吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2): 369-376.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230213
鹿茸多肽预处理通过miR-133a调控TGF-β/Smad信号通路对TBHP诱导心肌H9c2细胞损伤的保护作用
周高峰1,肖静1,2,周佳1,刘俊秀1,律广富3,王雨辰1,林贺1( ),黄晓巍1(
),黄晓巍1( )
)
- 1.长春中医药大学药学院临床药学与中药药理教研室,吉林 长春 130117
2.中国医学科学院药用植物研究所,北京 100094
3.长春中医药大学 吉林省人参研究科学院中药药理组,吉林 长春 130117
Protective effect of Velvet antler polypeptide pretreatment on myocardial H9c2 cell injury induced by TBHP through regulating TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway with miR-133a
Gaofeng ZHOU1,Jing XIAO1,2,Jia ZHOU1,Junxiu LIU1,Guangfu LYU3,Yuchen WANG1,He LIN1( ),Xiaowei HUANG1(
),Xiaowei HUANG1( )
)
- 1.Department of Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology of Chinese Medicine,School of Pharmacy,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
2.Institute of Medicinal Plant Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences,Beijing 100094,China
3.Department of Pharmacology of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Jilin Ginseng Academy,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
摘要:
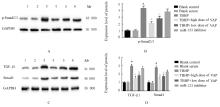
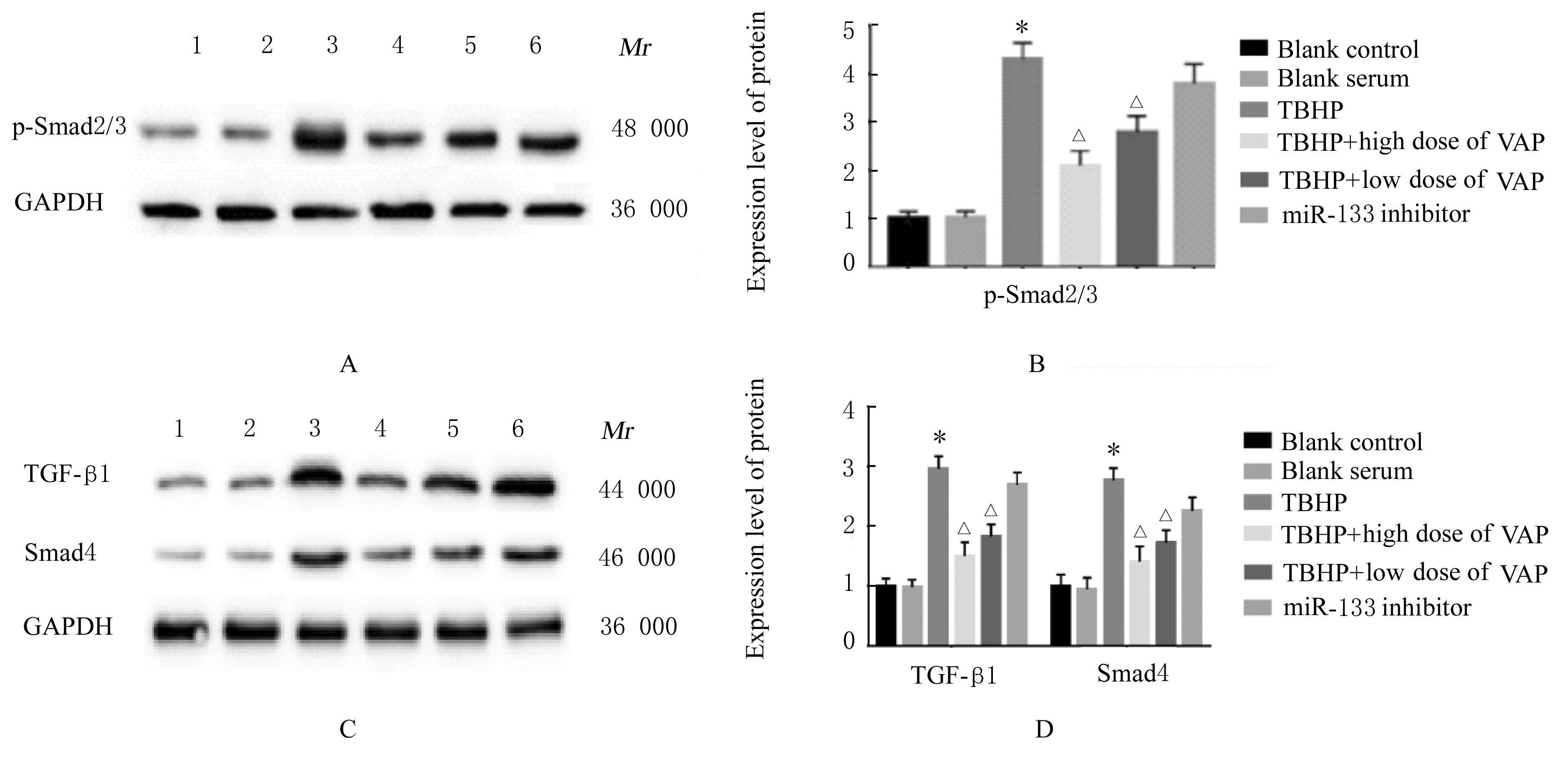
