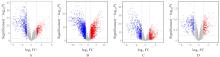
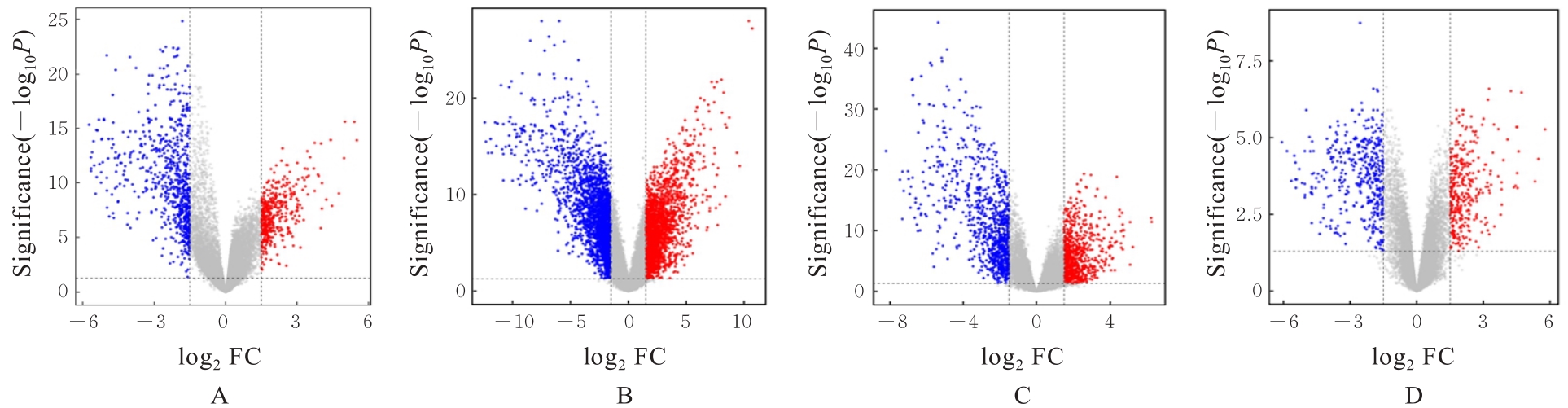
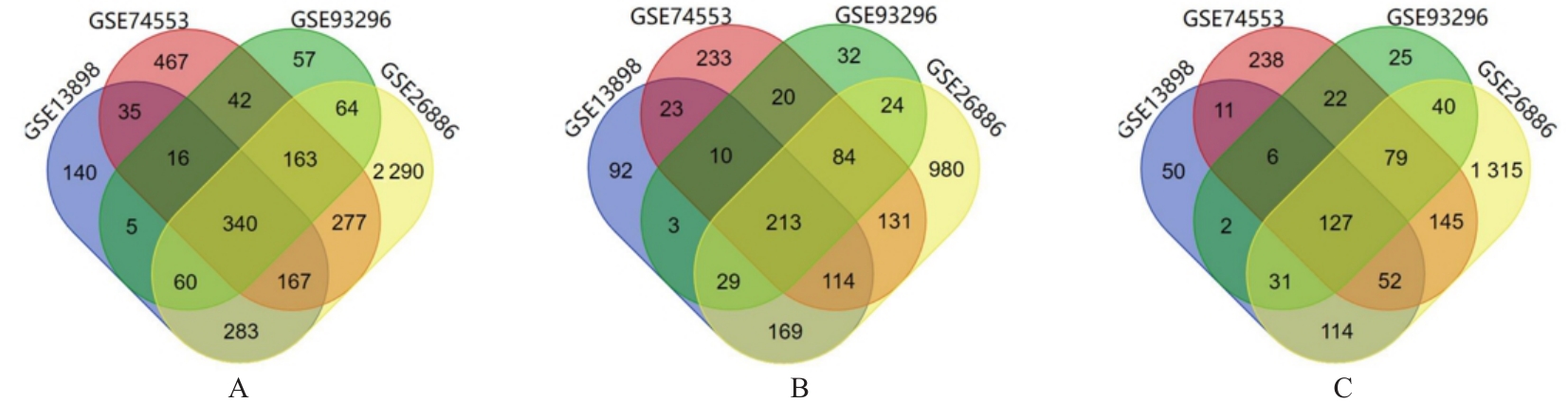
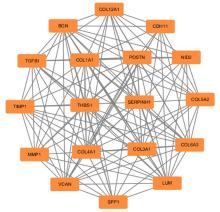
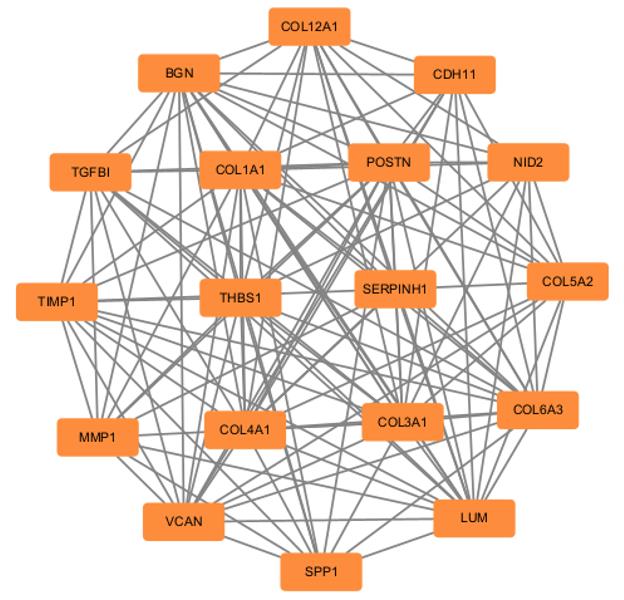
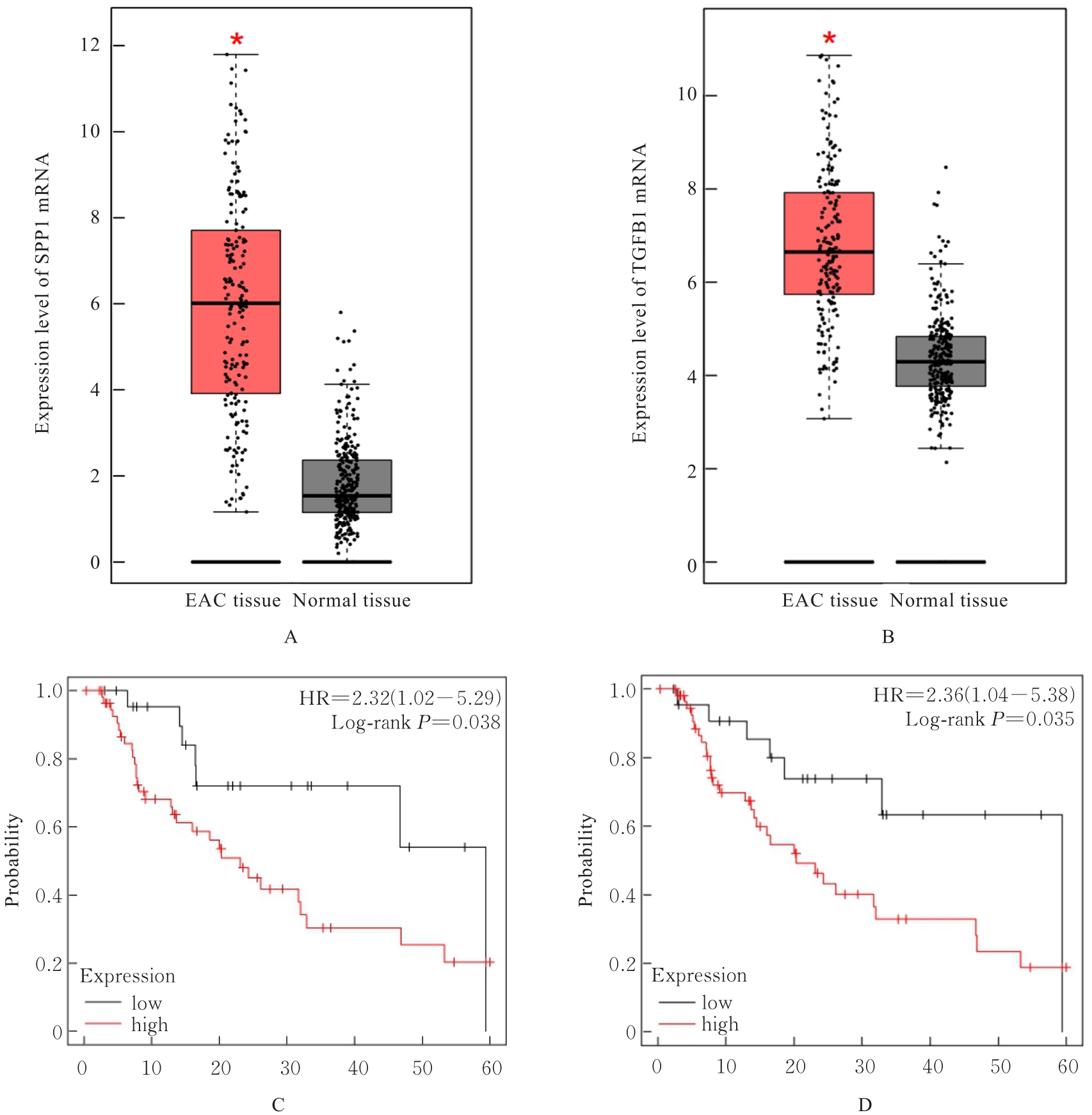
| 1 |
COLEMAN H G, XIE S H, LAGERGREN J. The epidemiology of esophageal adenocarcinoma[J]. Gastroenterology, 2018, 154(2): 390-405.
|
| 2 |
POLEBOYINA P K, ALAGUMUTHU M, PASHA A, et al. Entrectinib a plausible inhibitor for osteopontin (SPP1) in cervical cancer-integrated bioinformatic approach[J]. Appl Biochem Biotechnol, 2023, 195(12): 7766-7795.
|
| 3 |
ZHAO K D, MA Z, ZHANG W. Comprehensive analysis to identify SPP1 as a prognostic biomarker in cervical cancer[J]. Front Genet, 2022, 12: 732822.
|
| 4 |
XIE W, CHENG J, HONG Z J, et al. Multi-transcriptomic analysis reveals the heterogeneity and tumor-promoting role of SPP1/CD44-mediated intratumoral crosstalk in gastric cancer[J]. Cancers, 2022, 15(1): 164.
