吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2): 360-368.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230212
鼠尾草酸对慢性不可预见性轻度应激诱导的抑郁大鼠的抗抑郁作用及其SIRT1/ERS调控机制
- 1.江苏护理职业学院药学与中药学院药理药化教研室,江苏 淮安 223001
2.江苏省 淮安市 第五人民医院肿瘤科,江苏 淮安 223300
3.江苏护理职业学院药学与中药学院中药教研室,江苏 淮安 223001
Antidepressant effect of carnosic acid on chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression in rats and its SIRT1/ERS regulatory mechanism
Dongming TAN1,Hongying YIN2( ),Xiangmin DENG3,Xu DING1
),Xiangmin DENG3,Xu DING1
- 1.Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacochemistry,College of Pharmacy and Traditional Chinese Medicine,Jiangsu College of Nursing,Huai’an 223001,China
2.Department of Oncology,Fifth People’s Hospital,Huai’an City,Jiangsu Province,Huai’an 223300,China
3.Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine,College of Pharmacy and Traditional Chinese Medicine,Jiangsu College of Nursing,Huai’an 223001,China
摘要:
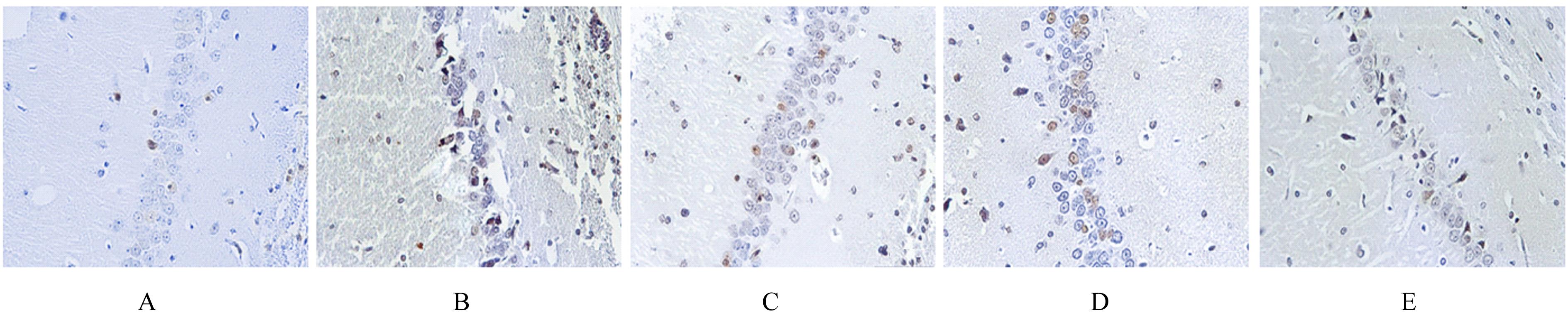
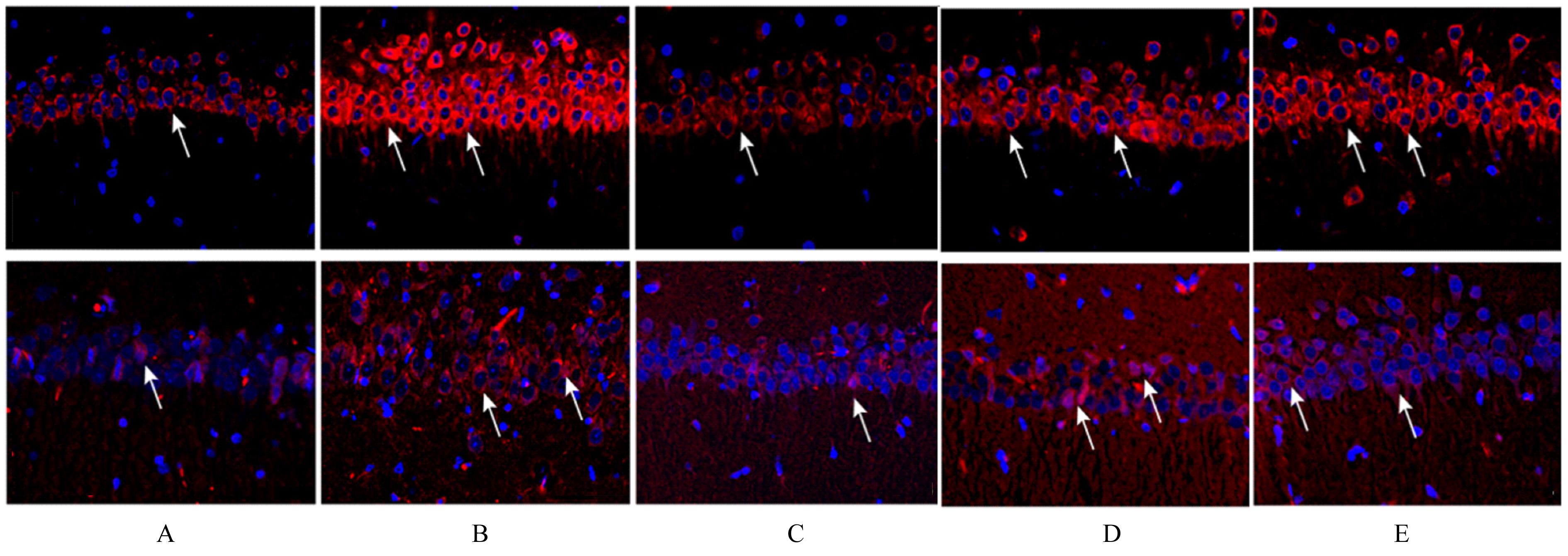
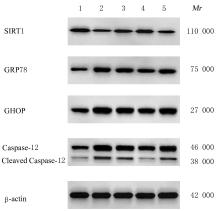