目的 探讨鹿茸多肽(VAP)预处理对叔丁基过氧化氢(TBHP)诱导大鼠心肌H9c2细胞损伤的保护作用,阐明VAP对miR-133a/转化生长因子β(TGF-β)/Smad轴的作用及其机制。 方法 将H9c2心肌细胞分为空白对照组、空白血清组、TBHP组、TBHP+低剂量(100 mg·kg-1 )VAP组、TBHP+高剂量(400 mg·kg-1)VAP组和miR-133抑制剂(miR-133 inhibitor)组。空白对照组不做任何处理,其余各组细胞经VAP处理24 h后,给予200 μmol·L-1 TBHP处理;miR-133 inhibitor 组细胞转染miR-133 inhibitor 24 h,给予400 mg·kg-1 VAP处理24 h,并给予200 μmol·L-1 TBHP处理。MTT法检测各组H9c2细胞存活率,酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法检测各组细胞培养上清液中肌钙蛋白T(cTnT)、肌钙蛋白I(cTnI)和肌酸激酶同工酶(CK-MB)水平,实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测各组H9c2细胞中miR-133表达水平,Western blotting法检测各组H9c2细胞中转化生长因子β1(TGF-β1)、磷酸化Smad2/3(p-Smad2/3)和Smad4蛋白表达水平。 结果 MTT法检测,与TBHP组比较,TBHP+低剂量VAP组和TBHP+高剂量VAP组H9c2细胞存活率升高(P<0.05),miR-133 inhibitor 组H9c2细胞存活率差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。ELISA法检测,与空白对照组比较,TBHP组H9c2细胞中cTnT、cTnI和CK-MB水平升高(P<0.05);与TBHP组比较,TBHP+低剂量VAP组和TBHP+高剂量VAP组H9c2细胞中cTnT、cTnI和CK-MB水平降低(P<0.05)。RT-qPCR法检测,与空白对照组比较,TBHP组H9c2细胞中miR-133a表达水平降低(P<0.05);与TBHP组比较,TBHP+低剂量VAP组和TBHP+高剂量VAP组H9c2细胞中miR-133a表达水平升高(P<0.05或P<0.01),miR-133 inhibitor 组H9c2细胞中 miR-133a表达水平明显降低(P<0.01)。Western blotting法检测,与空白对照组比较,TBHP组H9c2细胞中TGF-β1、p-Smad2/3和Smad4蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05);与TBHP组比较,TBHP+低剂量VAP组和TBHP+高剂量VAP组H9c2细胞中TGF-β1、p-Smad2/3和Smad4蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05)。 结论 VAP预处理通过miR-133a调控TGF-β/Smad信号通路保护TPHP诱导的大鼠心肌H9c2细胞损伤。
中图分类号:
- R285.5