|
| 5 |
STREEL G D, LUCAS S. Targeting immunosuppression by TGF-β1 for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2021, 192: 114697.
|
| 6 |
SOUKUPOVA J, MALFETTONE A, BERTRAN E, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) induced by TGF-β in hepatocellular carcinoma cells reprograms lipid metabolism[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(11): 5543.
|
| 7 |
MOREAU J M, VELEGRAKI M, BOLYARD C, et al. Transforming growth factor-β1 in regulatory T cell biology[J]. Sci Immunol, 2022, 7(69): eabi4613.
|
| 8 |
田 东, 付茂勇, 赵泽良, 等. 食管腺癌临床病理特征及影响预后的因素[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2013, 21(8): 1748-1753.
|
| 9 |
RUSTGI A K, EL-SERAG H B. Esophageal carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2014, 371(26): 2499-2509.
|
| 10 |
RUBENSTEIN J H, TAYLOR J B. Meta-analysis: the association of oesophageal adenocarcinoma with symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2010, 32(10): 1222-1227.
|
| 11 |
SNIDER E J, FREEDBERG D E, ABRAMS J A. Potential role of the microbiome in barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2016, 61(8): 2217-2225.
|
| 12 |
KHALAFI S, LOCKHART A C, LIVINGSTONE A S, et al. Targeted molecular therapies in the treatment of esophageal adenocarcinoma, are we there yet?[J]. Cancers, 2020, 12(11): 3077.
|
| 13 |
ZHANG X, WANG Y X, MENG L H. Comparative genomic analysis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma: new opportunities towards molecularly targeted therapy[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2022, 12(3): 1054-1067.
|
| 14 |
FATEHI HASSANABAD A, CHEHADE R, BREADNER D, et al. Esophageal carcinoma: towards targeted therapies[J]. Cell Oncol, 2020, 43(2): 195-209.
|
| 15 |
刘 迁, 祁国萍, 于华裔, 等. 结肠癌核心基因和独立预后因子筛选的生物信息学分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2022, 48(3): 755-765.
