吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 105-114.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250113
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
片仔癀在对乙酰氨基酚所致肝损伤中的保护作用及其机制
- 1.吉林大学第二医院肿瘤血液科, 吉林 长春 130021
2.吉林大学第一医院乐群院区药学部, 吉林 长春 130031
Protective effect of Pien-Tze-Huang on acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its mechanism
Chaohe ZHANG1,Xinwei ZHANG,Xiangfeng WANG2( )
)
- 1.Department of Hematology,Second Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130031,China
2.Department of Pharmacy,Lequn Branch,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
摘要:
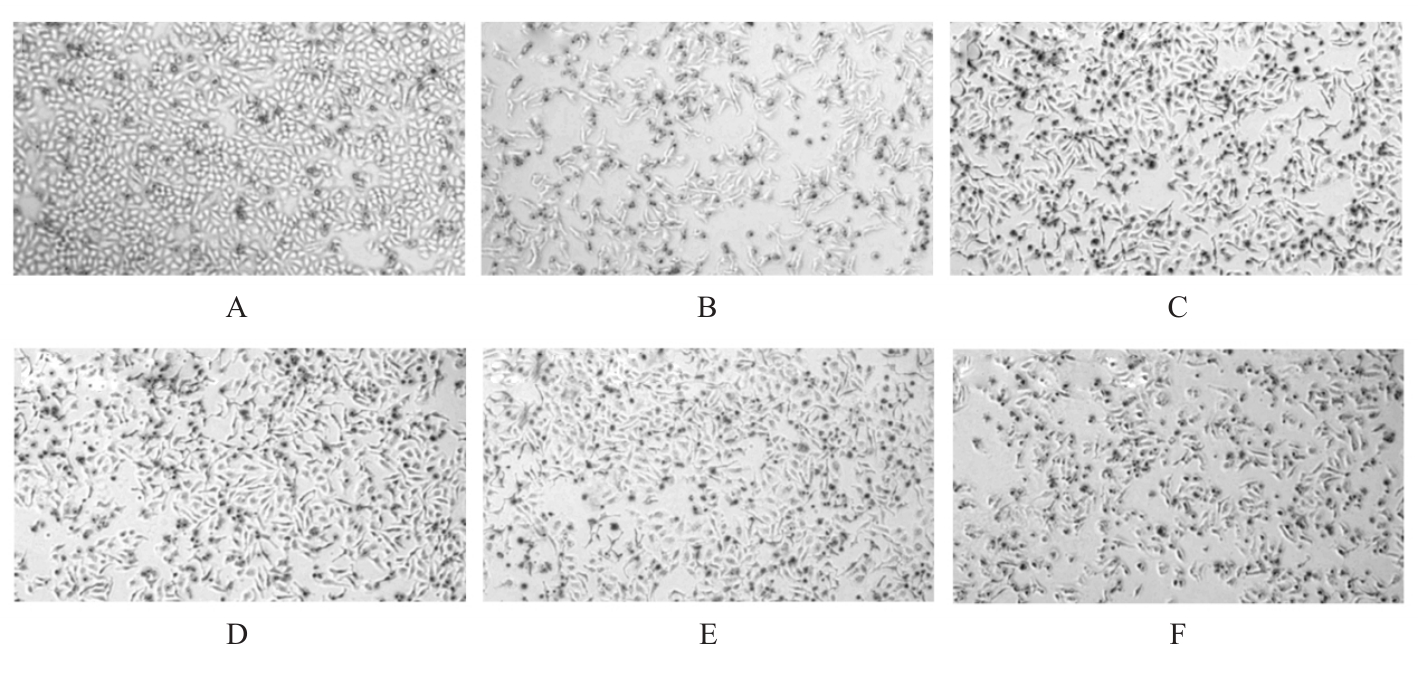
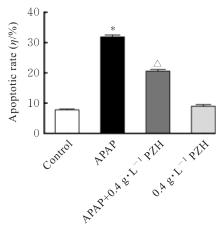
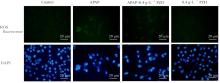
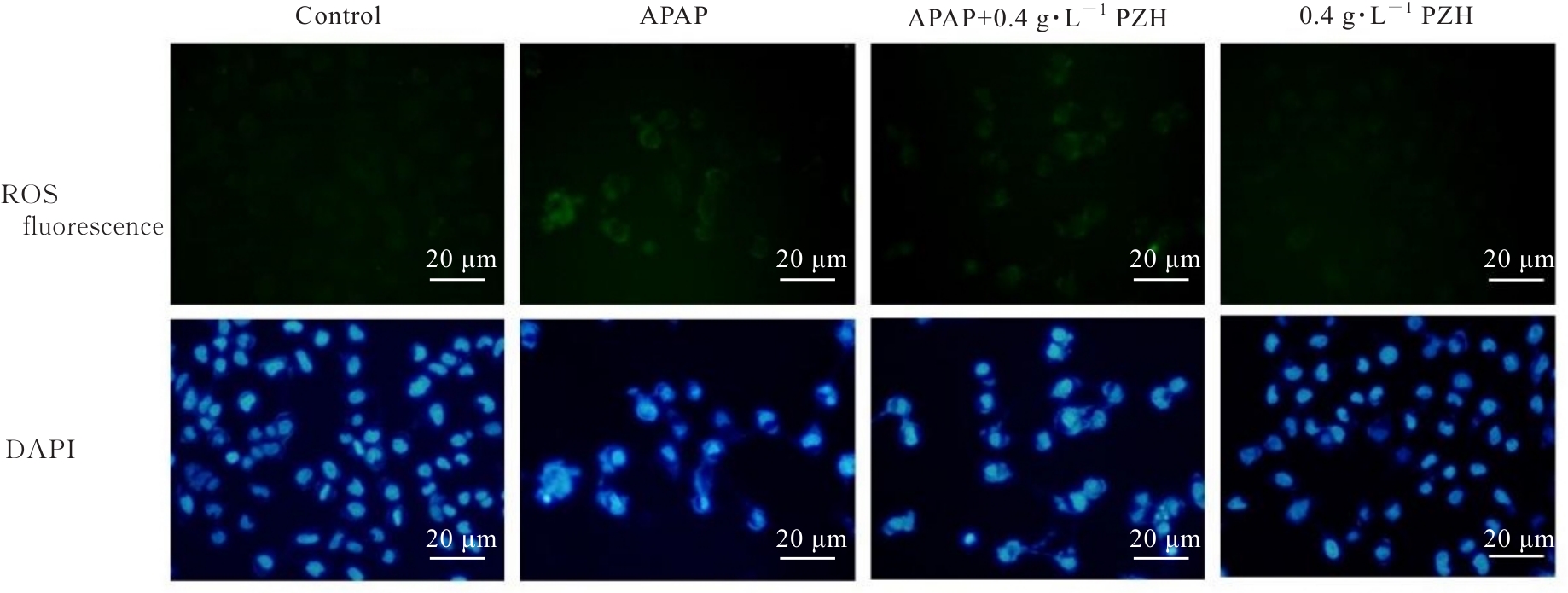
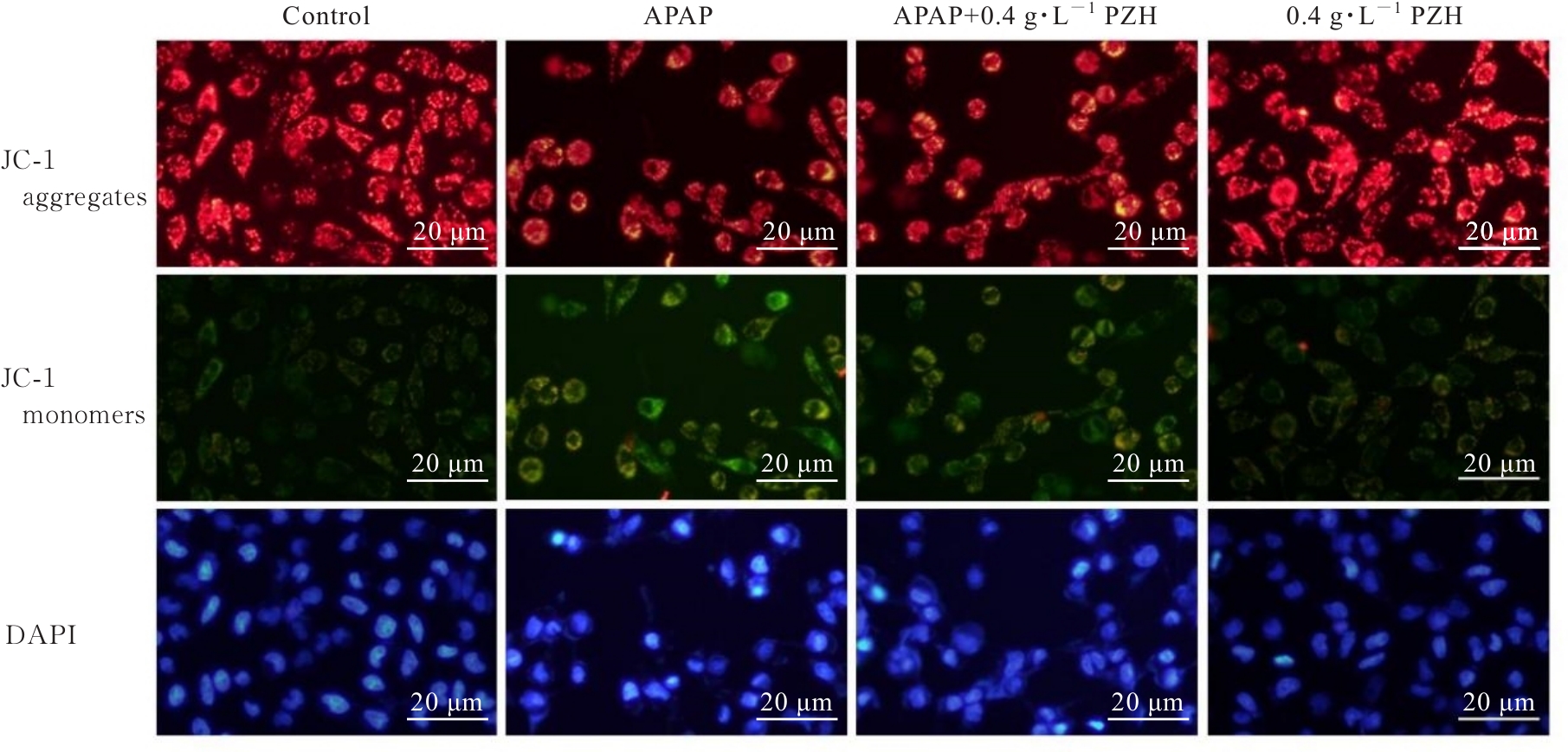
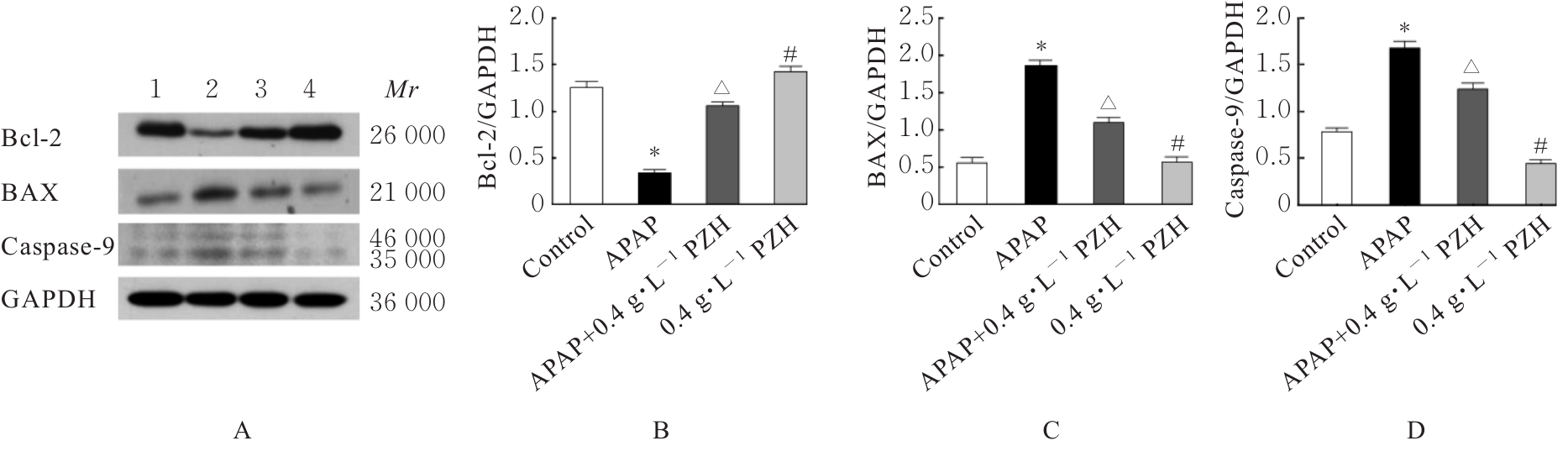
