吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 621-631.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250307
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
人脂肪干细胞和人真皮成纤维细胞来源外泌体对紫外线诱导裸鼠光老化皮肤皱纹的改善作用
- 新疆医科大学第一附属医院医学整形美容中心, 新疆 乌鲁木齐 830000
Improvement effect of exosomes derived from human adipose-derived stem cells and human dermal fibroblasts on ultraviolet-induced photoaging skin wrinkles in nude mice
- Medical Plastic Surgery Center,First Affiliated Hospital,Xinjiang Medical University,Urumqi 830000,China
摘要:
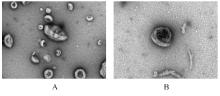
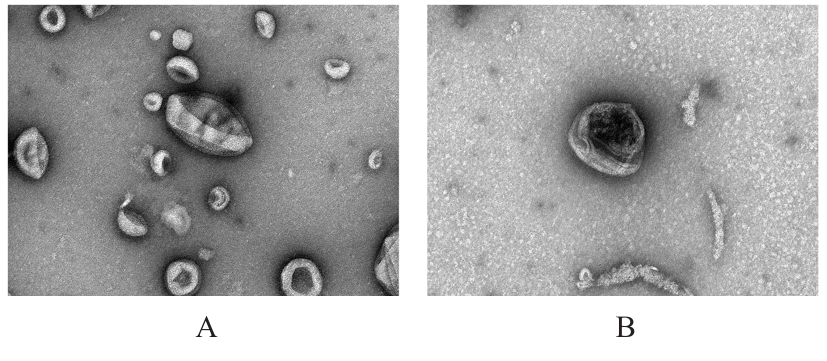
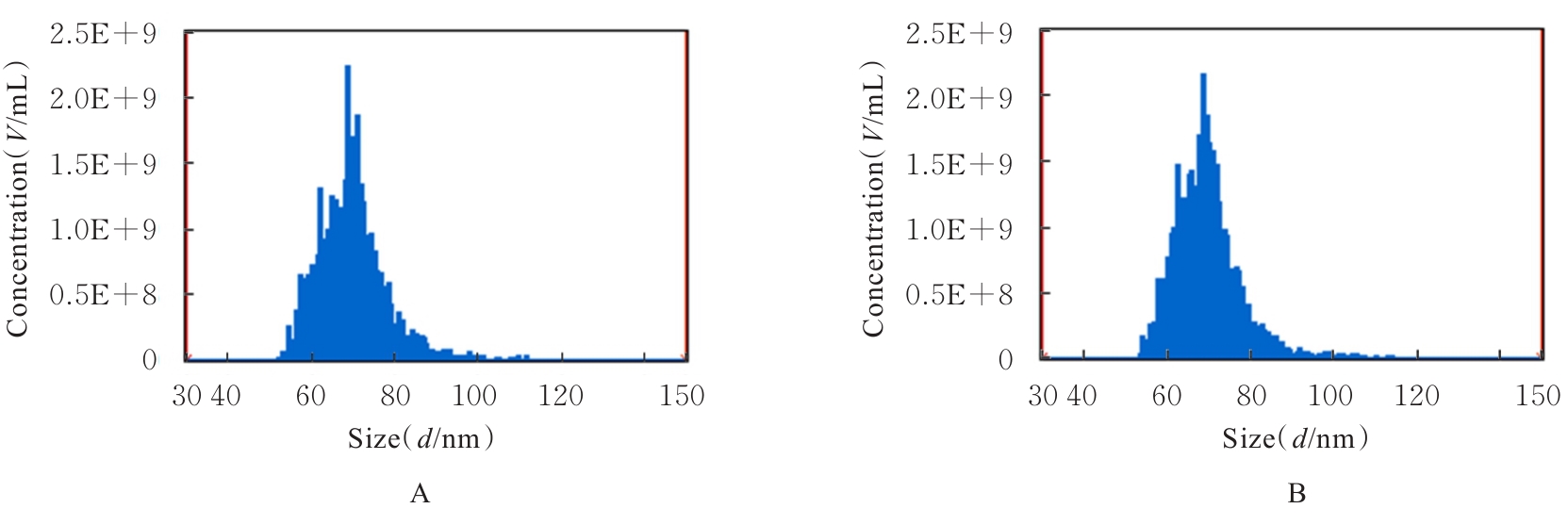