目的 探讨鼠尾草酸(CA)对慢性不可预见性轻度应激(CUMS)诱导的抑郁大鼠内质网应激(ERS)的影响,并阐明其抗抑郁机制。 方法 采用随机数字表法从66只SD大鼠中随机选取12只为对照组,剩余54只大鼠采用CUMS联合孤养诱导建立抑郁模型,取48只建模成功的大鼠随机分为模型组、氟西汀(3.17 mg·kg-1)组、CA(40 mg·kg-1)组和CA(40 mg·kg-1)+EX527沉默信息调节因子1(SIRT1)抑制剂(5 mg·kg-1)组,每组12只。给予相应的药物干预后,旷场实验(OFT)检测大鼠运动总距离和中间停留时间;强迫游泳实验(FST)检测大鼠强迫游泳时的不动时间;糖水偏好实验(SPT)检测大鼠糖水偏好度;TUNEL法检测各组大鼠海马组织中TUNEL阳性细胞百分率;免疫荧光法检测各组大鼠海马组织中C/EBP同源蛋白(CHOP)和葡萄糖调节蛋白78(GRP78)阳性表达强度;实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测各组大鼠海马组织中SIRT1、GRP78、CHOP和Caspase-12 mRNA表达水平;Western blotting法检测各组大鼠大脑海马组织CA1区中SIRT1、GRP78、CHOP、Caspase-12和裂解的Caspase-12(cleaved Caspase-12)蛋白表达。 结果 与对照组比较,模型组大鼠OFT中的总距离、中间停留时间、糖水偏好百分率及海马组织CA1区中SIRT1 mRNA和蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05);强迫游泳时的不动时间,TUNEL阳性细胞百分率,GRP78、CHOP、Caspase-12和cleaved Caspase-12蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05)。与模型组比较,氟西汀组和CA组大鼠OFT中的运动总距离、中间停留时间、糖水偏好度及海马组织CA1区中SIRT1 mRNA和蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05),强迫游泳时的不动时间,TUNEL阳性细胞百分率,GRP78、CHOP、Caspase-12和cleaved Caspase-12蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05);与CA组比较,CA+EX527组大鼠OFT中的总距离,中间停留时间,糖水偏好度,大脑海马组织CA1区中SIRT1 mRNA和蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05);强迫游泳时的不动时间,TUNEL阳性细胞百分率,GRP78、CHOP、Caspase-12和cleaved Caspase-12蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05)。 结论 CA可减轻CUMS引起的大鼠抑郁样行为,其抗抑郁机制可能与SIRT1介导的ERS抑制有关。
中图分类号:
- R966