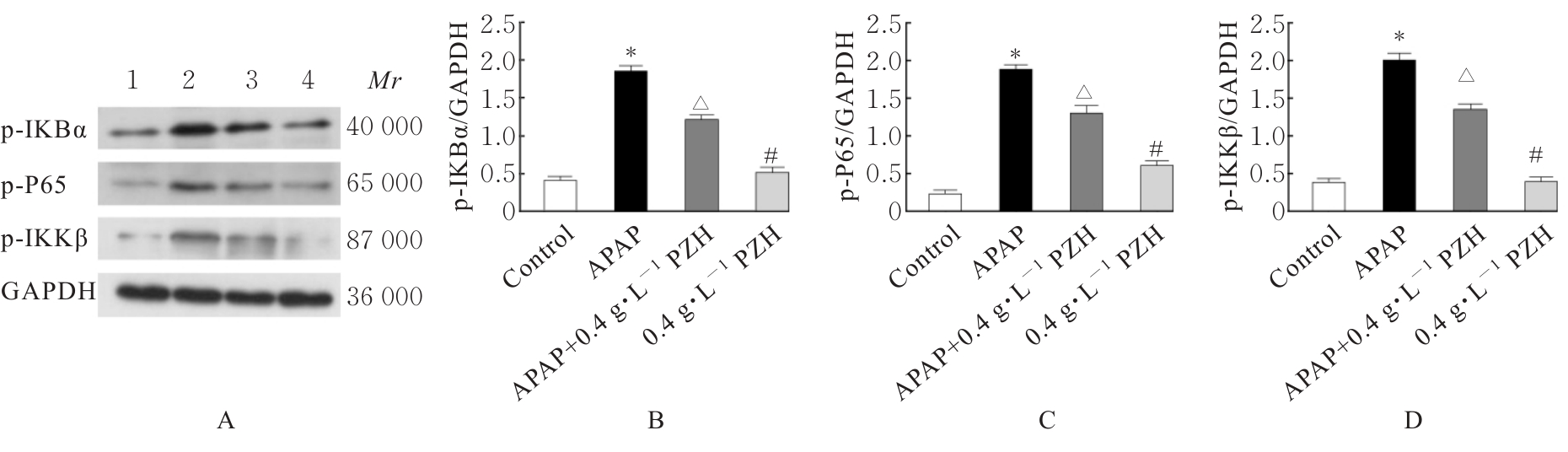
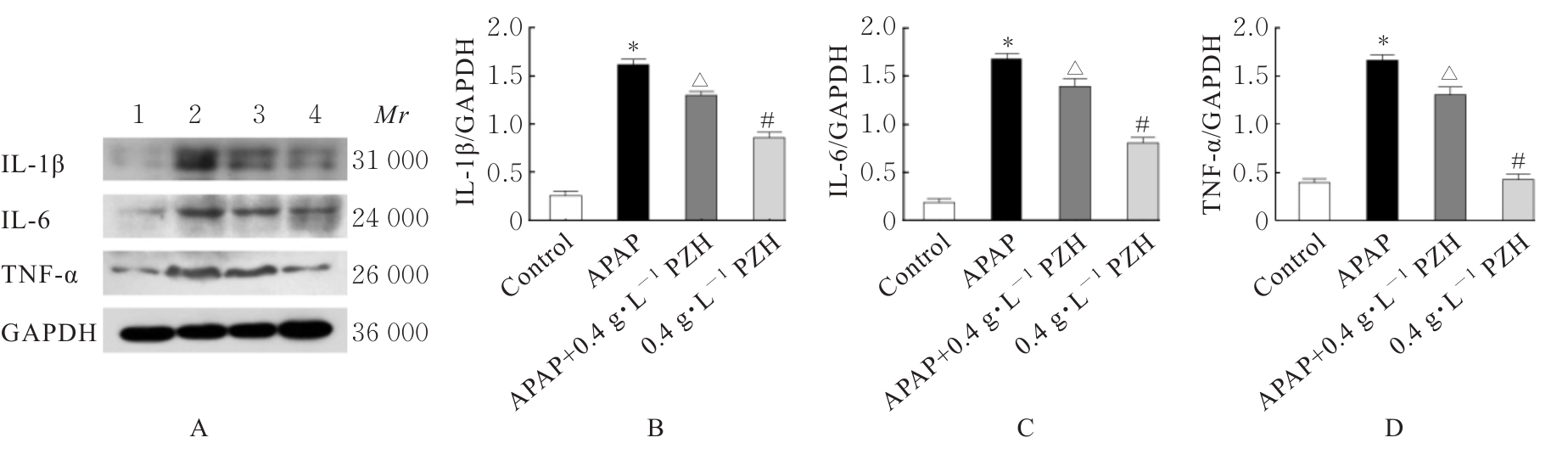
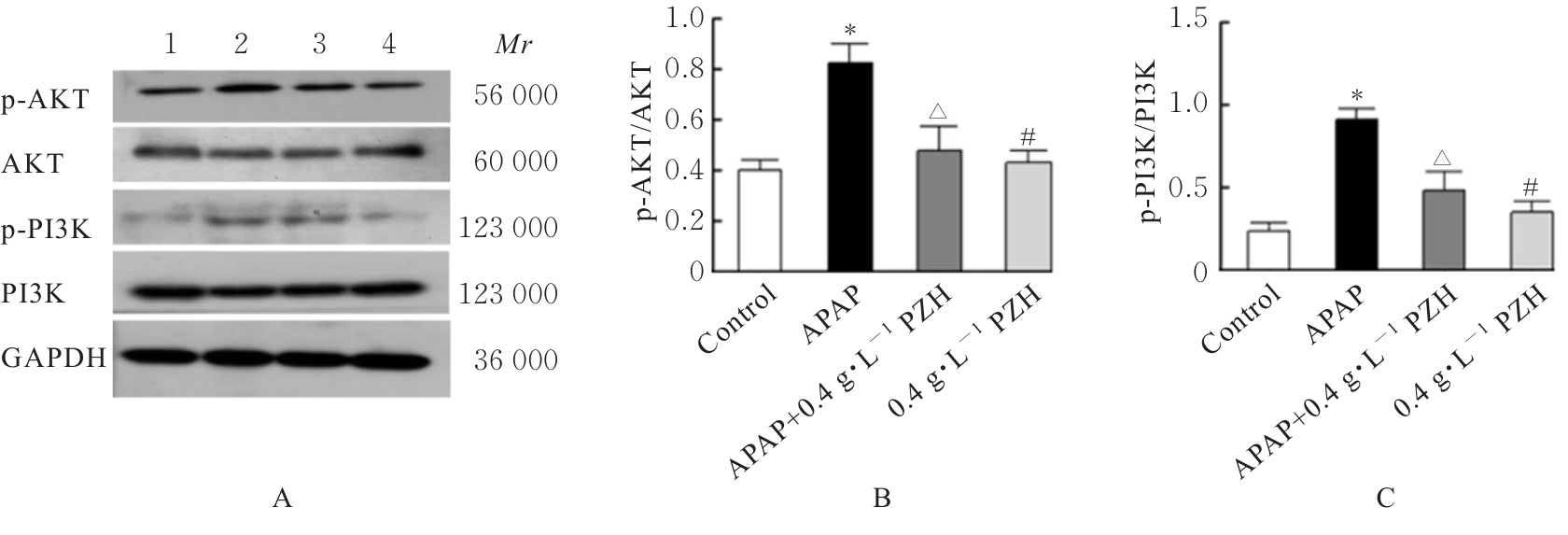
目的 探讨片仔癀(PZH)对对乙酰氨基酚(APAP)引起的肝损伤的保护作用,并阐明其可能的作用机制。 方法 将人正常肝细胞(L02细胞)分为对照组、APAP组(10 mmol·L-1 APAP)、APAP+PZH组(10 mmol·L-1APAP和0.4 g·L-1 PZH)和PZH组(0.4 g·L-1 PZH)。采用噻唑蓝(MTT)法检测各组细胞存活率,倒置显微镜观察各组肝细胞形态表现,流式细胞术检测各组肝细胞凋亡率,生化试剂盒检测各组细胞上清液中超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)和乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