结果 CC患者癌组织中甲基化发生率为58.33%,明显高于癌旁正常组织甲基化发生率(11.67%,χ2=42.725,P<0.01)。CC患者癌组织中MSX1基因高甲基化状态与患者高危型人类乳头状瘤病毒(HR-HPV)DNA、淋巴结转移和TNM分期有关联(P<0.05),与患者年龄、病理类型和肿瘤大小无关联(P>0.05)。Western blotting法,与癌旁正常组织比较,CC患者癌组织中MSX1蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.01)。细胞划痕实验,与对照组比较,siMSX1组细胞MSX1 mRNA表达水平明显降低(P<0.01),提示MSX1基因成功敲除;与对照组比较,siMSX1组细胞迁移活性明显升高(P<0.01)。MSX1基因甲基化者3年累积生存率为54.29%,明显低于MSX1基因未甲基化者(80.00%,χ2=9.717,P=0.002)。Logistic回归分析,阳性HR-HPV DNA、淋巴结转移、TNM分期Ⅲ-Ⅳ期和MSX1基因高甲基化是CC预后的独立危险因素(P<0.05)。 结论 MSX1基因甲基化与CC患者较差的临床病理特征及不良预后具有一定关联性,提示其可作为宫颈癌潜在生物标志物。
中图分类号:
- R737.33