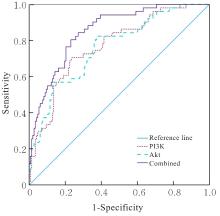
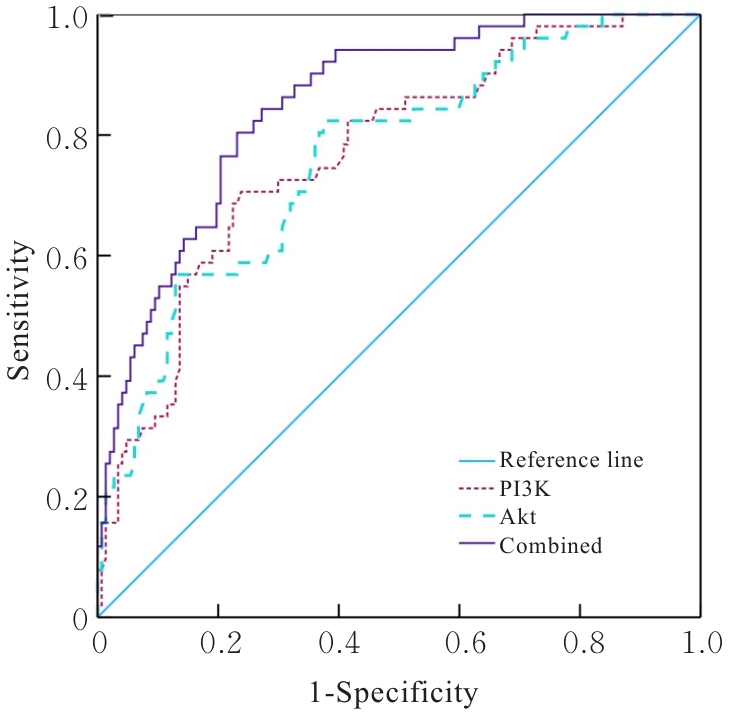
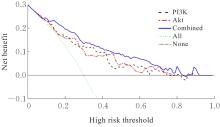
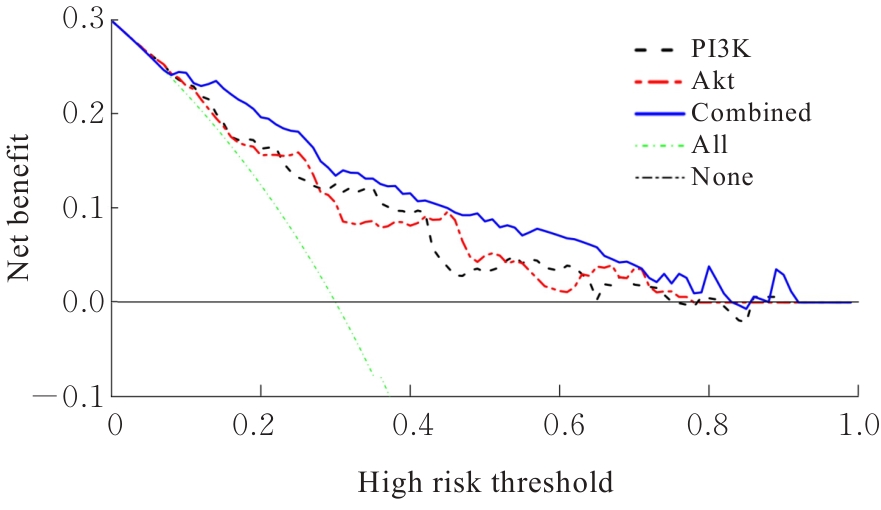
| [1] |
HAMMITT K M, NAEGELI A N, VAN DEN BROEK R W M, et al. Patient burden of Sjögren’s: a comprehensive literature review revealing the range and heterogeneity of measures used in assessments of severity[J]. RMD Open, 2017, 3(2): e000443.
|
| [2] |
张 文, 陈 竹, 厉小梅, 等. 原发性干燥综合征诊疗规范[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2023, 62(9): 1059-1067.
|
| [3] |
MALLADI A S, SACK K E, SHIBOSKI S C, et al. Primary Sjögren’s syndrome as a systemic disease: a study of participants enrolled in an international Sjögren’s syndrome registry[J]. Arthritis Care Res, 2012, 64(6): 911-918.
