吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (6): 1111-1116.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20200601
• 基础研究 • 下一篇
虎杖苷对实验性哮喘小鼠气道炎症的影响及其机制
朴玉华1,王知广1,朴艺花1,姜京植2,王重阳2,徐畅2,李良昌2,延光海2,朴红梅1( )
)
- 1.延边大学附属医院呼吸内科,吉林 延吉133002
2.延边大学医学院解剖学教研室 吉林省过敏性疾病重点实验室,吉林 延吉 133002
Effect of polydatin on airway inflammation in experimental asthmatic mice and its mechanism
Yuhua PIAO1,Zhiguang WANG1,Yihua PIAO1,Jingzhi JIANG2,Chongyang WANG2,Chang XU2,Liangchang LI2,Guanghai YAN2,Hongmei PIAO1( )
)
- 1.Department of Respiratory Medicine,Affiliated Hospital,Yanbian University,Yanji 133002,China
2.Department of Anatomy,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Yanbian University,Jilin Key Laboratory of Anaphylactic Disease,Yanbian University,Yanji 133002,China
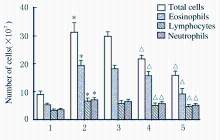
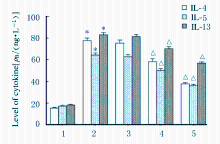
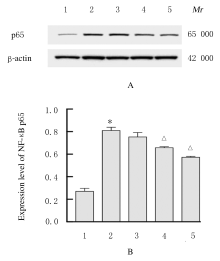
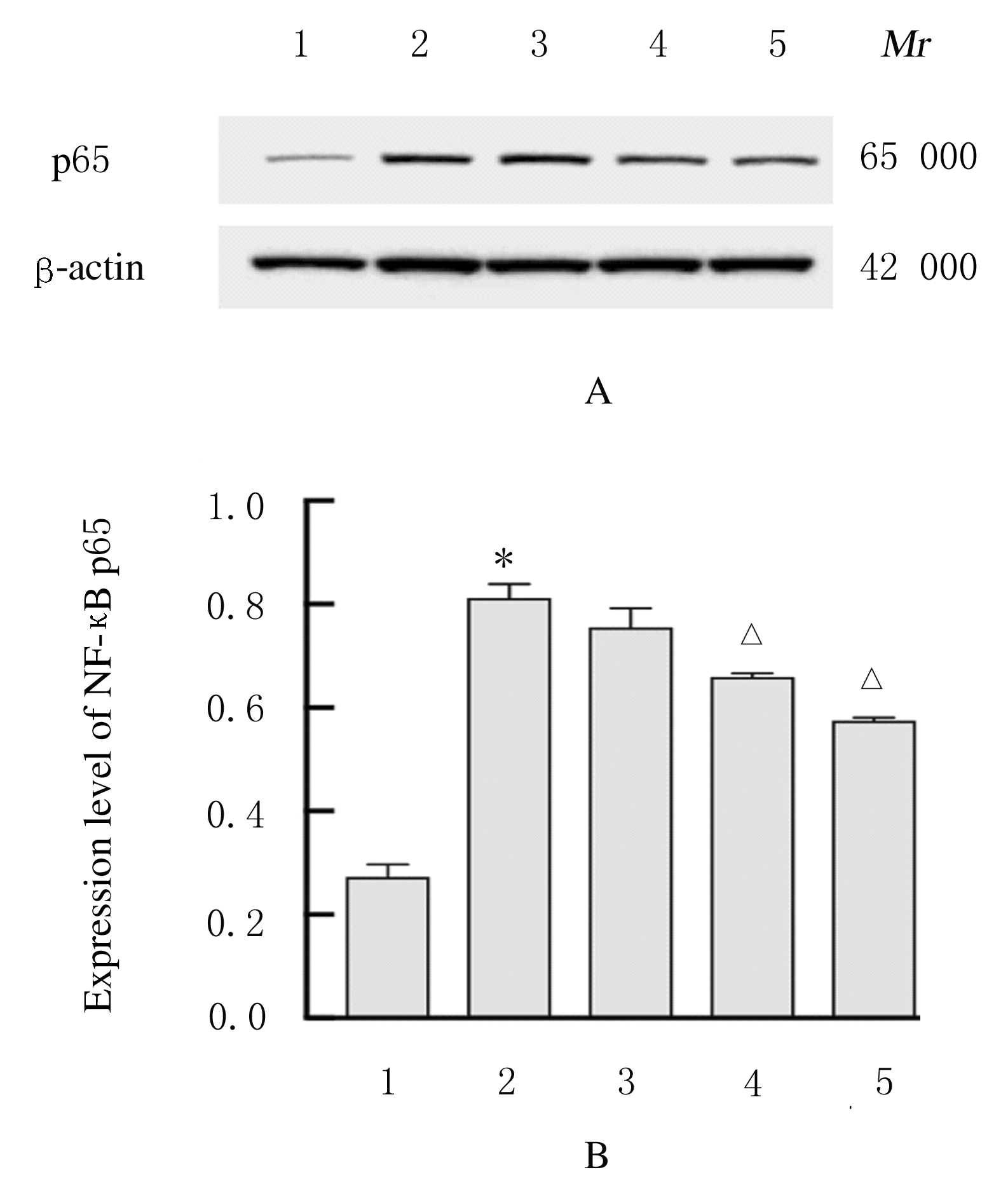