)活性及脂质过氧化物(MDA)水平,荧光探针技术检测各组肝细胞中活性氧(ROS)水平和线粒体膜电位(MMP),Western blotting法检测各组细胞中凋亡相关蛋白、磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(AKT)信号通路蛋白、核因子κB(NF-κB)信号通路蛋白和炎症因子的蛋白表达水平。 结果 MTT法,与对照组比较,APAP组细胞存活率明显降低(P<0.05);与APAP组比较,APAP+PZH组细胞存活率明显升高(P<0.05)。倒置显微镜观察,与对照组比较,APAP组细胞呈现数量减少且排列疏松的趋势;与APAP组比较,APAP+PZH组细胞数量及排列得到显著改善。流式细胞术检测,与对照组比较,APAP组细胞凋亡率明显升高(P<0.05);与APAP组比较,APAP+PZH组细胞凋亡率明显降低(P<0.05)。试剂盒检测,与对照组比较,APAP组细胞中LDH活性和MDA水平明显升高(P<0.05),SOD活性明显降低(P<0.05);与APAP组比较,APAP+PZH组细胞中LDH活性和MDA水平明显降低(P<0.05),SOD活性明显升高(P<0.05)。与对照组比较,APAP组肝细胞中ROS荧光强度明显升高;与APAP组比较,APAP+PZH组肝细胞中ROS荧光强度明显降低。与对照组比较,APAP组肝细胞中MMP明显降低;与APAP组比较,APAP+PZH组肝细胞中MMP明显升高。Western blotting法,与对照组比较,APAP组细胞中含半胱氨酸的天冬氨酸蛋白酶(caspase)-9、B细胞淋巴瘤2(Bcl-2)相关X蛋白(BAX)、磷酸化PI3K(p-PI3K)、磷酸化AKT(p-AKT)、磷酸化NF-κB抑制蛋白α(p-IKBα)、p-P65、磷酸化kappa B抑制因子激酶β(p-IKKβ)、白细胞介素1β(IL-1β)、白细胞介素6(IL-6)和肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05),Bcl-2蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05);与APAP组比较,APAP+PZH组细胞中caspase-9、BAX、p-PI3K、p-AKT、p-IKBα、p-P65、p-IKKβ、IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05),Bcl-2蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05)。 结论 PZH能够降低APAP引起的细胞内氧化应激和炎症反应,缓解L02细胞损伤,其作用机制可能与调控PI3K/AKT和NF-κB信号通路有关。
中图分类号:
- R285.5