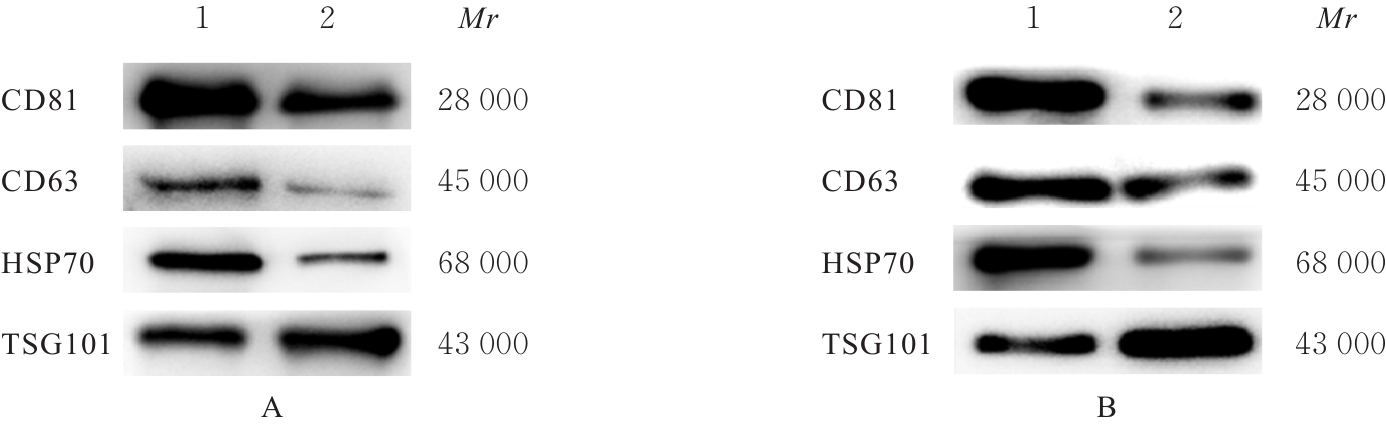
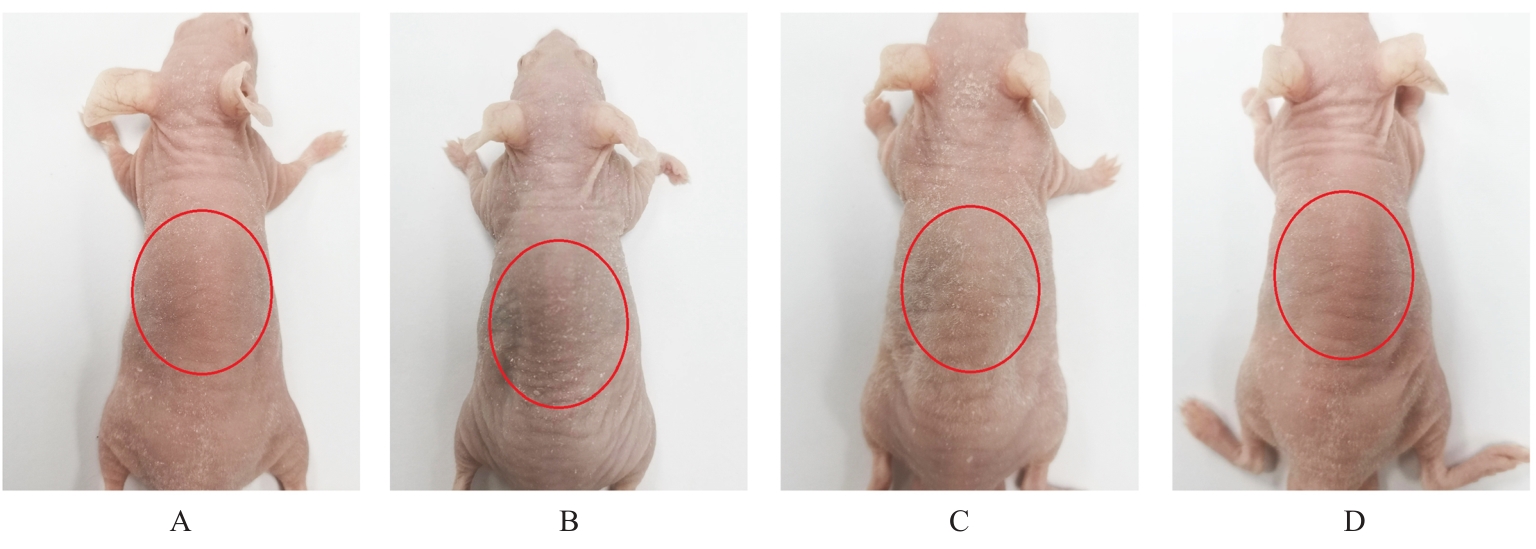
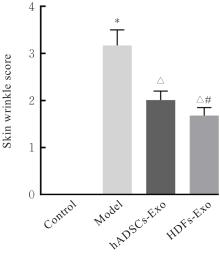
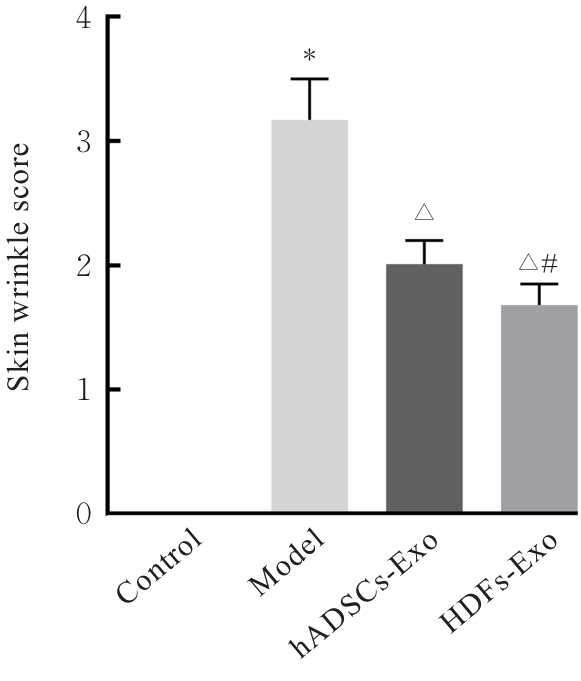
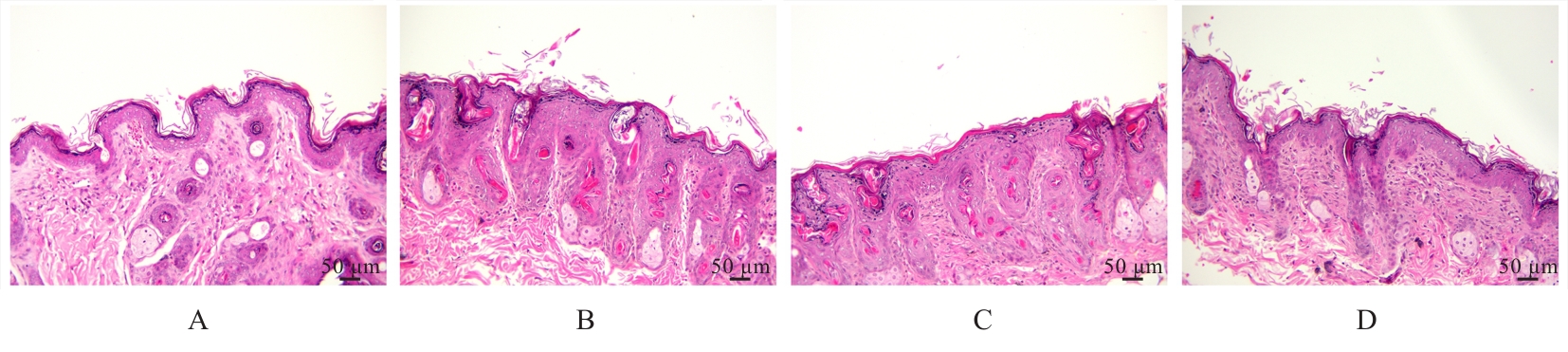
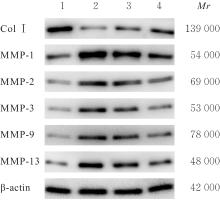
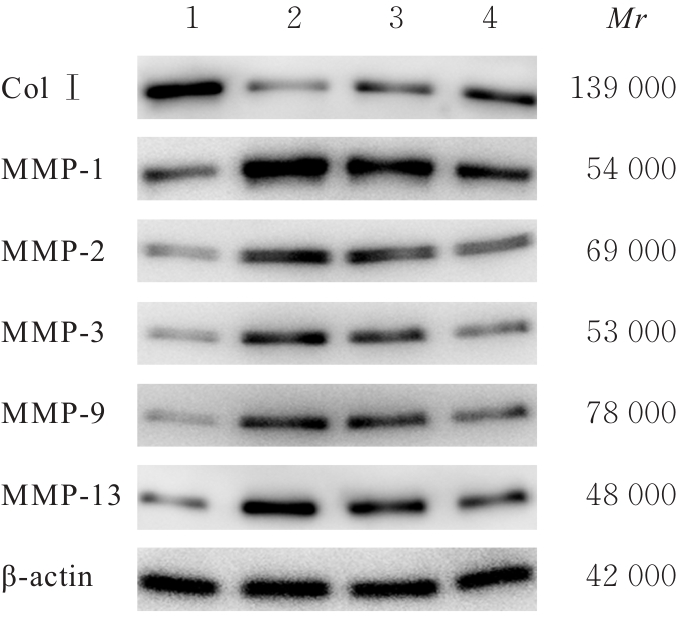
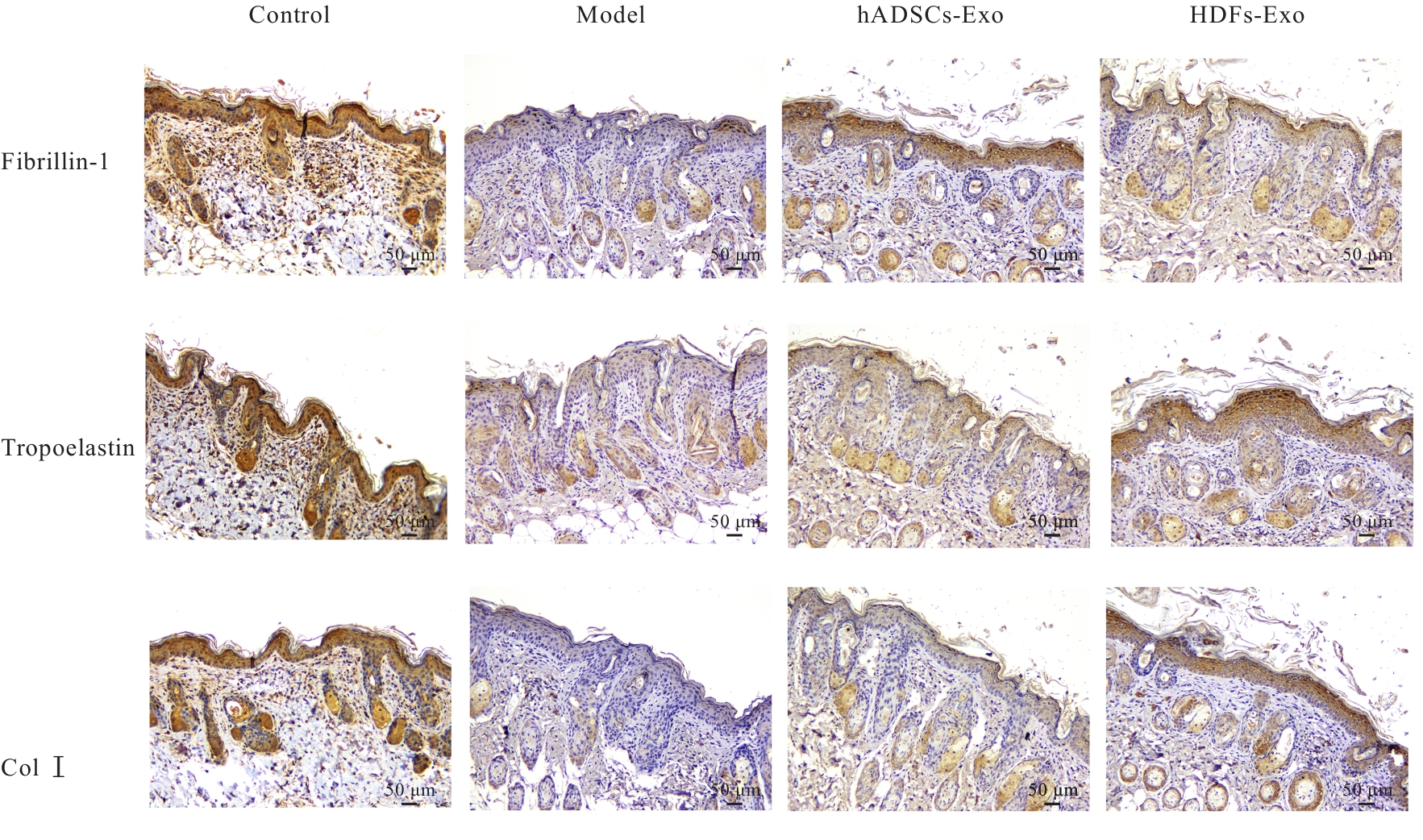
目的 探讨人脂肪干细胞(hADSCs)和人真皮成纤维细胞(HDFs)来源的外泌体(Exo)对紫外线诱导裸鼠光老化皮肤皱纹的改善作用,并阐明其作用效果。 方法 分别由hADSCs和HDFs中分离Exo,采用Western blotting法鉴定,记为hADSCs-Exo和HDFs-Exo。将28只裸鼠随机分为对照组、模型组[注射Hank’s平衡盐溶液(HBSS)]、hADSCs-Exo组(注射hADSCs-Exo)和HDFs-Exo组(注射HDFs-Exo),每组7只,除对照组外,其余3组裸鼠建立背部皮肤光老化模型,4周后,观察各组裸鼠背部皮肤大体形态表现并进行皮肤皱纹等级评分,HE染色观察各组裸鼠皮肤组织病理形态表现,酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法