|
| 16 |
MESSEX J K, BYRD C J, THOMAS M U, et al. Macrophages cytokine Spp1 increases growth of prostate intraepithelial neoplasia to promote prostate tumor progression[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(8): 4247.
|
| 17 |
GÖTHLIN EREMO A, LAGERGREN K, OTHMAN L, et al. Evaluation of SPP1/osteopontin expression as predictor of recurrence in tamoxifen treated breast cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 1451.
|
| 18 |
ZHANG W G, FAN J L, CHEN Q, et al. SPP1 and AGER as potential prognostic biomarkers for lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Oncol Lett, 2018, 15(5): 7028-7036.
|
| 19 |
PERIYASAMY A, GOPISETTY G, SUBRAMANIUM M J, et al. Identification and validation of differential plasma proteins levels in epithelial ovarian cancer[J]. J Proteomics, 2020, 226: 103893.
|
| 20 |
ZENG B, ZHOU M, WU H, et al. SPP1 promotes ovarian cancer progression via Integrin β1/FAK/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2018, 11: 1333-1343.
|
| 21 |
LIU L L, ZHANG R Y, DENG J W, et al. Construction of TME and Identification of crosstalk between malignant cells and macrophages by SPP1 in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2022, 71(1): 121-136.
|
| 22 |
PANG X C, ZHANG J L, HE X, et al. SPP1 promotes enzalutamide resistance and epithelial-mesenchymal-transition activation in castration-resistant prostate cancer via PI3K/AKT and ERK1/2 pathways[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021, 2021: 5806602.
|
| 23 |
RABJERG M, BJERREGAARD H, HALEKOH U, et al. Molecular characterization of clear cell renal cell carcinoma identifies CSNK2A1, SPP1 and DEFB1 as promising novel prognostic markers[J]. APMIS, 2016, 124(5): 372-383.
|
| 24 |
CHEN J W, HOU C X, ZHENG Z T, et al. Identification of secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1) as a prognostic factor in lower-grade gliomas[J]. World Neurosurg, 2019, 130: e775-e785.
|
| 25 |
BIE T W, ZHANG X W. Higher expression of SPP1 predicts poorer survival outcomes in head and neck cancer[J]. J Immunol Res, 2021, 2021: 8569575.
|
| 26 |
LIU Y H, ZHANG L, JU X Y, et al. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis reveals macrophage-tumor crosstalk in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 955390.
|
| 27 |
GAO W, LIU D L, SUN H Y, et al. SPP1 isa prognostic related biomarker and correlated with tumor-infiltrating immune cells in ovarian cancer[J]. BMC Cancer, 2022, 22(1): 1367.
|
| 28 |
GUASCH G, SCHOBER M, PASOLLI H A, et al. Loss of TGFbeta signaling destabilizes homeostasis and promotes squamous cell carcinomas in stratified epithelia[J]. Cancer Cell, 2007, 12(4): 313-327.
|
| 29 |
SYED V. TGF-β signaling in cancer[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2016, 117(6): 1279-1287.
|
| 30 |
IVANOV S V, IVANOVA A V, SALNIKOW K, et al. Two novel VHL targets, TGFBI (BIGH3) and its transactivator KLF10, are up-regulated in renal clear cell carcinoma and other tumors[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2008, 370(4): 536-540.
|
| 31 |
SHANG D H, LIU Y T, YANG P Q, et al. TGFBI-promoted adhesion, migration and invasion of human renal cell carcinoma depends on inactivation of von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor[J]. Urology, 2012, 79(4): 966.e1-966.e7.
|
| 32 |
FICO F, SANTAMARIA-MARTÍNEZ A. TGFBI modulates tumour hypoxia and promotes breast cancer metastasis[J]. Mol Oncol, 2020, 14(12): 3198-3210.
|
| 33 |
HAN B, CAI H L, CHEN Y, et al. The role of TGFBI (βig-H3) in gastrointestinal tract tumorigenesis[J]. Mol Cancer, 2015, 14: 64.
|
| 34 |
WEN G Y, PARTRIDGE M A, LI B Y, et al. TGFBI expression reduces in vitro and in vivo metastatic potential of lung and breast tumor cells[J]. Cancer Lett, 2011, 308(1): 23-32.
|