| 1 |
XIA C F, DONG X S, LI H, et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinants[J]. Chin Med J, 2022, 135(5): 584-590.
|
| 2 |
李 林, 杨双宁, 秦国慧, 等. 基于UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS的PD-1抑制剂治疗的晚期肺腺癌患者血清代谢组学研究[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2022, 57(5): 631-634.
|
| 3 |
CHEN Z, FILLMORE C M, HAMMERMAN P S,et al.Non-small-cell lung cancers: a heterogeneous set of diseases[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2014, 14(8): 535-546.
|
| 4 |
SIEGEL R L, MILLER K D, JEMAL A. Cancer statistics, 2018[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(1): 7-30.
|
| 5 |
BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2018,68(6):394-424.
|
| 6 |
BAO Y L, WANG L, SHI L, et al. Transcriptome profiling revealed multiple genes and ECM-receptor interaction pathways that may be associated with breast cancer[J]. Cell Mol Biol Lett, 2019, 24: 38.
|
| 7 |
ANDERSEN M K, RISE K, GISKEØDEGÅRD G F, et al. Integrative metabolic and transcriptomic profiling of prostate cancer tissue containing reactive stroma[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 14269.
|
| 8 |
YAN P, HE Y C, XIE K X, et al. In silico analyses for potential key genes associated with gastric cancer[J]. Peer J, 2018, 6: e6092.
|
| 9 |
RAHBARI N N, KEDRIN D, INCIO J,et al.Anti-VEGF therapy induces ECM remodeling and mechanical barriers to therapy in colorectal cancer liver metastases[J].Sci Transl Med,2016,8(360): 360ra135.
|
| 10 |
LIANG J H, LI H X, HAN J Y, et al. Mex3a interacts with LAMA2 to promote lung adenocarcinoma metastasis via PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(8): 614.
|
| 11 |
GU S J, QIAN L, ZHANG Y L, et al. Significance of intratumoral infiltration of B cells in cancer immunotherapy: from a single cell perspective[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2021, 1876(2): 188632.
|
| 12 |
XIONG S M, DONG L L, CHENG L. Neutrophils in cancer carcinogenesis and metastasis[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2021, 14(1): 173.
|
| 13 |
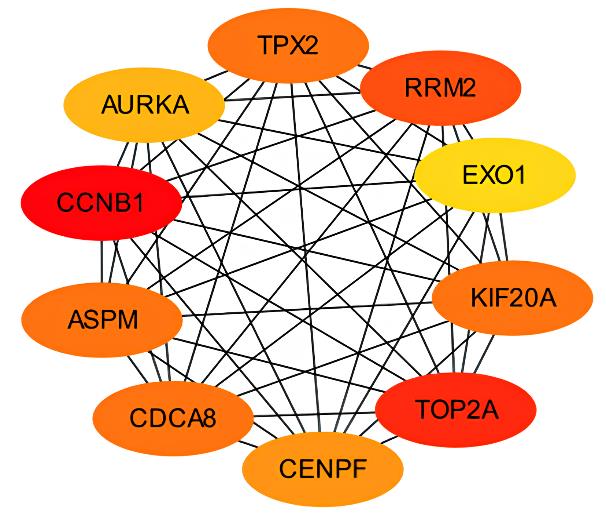
YU B W, CHEN L, ZHANG W N, et al. TOP2A and CENPF are synergistic master regulators activated in cervical cancer[J].BMC Med Genomics,2020,13(1):145.
|
| 14 |
GAO S Y, GANG J, YU M, et al. Computational analysis for identification of early diagnostic biomarkers and prognostic biomarkers of liver cancer based on GEO and TCGA databases and studies on pathways and biological functions affecting the survival time of liver cancer[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21(1): 791.
|
| 15 |
CUI Y J, PU R, YE J J, et al. LncRNA FAM230B promotes gastric cancer growth and metastasis by regulating the miR-27a-5p/TOP2A axis[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2021, 66(8): 2637-2650.
|
| 16 |
PEI Y F, YIN X M, LIU X Q. TOP2A induces malignant character of pancreatic cancer through activating β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2018, 1864(1): 197-207.