检测各组裸鼠皮肤组织中白细胞介素(IL)-1β、IL-6和肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)水平,实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法和Western blotting法检测各组裸鼠皮肤组织中胶原蛋白Ⅰ(Col Ⅰ)、基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)-1、MMP-2、MMP-3、MMP-9和MMP-13 mRNA及蛋白表达水平,免疫组织化学染色法观察各组裸鼠皮肤组织中Col Ⅰ、原弹性蛋白和原纤维蛋白1蛋白表达情况。 结果 由hADSCs和HDFs中分离的颗粒物均表现为典型的囊泡状结构,直径为50~100 nm,CD81、CD63、热休克蛋白70(HSP70)和肿瘤易感基因101蛋白(TSG101)均呈高表达,表明成功分离hADSCs-Exo和HDFs-Exo。对照组裸鼠背部皮肤光滑,未见松弛或皱纹;模型组裸鼠皮肤皱纹严重,可见表皮粗糙、干燥和色素沉积等损伤情况;与模型组比较,hADSCs-Exo组裸鼠背部皮肤有少量深皱纹和轻度皮肤松弛,HDFs-Exo组裸鼠背部皮肤皱纹深度明显减轻。皮肤皱纹等级评分,与对照组比较,模型组裸鼠皮肤皱纹等级评分明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,hADSCs-Exo组和HDFs-Exo组裸鼠皮肤皱纹等级评分明显降低(P<0.05);与hADSCs-Exo组比较,HDFs-Exo组裸鼠皮肤皱纹等级评分均明显降低(P<0.05)。