|
| [4] |
QIAN J Y, HE C M, LI Y, et al. Ten-year survival analysis of patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome in China: a national prospective cohort study[J]. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis, 2021, 13: 1759720X211020179.
|
| [5] |
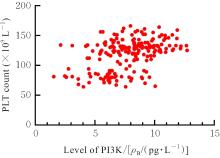
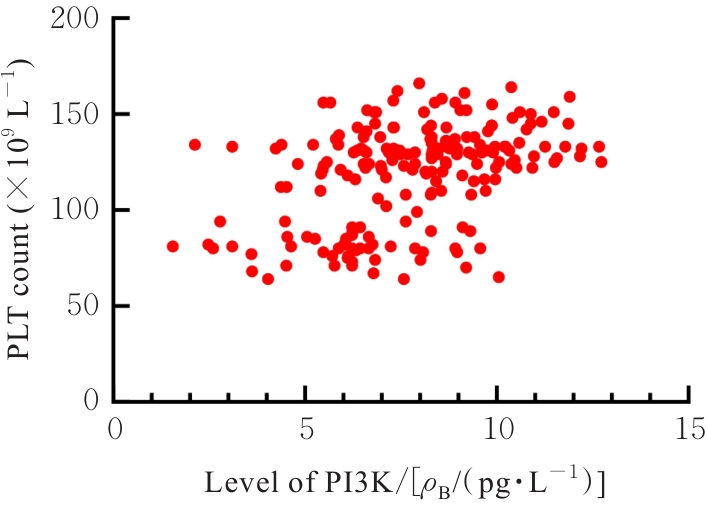
ZENG P, JIANG Z, HUANG Z W, et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway is downregulated by runzaoling (RZL) in Sjögren’s syndrome[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2022, 2022: 7236118.
|
| [6] |
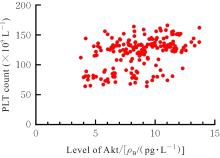
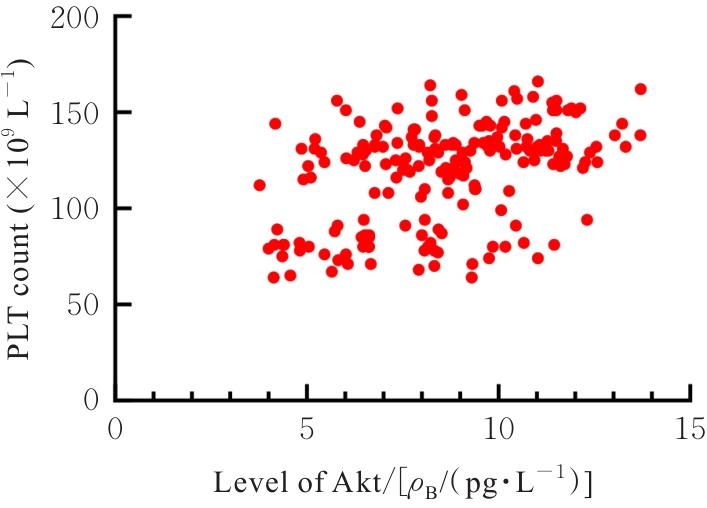
YANG H X, LI Y J, HE Y L, et al. Hydrogen sulfide promotes platelet autophagy via PDGFR-α/PI3K/Akt signaling in cirrhotic thrombocytopenia[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2024, 12(7): 625-633.
|
| [7] |
SHIBOSKI C H, SHIBOSKI S C, SEROR R, et al. 2016 American college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism classification criteria for primary Sjögren’s syndrome: a consensus and data-driven methodology involving three international patient cohorts[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2017, 69(1): 35-45.
|
| [8] |
中国成人血小板减少症急诊管理共识专家组. 中国成人血小板减少症急诊管理专家共识[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2022, 31(2): 161-168.
|
| [9] |
孙 佳. 原发性干燥综合征并发血小板减少临床特征研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北医科大学, 2020.
|
| [10] |
杨 柳. 原发性干燥综合征继发血小板减少患者临床特征及危险因素分析[D]. 石家庄: 河北医科大学, 2022.