|
| 17 |
WANG K, CHEN R, FENG Z, et al. Identification of differentially expressed genes in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Aging, 2019, 11(23): 11170-11185.
|
| 18 |
BAO B, YU X J, ZHENG W J. miR-139-5p targeting CCNB1 modulates proliferation, migration, invasion and cell cycle in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Mol Biotechnol, 2022, 64(8): 852-860.
|
| 19 |
ZHU H Y, ZHENG C N, LIU H T, et al. Significance of macrophage infiltration in the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma patients evaluated by scRNA and bulkRNA analysis[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 1028440.
|
| 20 |
WANG B J, LI X, ZHAO G N, et al. miR-203 inhibits ovarian tumor metastasis by targeting BIRC5 and attenuating the TGFβ pathway[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 37(1): 235.
|
| 21 |
WANG D C, LIU J, LIU S S, et al. Identification of crucial genes associated with immune cell infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma by weighted gene co-expression network analysis[J]. Front Genet, 2020, 11: 342.
|
| 22 |
WADSWORTH P. tpx2[J]. Curr Biol, 2015, 25(24): R1156-R1158.
|
| 23 |
ZHOU F, WANG M, AIBAIDULA M, et al. TPX2 promotes metastasis and serves as a marker of poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2020, 26: e925147.
|
| 24 |
WANG J, LIANG J H, LI H X, et al. Oncogenic role of abnormal spindle‑like microcephaly‑associated protein in lung adenocarcinoma[J].Int J Oncol,2021,58(5): 23.
|
| 25 |
DENG T T, LIU Y, ZHUANG J L, et al. ASPM is a prognostic biomarker and correlates with immune infiltration in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma and liver hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 632042.
|
| 26 |
DAI C, MIAO C X, XU X M, et al. Transcriptional activation of human CDCA8 gene regulated by transcription factor NF-Y in embryonic stem cells and cancer cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2015, 290(37): 22423-22434.
|
| 27 |
HU C X, WU J X, WANG L, et al. miR-133b inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma by targeting CDCA8[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2021, 223: 153459.
|
| 28 |
万志杰, 王 航, 杜志鹏, 等. 基于TCGA数据库的肺癌和结直肠癌放疗后差异基因筛选、功能及通路研究[J].同济大学学报(医学版),2022,43(4):467-473.
|
| 29 |
DU R J, HUANG C T, LIU K D, et al. Targeting AURKA in Cancer: molecular mechanisms and opportunities for Cancer therapy[J]. Mol Cancer, 2021, 20(1): 15.
|
| 30 |
JIN Z, TAO S, ZHANG C, et al. KIF20A promotes the development of fibrosarcoma via PI3K-Akt signaling pathway[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2022, 420(1): 113322.
|
| 31 |
ZHAO X, ZHOU L L, LI X Y, et al. Overexpression of KIF20A confers malignant phenotype of lung adenocarcinoma by promoting cell proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis[J]. Cancer Med, 2018, 7(9): 4678-4689.
|
| 32 |
YANG C L, YANG Y, WANG W,et al.CEP55 3'-UTR promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and enhances tumorigenicity of bladder cancer cells by acting as a ceRNA regulating miR-497-5p[J]. Cell Oncol, 2022, 45(6): 1217-1236.
|
| 33 |
FU L H, LI Z P, WU Y L, et al. Hsa-miR-195-5p inhibits autophagy and gemcitabine resistance of lung adenocarcinoma cells via E2F7/CEP55[J]. Biochem Genet, 2023, 61(4): 1528-1547.
|
| 34 |
CHEN H J, WU F B, XU H J, et al. Centromere protein F promotes progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through ERK and cell cycle-associated pathways[J]. Cancer Gene Ther, 2022, 29(7): 1033-1042.
|
| 35 |
SUN J B, HUANG J Z, LAN J, et al. Overexpression of CENPF correlates with poor prognosis and tumor bone metastasis in breast cancer[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2019, 19: 264.
|
| 36 |
TANG H X, BAI Y Q, XIONG L C, et al. Knockdown of CENPF inhibits the progression of lung adenocarcinoma mediated by ERβ2/5 pathway[J]. Aging, 2021, 13(2): 2604-2625.
|
 ),Lin YE(
),Lin YE( )
)