摘要: 探讨虎杖苷(PD)对卵清蛋白(OVA)诱导哮喘小鼠气道炎症的影响,阐明其可能作用机制。 将 50只雌性BALB/c 小鼠随机分成对照组, OVA组和低、中、高剂量PD组,每组10只。采用OVA致敏及激发制备实验性小鼠哮喘模型。于实验第1、7和14天采用OVA+Al ( OH)3 混合液腹腔注射致敏小鼠。从第21天起,低、中和高剂量PD组小鼠分别腹腔注射15、30和45 mg·kg-1PD治疗液,对照组和OVA组小鼠采用生理盐水代替。每次给药1 h后,OVA组和各剂量PD组小鼠连续采用3% OVA 雾化激发,对照组小鼠采用生理盐水代替。HE和PAS染色法观察各组小鼠肺组织病理形态表现,Diff-Quick法检测各组小鼠肺泡灌洗液中(BALF)细胞总数和嗜酸性粒细胞、中性粒细胞和淋巴细胞数,ELISA法检测各组小鼠支气管肺泡灌洗液(BALF)中白细胞介素4(IL-4)、白细胞介素5(IL-5)和白细胞介素13(IL-13)水平,免疫组织化学染色法观察各组小鼠肺组织中沉默信息调节因子 1 (SIRT1)及核因子κB (NF-κB) p65表达情况,Western blotting法检测各组小鼠肺组织中SIRT1和乙酰化NF-κB p65蛋白表达水平。 与对照组比较,OVA组小鼠气管壁增厚,气道周围大量炎症细胞浸润,杯状细胞明显增生;与OVA组比较,各剂量PD组小鼠上述表现改善。与对照组比较,OVA组小鼠BALF中细胞总数、嗜酸性粒细胞、中性粒细胞和淋巴细胞数明显增多(P<0.05),IL-4、IL-5和IL-13水平明显升高(P<0.05);与OVA组比较,中和高剂量PD组小鼠BALF中细胞总数、嗜酸性粒细胞、中性粒细胞和淋巴细胞减少(P<0.05),IL-4、IL-5和IL-13水平降低(P<0.05)。与对照组比较,OVA组小鼠肺组织中SIRT1和NF-κB p65及乙酰化NF-κB p65蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05);与OVA组比较,中和高剂量PD组小鼠肺组织中SIRT1乙酰化水平升高(P<0.05),NF-κB p65和乙酰化NF-κB p65蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05)。 PD能减轻哮喘小鼠气道炎症,其作用机制可能与SIRT1/NF-κB通路有关联。
中图分类号:
- R562.25