|
| [11] |
王丽丽, 黄鸿影, 王 信, 等. 原发性干燥综合征继发免疫性血小板减少症的临床特点及危险因素分析[J]. 蚌埠医学院学报, 2024, 49(2): 167-171.
|
| [12] |
DAI F, YANG G M, RAO P S, et al. Clinical characteristics of secondary immune thrombocytopenia associated with primary Sjögren’s syndrome[J]. Front Med, 2020, 7: 138.
|
| [13] |
王红权, 苏锦锋, 彭春晓, 等. 原发性干燥综合征继发血小板减少患者的临床特征及相关因素分析[J]. 风湿病与关节炎, 2024, 13(10): 9-14.
|
| [14] |
WANG Q R, ZHANG W L, HU J, et al. Lithium prevents glucocorticoid-induced chondrocyte autophagy: an in vitro study[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2023, 28(4).
|
| [15] |
罗雅琴, 黄 伟. 芪黄益气摄血方调控PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路和自噬治疗免疫性血小板减少症的作用机制[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2022, 37(10): 5627-5633.
|
| [16] |
刘珈言, 梅 蓉, 杨礼凤, 等. 雷公藤多苷减轻干燥综合征模型小鼠炎性反应[J]. 基础医学与临床, 2022,42(9): 1362-1366.
|
| [17] |
张春梅, 黄新惠, 胡锦秋, 等. 莱菔硫烷下调PI3K/Akt信号通路对高糖诱导人血小板凋亡的保护作用[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2024, 40(18): 2530-2536.
|
| [18] |
BALDINI C, BERARDICURTI O, GIACOMELLI R, et al. Is minor salivary gland biopsy still mandatory in Sjogren’s syndrome? Does seronegative Sjogren’s syndrome exist?[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2024, 23(1): 103425.
|
| [19] |
DING Y H, XIANG Q, ZHU P Y, et al. Qihuang Zhuyu formula alleviates coronary microthrombosis by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/αIIbβ3-mediated platelet activation[J]. Phytomedicine, 2024, 125: 155276.
|
| [20] |
宋维海, 李 琴, 茅建春. 一贯煎对干燥综合征模型大鼠及颌下腺PI3K/Akt/eNOS通路的影响[J]. 中药材, 2020, 43(7): 1721-1725.
|
| [21] |
SUN Y Y, WANG T, LV Y, et al. MALAT1 promotes platelet activity and thrombus formation through PI3k/Akt/GSK-3β signalling pathway[J]. Stroke Vasc Neurol, 2023, 8(3): 181-192.
|
| [22] |
SONG H D, YANG Y J, LI B. Tripeptide Hyp-Asp-Gly from collagen peptides inhibited platelet activation via regulation of PI3K/Akt-MAPK/ERK1/2 signaling pathway[J]. J Food Sci, 2022, 87(7): 3279-3293.
|
| [23] |
SUN Y Y, YANG M N, LI S J, et al. Alantolactone induces platelet apoptosis by activating the Akt pathway[J]. Platelets, 2023, 34(1): 2173505.
|
| [24] |
ZHAO H Y, ZHANG Y Y, XING T, et al. Correction: M2 macrophages, but not M1 macrophages, support megakaryopoiesis by upregulating PI3K-AKT pathway activity[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2024, 9(1): 240.
|
| [25] |
SCHWERTZ H, MIDDLETON E A. Autophagy and its consequences for platelet biology[J]. Thromb Res, 2023, 231: 170-181.
|
| [26] |
KAPSOGEORGOU E K, STERGIOU I E, CHATZIS L, et al. The role of the Akt signaling pathway in Sjögren’s syndrome[J]. Mediterr J Rheumatol, 2023, 34(1): 113-116.
|
| [27] |
XIN Z L, XU R Y, DONG Y, et al. Impaired autophagy-mediated macrophage polarization contributes to age-related hyposalivation[J]. Cell Prolif, 2024, 57(12): e13714.
|
| [28] |
QI W X, TIAN J X, WANG G, et al. Advances in cellular and molecular pathways of salivary gland damage in Sjögren’s syndrome[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15: 1405126.
|
 )
)