HE染色观察,对照组裸鼠皮肤组织分层结构清晰,表皮较薄;模型组裸鼠皮肤组织分层紊乱,结构松散,表皮明显增厚;与模型组比较,hADSCs-Exo组和HDFs-Exo组裸鼠皮肤组织病变减轻,且HDFs-Exo组裸鼠皮肤组织表皮变薄,组织分层较为清晰,皮肤结构趋于正常。ELISA法检测,与对照组比较,模型组裸鼠皮肤组织中IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α水平均明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,hADSCs-Exo组和HDFs-Exo组裸鼠皮肤组织中IL-1β、IL-6及TNF-α水平均明显降低(P<0.05);与hADSCs-Exo组比较,HDFs-Exo组裸鼠皮肤组织中IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α水平均明显降低(P<0.05)。RT-qPCR法和Western blotting法检测,与对照组比较,模型组裸鼠皮肤组织中Col Ⅰ mRNA和蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05),MMP-1、MMP-2、MMP-3、MMP-9和MMP-13 mRNA及蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,hADSCs-Exo组和HDFs-Exo组裸鼠皮肤组织中Col Ⅰ mRNA及蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05),MMP-1、MMP-2、MMP-3、MMP-9和MMP-13 mRNA及蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05);与hADSCs-Exo组比较,HDFs-Exo组裸鼠皮肤组织中Col Ⅰ mRNA和蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05),MMP-1、MMP-2、MMP-3、MMP-9和MMP-13 mRNA及蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05)。免疫组织化学染色法观察,与对照组比较,模型组裸鼠皮肤组织中原弹性蛋白、原纤维蛋白1和Col Ⅰ染色强度均明显减弱;与模型组比较,hADSCs-Exo组和HDFs-Exo组裸鼠皮肤组织中原弹性蛋白、原纤维蛋白1和Col Ⅰ染色强度均明显增强;与hADSCs-Exo组比较,HDFs-Exo组裸鼠皮肤组织中原弹性蛋白、原纤维蛋白1和Col Ⅰ染色强度更深。 结论 hADSCs和HDFs来源的Exo对紫外线诱导裸鼠光老化皮肤皱纹具有明显的改善作用,且HDFs来源的Exo作用效果要优于hADSCs来源的Exo。
中图分类号:
- R751